
Decreased Oxygen Saturation Levels Due to Suction of Endotracheal
Tube Mucus
Juni Mariati Simarmata, Syatriawati, Rosita Ginting, Isidorus Jehaman, Anita Purba and Samuel
Ginting
Institut Kesehatan Medistra Lubuk Pakam Deli Serdang, Sumatera Utara, Indonesia
Keywords: Oxygen Saturation, Suction, Endotracheal Tube Patient (ETT)
Abstract: The success of treatment in patients with respiratory failure depends not only on early detection, but also on
understanding the mechanism of the cause. One of the conditions that can cause respiratory failure is airway
obstruction, including obstruction of the Endotracheal Tube (ETT). This type of research uses the Pre
Experiment Method using One-Group Pre-test and Post-test Design research design. Determination of the
sample is done by accidental sampling, with a total sample of 20 people. Data analysis was performed using
the Wilcoxon test with a 95% confidence interval and a value of α = 0.05. The results obtained from this study
indicate that there are differences in oxygen saturation levels before and after mucus suctioning measures are
given where there is a difference in the value of oxygen saturation levels of 5.164% and p-value = 0.000 (α
<0.05).
1 INTRODUCTION
According to WHO (World Health Organization)
data the incidence of respiratory failure can result in
death and the incidence of data obtained in 2009 the
incidence of respiratory failure about 67% of all
patients treated in the ICU. And in 2012 respiratory
failure began to be prevented by providing care and
freeing the airway 58%. The incidence and
consequences of acute respiratory failure also depend
on the dysfunction of others. A procedure that
deserves particular attention, given its direct
relationship with the risk of infection, is the
endotracheal aspiration (ETA) of intubated patients.
A common procedure within intensive care units is
the suctioning of respiratory secretions in patients
who have been intubated or who have undergone
tracheostomy. When patients are unable to mobilize
their secretions, they may need suctioning of the
secretions from the oropharynx and/or trachea to
maintain their airway. Patients may be unable to clear
their own airway due to several different problems,
including neuromuscular disease, sedation or
neurological deficits, such as a CVA. In addition,
patients with an artificial airway, such as those who
have been intubated, usually require suctioning while
they are on a ventilator. Many patients are intubated
and mechanically ventilated because of respiratory
distress and respiratory failure. Respiratory failure is
an acute or chronic condition with impaired gas
exchange and pulmonary functions and is
characterized by elevated carbon dioxide or
decreased oxygen in the arterial blood. Respiratory
failure can result from diverse conditions such as
cardiac and respiratory diseases, defects in
neuromuscular systems that control breathing, injury
to chest, and several lung diseases.
Suctioning may be done through an endotracheal
tube, tracheostomy tube, or through the nose or mouth
into the trachea. Although each procedure is slightly
different, indications, supplies, procedures and risks
are similar.
Respiratory failure is one of the causes of increased
mortality and morbidity. Every year an estimated 1
million people are treated in ICU due to respiratory
failure (Wunssch, 2010). In the United States the
incidence of respiratory failure increased from
1,007,549 people in 2001 to 1,917,910 in 2009 (16).
Some cases of respiratory failure end up with
mechanical ventilation aimed at assisting or taking an
expert respiratory function. Based on data on rank 10
non-communicable diseases (PTM) which cause fatal
deaths based on case fetality rate (CFR) in hospital
admissions in 2010, the incidence of respiratory
failure ranks second at 20, 98%) (7).
Simarmata, J., Syatriawati, ., Ginting, R., Jehaman, I., Purba, A. and Ginting, S.
Decreased Oxygen Saturation Levels Due to Suction of Endotracheal Tube Mucus.
DOI: 10.5220/0009468001650171
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology (ICHIMAT 2019), pages 165-171
ISBN: 978-989-758-460-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
165

Treatment for airway obstruction due to the
accumulation of secretions in the Endotracheal Tube
(ETT) is to perform mucus suctioning by inserting a
suction catheter through the nose / mouth /
Endotrachel tube (ETT) which aims to free the
airway, reduce sputum retention and prevent sputum
suction lung infection. In general, patients who have
ETT installed have a poor body response to expel
foreign bodies, so suctioning is necessary. (9).
The American –European Consensus On
ARDS found an incidence of acute respiratory
distress syndrome (ARDS) between 12.6-28.0 cases /
100,000 population / year and deaths from respiratory
failure were reported to be around 40%. Under these
conditions, the optimal management of respiratory
failure patients is very important and we estimate
there is a relationship between the basic disease and
the results of its management (Bongard, 2014).
The use of mechanical ventilation is a
multinational survey of 5000 clients in Europe used
in cases of acute respiratory failure (69%), coma
(17%), chronic respiratory failure (13%) and
neuromuscular use (2%) (Rodriquez, Dojat, and
Brocard , 2005). Respiratory assistance should be
given adequately according to indications to prevent
muscle weakness in breathing because of rest
(Smelzer, 2012).
Research conducted by France, (2011) in 12
ICU rooms in Brazil found 843 people (49%) were
treated in ICU rooms due to acute respiratory failure
and 141 people suffered respiratory failure after being
treated in ICU, of the total sufferers of acute
respiratory failure 475 people died in the ICU room,
and 56 people died after leaving the ICU room.
From the results of studies in Germany and
Sweden reported that the incidence of acute
respiratory failure in adults 77.6-88.6 cases / 100,000
population / year. Respiratory failure is an indication
that the patient is being treated in an intensive care
unit (ICU).
One condition that can cause respiratory failure
is airway obstruction, including obstruction of the
Endotrachel Tube (ETT). Airway obstruction is an
abnormal condition due to the inability to cough
effectively, can be caused by thick secretions or
excess due to infectious diseases, immobilization,
static secretions, and ineffective cough due to
neurological diseases such as cerebrovascular
accident (CVA), effects of sedative treatment, and
others (Hidayat, 2013).
Data obtained from the ICU patient
registration book Prof. Dr. Dr.R.D. Kandou Manado
starting from January-October 2013 the total number
of patients treated at the ICU were 411 patients and
those who experienced respiratory failure as many as
132 patients (32.1%). The average patient treated in
the ICU is 41-42 patients / month and the average who
has experienced respiratory failure is 13-14 patients /
month died due to respiratory failure.
Respiratory failure occurs when the exchange
of oxygen to carbon dioxide in the lungs is unable to
maintain the rate of oxygen consumption (O2) and the
formation of carbon dioxide (CO2) in body cells. This
results in arterial oxygen pressure of less than 50
mmHg (hypoxemia) and an increase in carbon
dioxide pressure greater than 45 mmHg
(hypercapnia). Although advances in diagnostic
techniques and intervention therapy have progressed
rapidly, respiratory failure is still a cause of high
morbidity and mortality rates in the treatment room
intensive (Brunner & Suddarth, 2010).
According to Wiyoto (2010), if suction is not
performed on patients with impaired airway
clearance, these patients will experience a lack of O2
supply (hypoxemia), and if O2 supply is not met
within 4 minutes it can cause permanent brain
damage. An easy way to find out hpoxemia is by
monitoring oxygen saturation (SpO2) levels which
can measure how much percentage of O2 the
hemoglobin can carry. And data that can be obtained
and health services in each province of Riau, West
Sumatra and North Sumatra which says patients fail
to breathe in almost every hospital that has ICU room.
Starting from 2009-2013, it can be estimated that the
total number of patients treated in the ICU is 1,680
and 756 patients (46.7%) have experienced
respiratory failure. and it is estimated that patients
treated in the ICU in each hospital are 40 patients each
month and patients who experience respiratory failure
Between 12 patients each month and 8 patients each
month die of respiratory failure (Health Office, 2014).
Based on preliminary surveys conducted by
researchers, it is known that in the ICU room of
Grandmed Hospital, in 2016 there were 72 patients
who were installed with ventilators. In 2017, 86
patients were installed with ventilators. In 2018 a total
of 67 patients had ventilators. The average patient
who experienced respiratory failure as many as 9
patients per month, 3 patients died from respiratory
failure per month. And in early 2019 who were
treated in the ICU room as many as 27 patients who
installed ventilators. This is what prompted
researchers to conduct research on the Effect of
Suctioning Mucus Measures on Oxygen Saturation in
Patients with Endotracheal Tube (ETT) in the ICU at
Grandmed Lubuk Pakam Hospital in 2019.
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
166

2 RESEARCH METHODS
This type of research is quantitative research. This
study uses a Pre Experiment research design with a
One Group Pretest-Posttest Design, because this
study is directed to see how the Effect of
Endotracheal Suction on Suction Oxygen Saturation
Levels in the ICU at Grandmed Lubuk Pakam
Hospital in 2019.
Location and Time of Research Research on
the Effects of Endotracheal Tube Suction on Oxygen
Saturation Levels in ICU at Grandmed Lubuk Pakam
Hospital in 2019. The reasons researchers chose
research sites are 1) No research has been conducted
on the Effect of Suction of Endotracheal Tube
Suction in the ICU at Grandmed Lubuk Pakam
Hospital in 2019. The reasons for researchers
choosing research sites are 1) Research on the Effects
of Suction on Endotracheal TubeI (ETT) on Oxygen
Saturation Levels in the ICU Room of the Grandmed
Lubuk Pakam Hospital in 2019, b) The location of the
study is close to the researcher, c) There is a problem
regarding the action of mucus suctioning with
changes in oxygen saturation in patients who are
installed Endotrachel Tube (ETT).
The study was conducted in April to May 2019.
And the population of this study were patients who
installed Endotracheal Tube (ETT) in the ICU room
at the Grandmed Lubuk Pakam Hospital, in April-
May 2019 as many as 20 patients. The sampling
technique used in this study used an accidental
sampling technique where only patients who met with
researchers were sampled (Hidayat, 2011). So the
sample in this study is ICU patients who have
Endotracheal Tube (ETT) installed at Grandmed
Lubuk Pakam Hospital in April - May 2019.
Description:
01: The group before the Suction action is taken.
X: Suction Action Treatment Group
02: Group after Suction action
Figure1: Research Design
Inclusion Criteria
Patients who have ETT and Ventilator
installed
Patients with mucus buildup (secret) and
suction will be performed
Patients with SpO2 <95%
Exclusion Criteria
Patients in the process of CPR (Pulmonary
resuscitation)
Patients who have Post ROSC (Return Of
Spontaneous Circulation) <3 hours
The instrument used in this study is the
observation sheet consisting of the respondent's
general identity contained at the top of the
observation sheet. While at the bottom there are
results of the pre-test and post-test assessment of the
action of mucus suctioning.
The procedure in this study, preliminary data
about oxygen saturation levels were collected through
a pre-test. Including values from the measurement
results used an oximetry device. Then the respondent
will be given suction action. After taking action
through treatment, the final data of this study were
taken through a posttest including data on oxygen
saturation levels by monitoring using an oximetry
device
Collecting Data Techniques
Premier Data
This data was obtained based on statements in the
form of observation sheets filled out by researchers
that can be seen from the state of the patient while
being treated in the ICU room at the Grandmed Lubuk
Pakam Hospital.
Secondary Data
Secondary data from this research were taken from
nurses and doctors to determine the diagnosis of
patients while being treated in the ICU at Grandmed
Lubuk Pakam Hospital.
Research variable
The variables of this research are :
The independent variable (independent
variable) in this research is the act of mucus
suctioning
The dependent variable (dependent variable) is
the change in oxygen saturation.
Data analysis
Processing and analysis data were done using
computer software. Data analysis included univariate
analysis was used to obtain a description of the
distribution of research subjects of each variable from
the Effect of Endotracheal Tube Suction on Oxygen
Saturation Levels in ICU at Grandmed Lubuk Pakam
Hospital in 2019 and to establish further data analysis.
Analysis was needed to explain or find out
whether there are significant influences or differences
between the independent variables and the dependent
variable. Bivariate analysis was performed after the
characteristics of each variable are known. From the
01 X 02
Decreased Oxygen Saturation Levels Due to Suction of Endotracheal Tube Mucus
167
results of statistical calculations with the probability
value (p) with a real level α = 0.05 with a confidence
level of 95% (P Value <α) means that there is a
significant relationship between the independent and
dependent variables. To test the hypothesis used is to
use the Wilcoxo Test.
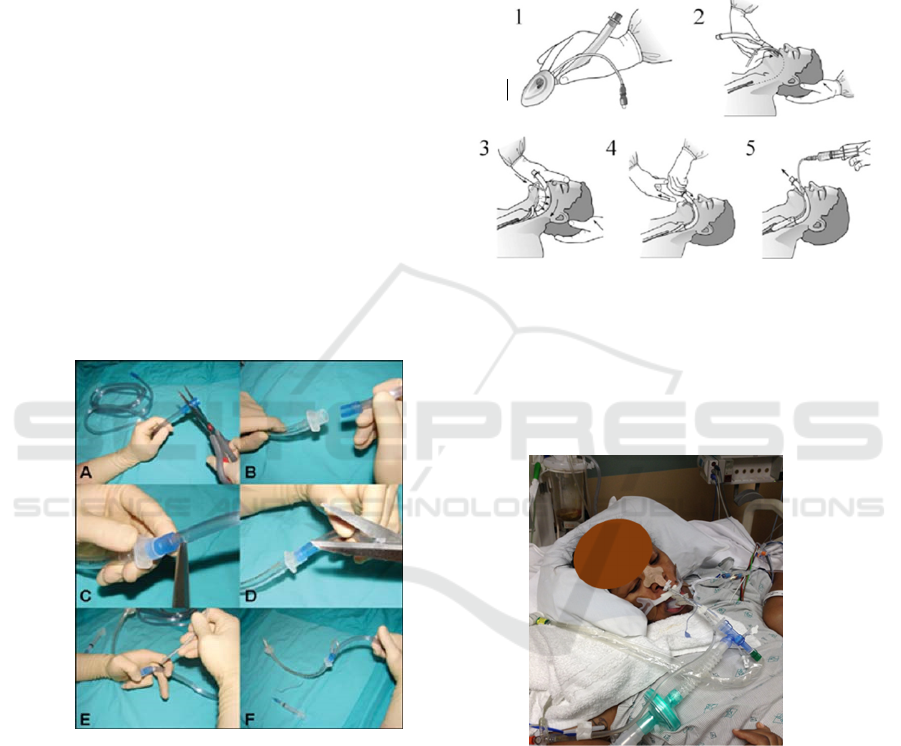
Endotracheal Tube Implementation Procedures:
Tools preparation (figure 2), A) The distal
expanded portion of the suction tubing
connector is cut off, B) The tip of the suction
tubing is wedged into the ETT connector, C)
Scissors are used to cut a proximal hole in the
suction tubing, D) Scissors are used to cut a
distal hole in the suction tubing, E) The stylet is
passed through the distal hole in the suction
tubing into the ETT, F) When suction is
required, an assistant occludes the proximal hole
in the suction tubing. Once the tip of the ETT is
in the larynx, the suction tubing and stylet are
removed together and positive pressure
ventilation can be provided (Abrons,
Zimmerman, ElHattab, 2017)
Figure 2: Construction of the ETT as a suction wand
Intubation installation (Figure 3): (1) Deflate
the laryngeal mask airway (LMA) cuff to a
smooth low profile shape. Grasp LMA between
thumb and index finger. (2) Extend the patient’s
head with the nondominant hand, while the
LMA is inserted with thumb and index finger
grip toward the hard palate. (3) Advance the
LMA into position by applying pressure with
the index finger along the palate. Advance until
resistance is felt in the orophaynx. (4) Withdraw
the dominant hand from the patient’s mouth,
while stabilizing the LMA shaft with the
nondominant hand. (5) Inflate the LMA cuff,
often the device will move slightly out of the
patient’s mouth with cuff inflation. Suggested
inflation pressure is 6 0 cm H2O, do not
overinflate (Hernandez, Klock, Ovassapian,
2012, 2012).
Figure 3: Manufacturer's recommended insertion
technique (Courtesy of LMA North America, San
Diego, CA)
The results of installing Endotracheal Tube
in patients
Figure 4: Pasien Endotracheal Tube
3
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Based on the results of the study in Table 1,
Characteristics of respondents by gender, namely 12
men (60.0%), and 8 women (40.0%).
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
168

Table 1: Characteristics of Respondents
Characteristic
Frequency
(people)
Percentage
(%)
Gender
Man 12 60,0
Woman 8 40,0
Total 20 100,0
Based on the results of the study in Table 2,
Characteristics of respondents by Mucus Suction in
Patients with Endotracheal Tube Installed
Table 2: Mucus Suction in Patients with Endotracheal
Tube Installed
Mucus Suctioning
Frequency
(Orang)
Percentage
(%)
Good 2 10,0%
Deficient 18 90,0%
Total 20 100%
Based on the research results in Table 3 of the
Effect of Endotracheal Tube (ETT) Suction againts
the Oxygen Saturation Level in the ICU in the
Grandmed Lubuk Pakam Hospital in 2019, before the
Suction of Endotracheal Tube (ETT) in the Good
category 2 people (10.0%) and deficient category as
many as 18 people (90.0%), and after the
Endotracheal Tube (ETT) mucus suctioning act the
good category as many as 17 people (85.0%) and
deficient category as many as 3 people (15.0%) at
ICU room Grandmed Lubuk Pakam Hospital in 2019.
Table 3: After the action of mucus suctioning
Mucus Suctioning
Frekuensi
(Orang)
(%)
Good 17 85,0%
Deficient
3 15,0%
Total 20 100%
Based on the results of the study in Table 4
about the Effect of Endotracheal Suction (ETT)
Suction on the Oxygen Saturation Level in the ICU in
the Grandmed Lubuk Pakam Hospital in 2019,
alteration in Oxygen Saturation Endotracheal Tube
(ETT) in the Grandmed Lubuk Pakam Hospital In
2019 there were 17 good categories (85.0%), and bad
mucus suctioning measures were 3 people (15.0%).
Table 4: Changes in Oxygen Saturation in Patients
with Endotracheal Tube (ETT)
Alteration in
Oxygen
Saturation
Frequency
(Orang)
(%)
Good 17 85,0%
Deficient 3 15,0%
Total 20 100%
Based on the results of the study in Table 5
This study was conducted on 20 patients treated at
Grandmed Lubuk Pakam Hospital and in 209 patients
on the Effects of Endotracheal Tube (ETT) Suction
on the Oxygen Saturation Level in the ICU Room at
Grandmed Lubuk Pakam Hospital in 2019 based on
sociodemography which includes Gender, it can be
seen the characteristics of respondents based on the
sex of the majority of men as many as 12 people
(60.0%) and the majority of women 8 people (40.0%).
Table 5: The Effects of Endotracheal Tube (ETT)
Mucus Suction on Oxygen Saturation Levels
Mucus
Suctioning
n
Me
an
Std.
Deviat
ion
Min Max
V
al
ue
Pre Suction 220 6,90 4.553 79 95
0
,00
Post Suction 220 95,85 4.760 84 100
According to the assumptions of research
conducted by Irawan (2014) regarding the effect of
endotracheal tube (ETT) suctioning action on oxygen
saturation levels in patients treated in ICU room of
RSUP Prof. Dr. Dr. R. D. Kandou Manado, 12
patients or about 75% of patients have male sex and
7 people (44%).
While in a study conducted by Irawan (2015)
regarding the effect of suction action on changes in
peripheral oxygen saturation in patients treated in the
ICU room at Abdul Wahab Sjahranie Hospital
Samarinda, as many as 20 people out of 26 samples
taken were male and 11 were male. used as a sample
having a head injury medical diagnosis.
Based on the total score of each dimension in
the table above, statistical analysis of the Wilcoxon
test means that Ho is rejected so there is available the
effect of Endotracheal Tube (ETT) Suction on the
Oxygen Saturation Level in the ICU of the Grandmed
Lubuk Pakam Hospital in 2019. Easier interpretation
of data is by looking at the P Value index of = .000 <
(0.05).
Therefore it can be concluded that Ho is
rejected. So there is the effect of Endotracheal Tube
Decreased Oxygen Saturation Levels Due to Suction of Endotracheal Tube Mucus
169

(ETT) Suction on the Oxygen Saturation Level in the
ICU of the Grandmed Lubuk Pakam Hospital in 2019.
And Distribution of Frequency and Percentage of
Endotracheal Tube (ETT) Suction on the Oxygen
Saturation Level in the ICU Grandmed Lubuk Pakam
Hospital in 2019.
In the Saskatoon Health Regional Authority
(2010) said that complications that may arise from the
action of sucking mucus one of which is hypoxemia /
hypoxia. And strengthened by Maggiore et al ,.
(2013) about the side effects of ETT mucus
suctioning, one of which is that there can be a
decrease in oxygen saturation levels of more than 5%.
So that patients suffering from diseases of the
respiratory system will be very vulnerable to
experience a significant decrease in the value of
oxygen saturation at the time of the action of mucus
suctioning.
The results obtained from this research indicate
that there are differences in oxygen saturation levels
before and after mucus suctioning action is given. The
results showed a decrease in the oxygen saturation
level of the respondents namely the difference in the
value of oxygen saturation levels by 5.174%. Besides
that, from the results of the t-Test statistical test on
respondents, there is a significant effect where the p-
value = 0,000 (α <0.05).
According to the assumptions of the research
conducted by Maggiore, et al (2013), about
Decreasing the Adverse Effects of Endotracheal
Suctioning During Mechanical Ventilation by
Changing Practice, where 46.8% of respondents
experienced a decrease in oxygen saturation and 6.5%
due to suction. Based on these studies it can be
concluded that the action of suction can cause a
decrease in oxygen saturation levels.
According to the assumptions of research
conducted by Maulidia, Rosina (2017), the effect of
mucus suction action on changes in oxygen saturation
levels in critical patients treated in the ICU room at
An-Nisa Hospital in Tangerang with a mean value
obtained is 1.475 with a standard deviation of 1.358
and the mean standard error of 0.215. The P value
obtained in this study is 0,000 (≤ 0.05), so it can be
concluded that there is an effect of suctioning on
changes in oxygen saturation levels in critical patients
treated in the ICU at An-Nisa Hospital Tangerang.
Based on the research conducted, the
researcher's assumption is that before 2 people
(10.0%) Good category of Endotracheal Tube (ETT)
mucus suction and 18 people (90.0%) less good
category, and after mucus suctioning Endotracheal
Tube (ETT) Good category as many as 17 people
(85.0%) and Poor category as many as 3 people
(15.0%) in the ICU Room Grandmed Lubuk Pakam
Hospital in 2019.
The experts recorded a 24% respiratory failure
rate with a 33.33% mortality rate. Mucus suction is
one of the components and bronchial toilets for
aspiration of mucus on clients with artificial airways.
Suctioning mucus (Suction) is the act of cleaning the
airway through an artificial airway using a suction
catheter and a suction device (Wilson, 2010).
And distribution of Frequency and Percentage
Change in Oxygen Saturation in Patients with
Endotracheal Tube (ETT) in the ICU of Grandmed
Lubuk Pakam Hospital in 2019.
According to the assumptions of research
conducted by Marlisa, Idjradinata, Kosasih (2013)
about the effect of oxygen supply through the catheter
mouth during suction on oxygen saturation in
ventilator head mounted patients, where the use of
catheter mouth is more effectively used during
suction to reduce the risk of decreasing saturation
oxygen in patients with severe head injury with
ventilators compared with those not using catheter
mouth.
According to the assumptions of research
conducted by Nizar, Haryati (2015) the results of this
study indicate an increase in oxygen saturation levels
after suction. That is because the free airway to
accumulate secretions makes oxygen transfer from
the atmosphere into the lungs effective. Therefore the
researcher took suction action on the respondent in
accordance with the inclusion criteria based on
standard operating procedures.
Based on the research conducted, the
researcher's assumption is that the Oxygen Saturation
Change in Endotracheal Tube (ETT) patients in the
ICU Room in the Grandmed Lubuk Pakam Hospital
in 2019 is good for 17 people (85.0%), and changes
in oxygen saturation are as good as 3 people (15.0%).
Frequency Distribution and Percentage Effect of
Endotracheal Tube (ETT) Mucus Suction Actions on
Oxygen Saturation Levels in ICU in Grandmed
Lubuk Pakam Hospital in 2019.
According to the assumptions of research
conducted by Bayu (2013) regarding the effect of
suction action on changes in peripheral oxygen
saturation in patients treated in the ICU room Abdul
Wahab Sjahranie Hospital Samarinda, before the
action of mucus suctioning, a mean value of 93.65
and a median of 94, with a standard deviation of
1,623, a minimum value of 90 and a maximum
saturation level of 96. After mucus suctioning, a mean
of 97.46 and a median of 98, obtained a standard
deviation of 1.606 with a minimum value of 94 and a
maximum of 100.9.
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
170

Based on the research assumptions of Kitong,
Mulyadi, & Malara (2014) entitled "The effect of the
action of aspiration of endotracheal tube mucus
(ETT) on oxygen saturation levels in patients treated
in ICU room of RSUP Prof. DR. D. Kandou Manado
"which shows the differences in oxygen saturation
levels before and after given mucus suctioning action
where there is a difference in the value of saturation
levels of 5.174% and pvalue = 0,000 (α <0.05).
Based on the total score of each dimension in the
table above, statistical analysis of the Wilcoxon test
means that Ho is rejected so that there is an Influence
of Endotracheal Tube (ETT) Suction on the Oxygen
Saturation Level in the ICU of the Grandmed Lubuk
Pakam Hospital in 2019. Easier interpretation of data
is by looking at the p value index of = .000 <(0.05).
Therefore it can be concluded that Ho is rejected. So
there is the effect of Endotracheal Tube (ETT) Mucus
Suction Act on the Oxygen Saturation Level in the
ICU in Grandmed Lubuk Pakam Hospital in 2019.
The action of mucus suctioning performed on patients
with ventilators installed at Grandmed Hospital has
an effect on changes in oxygen saturation in the ICU
at Grandmed Lubuk Hospital in 2019..
The obstacle found in this study is the
uniformity in using suction cannula size is not the
same, because the size is different so that it affects the
difference in the value of oxygen saturation in
patients with suctioning measures. The size of a larger
suction cannula (14 Fr) can reduce Oxygen Saturation
levels more than the smaller size (12 Fr). Another
obstacle found in this study is regarding the level of
education and tenure of nurses who perform
suctioning actions. This can have an indirect effect on
nurses' skills in performing suctioning actions.
4 CONCLUSION
For Bivariate analysis was got the results obtained
based on the Wilcoxon test have a significant
difference between before and after the results. The
value before the suction action includes the mean
value is 86.90%, the standard deviation value is
4.553%, the minimum value is 79%, the maximum
value is 95%, and the value after suction action
includes: the mean value is 95.85%, the standard
deviation value is 4760%, the minimum value is 84%,
the maximum value is 100%. Then conclusions There
is an influence before and after the suction action on
the value of oxygen saturation (p <0.005), so that Ha
is accepted.
REFERENCES
Abrons, Zimmerman, ElHattab, 2017 Nasotracheal
intubation over a bougie vs. nonbougie intubation: a
prospective randomised, controlled trial in older
children and adults using videolaryngoscopy. The
Association of Anaesthetists of Great Britain and
Ireland.
Brunner & Suddarth, 2010. Buku ajar keperawatan medikal
bedah. Edisi 8. Jakarta: EGC.
Hudak, M.C & Gallo, M.B. (2010). Keperawatan kritis
(Edisi ke-6, Volume II). Jakarta: EGC.
Hidayat, A.A.A. 2013. Pengantar kebutuhan dasar
manusia. Buku 2. Jakarta: Penerbit Salemba Medika.
Hidayat, Maftuchul, Farida, Dkk 2014. Buku ajar praktik
laboratorium keperawatan. Edisi 2. Jakarta: EMS.
Hernandez, Klock, Ovassapian, 2012. Evolution of the
extraglottic airway: a review of its history, applications,
and practical tips for succes.
Jacob, Rekha, Jadhav 2014 Buku ajar clinical nursing
procedures. Edisi 2. Tanggerang Selatan: EMS.
Kozier & Erb, 2012. Buku ajar praktik keperawatan klinis.
Edisi 5. Jakarta: EGC.
Kemenkes, 2012. Buletin jendela data dan informasi
kesehatan penyakit tidak menular (Vol. II). Jakarta:
Kementrian Kesehatan RI.
Maggiore, S.M. et al, 2013. Decreasing the adverse effects
of endotracheal suctioning during mechanical
ventilation by changing practice. continuing
respiratory care education, Vol 58, 1588-1597.
Nurachmah, E., Sudarsono, R.S. 2010. Buku saku prosedur
keperawatan medikal bedah. Jakarta: EGC.
Nofiyanto, M. Perbedaan nilai saturasi oksigen
berdasarkan ukuran kateter suction pada tindakan
open suction di ruang general intensive care unit rsup
dr. hasan sadikin bandung, (Online),
(http://www.unpad.ac.id/archieves/12 8770. diakses
tanggal 10 Juni 2014, jam 22.15 WITA).
Nursalam, 2010. Konsep dan penerapan metodologi
penelitian ilmu keperawatan. Edisi 2. Jakarta: Salemba
Medika.
Notoadmojo, S. 2012. Metode penelitian kesehatan.
Jakarta: PT. Rineka Cipta.
Price, S.A., Wilson, L.M. 2010. Patofisiologi konsep klinis
proses – proses penyakit. Edisi 6. Volume 2. Jakarta:
EGC.
Rab Tabrani, 2016. Buku ajar ilmu penyakit paru. Jakarta:
TIM.
Smeltzer, S.C. & Bare, B.G. (2012). Brunner and
suddarth’s textbook of medical – surgical nursing. 8th
Edition. Alih bahasa: Waluyo, A. Jakarta: EGC; (Buku
asli diterbitkan tahun 1996).
Stefan, M. S., Shieh, M.-S., Pekow, P. S., Rothberg, M. B.,
Steingrub, J. S., Lagu, T., & Lindenauer, P. K. (2013,
Pebruari). Epidemiology and outcomes of acute
respiratory failure in the united states, 2001 – 2009: A
National Survey. J Hosp.
Decreased Oxygen Saturation Levels Due to Suction of Endotracheal Tube Mucus
171
