Implementation of Technology, Efficiency, Knowledge, Risk on Trust
Level of Fintech Used in MSMEs in Tangerang City
Tjahjanto, Indah Rahayu Lestari, Rinny Meidiyustiani, Imelda
Universitas Budi Luhur
imelda@budiluhur.ac.id
Keyword: Technology, Efficiency, Knowledge, Risk, Fintech
Abstract: Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) are increasingly growing with the development of
technology, where MSMEs are one of the pillars of the strength of the Indonesian economy. Fintech is one
of the drivers in helping to improve finance for MSMEs, especially those in the middle and lower classes.
At least more than 40 Fintech businesses have emerged throughout 2017. By utilizing the development of
Fintech, in addition to increasing efficiency in the financial sector also minimizing the risk of fraud and
cybercrime in the financial sector. For this reason, it is necessary to increase knowledge to MSMEs
regarding the benefits of using Fintech, so that the level of trust in MSMEs towards Fintech is increasing,
and the use of Fintech is every day.
1. INTRODUCTION
Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs)
are increasingly growing with the development of
technology, where MSMEs are one of the pillars of
the strength of the Indonesian economy. It can be
said that MSMEs play a role in maintaining
economic stability. Rapid technological
developments in the digital era are increasingly
complete with the presence of Fintech. The term
Fintech is a financial service using a technology
base which of course will further facilitate the
technology base which certainly facilitates
transactions. This new financial model, Fintech, was
first introduced in 2004 by Zopa, the British
Financial Institution which runs a loan service which
later in 2008 was continued to become Bitcoin by
Satoshi Nakamoto.
Fintech can eliminate the role of banks or
financial institution services in providing financial
services to customers, assisting customers in making
financial decisions, reducing operating costs, risk of
losses due to bad loans, and developing markets.
The implication of Fintech in MSMEs makes it easy
for MSMEs to access financial service products
offered and apply for financing without having to
come directly to banking branches or other financial
institutions. Besides financing, Fintech is also used
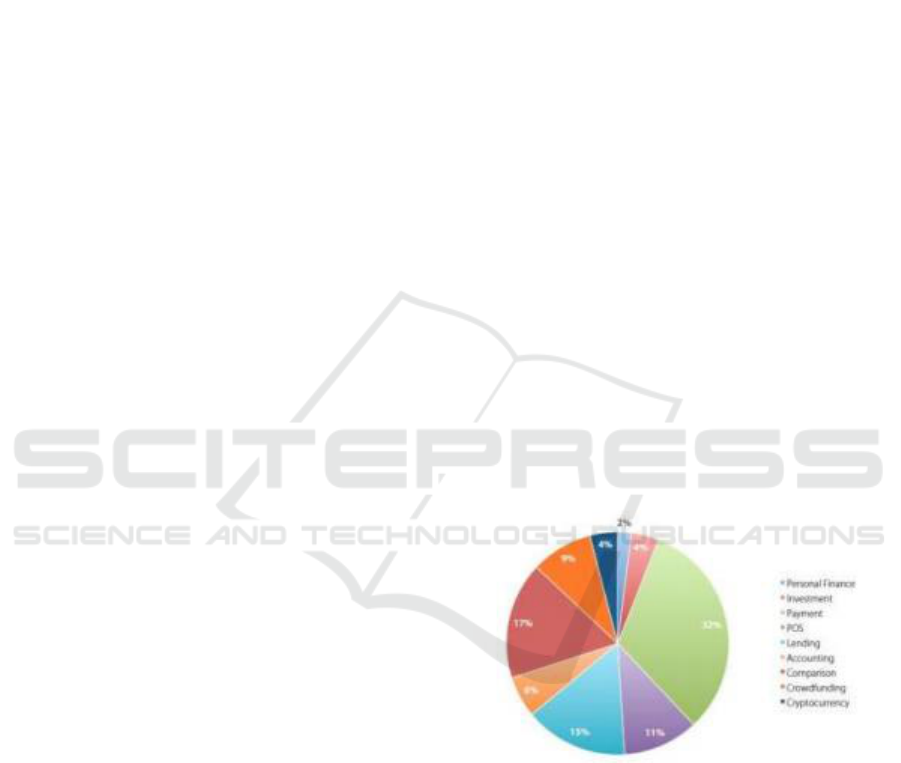
in payment transactions. Payment transactions are
the most developed activities. The data below shows
the distribution of Fintech technology activities in
Indonesia:
Figure 1. Distribution of Financial Technology Activities
in Indonesia
Source: Fintech Indonesia
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
Technology
The technological context refers to internal and
external technology, including equipment and
processes. This context also describes both new
technologies and old technologies that are relevant
122
Tjahjanto, ., Lestari, I., Meidiyustiani, R. and Imelda, .
Implementation of Technology, Efficiency, Knowledge, Risk on Trust Level of Fintech Used in MSMEs in Tangerang City.
DOI: 10.5220/0008930401220125
In Proceedings of the 1st Inter national Conference on IT, Communication and Technology for Better Life (ICT4BL 2019), pages 122-125
ISBN: 978-989-758-429-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

to the organization. The results of the study show
that on the technological aspects:
a) Relative Advantage
According to Rogers (1983), relative advantages
are technological factors that can be felt as
providers of benefits for companies.
b) Compatibility
Rogers (2003) argues that compatibility is the
extent to which it is innovation is perceived as
consistent with existing values, experience,
and the needs of potential adopters.
c) Complexity
Complexity is a level of difficulty in understanding
and using the system (Sonnenwald et al.,
2001).
Efficiency
Finance Technology or Fintech is a financial
services digitalization program that can improve the
efficiency of financial transactions. Also, it makes it
easier for people to get financial access. Lately,
Bank Indonesia (BI) seems to be pushing hard to
encourage Fintech to increase competitiveness in the
era of globalization of financial technology. At
present many financial sectors, especially banks, are
using Fintech as an effort to improve efficiency. The
trend of using cards more often than cash seems to
underlie the banking sector to be more efficient in
financial services. The Indonesia ICT Institute
Executive Director Heru Sutadi explained, even
though the use of technology in finance was not
cheap, if the entire community helped support BI's
efforts to develop Fintech, the costs would not be
large.
Knowledge
Knowledge about Fintech has a big contribution to
MSMEs in using Fintech itself. Lack of knowledge
about Fintech will cause the UMKM's low level of
confidence in using Fintech. According to Baihaqi
(2016) uses two indicators to measure the
knowledge of MSME actors, namely:
1) Declarative knowledge
Declarative knowledge is knowledge of facts and
based on concepts.
2) Procedural knowledge
Procedural knowledge is the knowledge that is
consistent with applicable accounting rules or
standards, usually depending on experience.
Risk
The three risks below are not only centered on the
risks experienced by users, but also for Fintech
owners, and even the state. Therefore, the
government, through OJK and BI made regulations
and solutions so that Fintech could still run safely.
1. Risk of cybercrime
This is the most potential risk. Fraud, misuse of
client data, digital signatures that can be
faked, and various other cybercrimes against
vulnerable data security need to be addressed.
2. Risk of default
For Fintech who runs a business as financing or
credit, the risk of default is quite worrying.
Investors themselves must be prepared from
the start that the risk of taking credit default
risk is their responsibility.
3. Risk of funds laundering and acts of terrorism
The presence of Fintech also has a risk of funds
laundering and funding for terrorism. Easier
and faster financial transactions cause this
risk.
So far, Bank Indonesia has also set conditions that
must be met in order to be able to make
transactions. These conditions are 1) must
have institutions that are in Indonesia, 2) all
types of transactions must be made in rupiah
currency, and 3) all funds must be placed in
banks. (Ana Fauziah, 2017).
Fintech
Fintech comes from the term Financial Technology,
which is defined as innovation in financial services
which is an innovation in the financial sector that
gets a modern touch (Ernama, 2017). Financial
transactions through this technology include
payment, investment, money lending, transfers,
financial plans, and comparison of financial
products. The financial industry technology
(Fintech) is one of the financial service's methods
that became popular in the digital era today. Digital
payments are one of the sectors in the Fintech
industry that is the most developed in Indonesia.
This sector is then most expected by the government
and society to encourage an increase in the number
of people who have access to financial services.
(Budi Wibowo). The picture below shows the
evolution of Fintech from year to year.
Figure 2. The evolution of Fintech
Implementation of Technology, Efficiency, Knowledge, Risk on Trust Level of Fintech Used in MSMEs in Tangerang City
123

Source: Auditia Setiobudi, et al. (2018)
3. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The method used in this study is descriptive
qualitative. This research was conducted to find out
more about indicators in the Technology, Efficiency,
knowledge, and risk framework for the level of trust
in Fintech use in MSMEs. The method of data
collection is conducted through semi-structured
interviews to describe the phenomenon of
application-based cashless payment. Interviews
conducted are with business people (SMEs) who use
financial technology such as TCash, OVO, and so
forth.
4. DISCUSSION
Fitri Nuraini, Rieska Maharani and Andrianto
(2016)
Based on the research conducted by Fitri
Nuraini, Rieska Maharani and Andrianto (entitled
The Strategy for Increasing MSME Competitiveness
and Cooperatives in Facing the ASEC (Asean
Economic Community): A Study of Library, the role
of MSMEs is very important in creating employment
for the community and contributing non-export
products. oil and gas which can increase the
country's foreign exchange income.
Nofita Wulansari, Wahyu and Yunus Kurniawan
(2017)
Based on the research conducted by Nofita
Wulansari, Wahyu and Yunus Kurniawan (entitled
Acceleration of Economic Growth Through MSME
Synergy and Good Governance in Indonesia, the
role of MSMEs in Indonesia is an crucial point in
driving economic growth. MSMEs can survive and
save the nation's economy when a crisis occurs.
Budi Wibowo (2017)
Based on research conducted by Budi Wibowo
(2017) with the title Fintech Analysis in Building
Economy in Indonesia, the presence of technology-
based financial services (FinTech) in Indonesia has
become a necessity in line with the development of
information and communication technology.
Auditia Setiobudi, Trianggoro Wiradinata (2018)
Based on the research conducted by Auditia
Setiobudi, Trianggoro Wiradinata (2018) entitled
SME Intention in Adopting Financial Technology in
East Java, the intention of the Indonesian people (in
East Java in particular) towards financial technology
products is quite high. From the UKM side or the
merchant and the customer side, there are lots of
advantages. The sustainability and development of
this product are supported by the company's
resources and competencies that are demonstrated.
5. CONCLUSION
The results of the study explain that mobile payment
services will be one of the influential factors,
especially in vertical Fintech and in general, in the
financial landscape. The challenge that has always
been there is to educate the public as customers to
optimize banking-based financial services. However,
the application-based approach seems to be able to
make the community educated on its own. The thing
offered by the application is user experience to solve
particular problems. Technology also affects user
acceptance of mobile payment services. This is
related to the way of conducting transactions. The
needs are unique, so it can be concluded that certain
technologies are not necessarily suitable for all
services. From what is currently available, the
average mobile payment utilizes three platforms for
payment, namely QR Code, NFC (Near-Field
Communication), and OTP (One-Time Password).
In terms of MSMEs or merchants and the customer
side, there are many advantages. The sustainability
and development of this product are supported by
the company's resources and competencies that are
demonstrated.
REFERENCE
Ana Fauziah. 2017. Recognize the Risk of Using Fintech.
https://www.digination.id/read/0141/kenali-risiko-
pengunakan-fintech.
Auditia Setiobudi, Trianggoro Wiradinata. 2018. Intention
of MSMEs in Adopting Financial Technology in East
Java. National Conference of Creative Industry:
Sustainable Tourism Industry for Economic
Development University of Bunda Mulia, Jakarta, 5-6
September 2018 e-ISSN No: 2622-7436.
Budi Wibowo. 2017. Fintech Regulation Analysis in
Building the Economy in Indonesia, Jakarta,
Indonesia.
D. H. Sonnenwald and L. G. Pierce, “Information
behavior in dynamic group work contexts:
interwoven situational awareness , dense social
networks and contested collaboration in
ICT4BL 2019 - International Conference on IT, Communication and Technology for Better Life
124

command and control,” Inf. Process. Manag.,
vol. 36, no. 1, pp. 461–479, 2001.
Ernama Santi, 2017. Supervision of financial services
authorities on financial technology (Financial services
authority regulations number 77 / pojk.01 / 2016,
diponegoro law journal, Volume 6, Number 3,
2017.https://fintech.id/.
Everett M. Rogers. 1983. Diffusion of Innovations.
London: The Free Press.
Everett M, Rogers (2003). Diffusion of Innovation.
5th Edition. New York: Free Press
Fitri Nuraini, et al. 2016. Strategies for Increasing
Competitiveness of MSMEs and Cooperatives in
Facing the AEC (Asean Economic Community): A
Literature Review. Proceedings of the FEB EMSIDA
National Economic and Business Seminar, p 480-496.
Nofita Wulansari, 2017. Acceleration of Economic
Growth through Community Synergy and Good
Governance in Indonesia, Proceedings of the National
Seminar and Call for Paper for Economics and
Business (SNAPER-EBIS 2017) - Jember, 27-28
October 2017 (pp. 262-268) ISBN: 978-602-5617- 01-
0.
https://fintech.id/
http://shiftindonesia.com/ improve-efficiency-and-daya-
saing-melalui-fintech/. 2016. Increasing Efficiency
and Competitiveness through Fintech.
Implementation of Technology, Efficiency, Knowledge, Risk on Trust Level of Fintech Used in MSMEs in Tangerang City
125
