
Developing Business Strategies for Featured MSMEs in North
Sumatera: SWOT Analysis Approach
Prihatin Lumbanraja, Ritha F. Dalimunthe and Elisabet Siahaan
Faculty of Economic and Business, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Competitiveness, Internal Capabilities, External Condition, Enterprises, Strategic Planning
Abstract: The role of micro, small and medium enterprises is always important to support the country’s economic
growth. As the market emerge and become larger, the competition within these enterprises has also risen to a
new stage. One of the key to formulate strategies to improve the enterprises’ competitiveness is through
SWOT analysis which employ internal capabilities and external condition assessments. This study aimed to
evaluate the current situation of MSMEs in Medan as well as their adaptative strategic planning. A number
of 300 MSMEs were participated in this research. This paper conclude that despite the vast opportunities
based on external analysis, our MSMEs were forced to maintain stability and take a baby steps to build their
own competitiveness as they also vulnerable with many weaknesses. Thus it is important not to tempted with
vast opportunities but maintain business stability and continuously improve the weakesses and translate them
to strengths.
1 INTRODUCTION
Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs)
acted as the backbone of the national economy are
still categorized as vulnerable to the development of
their businesses. Many businesses have to end
because of mismanagement and turmoil in market
demand. In this case, the achievement of business
competitiveness needs to be endeavored so that
businesses can last longer and contribute to
Indonesia's national development.
Indonesia and other ASEAN countries has agreed
to enter the new era of trade, Free Trade Agreement
(FTA) between ASEAN countries. It practically has
been applied since the begining of 2016. FTA without
a doubt increase the competition between
organization which can now freely trade with another
organization between countries. World economics
forum (2016) conclude that Indonesia’s
competitiveness index went down from 34th to 37th
in 2016. The situation also affecting Micro, Small and
Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) which lead to
downgrade of their product both for quality and price.
Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises played the
most important role to support economic
development in almost all countries as they gave the
major contribution for economic development
(Anggadwita and Mustafid, 2014). According to
Indonesia Statistics Bureau (2015), MSMEs
contributed for around 60% of GDP and absorb more
that 97% labour forces. Asian Productivity
Organization (2015) stated that the most important
role of MSMEs is to act as main core in economic
development and productivity. In line with the
statistics bureau, MSMEs was believed as the major
contributor toward one’s GDP. World Bank (2018)
stated that one key to sustainable growth of
economics was the growth of MSMEs in one’s
country. The growth will remain stable as long as it
supported by healthy MSMEs development. Despite
their importance to support economics growth,
MSMEs lack of managerial practice to help them to
develop their competitiveness.
In their quest to achieve and maintain
competitiveness, many of MSMEs learning to be
involved in a strategic planning. Strategic planning is
a way to help an organization be more productive by
helping guide the allocation of resources in order to
achieve goals. It is a strategic management tool. In
other words it is a part of strategic management. In
fact, strategic planning is a key to successful strategic
management.
MSMEs in the city of Medan in essence have
quite well implemented the analysis of strength in
business competition through the five forces method.
284
Lumbanraja, P., Dalimunthe, R. and Siahaan, E.
Developing Business Strategies for Featured SMEs in Nor th Sumatera: SWOT Analysis Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0009202602840290
In Proceedings of the 2nd Economics and Business International Conference (EBIC 2019) - Economics and Business in Industrial Revolution 4.0, pages 284-290
ISBN: 978-989-758-498-5
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

However, in the implementation of managing
business activities, the analysis carried out does not
have an impact on the formulation of strategies or the
next steps that will be implemented by business actors
in increasing the competitiveness of their businesses.
The mapping results indicate that in general MSMEs
in the city of Medan pay close attention to strengths
and relationships with suppliers, customers, and new
entrants to the business. They pay less attention to
issues related to business competition and substitute
goods. Analysis conducted by business actors is
generally natural. The steps taken based on the
analysis results are also generally spontaneous, there
is no good planning in managing business
competition.
Most of strategies were formulated based on
internal and external business analysis. One of the
most common strategic planning tools that used to
evaluate internal and external capabilities was SWOT
analysis, the Strength, Weaknesses, Opportunity, and
Threat (Osita et al. 2014). The first step in strategic
planning to achieve competitiveness was to identify
and evaluate the strategic factors, the SWOT, and
help organization to realize their full potential
(Houben, 1999). The strategic management oftenly
used to establish long-term activities of the business
(Yuksel and Dagdeviren, 2007). By conducting an
external analysis, an organization identifies the
critical threats and opportunities in its competitive
environment. It also examines how competition in
this environment is likely to evolve and what
implications that evolution has for the threats and
opportunities an organization is facing. While
external analysis focuses on the environmental
threats and opportunities facing an organization,
internal analysis helps an organization identify its
organizational strengths and weaknesses. It also helps
an organization understand which of its resources and
capabilities are likely to be sources of competitive
advantage and which are less likely to be sources of
such advantages. Based on SWOT Analysis,
organizations can choose the appropriate strategy.
In order to evaluate MSMEs competitiveness, it is
important to understand their internal capabilities and
external distrubance as in SWOT Analysis. Thus,
study aimed to evaluate the application of SWOT
analysis within MSMEs in Medan. The study focused
on mapping the SWOT analysis within industry to
identify their strength, weakness, opportunity, and
threat in the modern market.
This research was conducted in an effort to
improve business competitiveness; not only survive
in competition, but also take advantage of
opportunities by penetrating international markets, at
least the ASEAN regional market. Strong
competitiveness makes the market stronger.
Consumers will not easily switch to imported
products. Conversely, if MSME competitiveness is
weak, their position will soon be replaced by
increasingly intense business competition.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
SWOT analysis is a business analysis method that can
be used by each business entity in determining the
steps to be taken in the future to achieve maximum
business growth. Although called by the term
analysis, the SWOT analysis is not an analysis, but
rather the process of identifying internal and external
conditions of the company. Rangkuti (2011) states
that the results of the SWOT analysis are lists of the
company's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and
threats. This list is then analyzed again to develop an
optimal strategy in the future.
Team FME (2013) described the use of a SWOT
analysis to identify situations that occur in the
company. Analysis of the company's situation is done
by looking at the internal conditions and external
conditions of the company. Internal conditions are
conditions that can be controlled by the company,
while internal conditions cannot be controlled by the
company. Strengths and weaknesses are part of the
company's internal analysis. Opportunities and
threats are part of the company's external analysis.
The literature review surrounding the SWOT
analysis is based on two main elements, namely
internal factors which are then grouped into strengths
and weaknesses and external factors which are then
grouped into opportunities and threats. Munizu
(2010) applied four internal aspects that were used as
the basis for operational evaluations of MSMEs,
namely aspects of human resources, financial aspects,
technical and production aspects and marketing
aspects. These four aspects will be the basis for
evaluating the internal factors of the business actors
in this study.
External factors are various things whose growth
and development are beyond the ability of the
business to control them. These external factors
include political, economic, social and cultural
aspects, technological aspects, the role of
government, the role of financial institutions. These
aspects will be used as a basis in evaluating whether
these aspects become opportunities or threats for
business actors. The basic strategy of SWOT analysis
can be summarized in Figure 1.
Developing Business Strategies for Featured SMEs in North Sumatera: SWOT Analysis Approach
285
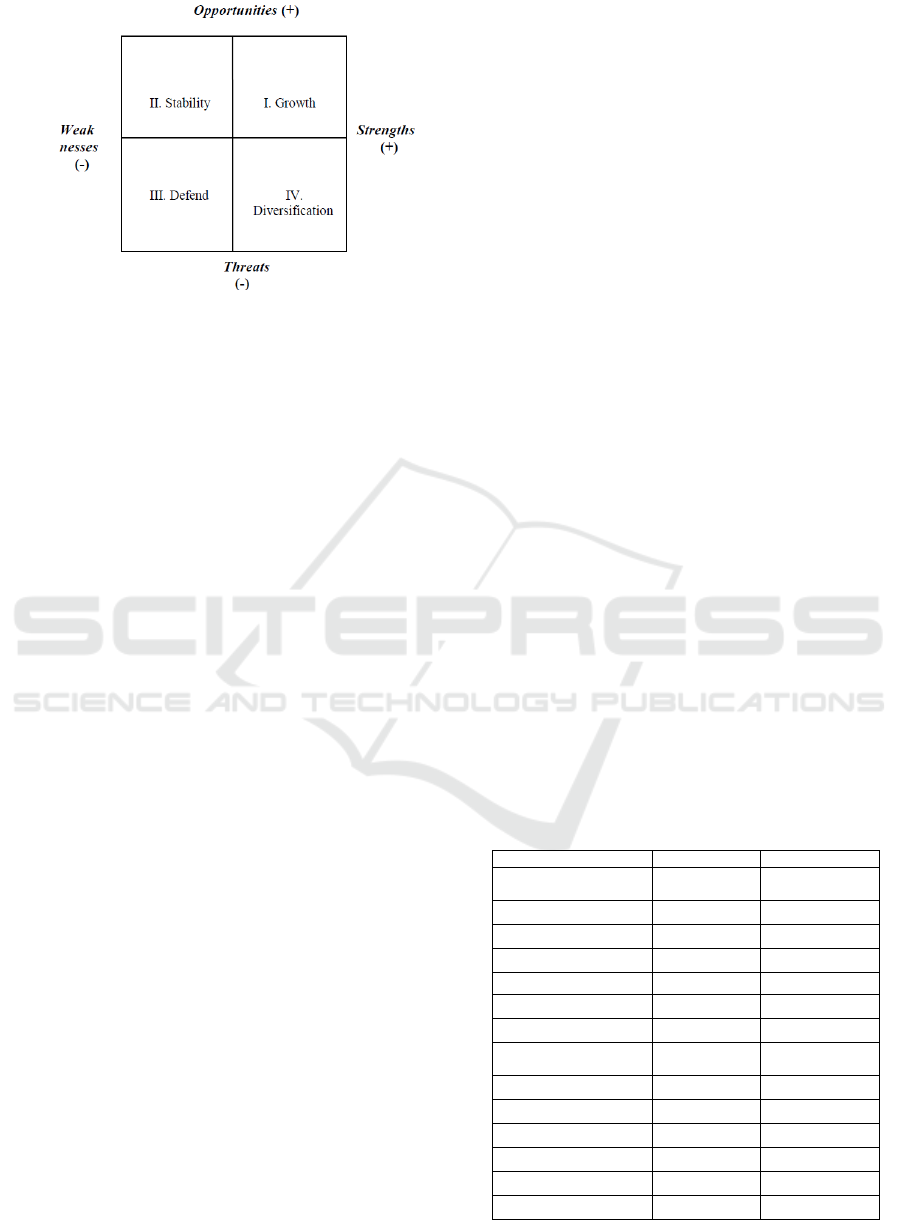
Figure 1. Basic SWOT Analysis Strategy
3 RESEARCH METHOD
3.1 Research Time
This study was conducted in Medan, North Sumatera,
Indonesia from April through August 2019. There is
no specific reason to conduct the research in mean
time. However we focused in Medan as the capital of
North Sumatera in which has the most developed and
maintained MSMEs.
3.2 Participant
There were no adequate data for registered MSMEs
in 2019 which force the use of non-random sampling
in this study. A non-random sampling technique and
the use of stratified-convenience sample were
employed in this study. There are six featured
MSMEs in Medan, classifed as Batik, Leather,
Rattan, Food, Embroidery, and Souvenirs. Each
MSMEs group were represented by fifty business
units to participated in this study. A number of 300
MSMEs in total were participated in this study, which
implying the final sample size of 300 MSMEs
participated in this study. The subject for this study
was the MSMEs’ owner.
3.3 Data Collection Method
Self-administered questionnaires were employed
during our research. The questionnaires were based
on the literature review in which adopted to satisfy
our needs and mindset of MSMEs. Furthermore, in
order to avoid biases, we conducted interview based
on the questionnaires. The questionnaires included
items that measured internal and external condition of
MSMEs by using five-point Likert scales.
Characteristics such as educational attainment, sex,
and opinion toward strategic planning were collected.
The distrubuted questionnaires were identical and
were merged into a single dataset for our study
purpose.
3.4 Data Analysis Method
The SWOT analysis approach in this study uses a
combination of concurrent embedded model
methods, which are research methods that combine
the use of qualitative and quantitative research
methods together, where qualitative research methods
are the primary methods and quantitative research
methods as secondary methods. Quantitative
approaches are used to evaluate whether internal
factors of business actors include strengths or
weaknesses; This approach is also used to evaluate
external factors whether included in opportunities or
threats.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Demographic
The demographics of the study participants were
presented with the aim of seeing a general picture of
the research sample. The characteristics of the
participants in this study were grouped based on the
characteristics of the respondents in this study based
on the business group, the sex of the business actor,
the level of the last education, and the approach to
strategy development. A summary of the respondents'
characteristics is presented in Table 1.
Table 1. Demographic Participants
N PERCENTAGE
SMES
CLASSIFICATION
300
252
84,00%
80,67%
45
15,00%
15,67%
3
1,00%
3,67%
SEX
300
189
63,00%
73,00%
111
37,00%
30,33%
EDUCATIONAL
ATTAINMENT
300
15
5,00%
7,00%
47
15,67%
11,67%
190
63,33%
66,00%
30
10,00%
10,67%
12
4,00%
3,33%
6
2,00%
1,33%
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
286

N PERCENTAGE
STRATEGIC
PLANNING
ADAPTATION
300
226
75,33%
85,33%
74
24,67%
14,67%
Table 1 provides a general description of MSMEs
in Medan that were sampled in this study. In general,
it can be stated that the majority of respondents are
microenterprises. The manager or owner of the
business unit is generally male. The most recent level
of education of the sampled business actors is
generally high school graduates, and most of the
study participants did not have a plan for their
business strategy..
4.2 Matrix Internal Factory Analysis
Summary (IFAS)
This study uses an equal weighting from each aspect
of the review on internal factors. Because all the
weights used are the same, the final score of each
internal factor comes from the evaluation used.
Classification based on strengths and weaknesses is
done by the middle value method, where the value
<3.0 will be grouped as weaknesses and above those
values are grouped as strengths. An evaluation of
internal business factors in Medan is summarized in
Table 2.
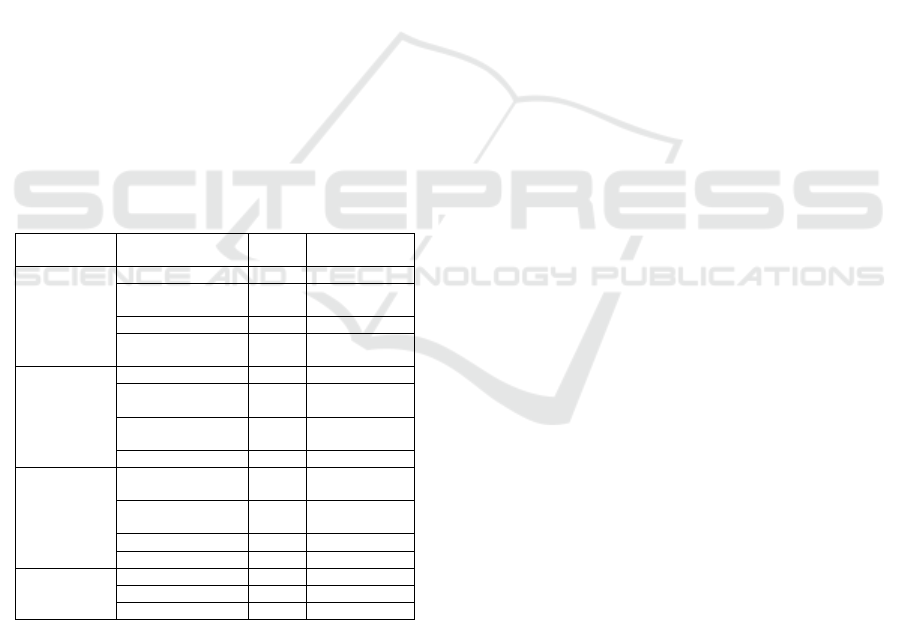
Table 2. Internal Factor Analysis
Internal
Capabilities
Indicator Score Classification
Human
Capital
Entre
p
reneurial 4,21 Stren
g
th
Motivation 3,98 Stren
g
th
Skills 2,21 Weakness
Visionary 2,33 Weakness
Financial Intern
Bud
g
etin
g
2,01 Weakness
Financial
Literac
y
2,91 Weakness
Financial
Recording
2,80 Weakness
Financial
Mana
g
ement
2,84 Weakness
Technical /
Operational
Materials 3,75 Strength
Production
Ca
p
acit
y
2,99 Weakness
Tools and
Machiner
y
2,15 Weakness
Quality
Control
2,90 Weakness
Market Product
Develo
p
ment
4,11 Strength
Internal
Ca
p
abilities
Indicator Score Classification
Distribution /
Chaneling
3,05 Strength
Pricing 2,95 Weakness
Promotion 2,80 Weakness
4.2.1 Strengths
The results of the evaluation of internal factors from
businesses in Medan generally indicate that there are
five things that are the strengths of businesses in
Medan. Entrepreneurial spirit, the evaluation carried
out indicates that there are a lot of creative ideas that
are owned by entrepreneurs in the city of Medan.
These ideas are also supported by the willingness to
take business risks. In terms of business motivation,
business actors have an unyielding attitude in running
a business and are supported with targets to be
achieved when carrying out business operations. In
terms of raw materials, businesses in the city of
Medan already have a stable supply of raw materials
related to good quality. This can encourage the
achievement of good product quality (Tobing,
Fathorazz, & Wulandari, 2018). From the marketing
aspect, businesses have strengths in terms of product
development as a realization of their creative ideas
and have a relatively good distribution channel.
4.2.2 Weaknesses
Behind the various strengths that have been described
previously, this business in Medan has various
weaknesses that make it vulnerable to external
exploitation and competition. In terms of business
resources, many of the businesses experience
constraints from the technical abilities of their
employees in running the business as optimal as
possible. In other words, the company's human
resources are generally uneducated and untrained.
The ability to see business opportunities (feasibility
study) owned is relatively low. Interesting ideas that
are not supported by good analysis in encouraging
and optimizing existing opportunities. All financial
aspects of a business in Medan City, on average, are
classified as weaknesses for the business. Many
businesses are difficult to develop with 'capital'
constraints that businesses do not want to try from
internal loans or retained earnings. Recording and
financial separation generally does not occur,
resulting in poor financial performance. Unclear
financial management also drives problems in the
financial aspect. In terms of the technical aspects of
production, equipment owned by business operators
Developing Business Strategies for Featured SMEs in North Sumatera: SWOT Analysis Approach
287
is generally simple and leaves plenty of room for
performance improvement. Unclear production
capacity makes the production system not run
efficiently. In addition, quality control is relatively
low among micro and small businesses. From the
marketing aspect, the weakness of the business in the
city of Medan lies in determining the price which
generally refers to the prevailing general price
regardless of the feasibility of the price with the
quality of the product. Besides promotion is often
considered as a cost-oriented activity rather than
investment to attract customers (Kartawinata &
Wardhana, 2013).
4.3 Matrix External Factory Analysis
Summary (EFAS)
This study uses an equal weighting from each aspect
of the review on internal factors. Because all the
weights used are the same, the final score of each
external factor comes from the evaluation used.
Classification based on opportunities and threats is
done by the middle value method, where the value
<3.0 will be classified as a threat and above that value
is classified as an opportunity. Evaluation of external
business factors is summarized in Table 3.
Table 3. External Factor Analysis
External
Aspect
Indicator Score Classification
Politic,
Economy, and
Social Aspect
Politic condition 3,06 O
pp
ortunit
y
Economic
condition
3,84 Opportunity
Social facto
r
3,33 O
pp
ortunit
y
Consumer
b
ehaviou
r
4,67 Opportunity
Governmental
Aspect
Public services 4,11 O
pp
ortunit
y
Enterprise
incubato
r
3,12 Opportunity
Enterprise
empowerment
3,54 Opportunity
Re
g
ulation 3,12 O
pp
ortunit
y
Financial
Institution
Aspect
Financial
Assistance
3,75 Opportunity
Monitoring and
Evaluation
2,12 Threat
Develo
p
ment 3,11 O
pp
ortunit
y
Partnershi
p
2,90 Threat
Competition Local com
p
etition 2,11 Threat
Internationalization 2,05 Threat
Free Trade 2,54 Threat
4.3.1 Opportunities
The political, economic and social conditions of the
business environment in Medan are relatively
conducive to business and business development.
Although this year's political turmoil is felt to be quite
strong, the conditions evaluated indicate that it is in a
category that is conducive to the leading cluster
business in Medan. The biggest opportunity is
obtained from the consumptive behavior of the
community which really makes the market in Medan
City very potential for various businesses. The role of
the government also provides promising
opportunities for business actors. Many business
development service units are provided by the
government for business conduciveness. The FTA
Center was opened in 2018 to help export
communities, especially micro, small and medium-
sized businesses by utilizing existing trade
agreements between countries. Regulations
established by the government tend to be pro-
business, such as tax relief to support the business
spirit of the community. In terms of financial
institutions, financial institutions provide benefits to
access to capital and also help the development of
human resources of business people through money
seminars.
4.3.2 Threats
The threat from the business environment in Medan
originates from business competition. Access to the
free market is essentially a double-edged sword
which will be an opportunity as well as a threat to
business people. Studies conducted indicate that the
current sharpness of the policy is more directed at
threats to the local market where businesses do not
want and are able to optimize the use of these
markets.
4.4 The Strategic Formulation
4.4.1 Strength-Opportunity Strategy
This strategy emerged as a product of a particular
company or business unit's perspective by optimizing
its strengths by exploiting the opportunities that exist.
The right strategy for the S-O quadrant is to focus on
exploiting opportunities by optimizing the strength of
the business (Inayati & Prasetya, 2017).
The main strengths of businesses in Medan are the
entrepreneurial spirit and good raw materials and
product development. The combination of these
strengths can form a variety of variations that build
market trends or improve the quality of market tastes
through product development and quality product
variants. As a control in this plan, an increase in
quality control efforts is needed. In addition, the
weaknesses that exist in the feasibility study need to
be improved so that they do not give morning losses.
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
288

4.4.2 Strength-Threat Strategy
The perspective on this S-T strategy is to focus on
strength while avoiding threats that might occur in the
business environment. In other words, businesses
must be able to master the slogan of keeping up the
good work without being affected by threats that can
reduce the strength of the business (Anggraeni,
Mawardi, & Sunarti, 2018).
One strategy that can be developed from the
conditions of MSMEs in Medan is by continuing to
strive for the best quality products from the best raw
materials while still competing at the level of the
global market and the free competition market.
Businesses should not be shaken because competition
is getting tougher with new players. It should not
cross the minds of business actors that local products
will always be inferior to foreign products. Good
work that has been owned by the business must be
continuously improved. In addition, innovation can
be applied in optimizing strength while transforming
existing threats into business opportunities.
4.4.3 Weakness-Opportunity Strategy
The perspective of the W-O strategy is basically
determining the priority scale of what is to be done in
optimizing market opportunities that exist in the
external environment (Prastika & Sadjiarto, 2018).
The strategy that appears dominant in this region is
the use of access to capital from the government and
financial institutions in an effort to develop the
business. Opportunities that exist also cover
weaknesses and transform them into a potential step
in developing business. In addition, the government's
concern in developing and fostering business can be
access in developing business skills while building
better relations between the trainees.
4.4.4 Weakness-Threat Strategy
The strategic perspective on a combination product
between W-T is a defensive strategy or a defense
against the vulnerability of the business owned and
various threats that can exploit the existing
weaknesses. Business competition as the main threat
from businesses in the city of Medan must be
maintained and taken into account by continuing to
maintain the quality of production, building on
existing skills, and preparing price and promotion
strategies in order to survive the increasingly fierce
competition with the free market.
5 CONCLUSION AND
RECOMMENDATION
Based on our focus group discussion, there were The
current paper set out to analyze the internal and
external factor of MSMEs in Medan as the basic
approach for a strategic planning to improve their
competitiveness. It should be pointed out that the
current study suggested that our MSMEs take a
sustainability approach as they must not exploit the
current opportunities with many weaknesses. They
should take a baby steps to grow, transforming
weaknesses to strengths while slowly take the
opportunities. This paper also showed that many of
our MSMEs were vulnerable as their internal
capabilities has a lot of room for improvements. We
should take note that these condition were not
compared with other MSMEs so we could not stated
that it will be a problem yet. However this result
suggested that MSMEs should take it into their
consideration to build up their internal capabilities to
maximize the opportunities in near future.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge that the present
research is supported by Ministry of Research and
Higher Education. The support is under the research
grant PDUPT for year 2019
REFERENCES
Anggraeni, P., Mawardi, M. K., & Sunarti. (2018). Analisis
swot pada umkm keripik tempe amel malang dalam
rangka meningkatkan daya saing perusahaan. Jurnal
Administrasi Bisnis, 43(1), 104–113.
Badan Pusat Statistik. (2015). Industri Mikro dan Kecil,
accessed from bps.go.id
Houben, G., Lenie, K., Vanhoof, K., A. 1999. Knowledge-
based SWOT-analysis system as an instrument for
strategic planning in small and medium sized
enterprises, Decision Support Systems, 26, 125–135
Inayati, T., & Prasetya, H. (2017). Perumusan strategi
dengan analisis swot pada usaha mikro kecil menengah
(. Seminar Nasional Manajemen Dan Bisnis, 3, 217–
231.
Kartawinata, B. R., & Wardhana, A. (2013). Marketing
Strategies and Their Impact on Marketing Performance
of Indonesian Ship Classification Society. International
Journal of Science and Research, 4(2), 2319–7064.
Retrieved from www.ijsr.net
Munizu, M. (2010). Pengaruh Faktor-Faktor Eksternal dan
Internal Terhadap Kinerja Usaha Mikro dan Kecil (
Developing Business Strategies for Featured SMEs in North Sumatera: SWOT Analysis Approach
289

UMK ) di Sulawesi Selatan. Jurnal Manajemen Dan
Kewirausahaan, 12(1), 33–41.
Osita, I.C., Onyebuchi, I., Justina, N. 2014. Organization’s
stability and productivity: the role of SWOT analysis
an acronym for strength, weakness, opportunities and
threat. International Journal of Innovative and Applied
Research, 2(9), 23-32
Prastika, M., & Sadjiarto, A. (2018). Analisis SWOT Usaha
Mikro Kecil Menengah (UMKM) Di Industri Kreatif
Sarang Lebah Salatiga. Ecodunamica, 1(3).
Rangkuti, F. (2011). SWOT and Balanced Scorecard.
Jakarta: PT Gramedia Pustaka Utama.
Team FME. (2013). SWOT Analysis: Strategy Skills. ebook:
Free Management Ebook.
Tobing, D. S. K., Fathorazz, M., & Wulandari, G. A.
(2018). Mapping the Competitive Advantage of
MSMEs in East Java, Indonesia. Jurnal Dinamika
Manajemen, 9(1), 23–32.
https://doi.org/10.15294/jdm.v9i1.14649
World Bank. (2018). Global Economic Prospects 2018:
Trade, Regionalism, and Development
World Economic Forum. (2016). Global Competitiveness
Report 2013-2015. [Online]
http://reports.weforum.org/
Yuksel, I., Dagdeviren, M. (2007). Using the analytic
network process (ANP) in a SWOT analysis–A case
study for a textile firm, Information Sciences, 177,
3364–3382
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
290
