
Gymnastics Multimedia Learning Development for Physical
Education
Riangga Dwi Martanti
1
, Sri Winarni
1
1
State University of Yogyakarta, Sleman, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Master of Sports Science, Faculty of Postgraduate
Keywords: Multimedia, Gymnastic, Junior High School.
Abstract: The purpose of this study is to develop gymnastics multimedia learning in physical education (PE) for
junior high school (JHS). This study adapted the research and development of Dick & Carey model of
education with 4 steps, namely (1) the needs analysis stage, (2) the product design stage, (3) the stage of
evaluation and evaluation, and (4) the final product stage. The subjects in this study were 1 material expert,
1 media expert, 2 PE teachers, and 126 students. The effectiveness test was carried out at Jatilawang JHS
1with 1 class of 34 students. Data were collected using questionnaire techniques and performance. The
results of the study were in the form of developing gymnastic learning on PE of JHS the form of an
Android-based application entitled "MaGym" consisting of 6 main menus, namely (1) main menu, (2)
introduction, (3) material, (4) instruction, (5 ) evaluation, and (6) author profile. Based on the assessment of
material experts, media experts, PE teachers, students and product effectiveness tests, it could be concluded
that the development of gymnastic learning in PE for JHS was feasible to apply to PE for JHS students and
the results of the study indicated that multimedia was effective in improving student gymnastics learning
outcomes.
1 INTRODUCTION
Education is a process of human self-development.
This is in accordance with Law No. 20 of 2003
concerning the National Education System which
explains that National Education is "a conscious and
planned effort to create a learning atmosphere and
learning process, so that students actively develop
their potential to have religious spiritual strength,
self-control, personality, intelligence, noble
character, and skills needed by him, society, nation
and state ". Schools as formal institutions have the
duty and responsibility to carry out the education
process. In the learning process, there are many
factors that influence the success of the learning
process, including factors such as students, teachers,
facilities, environment and school conditions. From
the several factors above, the two most influential
factors are student factors and teacher factors.
The purpose of the learning process is to provide
information and to transfer information from
learning resources to recipients. The learning
process can be done anytime and anywhere. A good
learning process should have good learning
resources. These learning resources will provide
some of the information that is useful for learning.
The source of learning is now diverse and can be in
the form of books, article magazines, the internet or
from the instructors themselves. Even with these
good learning resources, students are required to be
able to improve their own abilities.
To help students in motion, the approach to use
media with excess repetition of motion with
encouragement and examples directly or with the
help of the media is now crucial to have. Sound,
images, videos and simulations are examples of
media forms that can be used. Direct examples in
front of children and important videos are useful in
learning motion. The approach to motion from easy
to difficult in the form of examples of movement
with the media can help students learn to move well.
128
Martanti, R. and Winarni, S.
Gymnastics Multimedia Learning Development for Physical Education.
DOI: 10.5220/0009214601280135
In Proceedings of the 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science in conjunction with the 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports
(YISHPESS and CoIS 2019), pages 128-135
ISBN: 978-989-758-457-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

The demands of the 21st century on digital
literacy, the learning resources are no longer just
textbooks. Nowadays, it covers existing information
in technology. Technological developments for the
community, especially android, make teachers and
students no longer familiar with their roles in daily
life. In terms of learning, teachers should have tried
to improve learning achievement by integrating
technology, for example on how to use Android to
integrate with various media as learning multimedia.
The use of multimedia learning is helping students
not only to understand teaching material, but also to
practice their skills.
One of the technological advancements,that is
developed at this time, is a smartphone. Smartphone
is a device that allows for communication (call or
SMS). It has the functions as a PDA (Personal
Digital Assistant) and a computer.
Physical education requires learning media, so
that they will facilitate educators in delivering the
materials. One of the materials taught is gymnastics.
Also, learning media should be able to facilitate
students in understanding the materials provided.
However, in reality, there are many students who
underestimate this and considered this as boring,
unattractive, and also scary. Moreover, the condition
is worsen by conventional and limited learning
media, as well as teachers who lack mastering the
floor gymnastics materials since floor gymnastics
materials is considered unattractive by students.
Students assume that floor gymnastics is a scary
sport that makes the body sick and can cause injury.
The existence of important media can be the tool
for teachers in the teaching and learning process.
With media, students can learn more easily in
understanding the materials. The goal of learning
can be conveyed, so that the students are expected to
be able to apply the knowledge in everyday life. The
abundance of media and the increasing affordability
of access to technology make it possible to use it.
Choosing the right media to support the teaching and
learning process is important, so that the main
objectives of learning can be achieved.
In an effort to provide complete learning
resources, the researchers intend to create
multimedia-based android learning for floor
gymnastics learning. The learning application was
called MaGym.
The purpose of this study is to develop
multimedia that are suitable to be used as learning
media. These multimedia should be appropriate in
the opinion of the materials experts, instructional
media experts, teachers and students. Finally, it
should be able to effectively improve the skills of
floor gymnastic for junior high school students.
1.1 Multimedia Learning
Multimedia learning comes from two words, namely
multimedia and learning. The word multimedia is
also composed of a combination of two words
namely multi and media. Multi in Latin comes from
the word nouns which means various. Media comes
from the word medius in Latin, which means middle,
intermediary or introductory. The notion of
multimedia is an interrelated combination of text,
images, photos, sounds, animations and videos that
are made digitally. Based on the above meanings, it
can be concluded that multimedia is a combination
of various media that serves to convey information
to the public (
Vaughan, 2010).
Multimedia learning is actually part of a learning
environment facilitated by instructors or educators to
achieve learning goals. The idea is to use of various
media to display information (
Ivers, 2010). These
media can include writing, graphics, videos, images,
and sounds. Based on this statement, multimedia is a
learning tool whose content is a combination or
integration and integration of more than one media
for a personal interest or learning.
The multimedia term used as a combination of
text, still graphics, animations, audio and video
within a single technology, such as computer or
television. It means that multimedia is used to
describe a combination of writing, graphics,
animation, audio, and video in one technology, such
as computers and television (
Bates, 2003).
The choice of earning media used in learning
activities needs to consider factors in the curriculum.
The contents of the information and knowledge
should be good or up to date. In other words, the
media should be able to be updated regularly, as the
current technology is developing very rapidly.
Multimedia learning has many types, namely
computer-based learning, e-learning, 3D, mobile
learning and animation and presentation media
(
Darmawan, 2016). Multimedia used in this research
is mobile learning.
Mobile learning is a type of learning done
through portable devices that are easy to access and
easy to carry anywhere. Also, it makes it easy to
communicate with others and can be used anywhere
(
Goksu and Atici, 2013). Mobile devices used in
mobile learning can be in the forms of laptops,
palmtop computers or PDAs (personal digital
assistants), tablet PCs, and smartphones (
Valk,
Rashid, and Elder, 2010)
.
Gymnastics Multimedia Learning Development for Physical Education
129

Mobile learning is learning that utilizes
technology and mobile devices. Mobile here means
a PDA, cell phone, laptop, tablet PC and so on.
Users can access learning content anywhere and
anytime with mobile learning without having to visit
a certain place at a certain time. Thus, users can
access educational content without being bound by
time and space.
Mobile learning can be utilized and developed in
the form of a new learning culture that is more
modern, democratic and educational (
Miftah, 2013).
Learning culture is a small part of the culture of
society. The culture of the community here can be
interpreted as the integration of all objects, ideas of
knowledge, institutions, and ways of doing things;
patterns of behavior, values, habits, and attitudes of
a generation in a society, that is accepted by a
generation from its predecessor generation and is
passed often in a form that has changed to the
generation successor.
The characteristics of mobile learning are (1)
enabling student mobility through mobile devices,
(2) learning anytime and anywhere, (3) encouraging
collaborative learning, (4) engaging students with
constant connectivity, and (5) enabling authentic
learning (
Ibanez, 2016). Mobile learning tends to use
mobile devices such as mobile phones, smartphones,
PDAs, and so on.
1.2 Physical Education
Physical education is an essential educational
process that utilizes physical activities to produce
holistic changes in the individual physically,
mentally and emotionally (
Mahendra, 2003). Physical
education treats the children as a whole unit rather
than as someone who is separated from his physical
and mental qualities.
Physical education is included in the scope of
education, so that its objectives are also tailored to
the purpose of education in general. Physical
education is education about motion and all things
related to one's personal development physically,
mentally and socially. Physical education is an
integral part of mind education that tries to achieve
the goal of developing physical, mental, social, and
emotional fitness for the community, with a vehicle
for physical activity (
Sukintaka 2001).
To attract student involvement in learning, the
teacher must build a good relationship by
establishing a sense of sympathy and mutual
understanding. A good relationship will make the
bridge to the passionate life of students, lead the way
into the new world of students, know the strong
interests of students, speak in the hearts of students,
foster good relations can make it easier for teachers
to engage students, facilitate classroom
management, and extend focus time and increase
student excitement. The implementation of physical
education has an important meaning in the world of
education. The purpose of physical education
consists of four domains, namely physical,
psychomotor, affective, and cognitive domain. In the
four domains, physical education is part of education
with the aim of education as the final goal. Based on
the principles and foundation of physical education,
the purpose of physical education is to develop
physical, mental, social integration and form an
independent person; to choose the form of physical
education and physical activity that is in accordance
with the conditions of a person and social
environment; and to develop health in accordance
with standards (
Rosdiani, 2013).
The purpose of some views above about the
nature of physical education is that physical
education learning should be maximized as best as
possible for students, so that students' physical,
mental and emotional development can always be
maintained. Physical health will also be able to
facilitate students to carry out daily activities
effectively and efficiently produce something that is
optimal. In addition, physical education must also be
delivered as pleasant as possible, so that students can
enjoy the educational process and can achieve
optimal results and can achieve learning goals.
Gymnastics is one of the gymnastic materials in
physical education. Floor exercises are carried out
on the floor without using tools. Rolling, balance,
and spinning are the basic movements in
gymnastics. Gymnastics is part of gymnastics, and
the term "floor" shows that the movement of the
exercise is done on the floor using a mat or rug
(
Sholeh, 1992). Gymnastics is one of the sports in
which there are elements of bouncy bouncing,
balance, jumping and jumping (
Sutrisno and Khafadi,
2010)
.
A series of floor exercises is a series of two or
more movements in floor gymnastics (
Husdarta and
Eli, 2010)
. A series of gymnastic movements is a
combination of gymnastic movements carried out
sequentially without time to stop during a movement
(
Isnaini and Suranto 2010). The circuit motion is two
or more movements, carried out sequentially with
short gestures (
Wisahati, 2010). From some of the
information above, the writer can conclude that a
series of gymnastic movements is a combination of
two or more gymnastic movements which are
carried out sequentially without pauses.
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
130

Gymnastics is a body exercise that was chosen
and created intentionally, planned, and arranged
systematically, with the aim of forming and
developing a harmonious personality. Gymnastics as
a body exercise is chosen and constructed
deliberately. It is done, planned, and arranged
systematically with the aim of increasing physical
fitness, developing skills, and instilling mental and
spiritual values.
Gymnastics is effective to optimize children's
growth and development. The movements in
gymnastics are very suitable for filling out physical
education programs. Its movements stimulate the
development of physical fitness components, such as
strength and endurance of muscles from all parts of
the body.
Gymnastics learning requires special classroom
settings that are different from learning other PE
materials. This is because gymnastics requires tools,
such as mattresses. The purpose of this class
arrangement is to increase the amount of active
learning time and opportunities for students to do
more exercise, especially by reducing the amount of
time to wait their turns because the mattresses are
limited in number. This can be understood when
there are only 1 or 2 mattresses, while the number of
students can be around 30 children. If the teacher
does not think about how to make use of the existing
mattress and how the student's turn is carried out,
there will be a waste of time, because students will
wait longer for their turns rather than do the
exercises
Dominant movement patterns are the bases or
foundations for all the more difficult gymnastic
movement skills. They can be stepping stones in
developing all gymnastic skills. Learning
gymnastics for those who have never done
gymnastics at all with a high degree of difficulty
must be based on the dominant movement pattern
skills first.
Floor gymnastics materials taught for junior high
schools, especially in class VIII, include the forward
roll, backward roll, headstand, handstand, cartwheel,
neck spring, round off, tiger sprung, and a series of
movements. Some of these skills are the
continuation of class VII material.
Children in junior high school are included in
adolescence who are usually still in the period of
searching for self-identity. Usually, their emotions
still tend to be volatile. PE teachers must understand
and pay attention to the characteristics and needs of
students. The teacher will be able to make students
learn more effectively, and to make PE learning
goals to be more effective.
2 METHODS
2.1 Research Design
This type of research is research and development,
namely the type of research used to produce certain
products, and test the effectiveness of these
products. Research and development (R & D) is a
process used to develop and validate educational
products. We not only use things like textbooks,
instructional films, and computer software, but also
methods, such as methods of teaching, and programs
such as drug education programs or staff
development programs (
Sholeh, 1992).
The development model used in this study is the
model of Dick & Carey, namely (1) identifying
learning objectives, (2) analyzing learning and
context, (3) determining learning objectives, (4)
developing assessment instruments, (5) developing
learning strategies, (6) developing and selecting
materials learning, (7) designing and conducting
formative evaluations, revisions, and (8) designing
and conducting summative evaluations (
Sutrisno and
Khafadi, 2010).
2.2 Research Procedure
This research and development procedure used the
steps of Dick & Carey. Then, from the adaptation of
the research and development procedures, the
researchers carried out the steps of research and
development into 4 stages. The researcher tried to
adjust the pace of development of Dick & Carey's
learning with the step of developing the video. The
four stages included the Requirement Analysis
Phase, Product Design Phase, Validation and
evaluation phase, and Final Product Stage.
2.3 Product Trial Design
Products in the form of videos need to be tested to
determine their quality and feasibility. Product
testing is part of a series of validation and evaluation
stages. In this research, the product would be
consulted with supervisors, experts, junior high
school teachers, and junior high school students
especially eight graders, as potential users of
learning videos. The steps in the validation and
evaluation stages were pravalation, expert
validation, and due diligence.
The subjects of the assessment included 1 media
expert, 1 material expert, 2 PJOK SMP teachers, and
126 VIII grade junior high school students. For
Gymnastics Multimedia Learning Development for Physical Education
131

feasibility test, 1 class or 34 students was for product
effectiveness testing.
The instrument of data collection is useful to
obtain the data needed according to the research
objectives. Research instruments were in the form of
suggestions, comments sheets, and questionnaires. A
questionnaire is a number of written questions that
are used to obtain information from the respondent
in the sense of reports about the person or things that
are known. The contents of the questionnaire
included the form of assessing the feasibility of
learning videos using a Likert scale with alternative
answers, namely very good, good, sufficient, lacking
and very lacking. Efforts to obtain quantitative data
were given the alternative answers as well with a
score of very good = 5, good = 4, enough = 3, less =
2, very less = 1.
2.4 Data Analysis Techniques
The analysis of the results of the research data was
conducted using qualitative and quantitative
approaches. Data in the form of suggestions and
criticisms from experts and students were analyzed
using a qualitative approach, while the feasibility
data of learning videos and opinions on video
suitability were processed with a quantitative
descriptive approach. To analyze data about the
feasibility of video learning, it was done by the
following steps, namely:
a. conducting tabulation of assessment data,
b. calculating the average score of each indicator
with the formula:
𝑥
𝛴𝑋
𝑁
Description:
X = average score
N = number of test subjects
𝛴𝑋 = number of scores
c. summing the average score of each, and
d. interpreting the average number of qualitatively
using the following 5 scale score conversion
formula
Table 1: Average amount conversion guidelines score
becomes value with five categories
No. Range Score Value Category
1 Mi + 1.50Sbi <X 5 Very Good
2 MI + 0.50Sbi <X ≤ MI
+ 1.50Sbi
4 Good
3 MI - 0.50Sbi <X ≤ MI
+ 0.50Sbi
3 Fairly Good
4 MI + 1.50Sbi <X ≤ MI
- 1.50Sbi
2 Less
5 X ≤ MI + 1.50bi 1 Very Less
Description:
X = ideal mean Ideal
maximum score = number of indicators x highest
score
Ideal minimum score = number x lowest score
Mi = ideal mean = ½ (ideal mak score + ideal min
score)
Sbi = ideal standard deviation = 1/6 (min max-score
score)
For effectiveness tests, the following criteria were
set.
Table 2: Criteria for testing the effectiveness
No Scale Rating ( %) Qualifications
1 0-55 Very Poor Good
2 56-65 Less Good
3 66-80 Good
4 81-100 Very Good
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
132

3 RESULTS
This multimedia gymnastics learning application is
called MaGym. This product was developed in the
form of apk software that can be accessed or
installed via a smartphone device, so that later users,
teachers and students will easily use it in the
learning process. Based on the research procedure
adapted from Dick & Carey, the first step taken by
the developer was a needs analysis. Needs analysis
was done to collect data through field studies and
literature studies.
Development is the stage of manufacturing
products based on guidelines in the form of
storyboards that have been made at the design stage.
Developers used the Android studio application in
making this application, with the Java programming
language and could be operated with a minimum of
15 fire. At this stage, the product was made up to
review media experts and material experts as well as
revisions. The multimedia gymnastics learning
product floor included several sections and pages,
namely menu pages, introduction pages, material
pages, instructions pages, evaluation pages, history
pages, author profile pages and exit icons.
Product feasibility test was given to 126 students
or 3 classes of 8th grade and 2 teachers of Physical
and Health Education subjects in Junior High
School. The trial was carried out in Jatilawang
Junior High Schools 1 and 2. The process of
carrying out the feasibility test of this product was to
provide products in the form of floor gymnastic
learning multimedia applications in Junior High
School Sports and Health Physical Education which
were run on smartphones. Then, students were given
time to operate and make movements with videos.
The response to the multimedia application of
floor gymnastics learning in Physical Education for
Junior High School Sports and Health that was run
on smartphones in PE teachers had 4 aspects,
namely material quality, material content,
appearance and programming. The results of the
assessment data for each product component in the
form of a score were converted into a scale value of
five. The result of the score conversion became a
scale of five. Data from product evaluation by 2 PE
teachers showed that the multimedia application of
floor gymnastics learning in Junior High School
Physical and Sports Education which had been
developed well. The aspect of material quality got a
value of 46.5 with the category "Very Good". The
content aspect of the material got a value of 56.5
with the category "Very Good". The display aspect
got a score of 72.5 with the category "Very Good".
The programming scored 32.5 with the category
"Very Good".
The product evaluation data by the students in
the table showed that the application of gymnastics
multimedia learning in Junior High School Sports
and Health Physical Education had been well
developed. The aspect of material quality scored 47
with the category "Very Good". The content aspect
received a score of 55,7 with the category "Very
Good". The display aspect got a score of 69 with the
category "Very Good". Finally, the programming
aspect got the value 31 with the category "Very
Good".
Product revisions were done twice, namely
revision I and II. Revision I was carried out at the
validation stage. Revision II was carried out after the
product feasibility test. These revisions were based
on data on advice and input from experts in material
experts and media experts. The results of the
validation by the material experts got suggestions for
improvements and criticisms that became guidelines
in making product revisions. After being validated
by material experts, there were shortcomings in floor
gymnastic learning multimedia in Physical
Education for Junior High School, namely the
original images or videos. Validation by media
experts revealed several suggestions on gymnastics
multimedia learning in Junior High School Sports
and Health Education. First, on the title page, the
study program needed to be added. Next, the button
exit needed to be given a confirmation button. Then,
the profile should be more complete, and the labels
for next and back were revised. The video needed to
be given navigation buttons, and the narration was
clarified when play background music is off.
Overall, the assessment of the product showed
positive results.
Based on the results of the expert's assessment,
the PE teacher and the students indicated that the
Gymnastic Multimedia Learning in the Junior High
School had the feasibility of material quality,
material content aspects, excellent display and
programming aspects.
Tests of effectiveness were carried out by using
media in the learning process. The results of the
learning process could be seen from the percentage
of completeness of student learning outcomes on
floor gymnastic materials, which was referred as the
Minimum Completion Criteria Value. It included
affective, cognitive and psychomotor aspects. This
Gymnastics Multimedia Learning Development for Physical Education
133
effectiveness test was done by applying MaGym
multimedia in class VIII A. The class used a
learning method, namely the scientific approach.
The results from the two classes reflected the level
of achievement of competency indicators obtained
by students. Overall, the results of student learning
values including affective, cognitive and
psychomotor aspects were described in the table as
follows.
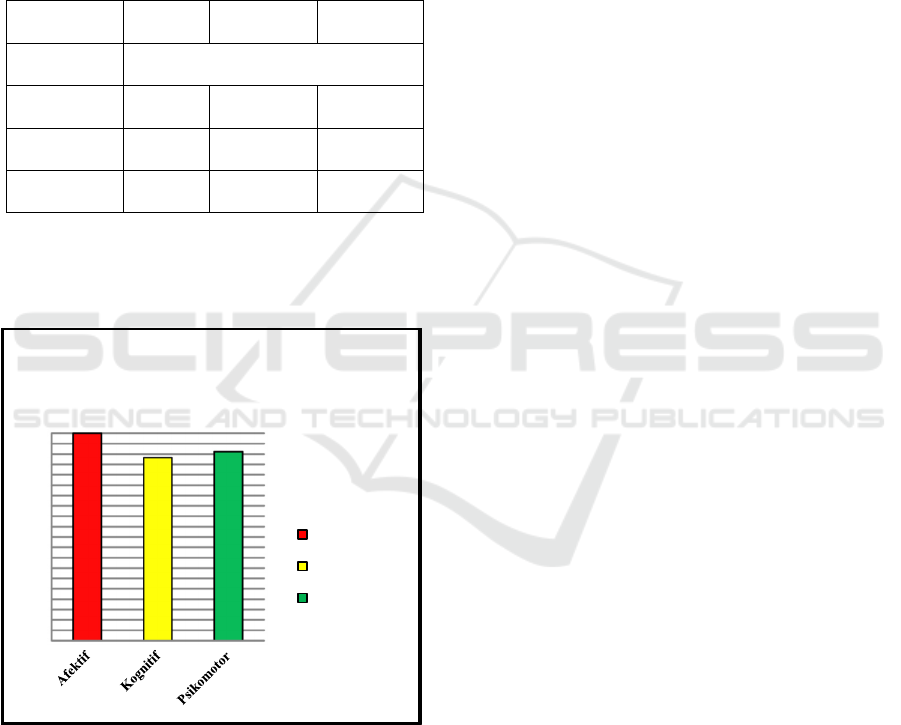
Table 3: Learning outcomes of class VIII PJOK
gymnastics at Jatilawang Junior High School 1
Value
F
(
KKM
)
Percentage Categories
Number of
Student
34
Affective
Value
34 100 Very Good
Cognitive
Value
30 88,24 Very Good
Psychomotor
Value
31 91,17 Very Good
The result of student learning values which
include affective, cognitive and psychomotor aspects
were described in the following diagram.
Figure 1: Student learning outcome values diagram by
using MaGym Multimedia in Physical Education Learning
of Gymnastic
The effectiveness test using percentage analysis
showed that the application of Android-based
MaGym multimedia, used by teachers and students
in the floor gymnastic learning process in class VIII,
was very effective. This could be seen from the
percentage of students who had fulfilled the
minimum completeness criteria. On the affective
aspect, 34 students or 100% completed and entered
in the excellent category. The cognitive values
amounted to 88.24% or 30 students completed and
included in the very good category. In the aspect of
psychomotor, there were 91.17% or 31 students
complete and fall into the very good category. The
assessment of product effectiveness test on the
development of floor gymnastics multimedia
learning in Junior High School Sports and Health
Education was in a very good category, so that this
product was suitable for use in the learning process
of physical education, sports and health.
4 CONCLUSIONS AND
SUGGESTIONS
4.1 Conclusions
Based on the results of the analysis and discussion
previously presented, it can be concluded that the
multimedia of gymnastics learning in junior high
school students was in the form of learning
applications, called MAGYM. This application
could be used as a medium for physical education
learning gymnastic material and was effectively
used to improve students' understanding in floor
gymnastic learning.
4.2 Suggestions
Based on development research, the multimedia in
this research can be used by physical education
teachers of Junior High School as an interesting,
easy and effective learning media, and by floor
gymnastics trainers as an analysis and variation in
the training process.
REFERENCES
Arikunto, S 2006, Prosedur Penelitian Suatu Pendekatan
Praktik Edisi Revisi VI, Jakarta : Rineka Cipta
Bates, AW. & Poole, G 2003, Effective teaching with
technology in higher education, foundation of success,
San Fransisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Darmawan, D 2016, Mobile learning sebuah aplikasi
teknologi pembelajaran, Jakarta: Raja Grafindo
Persada
Dick, W., Carey, L., and Carey, J.O 2009, The Systematic
Design of Instruction, New Jersey: Perason
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
75
80
85
90
95
100
Test of Effectiveness Gymnastic
Multimedia Lerning on Physical
Education
Afektif
Kognitif
Psikomotor
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
134

Goksu, I & Atici, B 2013, Need for Mobile Learning
Technologies and Opportunities, Procedia Social and
Behavioral Science, vol. 103(2013): 685-694
Hadi, S 2004, Metodologi research 2, Yogyakarta: Andi
Offset
Husdarta, J.S & Eli M 2010, Pendidikan jasmani,
olahraga & kesehatan smp/mts untuk kelas viii,
Jakarta: Pusat Perbukuan, Kementrian Pendidikan
Nasional.
Ibanez, M.B 2016, Suport for Augmented Reality
Simulation System: the Effects of Scanffolding on
Learning Outcomes and Behaviour Patterns, IEEE
Transactions on Learning Technology, vol. 9(1): 46-
56
Isnaini, F & Suranto 2010, Pendidikan jamani, olahraga,
dan kesehatan viii, Jakarta: Pusat Perbukuan,
Kementrian Penddidikan Nasional
Ivers, KS. & Barron, AE 2010, Multimedia in education
designing, producing and assesing, Santa Barbara,
CA: Libraries Unlimited
Mahendra, A 2003, Falsafah Pendidikan Jasmani, Jakarta:
Direktorat Pendidikan Luar Biasa
Mahendra, A 2001, Pembelajaran Senam, Jakarta:
Direktorat Jendral Olahraga
Miftah, M 2013, Penerapan Teori Belajar dan Desain
Instruksional dalam Program Mobile Learning, Jurnal
Kwangsan, vol. 1(1):46-56
Rosdiani, D 2013, Perencanaan Pembelajaran dalam
Pendidikan Jamani dan Kesehatan, Bandung:
Alfabeta
Saifuddin, A 2002, Sikap Manusia, Teori dan
Pengukurannya, Yogyakarta: Pustaka Pelajar
Sholeh, KM 1992, Olahraga Pilihan Senam, Jakarta:
Depdikbud.
Sugiyono 2013, Metode Penelitian Pendidikan
(Pendidikan Kuantitatif, Kualitatif, dan R&D),
Bandung: Alfabeta
Suharjana, F 2011, Pengemabangan Pembelajaran Senam
Melalui Bermain di Sekolah Dasar, Jurnal Pendidikan
Jasmani Indonesia, vol. 8(1): 18-23
Sukintaka 2001, Teori Pendidikan Jasmani, Solo: ESA
grafika
Sutrisno, B and Khafadi, MB 2010, Pendidikan Jasmani
Olahraga dan Kesehatan 2, Jakarta: Pusat Perbukuan
Kemendikna
Valk, J., Rashid, A.T & Elder, L 2010, Using Mobile
Phone to Improve Educational Outcomes: an Analysis
of Evidence From Asia, Inetrnational Review of
Research in Open an Distance Learning, vol. 11(1):
117-140
Vaughan, GM. & Michael, AH 2010, Social Psychology
(6
th
ed.), Australia: Pearson Education
Wisahati, AS 2010, Pendidikan Jamani Olahraga dan
Kesehatan, Semarang: Sejati
Gymnastics Multimedia Learning Development for Physical Education
135
