
The Effect of Dribbling Exercises with Tools and Dribbling with
Opponent and the Aye-foot Coordination in Increasing the Dribbling
Skill of Extracurricular Participants
Afif Rafiun
1
, Sugeng Purwanto
2
1
Magister of sport sciences, Yogyakarta State University, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
2
Physical Education, Yogyakarta State University, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Dribbling Exercises, Eye-Foot Coordination
Abstract: The aims of this research are to investigate: (1) the effect between dribbling exercises with tools and
dribbling exercises with opponent in increasing the dribbling skill of extracurricular participants, (2) the
effect between the aye-foot coordination (high aye-foot coordination and low aye-foot coordination) in
increasing the dribbling skill of extracurricular participants. (3) the interaction between dribbling exercises
with tools and dribbling exercises with opponent and the aye-foot coordination (high and low) in increasing
the dribbling skill of football extracurricular participants in Bima regency. This research used experimental
method with 2x2 factorial design.
1 INTRODUCTION
School is a place where children are guided and
trained so they have strong physical, mental, and
dexterous skills. The subjects discussing these
aspects are the subject of Physical Education. At
school, physical education was introduced as early
as possible related to basic techniques of several
sports as the initial provision to develop skills and
achievements in the future because maximum
achievement requires perfection of the techniques
obtained from the right basic techniques. In
Indonesia, sport in society is not only for
education, recreation, and physical fitness but also
considered as an achievement field. It is also stated
in Indonesian constitution No. 3 of 2015 about the
national sportsmanship system on article 4 is
described as follow. “National sportsmanship aims
to maintain and increase health and fitness,
achievement, human quality, sportivity, discipline,
tighten and develop association and unity of the
nation, strengthen national resilience, dignity and
honor of the nation.” It also occurs in soccer. In
soccer games, there are several basic techniques
that are very important to master, namely herding,
kicking, heading, holding, passing, and guarding
the goal. In this case, the most important basic
technique is dribbling.
Dribbling is the most important basic technique
need to be mastered in football. The abilities that
are important in dribbling are the techniques and
physical conditions. Factors that can affect the
dribbling skills are speed, agility and ball
crunching skills. This is in line with Mielke (2007)
who states that dribbling is the basic ability in
football because the players must be able to
dominate the ball while moving, standing or
preparing to make passes or shots.
Dribbling is an activity to control the
movement of the ball using feet. In addition, by
dribbling the ball, the player can protect the ball
from the attack of the opponent. Huijgen (2010)
argues that dribbling in soccer can be categorized
into two, dribble actions while accelerating and
dribble actions with quick changes of direction.
Moreover, the ability to dribble and take on
opponents is an essential part of every player’s
attacking skill set. You must never lose sight of the
fact that excessive dribbling in inappropriate
situations serves no useful purpose and can
actually undermine your team’s efforts
(Luxbacher, 2014).
Rafiun, A. and Purwanto, S.
The Effect of Dribbling Exercises with Tools and Dribbling with Opponent and the Aye-foot Coordination in Increasing the Dribbling Skill of Extracurricular Participants.
DOI: 10.5220/0009309802410243
In Proceedings of the 3rd Yogyakarta Inter national Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science in conjunction with the 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports
(YISHPESS and CoIS 2019), pages 241-243
ISBN: 978-989-758-457-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
241

Based on observations in some schools that
have football extracurricular activities in Bima
regency, most trainers complained that the ball
position of their club players was still not good
enough. This was seen when the ball was easily
captured by the opponent because the level of
dribbling ability was still not good.
Attaining an achievement is certainly
something that is not easy and it requires some
important supporting factors; one of them is
training. Nossek (1982) defines training as a
process of perfecting exercise through a scientific
approach in which it implements the education
principles regularly and plans to increase the
ability and readiness of the sportsmen.
In addition, aspects that can increase dribbling
ability is a good coordination. According to Bompa
(2004), coordination is complex motor skill which
is necessary in achieving high performance. Good
coordination makes the players can change and
move quickly from one pattern of motion to
another so that the movement becomes effective.
The method of dribbling training with tools and
dribbling exercises with opponents influence each
other, in which both exercises require eye-foot
coordination on high and low eye-foot
coordination. Players with high eye-foot
coordination with dribbling training with
opponents have better dribbling skills compared to
players with high eye-foot coordination who
receive treatment with dribbling training methods
with tools. Likewise, players who have low eye-
foot coordination with the application of forms of
training with tools are better than players who have
low eye-foot coordination but are trained by using
dribbling exercises with opponents. Thus, the
effectiveness of using the dribbling skill method is
influenced by the eye-foot coordination that each
player has.
Based on the description above, the authors are
interested in conducting this research on "The
effect of dribbling exercises with tools and
dribbling with opponents and eye-foot
coordination on increasing the dribbling skills of
football extracurricular participants in Bima
regency." To see how high the influence between
dribbling exercises with tools and dribbling with
opponents and influence between eye-foot
coordination (high eye-foot coordination and low
eye-foot coordination) as well as how the
interaction between exercise and tooling and
dribbling with opponents and eye-foot
coordination (high and low) on football
extracurricular dribbling skills in Bima regency.
2 METHOD
This research used experimental method with 2x2
factorial design. The experimental research method
is a series of experiments with the aim to
investigate something or a problem in order to
obtain results. Experimental methods must have
tried factors, in this case the tried and independent
or independent variables are dribbling training
methods with tools and dribbling with opponents
to know the difference in effect with the dependent
or dependent variable namely dribbling skills in
soccer games, and attribute variables namely eye
coordination feet high and low eye-foot
coordination.
The research population was extracurricular
participants of SMP NEGERI 4 BOLO and SMP
NEGERI 1 WOHA. This research used probability
sampling to determine the sample. Sample was
chosen by simple random sampling include 39
participants. The instrument in this research used
dribbling test and johnsonl soccer test. The data
analysis used ANAVA two-ways at the significant
level α= 0.05.
Data collection techniques carried out in this
study were tests and measurements. Before the
pretest and posttest measurements were taken, the
sample was first measured by eye-foot
coordination, to determine high and low eye-foot
coordination.
Given the research data analysis was carried
out using ANAVA, then before arriving at the use
of two-way ANAVA it is necessary to conduct a
prerequisite test which includes: (1) normality test
and variant homogeneity test and (2) hypothesis
testing.
3 RESEARCH RESULTS AND
DISCUSSION
The results of this research are the form of pretest
and posttest data which is a general description of
each of the variables involved in this research. The
result was from the ANAVA test.
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
242
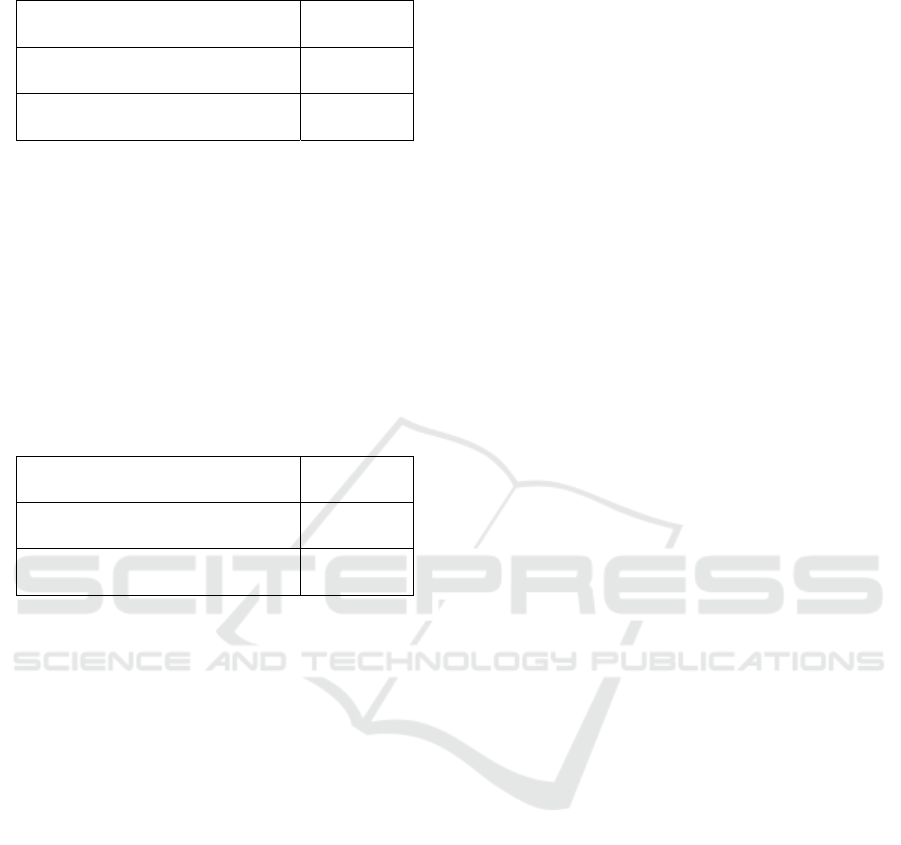
Table 1. The significance of dribbling exercises with
tools and dribbling with opponents
Source Sig
Dribbling with tools 0.047
Dribbling with opponents 0.204
The results of the table above can be seen that
the dribbling exercises with the tool did not give
effect to extracurricular participants with a
significant value of P = 0.047. Because the
significance value of p is 0.047 <0.05, it means
that Ho is rejected. Whereas dribbling with
opponents has a significant value of P = 0.204.
With the significance value of p is 0.047 <0.05,
meaning Ho is accepted.
Table 2. The significance of dribbling exercises with
Dribbling exercises with high eye-foot coordination and
dribbling exercises with low eye-foot coordination
Source Sig
Dribbling exercises with high eye-
foot coordination
0. 132
Dribbling exercises with low eye-
foot coordination
0. 030
From the results of the table above, it can be
seen that dribbling exercises with high eye-foot
coordination had high effect on extracurricular
participants with a significant value of P = 0.132.
Because the significance value of P is 0.132 <0.05,
it means that Ho is accepted. While dribbling
exercises with low eye-foot coordination have a
significant value of P = 0.030. Because the
significance value of P is 0.030 <0.05, it means
that Ho is rejected.
4 CONCLUSION
Based on the discussion and and looking at the
result of this research, the researcher put forward
some conclusions as follows (1) Dribbling with
opponents have a high influence on improving
dribbling skills of football extracurricular
participants than Dribbling with tools. (2) dribbling
exercises with high eye-foot coordination have
more effective on improving the football
extracurricular participant’s dribbling skills of
Bima regency than the exercises with low eye-foot
coordination, (3) there is an interaction between
dribbling and tooling and dribbling with opponents
and eye-foot coordination (high and low) on the
dribbling skills of Bima extracurricular members
of the district as evidenced by the increased ability
of participants after doing dribbling exercises with
these methods.
REFERENCES
Huijgen Barbara C. H & Visscher Chris., 2010.
Development of dribbling in talented youth soccer
players aged 12–19 years: A longitudinal study.
Journal of Sport Sciences
Luxbacher A. Joseph., 2014. Soccer step to success.
Human Kinestic inc. USA
Undang-Undang RI Nomor 3 Tahun 2005 tentang
Sistem Keolahragaan Nasional
The Effect of Dribbling Exercises with Tools and Dribbling with Opponent and the Aye-foot Coordination in Increasing the Dribbling Skill
of Extracurricular Participants
243
