
The Procurement Business Transformation 2.0: The Remedy of
Inefficient Procurement Operations
Ade Christian Sirait and Dodie Tricahyono
Magister Management, Telkom University, Jalan Gegerkalong Hilir, Bandung, Indonesia
Keywords: Procurement Business Transformation 2.0, Telkomsel, Indonesia.
Abstract: This present research is aim to analyze and evaluate the implementation of the procurement business
transformation 2.0 which has been going on from 2014 until 2017 in Telkomsel. Improvement in
procurement operation means increasing efficiency in procurement, decreasing of manual processes,
increasing self-service tools and reducing changes of order. The transformation aspect consists of three
categories: process, technology and people. As qualitative research, data were collected by in-depth
interviews with some experts in the procurement from internal Telkomsel as primary data, complemented
by observation and secondary data collection. The results confirmed that all aspects (process, technology
and people) are important elements in procurement business transformation. The present study suggests that
accuracy in the implementation of business transformation will help the company run the business to facing
digital industry nowadays to survive and growth for the long term.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to Sri Mulyani, the Minister of Finance,
the potential growth for digital business in Indonesia
is very high and reach 51.8% from total population.
Disruptive technology, startup development and
demand for digital products, requires the company to
be able to provide services and products that are in
accordance with consumer needs and adapt quickly
to changes that occur. As the 6th largest
telecommunication operator company in the world,
Telkomsel also deals with these challenges by
having a proper business strategy.
In the digital era, the procurement function as
well as an organization has been largely less
attention or investment (Accenture, 2017). The
digital revolution touches only a little to
procurement. What mostly organization do is simply
repeating the same processes with new software.
To deal with the digital revolution, an
organization should think beyond the traditional
processes. This is the reason why Telkomsel
implements Procurement Business Transformation
2.0 (PBT2.0). Especially in Requisition to Purchase
(R2P) stream, in order to become a true digital
procurement organization with high efficient and
potentially drive down costs.
To become a World Class Procurement, business
transformation needs to be done gradually. Because
procurement at Telkomsel is still in developing
stage. Procurement management determines the
operating model that will be applied in the PBT2.0.
Some important parameters, such as: process,
people, and Technology have been acknowledged.
The benchmarking process was done with a result
can be seen in Figure 1. Thus, the expected results of
the transformation are able to provide value creation,
cost leadership and faster time to market.
Figure 1: The Results of the Benchmarking Process.
The present study aims to analyze the
procurement business transformation to check
whether the processes are implemented smoothly or
wastefully, especially within the three aspects
Sirait, A. and Tricahyono, D.
The Procurement Business Transformation 2.0: The Remedy of Inefficient Procurement Operations.
DOI: 10.5220/0008434205950601
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World (ICIB 2019), pages 595-601
ISBN: 978-989-758-408-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
595

(process, people, technology). From the analysis,
the present study suggests some recommendation to
improve the future performance of PBT2.0 in
Telkomsel automated and improve the performance
of procurement services.
The PBT2.0 framework can be seen in Figure 2.
The framework focuses on process, people and
technology.
2 THEORICAL BACKGROUND
2.1 Business Transformation
Business transformation is a change in management
strategy that has goals in directing processes,
technology and people in the company to be more
directed towards the business vision and strategy set
by management (Aspera, Lamberg, Laukia, &
Tikkanen, 2011; Bititci, 2007; Nieminen, 2014;
Nixon, 2003; Saul, 2011; Shaughnessy, 2018). The
company implements business transformation in
procurement in order to achieve efficient and
effective management of procurement activities.
Procurement is one of business management
function that ensures identification, sourcing, access
and external resource management needed by the
organization for a strategic purpose (Accenture,
2017).
The business transformation is a consequence of
the rapid change of digital technology. Some articles
focus on business transformation that related to
some issue, for example: digital maturity model
(Gill & Van Boskirk, 2016), community engagement
(Arroyo, Derek, & Walker, 2010), new business
model (Saul, 2011), strategic planning
(Shaughnessy, 2018), and restructuring the
organization (Parikh, & Joshi, 2005).
2.2 Theoretical Framework
According to Bititci (2007) and Eckhardt et al.
(2014), in order to succeed, the business
transformation must have the following elements:
Process
Transformation is aimed to achieve an efficient
and effective process. The process relates to time
and cost. The transformation of the procurement
process should decrease the total cost of
procurement.
People
The business transformation will be carried out
by people within the organization. The quality of
transformation should make people increase their
capabilities.
Technology
Technology as an enabler of processes that have
been designed and used by people in the organization.
Technology will make the monotonous process to be
Figure 2: Framework Business Transformation
Procurement 2.0.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Research Methods and Object
Based on the problems and objectives that have been
determined, the present research conducts qualitative
research. To be more specific, the present study uses
a case study. The present study focuses on
Procurement 2.0 project in the first step (Request to
Purchase/R2P) transformation project in
Procurement Group under Finance Directorate
Telkomsel.
Although this project has already started since
2014, the results still far away from the position of
world class procurement. From an internal source,
out of five stages of world class procurement (from
stage-1/reactive, stage-2/developing, stage-
3/advancing, stage-4/high performing, and stage-
5/pioneering), Telkomsel still in the stage-2
(developing). In this stage, the organization has
characteristics of selected supplier base
consolidation, some sourcing strategy creation, and
track the commercial measure of performance and
saving.
3.2 Data Collection and Analysis
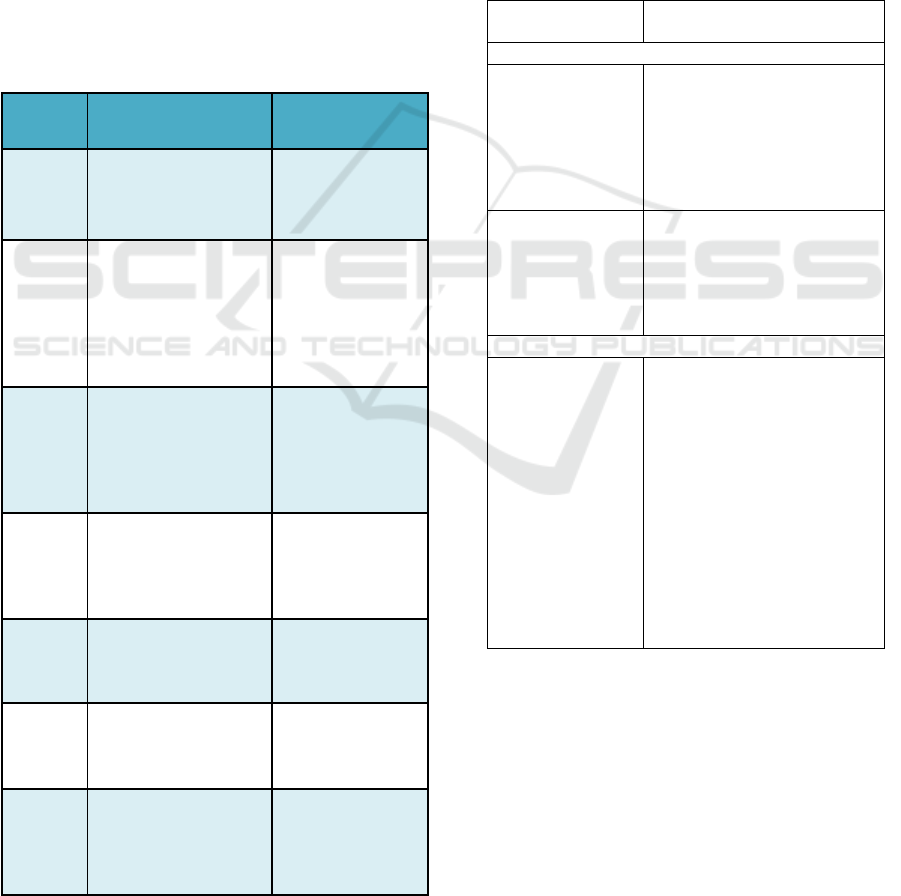
The present study interviewed seven experts from
internal who involve in the PBT2.0 in Telkomsel
procurement group. Three of them are General
Managers, three managers, and one operational
officer (see Table 1). Researchers use in-depth
ICIB 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World
596
interviews method by considering that method is
powerful enough on data collection. Data will be
collected in written form, audio recording, photo and
video as the main source this research (Wahyuni,
2011).
The data is defined as people, things or objects
that can provide information, facts, data, and reality
related to what was studied or examined (Indrawati,
2015). Sources of data in research can be classified
into primary data sources and secondary data. The
primary data stem from the interview of experts with
an in-depth interview. Meanwhile, the secondary
data is obtained from the data collection at Oracle
for purchase order period 2017 with sampling. Table
2 shows the sample of questionnaires for the in-
depth interview which comprise of two groups: the
general questions and specific questions.
Table 1: Interviewee’s characteristics.
Experts
Position
Criteria
1
GM Procurement
Support - Procurement
One of the lead
projects of
Procurement
Transformation 2.0
2
GM Finance
Transformation
Functional Development
- Finance
One of the lead
projects in Finance
transformation; The
functions involved
in implementing
procurement in the
budgeting section
3
GM Learning
Development and
Knowledge
Management - HCM
The function users
who direct impact
on changes in
business processes
in procurement and
an expert in HCM
4
Manager RAN Design
and Planning East -
Network
Function user who
directly impact on
changes in
procurement
business processes
5
Manager IT ERP Non-
Core - IT
Involved in the
procurement
transformation
project in IT
6
Manager Procurement
System Operation -
Procurement System
Developing and
implementing
procurement system
7
Senior Officer Finance
Transformation
Functional Development
- Finance
Function user who
directly impact on
changes in
procurement
business processes
To validate the collected data, the present study
implements the triangulation process and expert
validation. Triangulation is a verification process
that combines several points of view and methods.
In social science, it refers to a combination of two or
more theories, data sources, methods or investigators
in a study of a phenomenon so that a single construct
can be formed (Wahyuni, 2011). The present study
implements the triangulation process by comparing
the information with in-depth interview methods
from the speaker as managerial level (General
Manager and Manager) and operational (Officer,
Staff) in the Telkomsel business unit.
Table 2: A sampling of questionnaire interviews.
Operational
Definition
Interview Questions
General
Operating model
or framework
yang implement
in Telkomsel on
business
transformation
procurement 2.0
What framework or
parameters need to be
considered in implementing
a business transformation?
Inputs from
Implementation
of procurement
business
transformation
2.0
What input can you give to
the implementation of the
procurement transformation
2.0 that has been
implemented?
Specific
Implementation
related process,
technology and
people who have
been implemented
on procurement
business
transformation 2.0
How has the business process
changes in the procurement
2.0 business transformation
implementation?
How is the use of technology
in the procurement 2.0
business transformation
implementation?
How are people change in the
procurement 2.0 business
transformation
implementation?
Once data has been collected, the data will be
analyzed by focusing on the implementation side of
business transformation especially PBT2.0 with
respect to the process, people and technology. Table
3 shows how the present study scrutinizes the data.
The present study also implements key informant
who has detailed knowledge of ideas, concepts and
relationships that relate with the phenomenon under
study. The expert opinions will validate the results
of the present study. According to Miles and
The Procurement Business Transformation 2.0: The Remedy of Inefficient Procurement Operations
597
Huberman (1984), analytical activities will be
carried out interactively and continuously until the
data is saturated. Activities in data analysis include
data reduction, data display, and conclusion
drawing/verification
Table 3: Variables vs implementation aspects.
Implementation
aspects
Variables
Process
People
Technology
Business
transformation
implementation
PBT2.0
implementation
Impact of
PBT2.0
Inputs for
PBT2.0
implementation
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Results
4.1.1 The Implementation Aspects
Based on the results of the analysis, it was found that
all the interviewees confirmed that the three aspects
of the process, technology and people are crucial
parameters for carrying out the business
transformation in general and also for the specific of
PBT2.0.
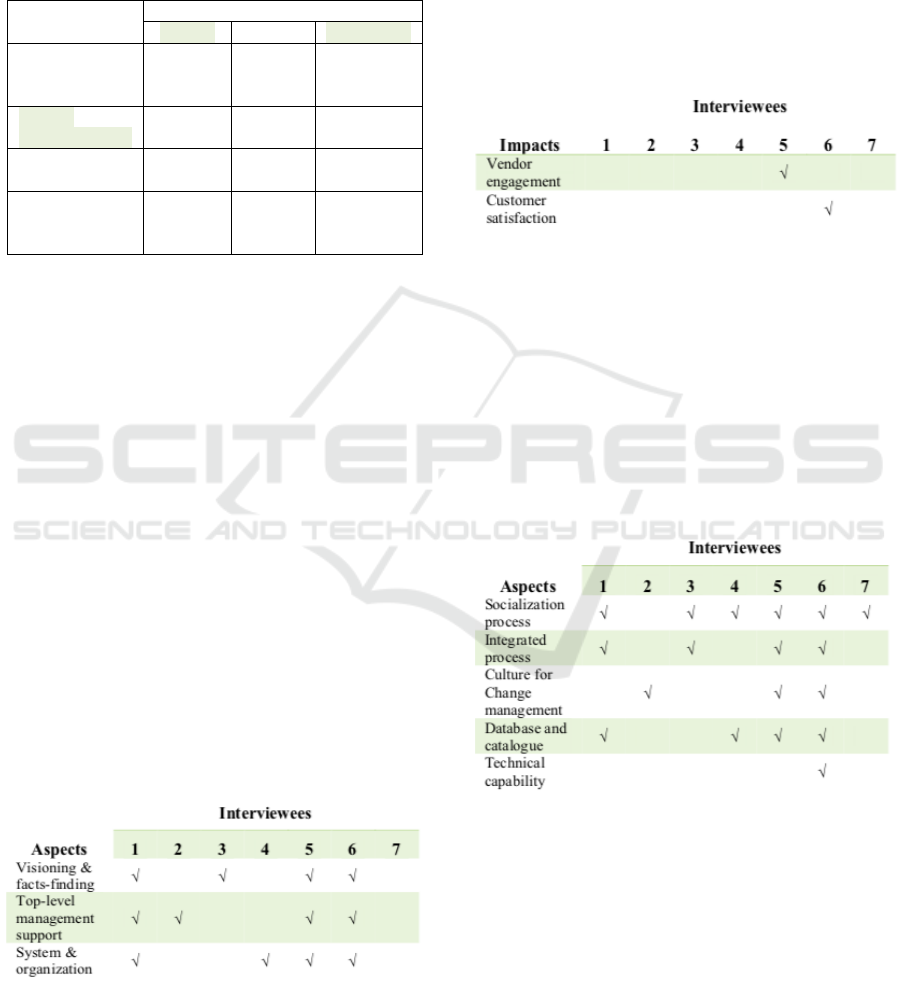
In addition to these parameters, some aspects
come to the surface, which is: visioning & facts-
finding; Top-level management support; and system
& organization. Table 4 shows the distribution of the
answers to all the interviewees.
Table 4: Other important implementation aspects.
4.1.2 The Impact of PBT2.0 Implementation
The response from the interviewees concerning the
impact of PBT2.0 implementation are as follows:
proactive system; automated & efficient; innovation
sustainability, compliance & accurate; vendor
engagement; and customer satisfaction. Table 5
shows the distribution of the impacts of all the
interviewees.
Table 5: The impacts of PBT2.0 implementation.
4.1.3 The Inputs for PBT2.0
Implementation
The informants also define the inputs for successful
PBT2.0 implementation, which are: socialization
process; integrated process; correct culture & change
management; data base & catalogue; and technical
capability. Table 6 shows the distribution of the
informants’ response.
Table 6: Inputs for PBT2.0 implementation.
4.2 Discussion
4.2.1 The Implementation Aspects
The results found that process, people and
technology are among the important aspects for the
implementation of business transformation in
general, as well as in procurement business
transformation (PBT2.0). Indeed, this result of the
present study supports what have already found by
ICIB 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World
598

the previous authors (e.g. Bititci, 2007; Eckhardt et
al., 2014; Kwak, Watson, & Anbari, 2008,
Shaughnessy, 2018). However, some details of the
results concerning the three aspects are as follows:
The process has a visibility horizon, faster
lead time, cutting manual process in helping
accelerate the process that has an impact on
the business and the results are better and more
efficient.
Technology has used catalogues and made
purchasing easier, paperless, helped for
analysis. Technology as an enabler in
supporting custom processes, digitization
and online.
People support faster transformation, less
control and more proactivity and involved
in helping determine needs, eagerness for
improvement program, organizations that
change, are open and helpful.
The present study also found other important
aspects that should be considered by the
organization if they are implementing business
transformation. First, the organization should have a
vision of how the project (PBT2.0) will change the
performance of the organization in the future. One of
the GM said:
“The visioning means we have as
aspiration, we will want like what? The
consultant may say that our organization can
become something.…. and then, our House of
Strategy
will define the operating model in order
to make a basic principle”.
Another manager added:
“We will start with a consciousness that
we need to transform…is it urgent or not….
So,
start from there, and from there we will
arrange the implementation program”.
Furthermore, the informant also added that the
organization also need to track the performance on a
periodic basis.
“I think we need also a monitoring
system than can check our performance on a
periodic basis to be benchmarked to our
targeted score”.
The second aspects that emerge from the present
study are top-level management support. This aspect
is important for making all the member of the
organization aware and get full attention to the
transformation project. One informant mentioned the
important to have an executive sponsor at the first
place. One GM also mentioned the important to have
top level support. She said:
“Tone-of -the-top, means it should be
pushed from the top level that transformation
is necessary to be implemented”.
The third aspect is about system and
organization. The system and organization will
guarantee that all members will understand who
does what and why. This is important to make the
transformation do not produce chaos and distrust
situation.
4.2.2 The Impact of PBT2.0 Implementation
There are five impacts of PBT2.0 implementation
has been discovered by the present study, which is:
proactive system; automated & efficient; innovation
& sustainability, compliance & accurate; vendor
engagement; and customer satisfaction. Two of them
are agreed by almost all the informants: automation
efficient, and proactive system. Automation means
there is no manual process anymore, especially the
monotonous and repeatable process. For example,
the auto approve feature that makes lead time faster
but with respect to compliance with the policy. In
consequence, the efficient in time, cost, and other
resources will be achieved. The proactive system
means that the system has the ability to give a
suggestion on what the best action should be taken
in the near future. The system may provide agility to
the organization. In the end, this system will
increase customer satisfaction. By having the
automation process, the problem of compliance that
stem from inaccurate data will reduce significantly.
One of the informants said:
“The more people involved in the
organization, the greater the error there
and more and more controls must be
inputted. People are very important to be
more proactive in transforming so the
transformation can support the company's
business”.
The Procurement Business Transformation 2.0: The Remedy of Inefficient Procurement Operations
599

Another important impact that the present study
found is innovation and sustainability. By
implementing PBT2.0, people may have times to
think of new ideas. This new idea will make an
impact on the sustainability of their business.
Eventually, this will make the customer happy and
engage more supports from the vendor.
4.2.3 The Inputs for PBT2.0
Implementation
Almost of the informants agree that the process of
socialization of the transformation project is the
important inputs that should be prepared by the
organization before the transformation project begin.
Other inputs that have been discovered were an
integrated process, database & catalogue, and
technical capability. These three inputs reflect the
hard side of an organization that should be prepared.
It is connected to resource allocation especially the
budget. These inputs ensure that people understand
their roles and responsibilities.
One of the informants responded:
“The key is integrated, now procurement
has been integrated and must be developed to
budgeting, and planning processes, and if
possible, allowing all departments to cross-
check the inventory…”.
The other important input that has been revealed
from the present research is culture for change
management. Business transformation is about
changes, mostly fundamentally. Part of this culture
is: see the big picture, joint planning sessions,
informally/formally communications, talk with data,
mutual respects, and trust.
This secondary data is obtained from the Oracle
system to measure the lead time for the procurement
of goods and/or services. Measurements are made
from the request until the issuance of purchase
orders. After the implementation of the procurement
2.0 business transformation, on average it becomes 4
working days which previously was an average of
16 working days.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The present study has been succeeding to understand
the triangle of people-process-technology in the
transformation process, especially in PBT2.0. The
PBT2.0 as a change program should be prepared
carefully in order to run smoothly and has a good
impact for the organization, for example to have a
good reputation, increasing customer satisfaction
and also vendor satisfaction, and so on.
In order to carefully prepare, the PBT2.0 should
consider all the stages: pre-transformation, in-
transformation, and post-transformation. As a
conclusion, the present study suggests all the stages
and all the aspects in each stage. Figure 3 shows
these stages.
Figure 3: Input-Transform-Impact of PBT2.0.
REFERENCES
Accenture (2017). “Next Generation Digital Procu-rement.
Upgrade Your Thinking”. https://www.accenture.
com/t20171023T071231Z__w__/us-en/_acnmedia/
PDF-63/Accenture-Next-Gene-ration-Digital-
Procurement-POV.pdf. Retrieve on 5 February 2019.
Amaratunga, D., Baldry, D., Sarshar Rita, M., & Newton,
R. (2002). Quantitative and qualitative research in the
built environment: application of “mixed” research
approach. Work Study, 51(1), pp. 17 – 31.
Arroyo A. C., Derek, H., & Walker, T. (2010). The role of
the Atlantic corridor project as a form of a strategic
community of practice in facilitating business
transformations in Latin America, International
Journal of Managing Projects in Business, 3(2),
pp.338-348.
Aspera, J., Lamberg, J-A., Laukia, A & Tikkanen, H.
(2011). Strategic management of business model
transformation: lessons from Nokia. Management
Decision, 49(4), pp.622-647.
Bititci, U. S. (2007). An executive's guide to business
transformation. Business Strategy Series, 8(3), pp.203-
213.
Chen, Ying‐ Ni, Kleiner, B. H. (2001). New
developments in creating cycle time reduction.
Management Research News. 24(3/4), pp.17-21.
Eckhardt, A., Laumer, S., Maier, C., & Weitzel, T. (2014).
The transformation of people, processes, and IT in e-
recruiting: Insights from an eight- year case study of a
German media corporation. Employee Relations,
36(4), pp.415-431.
Ghina, A., Simatupang, T. M., & Gustomo, A. (2015).
Building a Systematic Framework for.
Entrepreneurship Education. Journal of
Entrepreneurship Education, 18(2), pp. 73-97.
ICIB 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World
600

Indrawati (2015). Metode Penelitian Manajemen dan
Bisnis, Konvergensi Teknologi Komunikasi dan
Informasi. Bandung. PT Refika Aditama.
Kwak, Y. H., Watson, R. J., & Anbari, F. T. (2008)
Comprehensive framework for estimating the
deployment cost of integrated business transformation
projects. International Journal of Managing Projects
in Business, 1(1), pp.131-139.
Martin, G. & VanBoskirk, S. (2016). The Digital Maturity
Model 4.0. Cambridge: Forrester research, Inc.
Miles, M. B. & Huberman, M. 1992. Analisis Data
Kualitatif Buku Sumber Tentang Metode-metode Baru.
Jakarta: UIP.
Nieminen, J. (2014). Understanding and Managing
Digital Transformation – A case study of a large
Nordic retailer, Aalto University, School of Science,
Computer Science and Engineering.
Nixon, B. (2003). Leading business transformation –
learning by doing. Industrial and Commercial
Training. 35(4), pp.163-167.
Parikh, M. A., & Joshi, K. (2005). Purchasing process
transformation: restructuring for small purchases.
International Journal of Operations & Production
Management, 25(11), pp.1042-1061.
Saul, B. J. (2011). Digital transformation: opportunities to
create new business models. Vice President and
Partner of IBM Global Business Services.
Shaughnessy, H. (2018). Creating digital transformation:
strategies and steps. Strategy & Leadership, 46(2),
pp.19-25.
Sugiyono (2012). Metode Penelitian Kualtitatif, Kualitatif
dan Kombinasi (Mixed Methods). Bandung: Penerbit
Alfabeta.
Tennant, C. (2007). Measuring business Transformation at
a small manufacturing Enterprise in the UK.
Measuring Business Excellence, 11(4), pp.66-74.
Wahyuni, S. (2011). Qualitative Research Method: Theory
and Practice. Depok: Penerbit: Salemba Empat.
The Procurement Business Transformation 2.0: The Remedy of Inefficient Procurement Operations
601
