
The Influencing Factors for Business Start-up Intention
in Social Media by UTAUT Perspective
Yasmin Chairunisa Muchtar, Fadli, and Inneke Qamariah
Department of Management, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl. Prof. T.M Hanafiah, SH, Kampus USU, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Performance Expectancy, Effort Expectancy, Social Influence, Facilitating Condition, Social Media.
Abstract: According to Sox et al. (2014), Millennials are rising to 75% of the worldwide workforce by 2025 and
entrepreneurship is an interesting profession for Millennials. Millennials have been recognized as a distinct
generation which has higher exposure to internet-based business platform namely social media. Social media
has offered promising opportunities for business due to its flexibility and ability to reduce the complexity of
business entry barriers compared to traditional business platform. It has attracted Millennials to utilize social
media for business start-up especially for those who are interested to select entrepreneur as their profession.
Hence, this study aims to examine factors that influence the acceptance and use of social media for business
start-up. Result shows that partially, performance expectancy, effort expectancy, social influence and
facilitating condition have significant influence on the behavioral intention to use social media for business
start-up. Moreover, simultaneously performance expectancy, effort expectancy, social influence and
facilitating conditions have a significant effect on the behavioral intention to use social media for business
start-up.
1 INTRODUCTION
Millennials generation was born in the world of new
technology and adjusted to various forms of
information technology. They are well connected to
the internet which is identified by the use and
adoption of technology in their routine activity. Refer
to the Indonesian Internet Service Providers
Association (APJII), internet users in Indonesia in
2018 more 54.7% of the total population, where the
highest composition falls were at ages group 19-34
years old.
The number of millennials has increased to 75%
of the global workforce by 2025, their entrepreneurial
mindset has the potential to create employment in the
coming year (Sox et al., 2014). The Millennium
predicts entrepreneurship as an attractive life path.
Millennial as a digital generation is familiar with
social media. Almost 47% of smartphone owners visit
social media platforms every day. Users are now
increasingly using their smartphones to access social
media platforms (Nielsen, 2014). This has created
profitable business opportunities for Millennials who
are interested in choosing entrepreneurs as their
career path.
Nevertheless, among Millennials, there is
restricted research which peculiarly investigate the
intention to use social media for business start-up.
Previous research focused on the behavioral intention
to use internet marketing among entrepreneurs (Tan
et al., 2013) rather than the social media for business
start-up. Consequently, the focus of this research is to
analyze factors that influence the acceptance and use
of Social media for business start-up.
1.1 Research Aim
This study aims to examine factors that influence the
acceptance and use of social media for business start-
up.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Unified Theory of Acceptance and
Use of Technology (UTAUT)
Venkatesh et al. (2003) suggest the UTAUT and has
become a common model applied by scholars in
examining the intention and use of behavior towards
498
Muchtar, Y., Fadli, . and Qamariah, I.
The Influencing Factors for Business Start-up Intention in Social Media by UTAUT Perspective.
DOI: 10.5220/0009307904980503
In Proceedings of the 2nd Economics and Business International Conference (EBIC 2019) - Economics and Business in Industrial Revolution 4.0, pages 498-503
ISBN: 978-989-758-498-5
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

technology (Chua et al., 2018; Tan et al., 2012; Latif
et al., 2011). Adoption of technology with UTAUT
theory derives with the theory of Diffusion of
Innovation (DOI), Social Cognitive Theory (SCT),
Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) and Technology
Acceptance Model Theory (TAM). These theories
create four key constructs that influence behavioral
intentions and use behavioral. The four constructs
involve performance expectancy, effort expectancy,
social expectancy, and facilitating conditions.
2.2 Social Media
Social media is the media used by consumers to share
text, images, sound, and video information both with
others and companies and vice versa (Kotler and
Keller, 2016). Some social media sites that are
popular today include Instagram, Twitter, Facebook,
and YouTube. The use or utilization of social media
is divided into two, namely: 1) Social Media increases
the power of individuals by providing higher roads
without excessive support from users (Curran &
Lennon, 2011). 2) Using Social Media, can help or
restore relationships between new and old users, and
develop communities that collaborate to facilitate
problems and solutions for themselves and their
business (Meredith & O'Donnell, 2011). 3) Social
Media platforms have large audiences because of
their networking and community mobilization
capabilities and this creates an opportunity for
businesses to promote and sell products or services
directly to these users. 4) These revenue/business
models used by social media are very new
approaches, and more empirical research is required
to optimize these model for better returns (Rathore
and Ilavarasan, 2017)
Indicators of social media according to Mayfield
(2008) are 1) participation, social media encourages
contributions and feedback from everyone interested.
2) openness, most social media services are open for
feedback and participation. They encourage voting,
comments and the sharing of information. 3)
conversation, whereas traditional media is about
“broadcast” (content transmitted or distributed to an
audience) social media is better seen as a two-way
conversation. 4) community, social media allows
communities to form quickly and communicate
effectively. Communities share common interests,
such as photography, political issues or favorite
television and radio programs. 5) connectedness,
most kinds of social media thrive on their
connectedness, making use of links to other sites,
resources, and people.
2.3 Millenials
People born between 1980 and 2000 is called the
millennial generation( Lloyd et al. 2013). They are
labeled as Nexters, Generation Y, and the Nexus
Generation (Twenge, 2011). It is bigger than 25 % of
Millenials have a job whiches not required the
education level they have possessed. Millennials have
demonstrated the interest to create their job such as
starting up a new business. (Intuit Canada, 2013)
Ng et al. (2010) investigated about perceive
career decision making of Millenials and found that
they wish to have a different path of career than the
past generation. They prefer employers who support
the progress along the career path by providing
training. While Gursoy et al. (2013) discovered
millenials highlight work-life balance, desire good
payment and benefits, as well as hope for the potential
of rapid career advancement, a fruitful working
experience. Those combinations create
entrepreneurship as a favored option for Millenials.
2.4 Performance Expectancy
Brown et al. (2016), performance expectancy can be
defined as the belief of a person on how much the
technology will be beneficial for the increase of
performance. Al-Gahtani et al. (2007) produced
evidence that performance expectancy has a
significant role in influencing the behavioral intention
of teachers to utilize digital learning apps since it
eases their job and enhance the effect of education.
Among all the determinant factors of behavioral
intention to apply mobile apps, it was proved that
performance expectancy is the strongest determinant
(Chong, 2013). The similar result by Wong et al.
(2015) found that performance expectancy would
influence the behavioral intention significantly as
well as the use behavior for adopting the technology.
Therefore, the following hypothesis is proposed:
H
1
: Performance expectancy has a significant effect
on the behavioral intention to use social media for
business start-up.
2.5 Effort Expectancy
Venkatesh et al. (2012) proposed that effort
expectancy is the amount of ease linked with the use
of certain technology and acknowledged as a crucial
factor to determine the user's behavioral intention to
use the technology(Wong et al., 2015). In addition,
Zhou et al. (2010) stated there is a direct association
between effort expectancy and behavioral intention
The Influencing Factors for Business Start-up Intention in Social Media by UTAUT Perspective
499

based on UTAUT constructs. The lesser the effort to
understand that technology the higher the user’s
adoption of that technology. A study from Yang
(2015), analyzing young consumer's behavioral
intention of mobile shopping apps. Results showed
that effort expectancy was able to predict the adoption
of mobile apps positively. There are three constructs
namely perceived ease of use, complexity, and ease
of use.
H
2
: Effort expectancy has a significant effect on the
behavioral intention to use social media for business
start-up.
2.6 Social Influence
Social influence significantly affects the behavioral
intention of users to adopt mobile commerce (Chong,
2013). As conveyed by Martin and Herero (2012), an
individual is likely to follow the opinion and behavior
of their respected group. Venkatesh et al. (2013)
explains social influence as the degree to which of a
person care to the perception of others who are
essential for that person. Young adults who desire
social acceptance will be affected by their peers
instead of family members in terms of the intention to
use mobile apps (Taylor et al., 2011), especially in
social networking apps in comparison with other
mobile apps (Kucukemiroglu and Kara, 2015).
H
3
: Social Influence has a significant effect on the
behavioral intention to use.
2.7 Facilitating Condition
Facilitating conditions is a vital factor for
entrepreneurs to use IT innovation in the market.
Entrepreneurs tend to have higher interest to use the
technology if the infrastructure and special training
support are available. Technology with outstanding
user interface, simple access, navigation, and
searching are among the requirement of facilitating
condition that should exist which will support the
usage of internet marketing (Fang and Salvendy,
2003); Siddiqui et al, 2003; Yang, 2010), specifically
when the guidance is properly supplied. Other
importantly conditions namely cost and other
resources linked with the usage, as well as the prior
knowledge that should be possessed by the user
before using internet marketing. These are essential
factors of facilitating, conditions which influence
behavioral intention (Ajzen, 1991; Taylor and Todd,
1995). Based on those reasons, the following
hypothesis is:
H
4
: Facilitating condition has a significant effect on
the behavioral intention to use social media for
business start-up.
2.8 Behavioral Intention to Use Social
Media for Business Start-up
Aula (2010: 43) defines SM as a place where
customers can communicate directly with their
favorite organizations and collect more information
about the organizations’ products instead of simply
providing a platform for individuals to keep related
with their family and friends. Behavioral intention in
this study is defined as the users’ intention rather than
the actual use of social media. Behavior intention is
the intention to use social media in the near future
over the traditional business start-up. According to
Saphero (1982); Krueger and Brazel (1994), Intention
is an individual’s desire to pursue a given behavior
and represent an individual’s commitment toward a
specific behavior. In this study, behavior intention
refer to the degree to which Millennials plan to use
social media for business start-up.
3 METHOD
The type of this research is a case study located in
University of Sumatera Utara. The population in this
research is 894 students from the Faculty of
Economics and Business and Faculty of Public Health
batch 2017 in the University of Sumatera Utara that
had already received entrepreneurship courses. All of
the university students can be categorized as
Millennials, born from 1980-2000. As these faculties
have an entrepreneurship curriculum and the students
are willing to be entrepreneurs. Samples are selected
by utilizing the simple random sampling. A simple
random sample is a subset of a statistical population
in which each member of the subset has an equal
probability of being chosen. The number of samples
is 276 Millennials by using slovin method.
This research used two types of data resources,
which are: (1) Distribution of Questionnaires, and (2)
Documentations Studies. Multiple linear regression
analysis is used as data analysis technique to discover
the influence of the independent variables, which are
Performance Expectancy (X1), Effort Expectancy
(X2), Social Influence (X3), and Facilitating
Condition (X4) to the dependent variable that is
Behavioral Intention to Use Social Media for
Business Start-Up (Y). Also, this research is using
descriptive statistical analysis method.
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
500
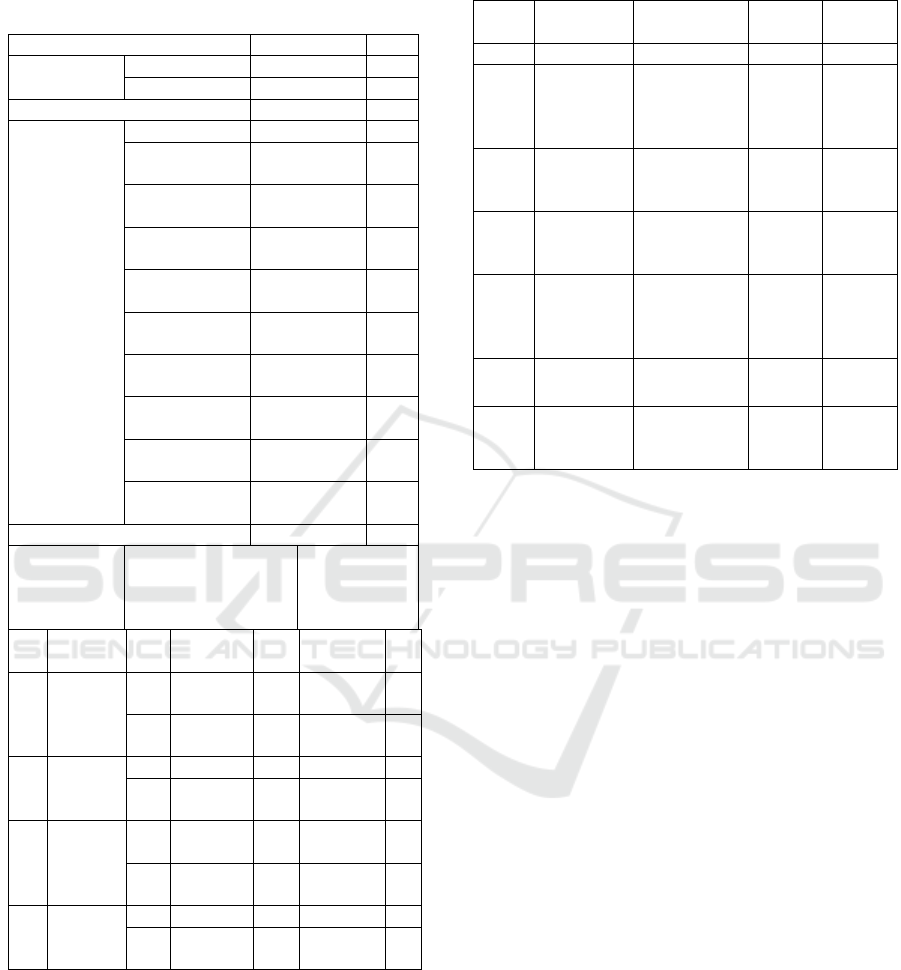
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Table 1: Characteristics of Respondents.
Frequenc
y
%
Business
Experience
Yes 108 39.1
No 168 60.9
Total 276 100
Duration of
Social Media
Use for
Shopping
0
–
1 Yea
r
0 0
1,1 Years – 2,1
Years
15 5.4
2,2 Years – 3,2
Years
7 2.5
3,3 Years – 4,3
Years
8 2.9
4,4 Years – 5,4
Years
52 18.8
5,5 Years – 6,5
Years
29 10.5
6,6 Years – 7,6
Years
59 21.4
7,7 Years – 8,7
Years
45 16.3
8,8 Years – 9,8
Years
15 5.4
9,9 Years – 10,
9 Years
46 16.7
Total 276 100
SHOPPING FROM
SOCIAL MEDIA
SELLING
FROM
SOCIAL
MEDIA
No Social
Media
Frequency % Frequency %
1
Faceboo
k
Yes
51 18.5
30
10.
9
No
225 81.5
246
89.
1
2 Twitter
Yes 7 2.5 0 0
No
269 97.5
276
10
0
3
Instagra
m
Yes
105 38.0
104
37.
7
No
171 62.0
172
62.
3
4 Etc.
Yes 82 29.7 15 5.4
No
194 70.3
261
94.
6
Table 1 demonstrates that the majority of millennials
have used social media for shopping for more than 6.5
years at 59.8% (165 peoples). The majority of social
media users through Instagram, while the lowest rank
uses Twitter. In making purchases, millennials prefer
to use Instagram to sell compared to other social
media applications.
Table 2: The Result of Multiple Linear Regression
Analysis.
No Variables Coefficients
t-
Values
Signif-
icant
1 Constant -0.417 -0.528 0.598
2 Performa-
nce
Expec-
tancy (PE)
0.486 8.469 0.000
3 Effort
Expectan-
c
y
(
EE
)
0.084 2.266 0.024
4 Social
Influence
(
SI
)
0.184 3.461 0.001
5 Facilitati-
ng
Conditi-
on
(
FC
)
0.036 1.019 0.309
6
𝑅
=
0.630
7 (F-
Statistic =
118.263
)
0.000
It is found the Multiple Regression Analysis Model
is:
Y = -0.417 + 0.486PE + 0.084EE + 0.184SI +
0.036FC + e
Table 2 shows the two predictor variables, partially
Performance Expectancy (Sig. = 0.000 < 0.05), Effort
Expectancy (Sig. = 0.024 < 0.05), and Social
Influence (Sig. = 0.001 < 0.05) are significantly
affecting Behavior Intention to Use Social Media for
Business Start-Up. On the other hand, the remaining
one variable, which is Facilitating Condition (Sig. =
0.309 > 0.05) is insignificantly contributing to
Behavior Intention to Use Social Media for Business
Start-Up. The coefficient determination of this
research is 0.630, which means that Performance
Expectancy, Effort Expectancy, Social Influence, and
Facilitating Condition contributed 63% to explain
Behavior Intention to Use Social Media for Business
Start-Up. While the remaining 37% is explained by
other variables.
The Influencing Factors for Business Start-up Intention in Social Media by UTAUT Perspective
501
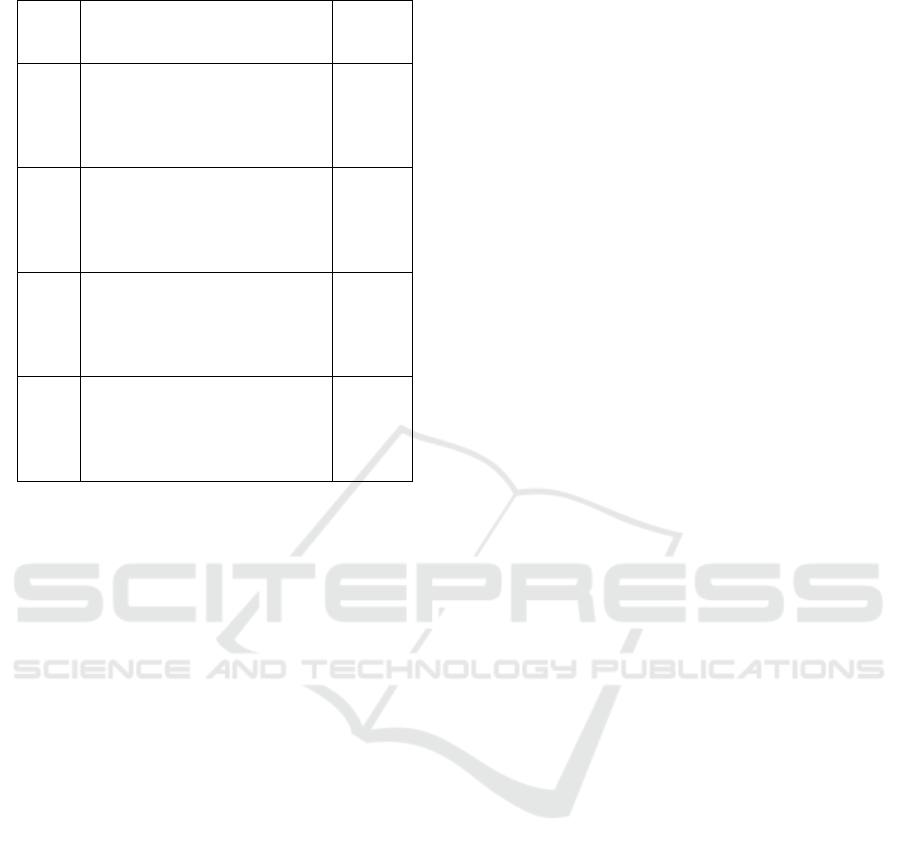
Table 3: Summary of Hypothesis Tests.
Hypo
thesis
No.
Statement
Decisio
n
H
1
Performance Expectancy has a
significant effect on the
behavioral intention to use
social media for business start-
u
p
Support
ed
H
2
Effort Expectancy has a
significant effect on the
behavioral intention to use
social media for business start-
up
Support
ed
H
3
Social Influence has a
significant effect on the
behavioral intention to use
social media for business start-
up
Support
ed
H
4
Facilitating Condition has a
significant effect on the
behavioral intention to use
social media for business start-
u
p
Not
Support
ed
Partially, performance expectancy, effort
expectancy, and social influence have a significant
effect on the behavioral intention to use social media
for business start-ups. Meanwhile, another variable,
namely facilitating conditions, does not significantly
influence behavioral intention for the use of social
media in starting a business.
Result indicates that performance expectancy
significantly influences behavioral intention by
utilizing social media in accordance with research by
Al-Gahtan et al. (2007). This proves that millennials
consider that using social media will facilitate them
in starting a business, which will certainly support
productivity and efficiency in business management
when they run their businesses.
The effort expectancy variable also significantly
influences behavioral intention by utilizing social
media in accordance with research by Zhou et al.
(2010). This shows that social media is a technology
that is easy to use, and not complicated so it does not
require much effort to use it. Therefore, it is very
reasonable to find from the results of research that
effort expectancy in millennial generation has a
significant effect on behavioral intention in starting a
business by utilizing social media.
Based on Chong (2013), social influence
influences behavioral intention to adopt Mobile
Commerce technology. This is consistent with the
results of research in which social influence also
influences behavioral intention to start a business by
utilizing social media. As Martin and Herero (2012)
pointed out, a person tends to follow the opinions and
behavior of a group of people whom he considers to
have an effect on him. Especially for the younger
generation who are very influenced by the opinions
of friends and family members in terms of the use of
social media that can be used in starting a business.
Facilitating condition is an important factor in a
person's behavioral intention to adopt a technology
such as social media. Some important facilities such
as cost, ease of navigation, search engines, and easy
access can influence a person's confidence to adopt a
technology (Ajzen 1991; Taylor and Todd 1995).
However, the results of this study indicate different
things where facilitating conditions do not
significantly influence behavioral intention in starting
a business by utilizing social media. Almatari et al.
(2012) and William et al. 2015 states that in several
previous studies facilitating conditions are not
variables that can influence one's behavioral intention
when performance expectancy and effort expectancy
exist. So it can be explained that today's young
generation can take advantage of social media
without depending on the user manual.
5 CONCLUSION
The conclusion of this research is performance
expectancy, social influence and effort expectancy
have a significant effect on the behavioral intention to
use social media for business start-up. Meanwhile,
facilitating condition is insignificantly affecting the
behavioral intention to use social media for business
start-up. Also, simultaneously performance
expectancy, effort expectancy, social influence and
facilitating conditions have a significant effect on the
behavioral intention to use social media for business
start-up.
REFERENCES
Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of Planned Behaviour.
Organizational Behavior and Human Decision
Process, 50 No. 2, 179-211.
Al-Gahtani, S. S., Hubona, G. S., & Wang, J. (2007).
Information Technology (IT) in Saudi Arabia: culture
and the acceptance and use of IT. Information and
Management, 44 (8), 681-691.
Almatari, A. Y., Lahad, N. A., & Balaid, A. S. (2012).
Factors influencing students' intention to use M-
Learning. Journal of Information Systems Research and
Innovation, 7 No. 5, 515-543.
Aula, P. (2010). Social media, reputation risk and ambient
publicity mangement. Stategy and Leadership , 38 No.
6, 43-49.
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
502

Brown, S. A., Dennis, A. R., & Venkatesh, V. (2016).
Predicting Collaboration Technology Use: Integrating
Technolgy Adoption and Collaboration Research.
Journal of Management Information Systems , 27, 9-53.
Chong, A. Y. (2013). Predicting M- Commerce adoption
Determinants: a neural network approach. Export
System with Application , 40 (2), 523-530.
Chong, A. Y. (2013). Predicting m-commerce adoption
determinants: a neutral network approach. Expert
System with Application , 40 No. 2, 523-530.
chua, P. Y., Rezaei, S., Gu, M. L., Oh, Y. M., &
Jambulingan, M. (2018). Elucidating social networking
apps decisions: Performance expectancy, effort
expectancy and social influence. Nankai Business
Review International , 9 (2), 118-142.
CNW. (2013, October 9). Intuit Inc. Dipetik September
2019, dari https://www.intuit.com
Curran, J., & Lennon, R. (2011). Participating in the
conversation:exploring adoption of online social media.
Academy of marketing studies journal , 15 (1), 21-38.
Fang, W., & Salvendy, G. (2003). Customer-centred rules
for design of e-commerce web sites. communication of
the ACM , 46 No. 12, 332-336.
Gursoy, D., Chi, C. G., & Karadag, E. (2013). Generational
Differences in work values and attitudes among
frontline and service contact employees. International
Journal of Hospitality Management , 32, 40-48.
Kotler, P., & Kevin, L. (2016). Marketing Management
15th edition. United States: Pearson Education.
Krueger, N., & Brazeal, D. V. (1994). Entrepreneurial
potential and potential entrepreneurs. Entrepreneurship
Theory and Practice Journal , 91-104.
Kucukemiroglu, S., & Kara, A. (2015). Online word of
mouth communication on Social networking sites.
International Journal of Commerce and Management ,
25, 2-20.
Latif, A. R., Adnan, J., & Zamalia, M. (2011). Intention to
Use Digital Library Based on Modified UTAUT
Model: Perspective of malaysian Postgraduade
Students. World Academy of Science, Engineering and
Technology , 116-122.
Lloyd, T., Shaffer, M. L., Stetter, C., Widome, M. D.,
Repke, J., Weitekamp, M. R., et al. (2013). Health
knowledge among the millenial generation. Journal of
Public Health Research , 2, 38-46.
Martin, H. S., & Herrero, A. (2012). Influence of the user's
psycological factor's on the online purchase intention in
rural tourism: integrating innovativeness to the UTAUT
framework. Tourism Management , 33 no. 2, 341-350.
Mayfield, A. (2008). What is Social Media? United
Kingdom: ICrossing.
Meredith, R., & O'Donnel, P. (2011). a framework for
understanding the role of social media in business
intelligence system. journal of decision system , 20 (3),
263-282.
Ng, E. S., Schweitzer, L., & Lyons, S. T. (2010). New
generation, great Expectations, a field study of the
millenial generation. Journal of Business and
Psychology , 25, 281-292.
Nielsen. (2014). Dipetik march 24, 2015, dari
http://www.nielsen.com/us/en/insights/reports/2014/th
e-us-digital-consumer-report.html
Rathore, A., & Ilavarasan, P. (2018). Social Media and
Business practices. Encyclopedia of Information
Science and Technology , 7126-7139.
Shapero, A. (1982). Social Dimensions of Entrepreneurship
in C. Kent, D. Sexton & K. Vesper (eds), The
Encyclopedia of Entrepreneurship. Englewood Cliffs,
New York.
Siddiqui, N., O'Malley, A., McColl, J., & Britwistle, G.
(2003). Retailer and Consumer perception of online
fashion retailers web sites design issues. Journal of
Fashion Marketing & Management , 17 No. 1, 20-35.
Sox, C. B., Kline, S. F., & Crews, T. B. (2014). Identifying
Best Practices, Opportunities and Barriers in Meeting
Planning for Generation Y. International Journal of
Hospitality Management , 36, 244 - 254.
Tan, G., Sim, J., Ooi, K., & Phusavat, K. (2012).
Determinants of Mobile Learning Adoption: An
Empirical Analysis. Journal of Computer Information
System , 82-91.
Taylor, D., Voelker, T. A., & Pentina, I. (2011). Mobile
Application adoption by young adults: a social network
perspective. International Journal of Mobile marketing
, 6 no. 2, 60-70.
Taylor, S., & Todd, P. (1995). Understanding Information
Technology Usage; a test of Competing Models.
Information System Research , 42 No. 1, 85-92.
Twenge, J. M., Campbell, S. M., Hoffman, B. J., & Lance,
C. (2010). Generational Differences in work values:
Leissure and extrinsic values increasing, social and
intrinsic values decreasing. Journal of Management ,
36, 1117-1142.
Venkatesh, V., Morris, G., Davis, G. B., & Davis, F. D.
(2003). User Acceptance of Information Technology:
Toward A Unified View. MIS Quarterly , 27 (3), 425-
478.
Venkatesh, V., Thong, J., & Xu, X. (2012). Consumer
Acceptance and Use of Information Technology:
Extending The Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use
of Technology. MIS Quarterly , 36, 157-178.
Williams, M. D., Rana, N. P., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2015). The
unified theory of acceptance and use of technology
(UTAUT): a litearture review. Journal of Enterprise
Information Management , 28 No. 3, 443-488.
Wong, C. H., Tan, G. W., Loke, S. P., & Ooi, K. B. (2015).
Adoption of Mobile Social Networking Sites for
learning. Online Information Review , 39 no.6, 762-
778.
Yang, K. (2010). Determinants of US consumer mobile
shopping services. Journal of Consumer Marketing , 27
No. 3, 262-270.
yang, K. (2015). Determinants of US Consumer Mobile
Shopping Services adoption: Implications for designing
mobile shopping services. Journal of Consumer
Marketing , 27 No. 3, 262-270.
Zhou, T., Lu, Y., & Wang, B. (2010). Integrating TTF and
UTAUT to explain mobile banking user adoption.
Computers in Human Behaviour , 13 No. 3, 760-767.
The Influencing Factors for Business Start-up Intention in Social Media by UTAUT Perspective
503
