
The Effects of Marketing Capabilities on Financial Performance
through Innovation Capabilities in Fashion Small and Medium
Enterprises in Medan
Yeni Absah
1
, Rismayani
1
, R. Hamdani Harahap
2
1
Department of Management, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl. Prof. T.M Hanafiah, SH, Kampus USU, Medan, Indonesia
2
Department of Anthropology, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl. Dr. Sofyan, Kampus USU, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Marketing Capabilities, Innovation Capabilities, Financial Performance, SMEs
Abstract: Every Small and Medium Enterprises should have their own characteristics that can be a strategic resource.
The utilization of strategic resources as core competencies optimally by SMEs will improve their financial
performance. The population of this study was Medan’s 93 fashion SMEs. This study uses quantitative
methods with inferential statistical analysis using path analysis to measure the effect of marketing capabilities
on financial performance through innovation capabilities. The results showed that directly marketing
capabilities had a positive and not significant effect on financial performance, marketing capabilities directly
had a positive and significant effect on innovation capabilities, innovation capabilities directly had a positive
and significant on financial performance, and marketing capabilities had a positive and significant effect
towards financial performance through innovation capabilities of fashion SMEs in Medan.
1 INTRODUCTION
Small-Medium Sized Enterprises (SMEs) have been
vital to the economy of Medan city. This sector
absorbed 4.950.955 workers in 2015 (republika.co.id,
accessed on 05 February 2017 at
19.30 Western Indonesian Time), which was an
increase from the 2014’s 4.676.143 workers. SMEs in
Medan have contributed significantly to the city’s
economy, which is obvious from the growth of SMEs
within 3 years (2013-2015), from 82.888 in 2013,
86.063 in 2014, and 99.002 in 2013 based on BPS (the
Statistical Bureau) of North Sumatra 2015
(Dongoran, 2016).
Fashion business is a potentially promising and
profitable business sector due to its nature as a
secondary need for people. In major holidays, there
are always significantly increased demands for
fashion products. The ever-dynamic trends for
fashion modes make fashion business worth a try.
Many entrepreneurs started their fashion business by
becoming resellers or dropshippers of famous
products due to their lack of skills in fashion
manufacturing.
There has been a significant increased number of
fashion businesses in Medan, which create tight
competitions for the owners and encourage them to
innovate to attract customers and to improve their
business performance as well. To upgrade its
performance, a firm must manage its resources and
capabilities (Barney, 1991).
Despite their growth, SMEs are often faced with
obstacles such as the lack of marketing capabilities
skills in terms of wider market access. Another
ignored issue is the tendency of product imitation
rather than innovations as generally desired by
customers.
1.1 Research Questions
1. Are marketing capabilities critical in innovation
capabilities of fashion SMEs in Medan?
2. Are marketing capabilities critical to financial
performance of fashion SMEs in Medan?
3. Are innovation capabilities critical to financial
performance of fashion SMEs in Medan?
4. Are marketing capabilities critical to financial
performance of fashion SMEs in Medan through
innovation capabilities?
Absah, Y., Rismayani, . and Harahap, R.
The Effects of Marketing Capabilities on Financial Performance through Innovation Capabilities in Fashion Small and Medium Enterprises in Medan.
DOI: 10.5220/0009204003510355
In Proceedings of the 2nd Economics and Business Inter national Conference (EBIC 2019) - Economics and Business in Industrial Revolution 4.0, pages 351-355
ISBN: 978-989-758-498-5
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
351

1.2 The Usefulness of Research
1. As an input for SMEs to upgrade their financial
performance through an improved marketing and
innovation capabilities,
2. As an input for academics to develop science,
especially in marketing, strategic management,
and SMEs.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Marketing Capabilities
Marketing Capabilities belong to the category of
resources and skills in marketing sector which arise
from accumulated knowledge and integration of
values and norms developed within an organization.
Marketing capabilities are an integrated process
designed to create an accumulated knowledge, skills,
and resources from a firm to a business related to a
market (Lovelock dan Lauren, 2007). Marketing
capabilities of a firm in performing various marketing
objectives will provide with sustained competitive
advantages. Marketing capabilities are an evaluation
concept on process performance in marketing.
Marketing capability classified into two
categories, specialized and architectural capabilities
which guide firms gain performance and competitive
advantages. The specialized reflects marketing
employees' knowledge that is utilized in such
activities like selling, communication abilities and
pricing and etc. Moreover, communication with
existing and future consumers depends on this
capability (Boulding, et al., 1994; Day, 1994).
The literature on the effects of marketing
capabilities on business competitiveness is recent,
and the performance indicators used differ among
researchers. A number of available researches
reflected analysis of the link between business
capabilities and financial performance, (profits,
returns, etc.) indicators. Such an approach is evident
in the studies of Fahy et al. (2000), Tsai and Shih
(2004), and Vorhies and Morgan (2003), who
confirmed a positive link between marketing
capabilities and financial performance.
Marketing capability criteria must be satisfied to
generate superior performance of the resources
possessed (Andersén, 2011). Having strong
marketing capabilities is an important parameter in
succeeding product development (Drechsler et al.,
2013) and effects different types of innovation
(Mariadoss et al., 2011; Weerawardena, 2003).
Marketing capability is critical at the product
development stage where consumer needs and
competition must be assessed and information shared
for comprehensive new product ideas to be advanced
into the development stage (Weerawardena, 2003).
Based on this discussion, we argue that marketing
capability is related at all types of innovations
pursued by the firm. Marketing capability can be a
key source of competitive advantage, and can
influence firm’s innovation. Accordingly, the
relationship between marketing capability and
organizational innovation is hypothesized (Potočan,
2013).
Marketing capabilities could improve financial
and market performance (Tsai and Shih, 2004) and is
an important source of competitive advantage for
firms (Fahy, 2000).
H1: marketing capabilities are positively and
significantly critical to innovation capabilities of
fashion SMEs in Medan
H2: marketing capabilities are positively and
significantly critical to financial performance of
fashion SMEs in Medan
2.2 Innovation Capabilities
A critical character to be owned by an entrepreneur is
the capability to innovate. One projecting to be an
entrepreneur must be innovative (Larsen, 2007),
Innovation capabilities are an ability to develop
new products or markets through strategic innovation
orientation adjustment with innovative attitude and
process (Wang & Ahmed, 2004). Capabilities owned
by a firm in devising new ideas to produce
innovations is a concept of innovation capabilities
(Lawson dan Ben, 2001). Furthermore, Terziovski
(2010), stated that innovation capabilities provide
with potentially effective innovation.
Hastuti’s research (2018) revealed direct and
positive effects of innovation capabilities towards
financial performance of SMEs. The capability
configuration approach requires a firm to remain
original and creative, rather than an imitator, in
creating a sustainable competitive advantage
(Taghian, 2010: 829).
H3: innovation capabilities are positively and
significantly critical to financial performance of
SMEs in Medan.
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
352
2.3 Financial Performance
Financial performance is the accomplished result by
the firm’s management in running its function to
manage the firm’s assets effectively in a given period
(Rudianto, 2013:189). Financial performance is
required to measure or evaluate a firm’s level of
profitability based on its accomplished financial
objectives.
H4: marketing capabilities are positively and
significantly critical to financial performance of
fashion SMEs in Medan through innovation
capabilities.
3 METHOD
The research used a quantitative approach to test the
hypothesis. Sample of the research is 93 fashion
SMEs in Medan. The sampling was done through area
clustering, while the primary data collection was done
through questionnaire. Data used in this study are
quantitative data in the form of numbers, consisting
of the results of statistical data management. Sources
of data in this research are the primary data source,
data obtained directly from respondents through
questionnaires related to marketing and innovation
capabilities, and financial performance on SMEs that
are located in Medan. The data analysis method used
was model analysis to test the direct and indirect
effects of the research variables.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Inferential Analysis
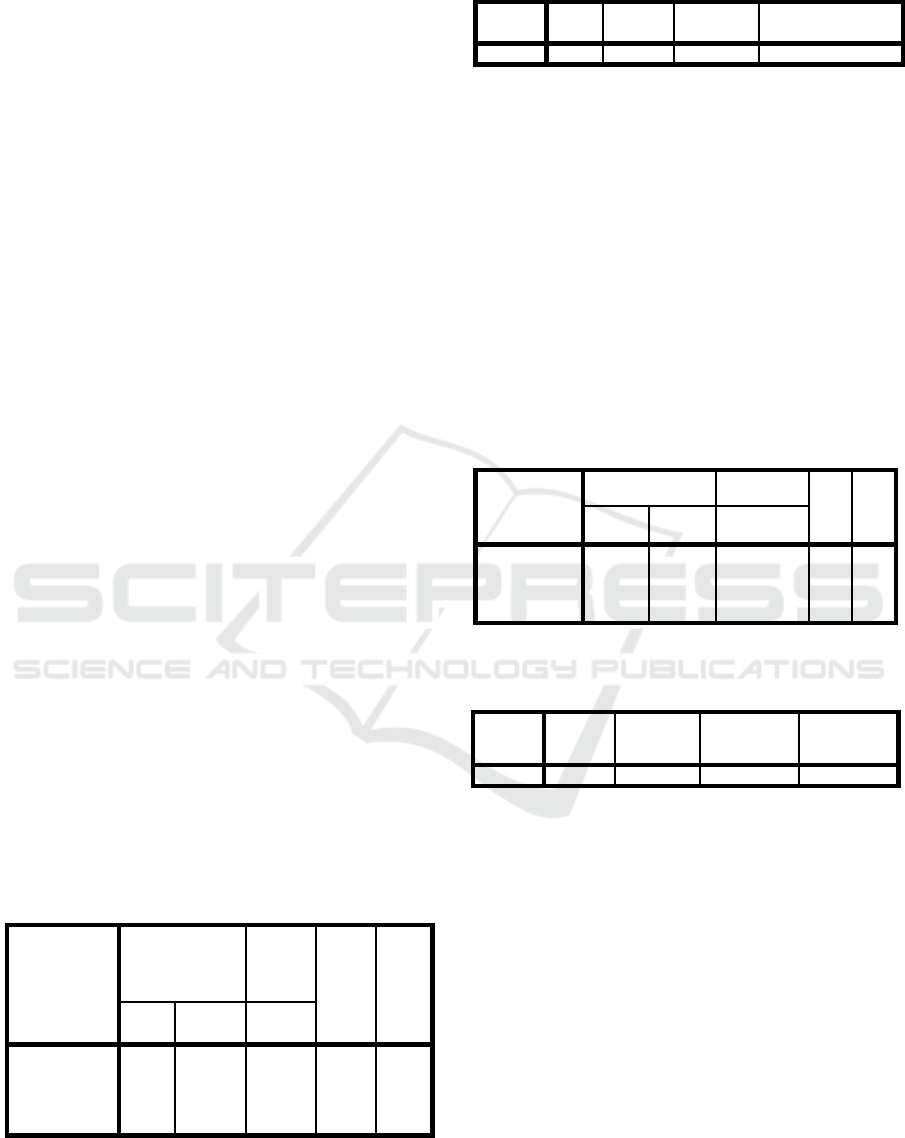
Table 1 Model I Analysis
Coefficients
a
Model
Unstandardized
Coefficients
Standa
rdized
Coeffici
ents
t
Sig.
B
Std.
Erro
r
Bet
a
(Constant)
22.886 5.497
.241
4.1
63
.000
1
Marketing
Capabilities
.264 .111 2.3
69
.020
a. Dependent Variable: Innovation Capabilities
Table 2 Model Summary
Model
R
R
Square
Adjusted
R Square
Std. Error of the
Estimate
1
.241
a
.058 .048 3.95927
a. Predictors: (Constant), Marketing Capabilities
4.1.1 Coefficient of Model 1
Table 1 shows regression result of model 1. The
regression output of model 1 on its coefficient table
shows significance value of marketing capabilities is
0,020 < 0,05. This result suggests, as for model 1
regression, marketing capabilities are significantly
critical to innovation capabilities. The R2 value in
table 2 of Model Summary is 0,058, which means that
the effect of marketing capabilities contributes to
innovation capabilities for 5,8%, while the remaining
94,2% is shared by other variables not under research.
Table 3: Model II Analysis
Coefficients
a
Model Unstandardized
Coefficients
Standardized
Coefficients
t
Sig.
B
Std.
Erro
r
Beta
(Constant) -9.068 8.279
-
1.095
.276
1
X
.193 .159
.118
1.218 .226
Y1 .617 .145
.412
4.264 .000
a. Dependent Variable: Financial Performance
Table 4 Model Summary
Model
R
R Square Adjusted R
Square
Std.
Error of the
Estimate
1
.455
a
.207 .190 5.46506
a. Predictors: (Constant), Innovation Capabilities, Marketing
Capabilities
4.1.2 Coefficient of Model 2
Model 2 regression output on coefficient table
column showed the significance value of marketing
capabilities is 0,226 > 0,05, while the significance
value of innovation capabilities of innovation
capabilities is 0,000 < 0,05. Such result concluded
that marketing capabilities produced positive but
insignificant influence towards financial performance
on. On the other hand, innovation capabilities are
positively and significantly critical to financial
performance. The value of R2 on Model Summary
table is 20,7% with the remaining 79,3% value is
contributed by variables not under research.
Furthermore, table 3 revealed direct effect of
marketing capabilities towards financial performance
The Effects of Marketing Capabilities on Financial Performance through Innovation Capabilities in Fashion Small and Medium Enterprises
in Medan
353

for 0,118 and indirect effect of marketing capabilities
towards innovation capabilities for 0,241 x 0,412 =
0,0993. Thus, the total effect of marketing
capabilities towards marketing performance is adalah
0,118 + 0,0993= 0,217. This concluded that through
innovation capabilities marketing capabilities
indirectly are positively and significantly critical to
financial performance.
5 DISCUSSION
The research result showed that marketing
capabilities directly contribute positively and
significantly towards innovation capabilities.
Marketing capabilities have an influence on
innovation development and facilitate innovation
success and creativity in the market (Weerawardena
and O’Cass, 2004; Dutta et al., 1999). Marketing
capabilities play a significant role in improving
innovation in firms and create competitive
advantages for companies (Shahhoseini and
Ramezani, 2015). Marketing and innovation are
necessary for firm to gain competitive and vantages
(Song et al., 2005; Moorman and Slotegraaf, 1999;
Möller and Anttila, 1987).
The research result showed a directly positive yet
insignificant effect of marketing capabilities towards
financial performance. As a matter of fact, marketing
capabilities without product innovation often troubles
fashion SMEs to boost their financial performance.
Another research result revealed directly positive
and significant effect of innovation capabilities
towards the financial performance of SMEs in
Medan. Therefore, SMEs owners must be innovative
in developing not only products but also services,
technology, and market. Product innovation is
possible through new model development by using
new designs, materials, and colour variations
compatible with the target market. Furthermore,
service innovation may use technology to enable
more responsive and accurate service; while
technology innovation is applicable through ordering
and payment systems. On the other hand, market
innovation is made possible through sustainable
market development or niche. Various innovations
may boost selling and, thus, should improve the
selling performance.
The last research result found that marketing
capabilities directly have positive and significant
effects towards financial performance through
innovation capabilities, while indirectly insignificant
to financial performance. Thus, it may be concluded
that only innovation capabilities will improve
financial performance. Marketing capabilities include
entrepreneurs’ skills in maximizing their marketing
mix strategies, which should help boost financial
performance of SMEs.
The marketing capabilities aim to fulfil the market
related needs of the business, allowing firms to
provide superior added value and to adapt better to
changing market conditions (Vorhies, 1998).
Marketing capabilities are evident when individuals
use accumulated knowledge of clients, markets, and
the environment; their experience; and the firm’s
resources to resolve commercial problems, to
generate higher value for the organization’s clients
and to be competitive (Tsai and Shih, 2004; Vorhies,
1998; Weerawardena, 2003).
6 CONCLUSIONS
Research results and discussions reveal that
marketing capabilities directly contribute positively
and not significant on financial performance,
marketing capabilities directly had a positive and
significant effect on innovation capabilities,
innovation capabilities directly had a positive and
significant on financial performance. On the other
hand, marketing capabilities are positively and
significant critical to financial performance through
innovation capabilities.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge that the present
research is supported by Ministry of Research and
Technology and Higher Education Republic of
Indonesia. The support is under the research grant
DRPM Dikti of Year 2019.
REFERENCES
Barney, Jay, 1991, Firm Resources and Sustained
Competitive Advantage, Journal of Management,
Vol.17, No.1, p.99-120
Boulding, W., Lee , E. and Staelin, R., 1994. Mastering the
Mix: Do Advertising, Promotion, and Sales Force
Activities Lead to Differentiation?, Journal of
Marketing Research, Vo.31, No.2, p.159-172.
Day, G.S., 1994. The Capabilities of Market-Driven
Organizations, Journal of Marketing, Vol.58, No,4,
p.37-52.
Drechsler, W., Natter, M. and Leeflang, P. S. H., 2013.
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
354

Improving Marketing's Contribution to New Product
Development, Journal of Product Innovation
Management, Vol.30, No.2, p.298-315.
Dutta, S., Narasimhan, O. and Rajiv, S., 1999. Success in
High-Technology Markets: Is Marketing Capability
Critical?, Marketing Science, Vol.18, no.4, p.547-568.
Fahy, J., 2000. The Resource-based View of the Firm:
Some Stumbling-blocks on the Road to Understanding
Sustainable Competitive Advantage, Journal of
European Industrial Training, Vo.24, No.2-4, p.94-
104.
Fahy, J., Hooley, G. J., Cox, A. J., Beracs, J., Fonfara, K.,
and Snoj, B., 2000. The Development and Impact of
Marketing Capabilities in Central Europe. Journal of
International Business Studies, Vol.31, No.1, p.63-81.
Hastuti, Anita Sukma, 2018. Pengaruh Kapabilitas Inovasi
Terhadap Kinerja Usaha Kecil Menengah (UKM)
(Studi pada UKM Kerajinan Bambu Dusun Sendari,
Tirtoadi, Mlati, Sleman, Yogyakarta). Skripsi,
Universitas Pembangunan Nasional "Veteran"
Yogyakarta.
Larsen, P. and Lewis A., 2007. Haw Award Winning SMEs
The Barriers to Innovation, Journal Creativity and
Innovation Management, p.141-151.
Mariadoss, B. J., Tansuhaj, P. S. and Mouri, N., 2011.
Marketing Capabilities and Innovation based Strategies
for Environmental Sustainability: An Exploratory
Investigation of B2B Firms, Industrial Marketing
Management, Vol.40, No.8, p.1305-1318.
Möller, K. and Anttila, M., 1987. Marketing Capability - A
key Succes Factor in Small Business?, Journal of
Marketing Management, Vol., No.2, p.185-203.
Moorman , C. and Slotegraaf, R., 1999. The Contingency
Value of Complementary Capabilities in Product
Development, Journal of Marketing Research, Vol.36,
No.2, p.239-257.
Potočan, Vojko, 2013. Marketing Capabilities for
Innovation-Based Competitive Advantage in The
Slovenian Market, Innovative Issues and Approaches in
Social Sciences, Vol. 6, No. 1, p.118-134.
Rudianto, 2013. Akuntansi Manajemen: Informasi untuk
Pengambilan Keputusan Strategis, Gelora Aksara
Pratama, Jakarta.
Shahhoseini, Mohammad Ali and Ramezani, Kimia, 2015.
Mediating Effect of Ambidexterity on Marketing
Capability and Innovation Capability, The Proceedings
of the International Conference “Marketing-From
Information to Decision”, CLUJ- Napoc, 80-92, CLUJ-
Napoca: Babes Bolyai University.
Song, M., Droge, C., Hanvanich, S. and Calantone, R.,
2005. Marketing and Technology Resource
Complementarity: an Analysis of Their Interaction
Effect in Two Environmental Contexts, Strategic
Management Journal, Vol.26, No.3, p.259-276.
Taghian, Mehdi, 2010, Marketing planning:
Operationalising the Market Orientation Strategy.
Journal of Marketing Management. Vol.26, No.9–10,
p.825–841.
Terziovski, M. (2010). Innovation practice and its
Performance Implications in Small and Medium
Enterprises (SMEs) in the Manufacturing Sector: a
Resource-based View. Strategic Management Journal,
Vol. 3, No.1, p.892-900.
Tsai, MT and Shih, C.M., 2004. The Impact of Marketing
Knowledge among managers on Marketing Capabilities
and Business Performance, International Journal of
Management, Vol.21, No.4, p.524-530.
Vorhies, D. W., 1998. An Investigation of the Factors
Leading to the Development of Marketing Capabilities
and Organisational Effectiveness. Journal of Strategic
Marketing, Vol.6, No.1, p.3-23.
Vorhies, D. W., and Morgan, N. A., 2003. A Configuration
Theory Assessment of Marketing Organization Fit with
Business Strategy and Its Relationship with Marketing
Performance, Journal of Marketing, Vol.67, No.1,
p.100-115.
Weerawardena, J., 2003. The Role of Marketing Capability
in Innovation-based Competitive Strategy. Journal of
Strategic Marketing, Vol.11, No.1, p.15-36.
Weerawardena, J. and O'Cass, A., 2004. Exploring the
Characteristics of the Market-Driven Firms and
Antecedents to Sustained Competitive Advantage,
Industrial Marketing Management, Vol.33, No.5,
p.419-428.
The Effects of Marketing Capabilities on Financial Performance through Innovation Capabilities in Fashion Small and Medium Enterprises
in Medan
355
