
Determinants That Affecting Accounting Information System Success
and Its Implication on
Accounting Information Quality in ERP Environment:
Empirical Study on the Indonesian Plantation Company
Anita Wahyu Indrasti, Dewi Puspaningtyas Faeni, Indah Rahayu Lestari, Berlian Karlina
Universitas Budi Luhur
berlian.karlina@budiluhur.ac.id
Keywords: Enterprise resource planning (ERP), user competence, organizational commitment, internal control,
accounting information systems, the quality of accounting information.
Abstract: Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are integrated software solutions that cover all aspects of a
company's business. ERP implementation will affect the quality of information produced by the company.
The financial statements used by organizations to provide financial information for decision making. This
study aims to analyze the factors that influence the quality of accounting information in a work environment
that has implemented an ERP system in its operational activities. These factors include the influence of user
competence, organizational commitment, and internal control by the company both directly and indirectly on
the quality of accounting information, with the accounting information system as a mediating variable. This
research was conducted on the main sector companies of the plantation sub-sector listed on the Indonesia
Stock Exchange in 2017, which have implemented an ERP application system in its operational activities.
The data used in this study are primary data with an analysis tool used in Structural Equation Modeling -
Partial Least Squares (SEM-PLS). Based on the test results known that accounting information system
success, organization commitment, and user competence have a significant relationship to the quality of
accounting information. However, internal control has no significant direct effect on the quality of accounting
information. Internal control and organizational commitment have a significant effect on the accounting
information system success. However, user competence has no significant effect on the accounting
information system success.
1. INTRODUCTION
General-purpose financial statements are to provide
financial information for a company, both at certain
times and in specific periods that are useful for a
number of users for retrieval decision (Kasmir, 2016).
The four qualitative characteristics of accounting
information, among others: understandability,
relevance, reliability, and compatibility. One
indicator of the relevance timeliness. Timeliness is
information that there are ready to be used before the
loss of meaning by the users of the financial
statements and certainty still available in decision
making (Susanto, Azhar, 2015).
The accounting information system is a crucial
part of improving organizational efficiency and
supporting competitiveness by providing financial
information and accounting for management
(Ratnaningsih, Kadek Indah, I Gusti Ngurah Agung
Suaryana, 2014).
The Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system
is an integrated software solution that covers all
aspects of the company's business. ERP
implementation will affect the quality of information
produced by the company, one of which is to improve
the quality of the financial statements produced by the
company (Kurniawaty, Dian Dwinita, Sri Restu
Yulia, 2009).
The quality of accounting information systems
can be influenced by several factors, one of which is
user involvement that can be measured by the level of
competence of users in utilizing existing information
technology in the company. As technology becomes
more sophisticated, higher expertise is needed; this is
108
Indrasti, A., Faeni, D., Lestari, I. and Karlina, B.
Determinants That Affecting Accounting Information System Success and Its Implication on Accounting Information Quality in ERP Environment: Empirical Study on the Indonesian Plantation
Company.
DOI: 10.5220/0008930101080112
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on IT, Communication and Technology for Better Life (ICT4BL 2019), pages 108-112
ISBN: 978-989-758-429-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

to be able to produce quality information. If the
system is excellent, and the users are not experts, the
information produced will not be of quality
(Ratnaningsih et al., 2014).
Organizational commitment is employee loyalty
and involvement to achieve organizational goals to
remain within the organization. One factor to be able
to implement accounting information systems within
the company, support, and commitment to the
organization is needed (Syaifullah, Muhammad,
2014).
Internal control is necessary to ensure that the
accounting information system works as it should be,
so the risk to the deviation from organization
objectives can be avoided (Azhar Susanto, 2013).
Implementation of security and an internal control
can effectively improve the quality and reliability of
the information system (Laudon, Kenneth C., and
Laudon Jane P, 2012).
The quality of accounting information systems is
related to the quality of accounting information
produced (Bachmid, Faiz Said, 2016). Without the
quality of an accounting information system, there
will be no quality accounting information (Sacer,
Ivana Mamic, Katarina Zager, Boris Tusek, 2006).
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1. Accounting Information Quality
The quality of accounting information is the
information that contains the value of relevance to
accounting where such information is available when
needed to meet the needs of users in the decision-
making (Susanto, Azhar, 2015). Quality information
is a characteristic of information to meet individual
requirements when needed. Preparation is the process
of preparing, organizing, formatting, and presentation
of information to the user.
2.2. Accounting Information Systems
(AIS)
The information system is an integrated set of
components that collect, process, store and distribute
information to support decision making and control in
an organization (Susanto, Azhar, 2015). In addition to
supporting decision-making, coordination, and
control, information systems can also help managers
and employees to analyze problems, visualize
complex objectives, and to meet organizational goals.
The accounting information system is an integration
of the system components that process financial data
into financial information to produce financial
information that is useful and needed by the user in
decision making.
The quality of accounting information system is
measured by the efficiency, effectiveness, and
integration. Efficiency is the minimal use of resources
to obtain maximum results (Syaifullah, Muhammad,
2014). Effectiveness is a measure of how a system
can achieve its goals, while integration is the
attachment between the components in the
accounting information system to produce quality
accounting information.
2.3. Implementation of Enterprise
Resource Planning (ERP)
ERP is a system that integrates all aspects of the
company's business, such as accounting, finance,
marketing, human resources, manufacturing also
inventory management into one system (Syaifullah,
Muhammad, 2014). Implementation, a well designed
ERP, will provide good access management to
innovate the information regarding the company's
business activities to plan, control, and evaluate the
company's business processes to be more productive.
Benefits provided to the company's ERP, include:
improving the quality and efficiency of the
organization; reduce the costs associated with the
providing information to the organization; ERP helps
management in decision making by providing
information quickly, complete and timely (O’Brien,
James A., George M. Marakas, 2014).
2.4. User competence
Competence is individual characteristics associated
with effective performance in a particular job.
Competence is also said to be the fundamental
characteristics (underlying characteristic) that are
characteristic of an individual who is a depth section
and attached to the personality of a person that can be
used to predict a variety of situations specific job, the
level of knowledge, skills can measure competence,
and fundamental values are reflected in the habit
think, and act. Competence can also be defined as a
person's ability to carry out tasks that acquired
through education and training (Hazrita, Fadilah, M.
Rasuli, Kamaliah, 2014).
2.5 Organizational commitment
Commitment is the attitude and behavior of the
individual towards the organization. Organizational
Determinants That Affecting Accounting Information System Success and Its Implication on Accounting Information Quality in ERP
Environment: Empirical Study on the Indonesian Plantation Company
109

commitment is a person's ability and willingness to
align private behavior with the needs, priorities, and
goals of the organization (Ratifah, Ifa, Mochammad
Ridwan, 2012). The concept of organizational
commitment is defined as loyalty and employee
involvement to achieve organizational goals to
remain in the organization (Syaifullah, Muhammad,
2014),
2.5. Internal Control
Implementation of security and an internal control
can effectively improve the quality and reliability of
the information system (Laudon, Kenneth C., and
Laudon Jane P, 2012). Internal control is necessary to
ensure that the accounting information system works
as it should be, so the risk to the deviation from
organization objectives can be avoided (Azhar
Susanto, 2013).
In organizations that do not carry out internal
controls properly, the risk of irregularities will
increase, this has an impact on the decline in the
quality of accounting information system, so that
potential losses in decision-making increase due to
the low relevance and reliability of accounting
information produced (Moller, Robert R, 2011).
2.6. Technology Acceptance Model
(TAM)
Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) was adapted
from the Theory of Reasoned Action proposed by
Davis (1989). TAM assumes that individual
acceptance of information technology is influenced
by two main variables, namely Perceived Usefulness
and Perceived Ease of Use. Both of these perceptions
affect the Attitude Toward Using Individuals to the
use of technology (Hazrita, Fadilah, M. Rasuli,
Kamaliah, 2014). This model describes the driving
factors underlying the behavior of users of
information technology to the acceptance of
information technology of adoption of information
technology (Ratifah, Ifa, Mochammad Ridwan,
2012).
Technology Acceptance Model is theory
explaining that the acceptance of the individual, in
this case, the employee and the organization as users
of technology on information technology is strongly
influenced by the ease in using the technology as well
as factors such technological benefits for the
organization. Technology will be accepted and used
by the user if the technology can facilitate the user in
completing the work and the user confidence when
using these technologies, then performance will
increase. In this study used the Technology
Acceptance Model theory to analyze variables user
competence and organization commitment, related to
the perception of the usefulness and perceived ease of
use of information technology.
3. METHODOLOGY
In this study, using a survey method to obtain primary
data. This study uses Partial Least Squares Structural
Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) for data analysis.
This research is a quantitative study to identify an
association between the variables studied.
Quantitative research is an inquiry about the social
problems based on the theory test consists of multiple
variables, as measured by the number and analyzed
by statistical procedures to determine whether the
predictive generalizations are accurate (Moller,
Robert R, 2011).
The population in this study were all employees
of the plantation companies that use either directly or
indirectly of an ERP system as a system that produces
accounting information. Methods Convenience
Sampling has been associated with the limited time
available to conduct research.
4. RESULT
SEM-PLS method is used to analyze multivariate
models. The model consists of three exogenous latent
variables, namely user competence, organizational
commitment, and internal control, while the
endogenous latent variables, namely accounting
information system success and the quality of
accounting information.
4.1. Measurement Model Test
Measurement test this model consists of the validity
and reliability because test results measuring the outer
consistency in explaining construct models.
Recommended measurement test results of this model
affect the structural test models.
4.2. Internal Test for Consistency
Reliability
Reliability of composite value varies between 0-1; the
higher the reliability of composite showed, the higher
the degree of reliability of variables. In general, the
composite reliability interpreted as Cronbach's Alpha.
ICT4BL 2019 - International Conference on IT, Communication and Technology for Better Life
110
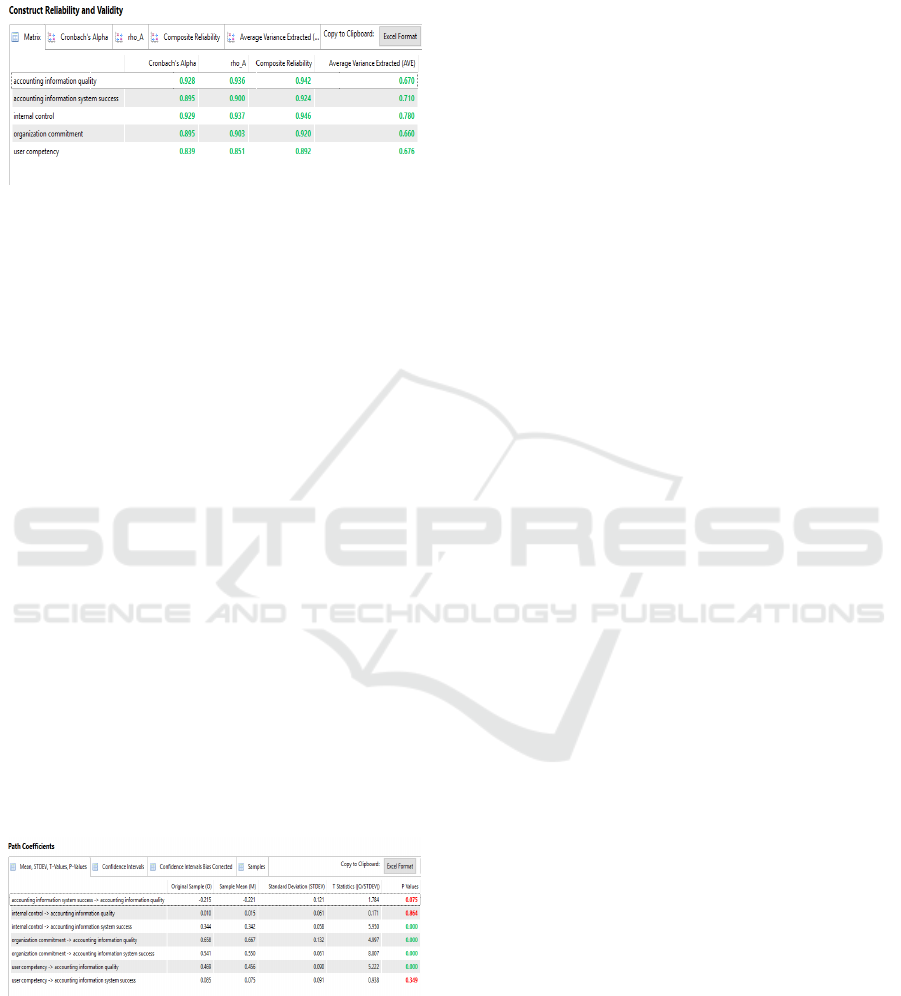
For exploratory research, the reliability of the
composite score must be above 0.60-0.70 (Ardi,
Bagus Kusuma, 2013).
Table 1: Construct Reliability and Validity
Table 1 shows that the entire latent variable has a
value of composite reliability above 0.70. The test
results stated that the model could meet the reliability
test.
4.3. Validity Test
To test the convergent validity, we evaluated the
value of Average Variance Extracted (AVE) on each
of the latent variables. 0.50 AVE value above shows
that on average constructs can account for more than
half a variant of the indicators (Ardi, Bagus Kusuma,
2013).
Table 1 also shows that all latent variables have
AVE value above 0.50, this means that the latent
variables in the study passed the test of convergent
validity, showed that on average constructs can
account for more than half a variant of the indicators.
4.4. Path Coefficient Test
In this study, the structural model test using T-test (2-
tailed) with a significance level of 10%, then the path
coefficient significant when t practical value is higher
than the critical value is 1.65 (Ardi, Bagus Kusuma,
2013).
Table 2: Path Coefficients
5. CONCLUSION
Based on the test results known that accounting
information system success, organization
commitment, and user competence have a significant
relationship to the quality of accounting information.
However, internal control has no significant direct
effect on the quality of accounting information.
Internal control and organizational commitment have
a significant effect on the accounting information
system success. However, user competence has no
significant effect on the accounting information
system success
REFERENCES
Ardi, Bagus Kusuma, 2013. Analisis Pengaruh Persepsi
Pengguna, Sikap, Dukungan, Teknologi Terhadap Niat
yang Berdampak Penggunaan Senyatanya Software
Myob Pada Lembaga Pendidikan Kursus Di Kota
Semarang. Jurnal Ekonomi Manajemen Akuntansi
No.34. ISSN: 0853-8778
Azhar Susanto, 2013. Sistem Informasi Akuntansi, Struktur-
Pengendalian Resiko-Pengembangan. Bandung:
Lingga Jaya.
Bachmid, Faiz Said, 2016. The Effect of Accounting
Information System Quality on Accounting Information
Quality. Research Journal of Fianance and Accounting
Vo.7 no. 20. ISSN: 2222-2847
Cakmak, Ahmet Ferda, Serkan Benk, Tamer Budak, 2011.
The Acceptance of Tax Office Automation System
(VEDOP) By Employees: Factorial Validation of
Turkish Adapted Technology Acceptance Model
(TAM). International Journal of Economics and Finance
Vol.3 No.6. 107-116. ISSN: 1916-9728
Hair, Joseph. F, 2014. A Primer On Partial Least Squares
Structural Equation Modelling (PLS-SEM). Los
Angeles: SAGE
Hazrita, Fadilah, M. Rasuli, Kamaliah, 2014. Pengaruh
Kompetensi dan Sistem Akuntansi Terhadap Kualitas
Pertanggungjawaban Laporan Keuangan Pada Satuan
Kerja Di Lingkungan Kanwil Kementrian Agama
Provinsi Riau. Jurnal SOROT Vol.9 No.1. 59-69.
ISSN: 1907-364X
Kasmir, 2016. Analisis Laporan Keuangan. Jakarta: Raja
Grafindo Persada
Kurniawaty, Dian Dwinita, Sri Restu Yulia, 2009.
Pengaruh Implementasi Enterprise Resource Planning
(ERP) Terhadap Kualitas Informasi Akuntansi pada
PT.PLN. Jurnal Riset Akuntansi Universitas Komputer
Indonesia (Unikom) Vol.I No.1
Laudon, Kenneth C. and Laudon Jane P, 2012. Essential of
Management Information System: Managing the
Digital System. Canada: Prentice Hall.
Moller, Robert R, 2011. COSO Enterprise Risk
Management – Establishing Effective Governance,
Risk, and Complience Processes. Canada : John Wiley
& Sons Inc
O’Brien, James A., George M. Marakas, 2014. Sistem
Informasi Manajemen. Jakarta: Salemba Empat
Ratifah, Ifa, Mochammad Ridwan, 2012. Komitmen
Organisasi Memoderasi Pengaruh Sistem Akuntansi
Determinants That Affecting Accounting Information System Success and Its Implication on Accounting Information Quality in ERP
Environment: Empirical Study on the Indonesian Plantation Company
111

Keuangan Daerah Terhadap Kualitas Laporan
Keuangan. Trikonomika Vol.11 No.1. 29-39. ISSN:
1411-514X
Ratnaningsih, Kadek Indah, I Gusti Ngurah Agung
Suaryana, 2014. Pengaruh Kecanggihan Teknologi
Informasi, Partisipasi Manajemen dan Pengetahuan
Manajer Akuntansi Pada Efektivitas Sistem Informasi
Akuntansi. E-Jurnal Akuntansi Universitas Udayana
Vol.6 No.1. 1-16. ISSN: 2302-8556
Romney, Marshal B., Paul John Steinbart, 2015. Sistem
Informasi Akuntansi. Jakarta: Salemba Empat
Sacer, Ivana Mamic, Katarina Zager, Boris Tusek, 2006.
Accounting Systems Informastion as The Ground for
Quality Business Reporting. IADIS International
Conference E-Commerce.
Silalahi, Uber, 2015. Metode Penelitian Sosial Kuantitatif.
Bandung: Refika Aditama
Susanto, Azhar, 2015. Influence The Quality of Accounting
Information on The Implementation Good Study
Program Governance. International Journal of
Scientific and Technology Research Vol.4 Issue.12.
ISSN: 2277-8616
Syaifullah, Muhammad, 2014. Influence Organizational
Commitment on The Quality of Accounting Information
System. International Journal of Scientific and
Technology Research Vol.3 Issue.2.299-305. ISSN:
2277-8616.
ICT4BL 2019 - International Conference on IT, Communication and Technology for Better Life
112
