
The Effect of Imagery and Concentration Training on Smash
Accuracy
Vistor Syapri Maulana
1
, Guntur
1
1
Sport Science Department, Postgraduate Faculty, Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Mental Imagery, Concentration, Smash Accuracy
Abstract: This study aims to examine: (1) different impacts of internal and external imagery training methods on
smash accuracy; (2) different impacts of high and low concentrations on smash accuracy; and (3) the
interaction between training methods (internal and external imagery) and concentration (high and low) on
smash accuracy. This research method uses a 2 x 2 factorial. This study employed the modified Laveage
smash accuracy test and the data were analysed using ANAVA. This study can be concluded that (1) there is
a significant difference between the internal imagery training method and the external imagery training
method on the accuracy of the smash, (2) there is a significant difference between players who have high
concentration and low concentration on smash accuracy, (3) there is a significant interaction between the
imagery training method (internal and external) and concentration (high and low) on smash accuracy
1 INTRODUCTION
Volleyball is a team sport that each team consists of
six people in 9 square meter field that is separated
by a net. One technique in volleyball game is smash
(Viera, 2000).
The basic technique of smash is very preferred
by volleyball players or athletes, since this technique
is very artistic in volleyball, which requires a player
to pass the ball on the net, by the possible highest
jump to be able to pass the block and enter the target
enemy defense area. This technique requires good
skill and also precise accuracy where a volleyball
player must be able to quickly determine the
direction of the ball so as not to be blocked by the
opponent. It also requires a technique to avoid the
ball to enter in his own area (not over the net), and to
direct the ball to the opponent's field area. This
demands ingenuity as well as the experience of an
athlete. Smash is a technique that has complex
movement which consists of: (1) prefix steps, (2)
repulsion to jump, (3) ball hit when floating in the
air and, (4) landing after hitting the ball (Kemal,
2013). Difficulties experienced by a volleyball
player in mastering this technique consist of
problems of timing the ball/ the point when the ball
will be smashed, the position of the hand when the
ball is subjected, the distance of the hand hit to the
net, the smash step, and so on (Suhadi & Sujarwo,
2009).
Many players did not concentrate well when they
were practicing smash in terms of the range of
motion and purpose of the smash. Players did not
optimize time while practicing concentration and
aiming to the target.
They just did the smash technique as they want
and did not maximize time to concentrate on the
series of movements and direction of the smash
target. As a result, the player did not get a correct
smash motion automation series. This has an impact
when they were in a competition. There were many
players fail to do the smash technique when
competing and they had low accuracy. This
happened because a set of motion that was prepared
inappropriately leads them to loose concentration on
the target direction.
Mental training that is beneficial to improve
performance in psychological terms has never been
given. Thus, the player’s psychological aspects will
be trained by the mental imagery training method.
Mental imagery training methods in practicing
smash technique are still less familiar. The trainers
prefer to use the drilling method.
Inconsistency of the success rate and the low smash
accuracy when practicing and competing indicates
that the player’s concentrationhas not been
established and is not yet stable. Meanwhile, the
244
Maulana, V. and Guntur, .
The Effect of Imagery and Concentration Training on Smash Accuracy.
DOI: 10.5220/0009310602440247
In Proceedings of the 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science in conjunction with the 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports
(YISHPESS and CoIS 2019), pages 244-247
ISBN: 978-989-758-457-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

quality of the smash technique performed by each
player is quite well. This happens because the level
of attention and concentration decreases or the
players aredisturbed when there are several stimuli
that appear within the same time (Sukadiyanto,
2006). A mental training program needs to be
conducted as an effort to improve the player's
concentration in smashing and its accuracy.
There are two types of perspectives or views,
namely internal imagery perspective and external
imagery perspective (Wienberg & Gould, 2007).
Further explanation states that the implementation of
both training types requires mentoring. Associated
models of external perspective imagery requires an
external stimulus in the form of video or images that
aim to help players being concentrate on a smash
technique. It is expected that the existence of mental
training through the method of imagery internal
perspective and imagery external perspective will be
able to help volleyball players improving
concentration in performing smash techniques with a
high degree of accuracy
2 RESEARCH METHOD
2.1 Research Type
This research is an experimental method using a 2x2
factorial design. Sudjana (2009: 49) states that
factorial experiment is a design that can treat two or
more independent variables at the same time. This
attempt is intended to see the effect of each
independent variable separately and simultaneously
on the dependent variable due to the interaction of
several variables.
2.2 Population and Research Samples
The population in this study consists of 37 players of
volleyball extracurricular participants at SMK
Muhammadiyah Salaman.
From the total players who meet the sampling
criteria, the concentration test were being conducted
to classify players who have high and low
concentration. After the concentration test was
performed, the rank was arranged based on players’
concentration from the highest to the lowest score.
The next step was determining the percentage,
which resulted in 27% of the players got high score
and 27% of the players got low score.
2.3 Research Instrument
Data collection instrument in this study was a smash
accuracy test from Laveage (1933) that was
modified by the Sports Science Faculty (FIK)
Lecturer Research Team (Putut Marhaento, et al).
This test aims to measure the ability of the smash in
relation to the smash accuracy using a hard ball to a
specific target.
2.4 Data Analysis Technique
The data were analysed using SPSS 20 by two-way
ANAVA at a significance level of 0.05. Considering
that the analysis of research data is carried out using
ANAVA, it is necessary to conduct prerequisite tests
which include: (1) normality test, (2) variant
homogeneity test and hypothesis test.
3 RESEARCH RESULT
The first hypothesis states "There was a significant
difference between the internal imagery training
method and the external imagery training method on
smash accuracy". The analysis results are presented
as follows:
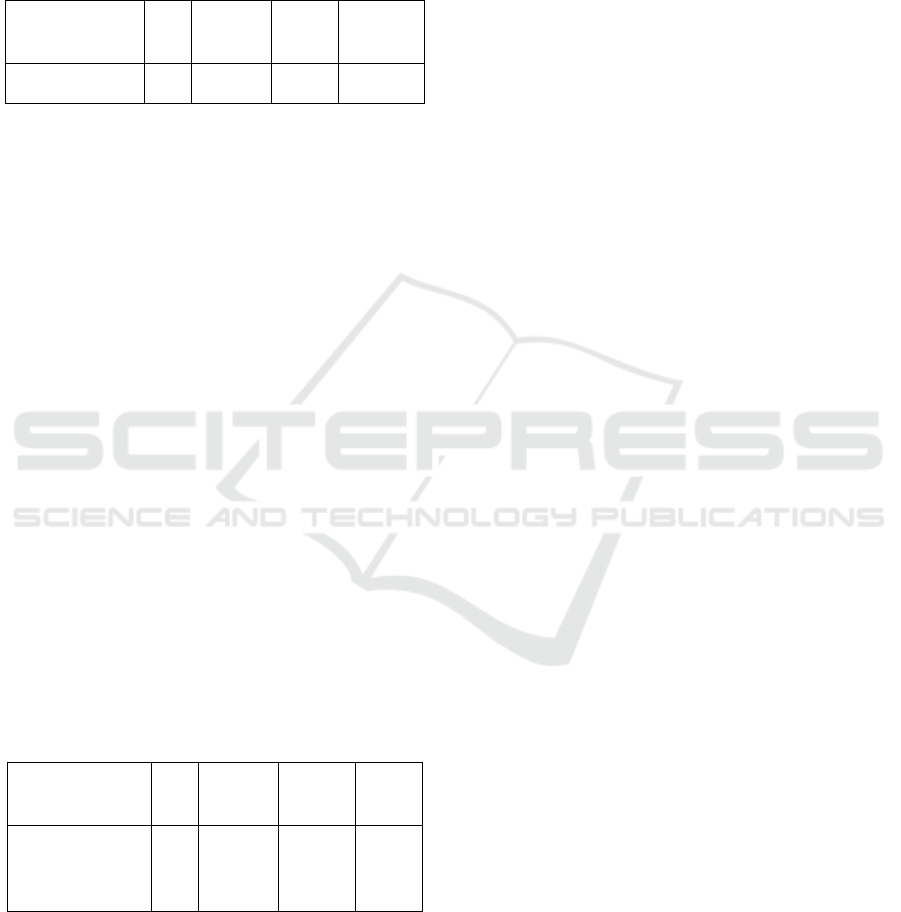
Table 1: ANAVA results of the internal imagery and
external imagery training method
Source df
Mean
Square
F Sig
Training
method
1 7,200 5,143 0,038
From the ANAVA test results, it can be seen that
the significance value of p is 0.038. Since the
significance value 0.038 <0.05, it means that H
o
is
rejected. Thus there is a significant between the
internal imagery training method and the external
imagery training method on smash accuracy. Based
on the analysis, the results of the internal imagery
training method is higher (good) with an average
post-test score of 38.5 compared to the results of
external imagery exercise method with an average
post-test score of 37.3. It implies that there is a
significant difference of the internal imagery
training method and the external imagery training
method on smash accuracy, has been proven.
The Effect of Imagery and Concentration Training on Smash Accuracy
245
The second hypothesis states "There was a
significant difference in the effect of players who
have high concentration and low concentration on
smash accuracy the ". The results are as follows:
Table 2: ANAVA results differences in
concentration from high and low to smash accuracy
Source df
Mean
Square
F Sig
Concentration 1 39,200 28,00 0,000
From the ANAVA test results shown in the table
above, it can be seen that the significance value of p
is 0,000. Since the significance value of p is 0,000
<0.05, it means that H
o
is rejected. Based on the
result, it means that there are significant differences
between players who have high concentration and
low concentration on smash accuracy. Based on the
results of the analysis, it turns out that players who
have high concentration have higher score with an
average post-test score 39.3 compared to players
who have low concentration with an average
post-test score 36.5. This means that the research
hypothesis stating that there are significant
differences between players who have high
concentration and low concentration on the smash
accuracy, has been proven.
The third hypothesis states that there is a
significant interaction between the types of imagery
training method (internal imagery and the external
imagery exercise method) and level of concentration
(high and low) on the smash accuracy. The results
are presented as follows:
Table 3: ANAVA interaction results
Source df
Mean
Square
F Sig
Concentration
training
method
1 245,00 175,00 0,000
From the ANAVA test results in Table 3, it is
clear that the significance value of p is 0,000. Since
the significance value of p 0,000 <0.05, it means that
H
o
is rejected. Thus, the hypothesis stating that there
is a significant interaction between the types of
imagery training method (internal imagery and the
external imagery training method) and level of
concentration (high and low) on the smash accuracy,
has been proven.
4 DISCUSSION
Internal imagery training methods have been proven
to be more effective inincreasing smash accuracy
and players’ concentration when performing smash.
This is in line with the theory that imagery training
can improve player performance (Olsson, 2008).
Mental training activates peripheral activities, which
provide afferent information to the motor cortex and
functions to strengthen motor programs (Halgren,
Dale, Sereno, & Tootell, 1999). They further stated
that with the development of neuroimaging
technology, researchers can test various imagery
theories. During mental training, the same
neuromotor pathways was involved in carrying out
certain physical motor task activities (Kosslyn,
Ganis, & Thompson, 2001). Motoric program in the
motor cortex, which is responsible for movement, is
then strengthened as a result of nerve pathways
during mental imagery training. As a result, mental
imagery can assist in practicing skills by increasing
appropriate coordination patterns and by priming the
appropriate motor neurons of the muscles needed to
carry out certain motor tasks.
Concentration has an important role in
influencing a technique or the results of a sports
competition. Attention and concentration are often
interpreted similarly even though they have different
definitions. Attention is a process of direct
awareness of the information (stimuli) received to
decide an action (response) (Sukadiyanto, 2006).
Whereas, concentration is a person's ability to focus
attention on the selected excitement (one object) in a
certain time. Concentration is very important for a
player in performing on the field. The main
component of concentration is the ability to focus
the attention on a certain thing and is not interrupted
by internal stimuli or irrelevant external stimuli
(Schmid & Peper in Satidarma, 2000).
From the results of the interaction, it appears that
the two factors show significant interactions. The
results of this study show that there are significant
differenceswithin each group as a result of different
treatment,.
After trained by internal imagery training
methods, volleyball players who have high
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
246

concentration will get better results than those who
do not. Conversely, players who have low
concentration will get better results if they were
trained with the external imagery training method.
This can happen because the implementation of
internal imagery exercises can improve the athlete’s
concentration, thus it will be more effective to be
applied for the players who have high concentration.
The internal imagery training method will be more
effective to be applied for the players who have high
concentration, since it will be easier to focus on the
targets when striking a smash. From this statement,
it can be concluded that the effectiveness applied to
improve smash accuracy was influenced by the
players’ concentration level. Thus, exercises applied
must be adjusted to the players’ abilities and
characters so that they can achieve optimal results.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results above, several conclusions were
derived. There was a significant difference between
the internal imagery training method and the
external imagery training method on smash accuracy.
The internal imagery training method is better than
the external imagery one in terms of smash
accuracy.
Besides, there was a significant difference of
high concentration and low concentration on smash
accuracy. Players who are highly concentrated on
the game are better than those who have low
concentration to perform smash accuracy.
There is a significant interaction between types
of imagery training methods (internal imagery and
external imagery) and players’ concentration level
(high and low) on smash accuracy.
REFERENCES
Halgren, E., Dale, M., Sereno, R., Tootell R., 1999.
Location of human faceselectivecortex with respect to
retinotopic areas. Human Brain Mapping, Vol. 7, pp.
29-37.
Kemal., 2013. Pengaruh latihan skipping terhadap
kemempuan smash dalam permainan bola voli pada
siswa SMA Negeri 4 Palu. Journal E-JTPEHER Vol. 3
No. 1.
Kosslyn, S., Ganis, G., & Thompson, W., 2001. Neural
foundations of imagery. Journal Nature Reviews
Neuroscience. Vol. 2, 635-642.
Olsson, C.J., Jonsson, B & Nyberg, L., 2008. Internal
imagery training in active high jumpers. Scandinavian
Journal Of Psychology, Vol.49. Pp. 133-140.
Satiadarma, P.M., 2000. Dasar-dasar psikologi olahraga.
Pustaka Sinar Harapan. Jakarta.
Sudjana, N., 2009. Penelitian dan penilaian pendidikan.
Sinar Baru Algesindo. Bandung.
Suhadi & Sujarwo., 2009. Volleyball for all. UNY Press.
Yogyakarta.
Sukadiyanto., 2006. Konsentrasi dalam olahraga.
Yogyakarta. Majalah Ilmiah Olahraga FIK UNY,
Volume 12.
Weinberg, R,S. & Gould, D., 2007. Fourth edition:
foundations of sport and exercise psychology. Human
Kinetics. United States.
The Effect of Imagery and Concentration Training on Smash Accuracy
247
