
The Influence of Corporate Governance on Disclosure of Corporate
Social Responsibility and Corporate Financial Performance as
Intervening Variable
Ivo Maelina Silitonga and Arthur Simanjuntak
Accounting Department Universitas Methodist Indonesia Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Corporate Governance, Corporate Social Responsibility, Corporate Financial Performance
Abstract: The objective of the research was to determine and analyze the influence of Corporate Governance
(Managerial ownership, Institutional Ownership, Audit Committee, Independent Commissioner), On
Disclosure of Corporate Social Responsibility simultaneously and partially on manufacturing companies
listed on the Indonesian Stock Exchange 2014 - 2018. The study also tested the influence of intervening
Corporate Financial Performance for Corporate Governance (Managerial Ownership, Institutional
Ownership, Audit Committee, Independent Commissioner), On Disclosure of Corporate Social
Responsibility. Total population of this research was 136 manufacturing companies. Samples were selected
using purposive sampling method amounted to 83 companies, the data is processed by using residual test
using SPSS. Result of the research showed that the variables of Corporate Governance (Management
Ownership, Institutional Ownership, Audit Committee and Independent Commissioner) direct positive
influence on Corporate Social Responsibility. Corporate Governance (Audit Committee and Independent
Commissioner) direct positive influence on Corporate Social Responsibility. Corporate Governance
(Management Ownership and Institutional Ownership) indirect positive influence on Corporate Social
Responsibility. The variables of Corporate Financial Performance as intervening variables to explain
influence Corporate Governance (Management Ownership and Institutional Ownership) on Corporate Social
Responsibility.
1 INTRODUCTION
Elkington packs CSR into three focus 3Ps, namely
Profit, Planet, and People. A good company does not
only hunt for economic profit (profit), but also has
concern for the preservation of the environment
(planet) and the welfare of the people (people). In line
with the rapid development of the business sector as
a result of economic liberalization, various private
sector community organizations and education have
sought to formulate and promote the social
responsibility of the business sector in relation to
society and the environment, and Corporate
Responsibility Disclosure is one part of the principles
of Good Corporate Governance (GCG)).
(www.info.ekonomi.com ).
In this case, reporting on environmental
responsibility in the annual report is still voluntary
because previously the obligation to report on
environmental impacts stipulated by the Indonesian
Ministry of the Environment was only a non-public
disclosure (specifically to relevant government
institutions). This should not only be the case because
when viewed companies in developed countries
reporting environmental and social responsibility is
the main thing in reporting the company's
performance in addition to being seen from its
financial statements. Increasingly the mining industry
in Indonesia resulted in many areas that had been
isolated began to be opened for mining areas, not least
for manufactured. This is what makes each region
have a more advanced life.
In case there are cases of environmental damage
caused by PT. Nusa Halmahera Mineral (NHM) is
engaged in gold mining which causes the spread of
waste in Kao Bay, Ternate, North Maluku, which
causes the surrounding community to suffer lumps
upfront. It is unfortunate due to the pollution of the
waste in addition to harming the surrounding
community besides that the rivers are contaminated
Silitonga, I. and Simanjuntak, A.
The Influence of Corporate Governance on Disclosure of Corporate Social Responsibility and Corporate Financial Performance as Intervening Variable.
DOI: 10.5220/0009203203310337
In Proceedings of the 2nd Economics and Business International Conference (EBIC 2019) - Economics and Business in Industrial Revolution 4.0, pages 331-337
ISBN: 978-989-758-498-5
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
331

with limbar even though Kao Bay is the largest
anchovy producing area in Indonesia.
Criminal sanctions regarding CSR Disclosure are
also contained in Law of Republic Indonesian
Number 23 year 1997 concerning Environmental
Management (UUPLH) Article 41 paragraph (1)
which states: "Whoever violates the law intentionally
commits acts that result in environmental pollution
and/or damage, face a maximum prison sentence of
ten years and a maximum fine of five hundred million
rupiah". Furthermore Article 42 paragraph (1) states:
"Anyone who for his negligence does an act which
results in environmental pollution and/or damage, is
threatened with a maximum imprisonment of three
years and a maximum fine of one hundred million
rupiah" (Sutopoyudo, 2009).
Based on the explanation above, the importance of
the influence of the concept of economic performance
in influencing company policy, the authors are
interested and intends to do the research to establish
the title: " The Influence of Good Governance
(Managerial Ownership, Institutional Ownership,
Audit Committee, Independent Commissioner) on
Disclosure of Corporate Social Responsibility to
Corporate Financial Performance as variabel
intervening on the Company Manufacturing listed
in Indonesia Stock Exchange ".
Problem Formulation
Based on the background above, the problems in
this study can be formulated as follows:
1. Does Corporate Governance (Managerial
Organization, Institutional Ownership, Audit
Committee, Independent Commissioner)
influence the partial and simultaneous disclosure
of Corporate Social Responsibility to
Manufacturing Companies that are listed on the
Indonesian Stock Exchange?
2. Does Corporate Governance (Managerial
Ownership, Institutional Ownership, Audit
Committee, Independent Commissioner) the
influence on Disclosure of Corporate Social
Responsibility through Corporate Financial
Performance in Company Manufacturing is listed
on the Indonesian Stock Exchange?
2 LITERATURE REVIEWS
2.1 Disclosure of Corporate Social
Responsibility
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is a natural
mechanism for a company to 'clean' big profits. As is
known, the company's ways to obtain profits
sometimes harm others, both unintentional or
intentional. It is said to be a natural mechanism
because CSR is a consequence of the impact of
decisions or activities made by the company, so the
obligation of the company is to reverse the situation
of the people experiencing the impact to a better
situation (Prastowo and Huda 2011: 17).
Corporate social responsibility or commonly
referred to as Corporate Social Responsibility is a
concept that the organization, in this case is more
specified to the company, is having a responsibility to
consumers, employees, shareholders, the community,
and the environment in all aspects of the company's
operations.
2.2 Corporate Financial Performance
Financial Performance is the level of performance of
a business in a certain time period, which is
manifested in profit and loss in the relevant time
period. Thus, it can be concluded that financial
performance is a measure of how well a company can
use its assets in running a business and earning
revenue. Financial Performance is also a term to
compare several companies engaged in the same
industry or field.
Financial performance is a picture of the
company's success in the form of results that have
been achieved thanks to various activities that have
been carried out. Financial performance is an analysis
to assess the extent to which a company has carried
out activities according to the rules of financial
implementation (Fahmi, 2012).
2.3 Corporate Governance
The term Corporate Governance itself was first
introduced by Cadbury Committee in 1992 which
uses the term. In their report known as the Cadbury
Report , this report is seen as a turning point that is
crucial for corporate governance practices around the
world . Cadbury Report defines corporate governance
as: "A system that functions to direct and control the
organization". Another definition from the Cadbury
Report sees Corporate Governance as managers,
creditors, the government, employees and other
interested parties both internal and external with
respect to their rights and responsibilities. "
Kaen (2003) defines Corporate Governance as
something about who controls the company and why
it controls. The Cadburry Committee in 1992 defined
Corporate Governance as a principle that guides and
controls the company in order to achieve a balance
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
332
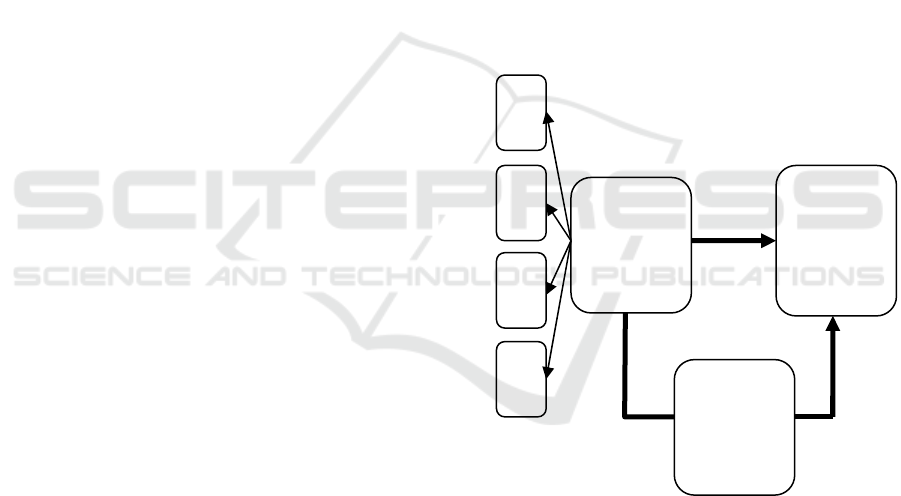
O
O
C
C
Corporate
Governance
(X)
Corporate
Financial
Performanc
e (Z)
Disclosur of
Corporate
Social
Responsibil
ity(Y)
between strength and authority of the company in
order to achieve a balance between the strengths and
authority of the company in providing accountability
to shareholders and stakeholders in general.
Meanwhile the Forum for Governance in Indonesia
(FCGI) defines Corporate Governance as a system
that directs and controls the company. Shleifer and
Vishny (1997) define Corporate Governance as ways
to provide assurance to suppliers of corporate funds
that a return on their investment will be obtained
(Darmawati, 2006).
2.4 Managerial Ownership
Managerial ownership is a situation where the
manager owns the company's shares or the manager
as well as the company's shareholder as indicated by
the percentage of company share ownership by the
manager. Conflicts of interest between managers and
owners become greater when ownership between
managers and the company gets smaller. In this case
the manager will try to maximize his interests
compared to the interests of the company. Conversely
the greater the manager's ownership in the company,
the more productive the manager's actions in
maximizing the value of the company.
Managerial ownership is a situation where the
manager owns the company's shares or in other words
the manager is also a shareholder (Tjeleni, 2013).
2.5 Institutional Ownership
Institutional ownership is the percentage of share
ownership by institutional investors such as
investment companies, banks, insurance companies
and ownership of other institutions and companies.
Institutional ownership will encourage more optimal
supervision of company performance. This means
that the greater the percentage of shares owned by
investors.
2.6 Audit Committee
In accordance with Kep. 29/PM/2004, the audit
committee is a committee formed by the Board of
Commissioners to help carry out its duties and
functions. The Audit Committee has a separate task
in assisting the Board of Commissioners to fulfill
their responsibilities in providing overall oversight
(FCGI, 2002).
2.7 Independent Commissioner
The function of an independent commissioner is
intended to encourage and create a more independent
and objective climate for public companies. As the
name implies, an independent commissioner must be
independent in the sense that the commissioner is not
involved in the management of the company and is
expected to be able to carry out his duties as an
independent party, and carry out his duties solely for
the benefit of the company and regardless of the
influence of various parties who have conflicting
interests with other parties.
2.8 Conceptual Framework
Conceptual Framework Based on the above
theoretical basis and problem formulation, the
researchers develop the research framework. The
conceptual framework to be studied by the researcher
is as the following.
2.9 Research Hypothesis
Based on the previous problem formulation, the
hypothesis of this study are:
H
1
: Corporate Governance (Managerial Ownership,
Institutional Ownership, Audit Committee,
Independent Commissioner) simultaneously
and partially and significantly influence the
Disclosure of Corporate Social Responsibility in
Manufacturing Companies listed on the
Indonesia Stock Exchange.
H
2
: Corporate Governance (Managerial Ownership,
Institutional Ownership, Audit Committee,
The Influence of Corporate Governance on Disclosure of Corporate Social Responsibility and Corporate Financial Performance as
Intervening Variable
333

Independent Commissioner) simultaneously
and partially and significantly influence the
Disclosure of Corporate Social Responsibility
with Corporate Financial Performance as an
intervening variable on Manufacturing
Companies listed on the Indonesia Stock
Exchange .
3 RESEARCH METHODS
3.1 Types of The Research
This research is a causal research (Causal Influence),
namely research that is intended to reveal the causal
relationship between related variables (Sularso, 2004:
13). The purpose of causal research is to investigate
the possibility of a causal relationship in a manner
based on observations of existing the influences and
re-search for factors that might have caused the cause
through certain data.
3.2 Research Location
The location of this research was conducted on the
IDX through the sites www.idx.co.id and
www.bi.go.id, namely Manufacturing Companies
listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange in the period
2014 - 2018 .
3.3 Population and Sample
3.3.1 Population
Population is "a generalization area consisting of
objects or subjects which become certain quantities
and characteristics determined by researchers to be
studied and then conclusions can be drawn". (Erlina,
2011). The population in this study were 136
companies.
3.3.2 Sample
The sample according to Erlina (2011) is "part of the
population used to estimate population
characteristics". Sampling is done by purposive
sampling method, which is sampling based on certain
criteria (Ghozali, 2013) . The samples in this study
were 83 companies. So the number of observations is
415 observations with details (83 companies X 5
years of observation)
.
3.4 Data Analysis Model
Model data analysis used is multiple linear regression
analysis aimed to test and analyze the the influence of
Good Governance (Managerial Ownership,
Institutional Ownership, Audit Committee,
Independent Commissioner) on Disclosure of
Corporate Social Responsibility in Corporate
Financial Performance as Variabel intervening on the
Company Manufacturing registered on the Indonesia
Stock Exchange . The form of the regression equation
is:
Y = b
0
+ b
1
X
1
+ b
2
X
2
+ b
3
X
3
+ b
4
X
4
+ b
5
Z + є
Z= b
0
+ b
1
X
1
+ b
2
X
2
+ b
3
X
3
+ b
4
X
4
4 FINDINGS
In the Descriptive Statistics indicates the description
of the research variables that shows the minimum
value, maximum value, average value and standard
deviation. In this study the standard deviation value is
smaller than the average value so it can be concluded
that the study is distributed normally.
4.1 The Influence of Corporate
Governance (Managerial
Ownership) on Corporate Social
Responsibility through Corporate
Financial Performance
From the data and research concept framework
above, it can be interpreted that the direct and indirect
influences of Corporate Governance (Managerial
Ownership) on Corporate Social Responsibility
through Corporate Financial Performance using path
analysis can be calculated as follows:
Direct
Influence:
- MO to CSR = - 0,052
Indirect Influence :
- MO to CSP to CSR = 0,452 x 0,216 = 0,098
Total Influence = 0,046
From the results above, the influence of Corporate
Governance (Managerial Ownership) on Corporate
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
334
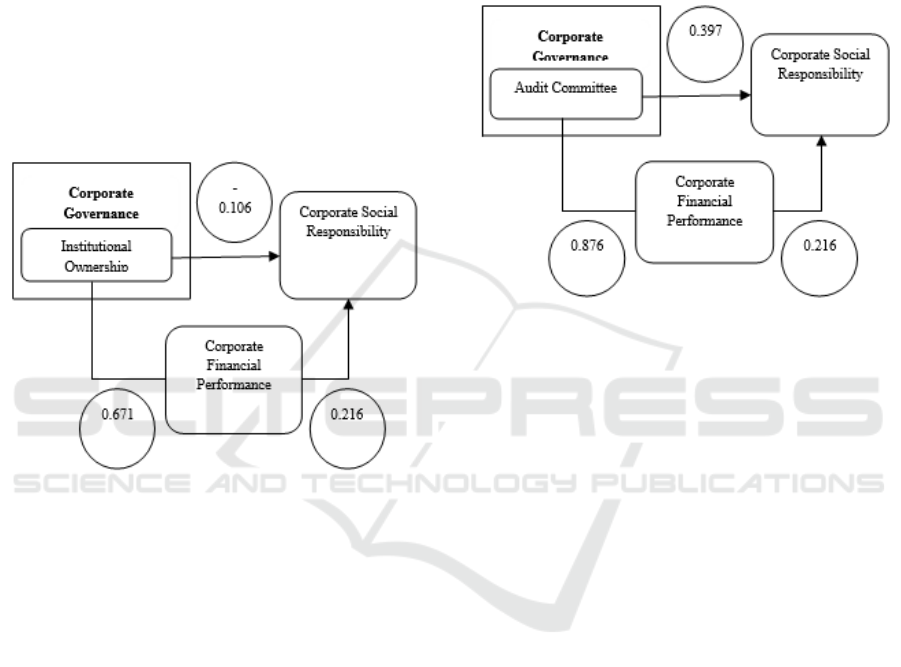
Social Responsibility through Corporate Financial
Performance is greater than the value of indirect
influence rather than direct influence. Therefore the
Corporate Financial Performance variable is a good
intervening variable. It can be concluded that the
influence of Corporate Governance (Managerial
Ownership) influences Corporate Social
Responsibility through Corporate Financial
Performance .
4.2 The Influence of Corporate
Governance (Institutional
Ownership) on Corporate Social
Responsibility through Corporate
Financial Performance
From the data and research concept framework
above, it can be interpreted that the direct and indirect
influences of Corporate Governance (Institutional
Ownership) on Corporate Social Responsibility
through Corporate Financial Performance using path
analysis can be calculated as follows:
Direct Influence
:
- IO to CSR = - 0,106
Indirect Influence:
- IO to CSP to CSR = 0,671 x 0,216 = 0,145
Total Influence = 0,039
From the results above, the influence of Corporate
Governance (Institutional Ownership) on Corporate
Social Responsibility through Corporate Financial
Performance is greater than the value of indirect
influence rather than direct influence. Therefore the
Corporate Financial Performance variable is a good
intervening variable. Then it can be concluded that
the influence of Corporate Governance (Institutional
Ownership) influences Corporate Social
Responsibility through Corporate Financial
Performance.
4.3 The Influence of Corporate
Governance (Audit Committee) on
Corporate Social Responsibility
through Corporate Financial
Performance
From the data and research concept framework
above, it can be interpreted that the direct and indirect
influences of Corporate Governance (Audit
Committee) on Corporate Social Responsibility
through Corporate Financial Performance using path
analysis can be calculated as follows:
Direct
Influence :
- AC to CSR = 0,397
Indirect Influence :
- AC to CSP to CSR = 0,876 x 0,216 = 0,189
Total Influence = 0,586
From the results above, the influence of Corporate
Governance (Audit Committee) on Corporate Social
Responsibility through Corporate Financial
Performance is smaller than the indirect influence
value. Therefore the Corporate Financial
Performance variable is not a good intervening
variable. Then it can be concluded that the influence
of Corporate Governance (Audit Committee) has a
direct influence on Corporate Social Responsibility.
The Influence of Corporate Governance on Disclosure of Corporate Social Responsibility and Corporate Financial Performance as
Intervening Variable
335
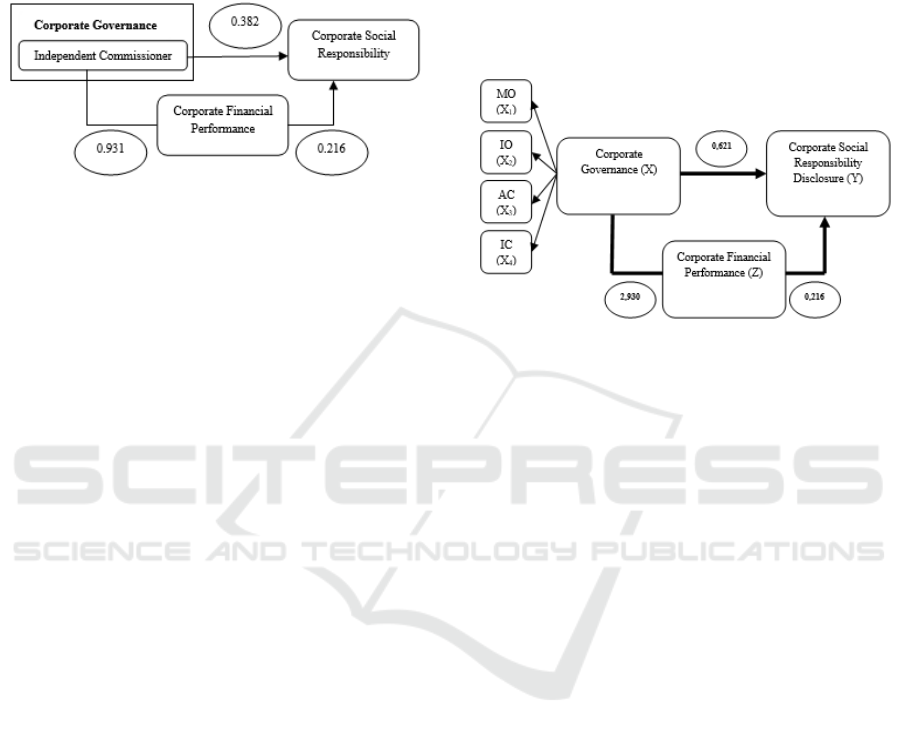
4.4 The Influence of Corporate
Governance (Independent
Commissioner) on Corporate Social
Responsibility through Corporate
Financial Performance
From the data and research concept framework
above, it can be interpreted that the direct and indirect
influences of Corporate Governance (Independent
Commissioner) on Corporate Social Responsibility
through Corporate Financial Performance using path
analysis can be calculated as follows:
Direct
Influence :
- IO to CSR
= 0,382
Indirect Influence :
- IO to CSP to CSR = 0,931 x 0,216 = 0,201
Total Influence
= 0,583
From the results above the influence of Corporate
Governance (Independent Commissioner) on
Corporate Social Responsibility through Corporate
Financial Performance is smaller than the value of
indirect influence rather than direct influence.
Therefore the Corporate Financial Performance
variable is not a good intervening variable. Then it
can be concluded that the influence of Corporate
Governance (Independent Commissioner) has a
direct influence on Corporate Social Responsibility.
4.5 The Influence of Corporate
Governance (Management
Ownership, Institutional
Ownership, Audit Committee and
Independent Commissioner) on
Corporate Social Responsibility
through Corporate Financial
Performance
From the data and research concept framework
above, it can be interpreted that the direct and indirect
influences of Corporate Governance (Management
Ownership, Institutional Ownership, Audit
Committee and Independent Commissioner) on
Corporate Social Responsibility through Corporate
Financial Performance by using path analysis can be
calculated as follows:
Direct Influence :
-
(
MO, IO, AC, and IC
)
to CS
R
= 0,621
Indirect Influence :
-
(MO, IO, AC, dan IC) to CSP to CSR = 2,930 x 0,216
= 0,633
Total Influence = 1,254
From the results above, the influence of Corporate
Governance (Management Ownership, Institutional
Ownership, Audit Committee and Independent
Commissioner) on Corporate Social Responsibility
through Corporate Financial Performance is smaller
than the indirect influence value. Therefore the
Corporate Financial Performance variable is a good
intervening variable. So it can be concluded that the
influence of Corporate Governance (Management
Ownership, Institutional Ownership, Audit
Committee and Independent Commissioner) has a
direct influence on Corporate Social Responsibility.
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
336

5 CONCLUSIONS
The result of the research showed that the variables of
Corporate Governance (Management Ownership,
Institutional Ownership, Audit Committee and
Independent Commissioner) direct positive influence
on Corporate Social Responsibility. Corporate
Governance (Audit Committee and Independent
Commissioner) direct positive influence on
Corporate Social Responsibility. Corporate
Governance (Management Ownership and
Institutional Ownership) indirect positive influence
on Corporate Social Responsibility. The variables of
Corporate Financial Performance as intervening
variables to explain influence Corporate Governance
(Management Ownership and Institutional
Ownership) on Corporate Social Responsibility.
REFERENCES
Darmawati, Deni (2006): "The Influence of Company
Characteristics and Regulatory Factors on the Quality
of Implementation of Good Corporate Governance".
National Symposium on Accounting IX.23-26 August
2006. Padang.
Erlina. 2011. Research Methodology: For Accounting .
USU PRESS. Field.
Fahmi, Irham. 2012. Analysis of Financial Statements . 2nd
printing. Bandung: Alfabeta .
Forum For Corporate Governance (FCGI), 2002. Corporate
Governance Series - Corporate Governance (Vol. I, II,
& III) Second Edition . Jakarta.
Ghozali, Imam. 2013. Multivariate Analysis Application
with SPSS Program . Seventh Edition. Semarang:
Diponegoro University Publisher Agency.
Kaen, Fred. R, 2003. A Blueprint for Corporate
Governance: Strategy, Accountability, and the
Preservation of Shareholder Value . USA: AMACOM.
Prastowo, Joko and Miftachul Huda. 2011. Key Corporate
Social Responsibility Achieve Business Glory .
Yogyakarta: Blue Ocean.
Shleifer, A and RW Vishny. 1997. A Survey of Corporate
Governance. Journal of Finance . 52 (2), 737-783.
Sularso, Kiyokatsu Suga, (2004). Basic Planning and
Selection of Machine Elements . Jakarta: Pradya
Paramita .
Sutopoyudo. 2009. The influence of Application of
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) on Company
Profitability . s utopoyudo.wordpress.com.
Tjeleni, Indra E. 2013. Managerial Ownership and Its
Impact on Debt Policy in Manufacturing Companies on
the Indonesia Stock Exchange. Emba Journal , Vol.1
No.3, Pg. 129139. Faculty of Economics and Business,
University of Ratulangi Manado.
The Influence of Corporate Governance on Disclosure of Corporate Social Responsibility and Corporate Financial Performance as
Intervening Variable
337
