
Development of Implementation Guidelines for Maintenance and
Treatment Work of Electrical Components in University of Indonesia
Buildings and Area based on Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Tito Tegar Irawan and Yusuf Latief
University of Indonesia, Jl. Margonda Raya, Kota Depok, Indonesia
Keywords: Guidelines, Maintenance, Treatment, Electrical Work, Work Breakdown Structure.
Abstract: Maintenance and treatment work of buildings is important in maintaining the reliability of buildings. the the
absence of standards for the implementation of electrical maintenance and treatment work in buildings at the
University of Indonesia is also one of the causes of building fires, electrical short circuit, and damage to
building transformers in the last 4 years. The purpose of this study is to develop standards for the
implementation of maintenance and treatment work of electrical components in buildings at the University
of Indonesia based on Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) using literature studies and the Delphi method.
The independent variable in this study is Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) includes the work type, work
package, alternative design, implementation requirements, activities, resources, and material specifications,
while the dependent variable in this study is the implementation standard. The results of this study are in the
form of developing an implementation standard based on Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) which can be
used as a reference for the maintenance and treatment of electrical components in buildings at the
University of Indonesia, which is expected to increase building user safety and convenience as well as
effectiveness and efficiency in building management.
1 INTRODUCTION
Based on the Regulation of the Minister of Public
Works No. 24 / PRT / M / 2008, maintenance of the
building is the activity of maintaining the reliability
of the building along with the infrastructures and the
ingredients so that the building is always worthy
function. While the treatment is an activity building
treatment replace parts of buildings, components,
construction materials, and / or infrastructure and
facilities in order to remain eligible buildings
function. Building maintenance is defined as work to
maintain, restore or repair every part of the building,
to maintain the performance of building and service
fabric and its surroundings, meet standards and
maintain the utility and value of buildings. This
includes repairs, improvements, and repairs to works
from existing facilities (Plavina & Geipele, 2013).
Building performance can be measured from 4 (four)
requirements, namely: functional requirements,
performance requirements, legality requirements and
compliance with regulations, and user requirements
(Son & Yuen, 2002). In the case of maintaining
function-worthy requirements, maintenance,
maintenance and inspection work must be carried
out on building buildings on a regular basis
(Republik Indonesia, 2002)
The University of Indonesia must have a source
of funds and resources are sufficient and reliable for
research activities and community services so that
research activities and community services can
generate new discoveries that benefit humanity and
contribute to the accumulation of knowledge
(BPMA, 2007), Buildings used to support the
achievement of the objectives and main functions of
an organization optimally users, and is expected to
follow the changes that may occur in its organization
(Achmada, 2013).
Based on an interview with Mr. Budi Prayitno as
Head of Management of Energy Saving Sustainable
UI and Mr. Beny Rahman, Head of Section for
Planning and Care and Maintenance of Mechanical,
Electrical, and Transportation UI in October 2018,
there were 5 phenomenon of fire, short circuit, as
well as damage to substations and transformers in
the last 4 years on the job of maintenance and
Irawan, T. and Latief, Y.
Development of Implementation Guidelines for Maintenance and Treatment Work of Electrical Components in University of Indonesia Buildings and Area based on Work Breakdown Structure
(WBS).
DOI: 10.5220/0008428801650173
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World (ICIB 2019), pages 165-173
ISBN: 978-989-758-408-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
165

upkeep of buildings and electrical components of the
University of Indonesia region which causes
kerugaian material up to 40 billion rupiah.
Besides avoiding damage incidents that may
occur, maintenance and treatment work of electrical
component can also increase the level of satisfaction
of building occupants (Au-Yong, 2014), Research
This will produce guidelines for the implementation
of maintenance and treatment of electrical work in
the building at the University of Indonesia based
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) to be structured,
managed, measured, and scheduled.
The novelty of this research is the
implementation guidelines are made based on Work
Breakdown Structure and the addition of the
University of Indonesia area components to
electrical maintenance and treatment work package
such as power house, telephone, and backup power
generators. This research will contribute to the
University of Indonesia in the hope that it will
impact the implementation guidelines so the
guidelines become structured, complete, and avoid
all components mistakes of maintenance and
treatment electrical work, where electrical work is
very important because of all building facilities
supported by electrical components. Also become a
reference in making guidelines for maintenance and
treatment work of buildings, especially for electrical
components for other institution. For academic
purpose, this provides knowledge about the process
of making WBS-based implementation standards.
2 RESEARCH OBJECTIVES
The objectives of this research are:
To identify the work section, work type, and
work package of WBS for maintenance and
treatment work of electrical components in
buildings and areas at Univesitas Indonesia.
To identify alternative design/method and
activity in each package of maintenance and
treatment work of electrical components in
buildings and areas at Univesitas Indonesia.
To identify resources for each activity in the
maintenance and treatment work of electrical
components in buildings and areas at the
University of Indonesia.
To identify technical specifications used in each
activity of maintenance and treatment work of
electrical components in buildings and areas at
the University of Indonesia.
To identify ways to develop guidelines based on
the WBS (Work Breakdown Structure) for the
maintenance and treatment work of electrical
components in buildings and areas at the
University of Indonesia
3 LITERATURE STUDY
3.1 University of Indonesia Buildings
and Area
The University of Indonesia certainly has sufficient
and reliable sources of funds and resources for
research and community service activities so that
research and community service activities can
produce new findings that are beneficial to humanity
and contribute to the accumulation of knowledge
(BPMA, 2007). The building is used to support the
achievement of the main goals and functions of a
user organization optimally, and is expected to be
able to follow changes that can occur in the user
organization (Achmada, 2013). The University of
Indonesia consists of 85 buildings located in an area
of 320 hectares (Prayitno, 2018). To support this,
good maintenance and treatment need to be done,
one of which is in the electrical components of the
building.
3.2 Maintenance and Treatment Work
There are four aspects that need to be considered and
become the requirements for the success of
maintenance and treatment of building buildings,
namely the safety of buildings, the health of
buildings, the comfort of buildings, ease of building
(Direktorat Jenderal Cipta Karya, 2008).
3.2.1 Maintenance Work
Maintenance of building is an activity to maintain
the reliability of buildings and infrastructure and
facilities so that buildings are always functional.
Maintenance work includes several activities such as
cleaning, tidying, inspecting, testing, repairing, and
replacing building materials or equipment
(Direktorat Jenderal Cipta Karya, 2008).
3.2.2 Treatment Work
Treatment of building is an activity to repair and / or
replace parts of a building, components, building
materials, and / or infrastructure and facilities so that
the building remains functionally feasible.
Treatment work includes repairing and / or replacing
building materials, components, building materials,
ICIB 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World
166

and / or infrastructure and facilities based on the
technical plan for maintenance of buildings. There
are three types of building maintenance work,
rehabilitation, renovation and restoration.
Building damage is the non-functioning of
buildings or building components due to shrinkage /
expiration of the age of the building, or due to
human behavior or natural behavior such as
excessive functional load, fire, earthquake, or other
similar causes. Based on the intensity of the damage,
damage to buildings can be divided into three levels,
minor damage, medium damage, and high damage
.Minor damage is damage mainly to non-structural
components, such as roof cover, ceiling, floor
coverings and fills walls. The maximum
maintenance cost is 35% of the highest unit price of
the new building construction that applies, for
buildings with the same class. Medium damage is
damage to some non-structural components, and or
structural components such as roof structures, floors.
The maximum maintenance cost is 45% of the
highest unit price of the new building construction
that applies, for buildings with the same class.
Heavy damage is damage to most building
components, both structural and non-structural,
which, after a repair, can still function properly. The
maximum maintenance cost is 65% of the highest
unit price of the new building construction that
applies, for buildings with the same class (Direktorat
Jenderal Cipta Karya, 2008).
3.2.3 Electrical Maintenance and Treatment
Work
Regarding the Guidelines for maintenance and
treatment of buildings, it is explained about the
scope of building maintenance for electrical
components as follows (Direktorat Jenderal Cipta
Karya, 2008):
Conduct periodic checks and maintain backup
power plants.
Conduct periodic checks and maintain on
lightning protection equipment.
Conduct periodic checks and maintain electrical
installation systems, both for electric power
supply and for room lighting.
Conduct periodic checks and maintain a network
of sound and communication (telephone)
installation and data.
Conduct periodic checks and maintain a network
of alarm systems and alarms.
3.3 Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
The WBS is a structured decomposition of the entire
scope of work that must be done by the project team
to achieve project objectives and complete the
required results. The main benefit of the WBS
process is to provide a framework for what needs to
be done or done (Project Management Institute,
2013).
3.3.1 Power Source System
An electricity source system is an electrical system
that produces, processes or temporarily stores
electrical energy, and its protection so that it can be
used by electrical equipment. Some of the
components included in this system are a
transformer, uninterruptible power supply, backup
power source, and renewable power source.
3.3.2 Distribution System
This system functions to channel electrical energy so
that it can be used by the electric load. The
distribution system consists of several components,
namely medium voltage panels and low voltage
distribution panels.
3.3.3 Electric Load
The components included in this work package are
equipment that consumes electrical energy for the
operation of the building and its accessories. The
electrical load components are load panel panels,
cabling, lighting control systems, lightning rod
systems, artificial lighting systems, land systems,
sockets and switches, and under floor duct.
3.3.4 Electronic System
The system included in this component is equipment
installed in buildings whose parts consist of
electronic components such as CCTV systems, fire
alarm systems and detectors, computer and internet
network systems, signal amplifier systems, sound
systems, and telephones.
3.4 Alternative Design/Method
The method chosen or used in each component and /
or work package depends on the requirements of the
building. In this study will consider the requirements
of the Ministry Regulation of PUPR No. 24 of 2008,
Ministry Regulation of PUPR no. 45 of 2007, DKI
Development of Implementation Guidelines for Maintenance and Treatment Work of Electrical Components in University of Indonesia
Buildings and Area based on Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
167
Governor Regulation no. 38 of 2012. Alternative
designs are chosen based on literature studies.
3.5 Activities
Forms of activities related to systems and electrical
equipment that are in a building, in principle, are
divided by phase. The phase is divided into
development phases with maintenance and treatment
phases. In the development phase there are two main
activities, namely design, installation and testing. In
design activities, electronic equipment is determined
by specifications and performance. The installation
aims to install equipment and systems in accordance
with their specifications while testing functions to
ensure that the system and equipment work in
accordance with the desired performance. While in
the maintenance and treatment phase there are
activities of inspection, service, replacement of
parts, and testing.
3.6 Resources
Every maintenance and treatment work requires
resources to complete its objectives. The resources
needed can be grouped into human resources, tool
resources, and material resources. Each resource
must be fulfilled both in terms of quantity and
quality.
4 METHODOLOGY
To answer questions in research and determine the
method used, it is recommended to use a strategy
(Yin, 2013). According to the form, there are several
kinds of instruments that can be used in general
research, namely Questionnaire / Questionnaire,
Interview, Observation, Documentation, Test
(Arikunto, 2000).To achieve the research objectives,
a qualitative method was used with inputs consisting
of primary data there are ministerial regulations,
Explanation of General Requirements for Electrical
Installation document, SNI, and previous research.
As for secondary data, researchers used
questionnaire instruments, expert judgment, and
interviews. Validity test is a step of testing carried
out on the content or content of an instrument
(Sugiyono, 2006). Validity is divided into three,
namely content validity, construct validity, and
criterion-related validity (Kerlinger, 1973).
Data analysis is the most important part of the
scientific method, because data analysis is used to
solve research problems (Basrowi & Suwandi,
2012). After that the data is analyzed, processed and
validated again by experts using the Delphi method.
The delphi method is a systematic method of
gathering opinions from a group of experts through a
series of questionnaires, where there is a feedback
mechanism through a round of questions held while
maintaining the anonymity of respondents' responses
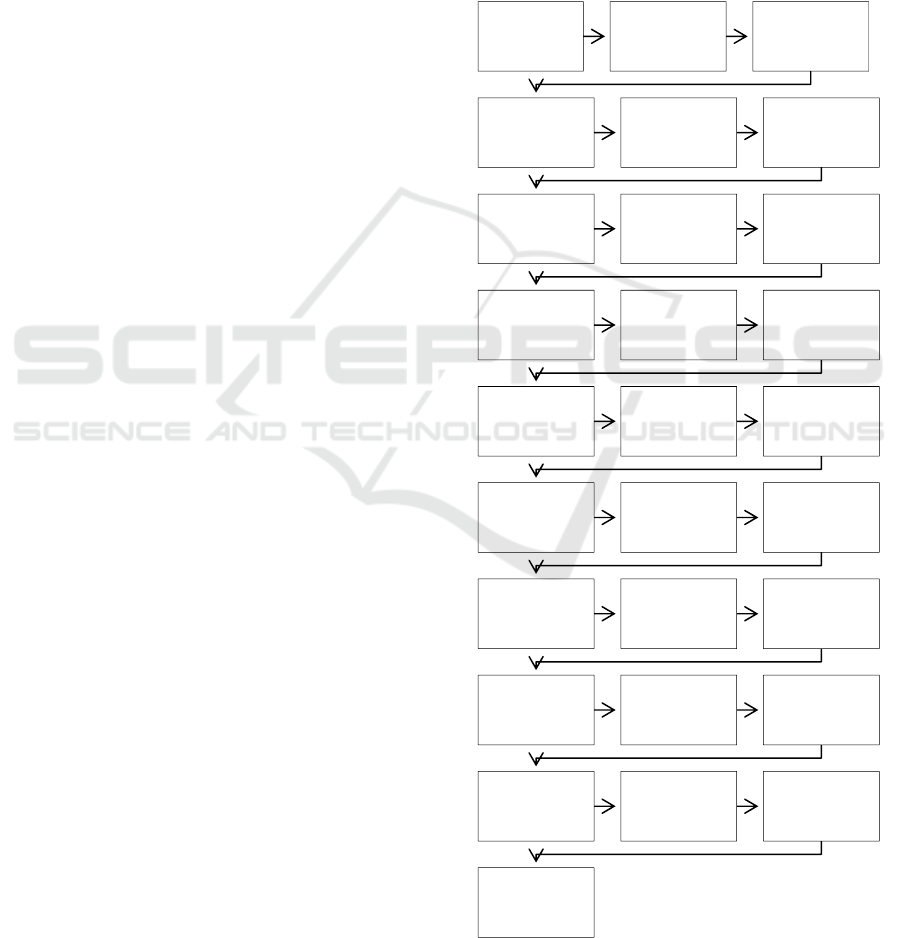
(Foley, 1972). There are 10 steps to the theory of the
Delphi method (Hills & Fowles, 1975). The
following figure is a flow diagram that shows the
stages of how this research will be carried out:
Figure 1: Research Process.
Start
Problems
identification
Research
questions
Literature Study
Research
methodology
identification
Research
variables
identification
Archive Analysis
Expert Validation
1
(Interview &
Questionnaire)
Data Analysis 1
(Descriptive
Analysis)
Forms, types, and
work packages of
WBS
Literature study
and archive
analysis
Expert Validation
2
(Interview &
Questionnaire)
Data Analysis 2
(Descriptive
Analysis)
Alternatives
Design
Literature study
and archive
analysis
Expert Validation
3
(Interview &
Questionnaire)
Data Analysis 3
(Descriptive
Analysis)
Resources and
implementation
requirements
Literature study
and archive
analysis
Expert Validation
4
(Interview &
Questionnaire)
Data Analysis 4
(Descriptive
Analysis)
Material
spesifications
Literature study
and archive
analysis
Expert Validation
5
(Interview &
Questionnaire)
Data Analysis 5
(Descriptive
Analysis)
Implementation
guidlines of
maintenance and
treatment work
Conclusion
End
ICIB 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World
168
5 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
5.1 Level 1 to 4 WBS
To get the results in the first phase, the researcher
used SNI 0225:2011, Ministry Regulation of PUPR
no.24 of 2008, electrical WBS, and literature study
for inputs. Then for the analysis, I used the delphi
method to collect opinions from several experts
using questionnaires. After expert validation, Work
Breakdown Structure in table 1 is detailed every
work package concerning the work and maintenance
of electrical components in dungung and regional
buildings at the University of Indonesia. The
difference in WBS between office buildings and
University of Indonesia buildings is in the electricity
sources that are power house consisting of three
work packages. There are liquid transformers,
LVMDB, and medium voltage chambers.
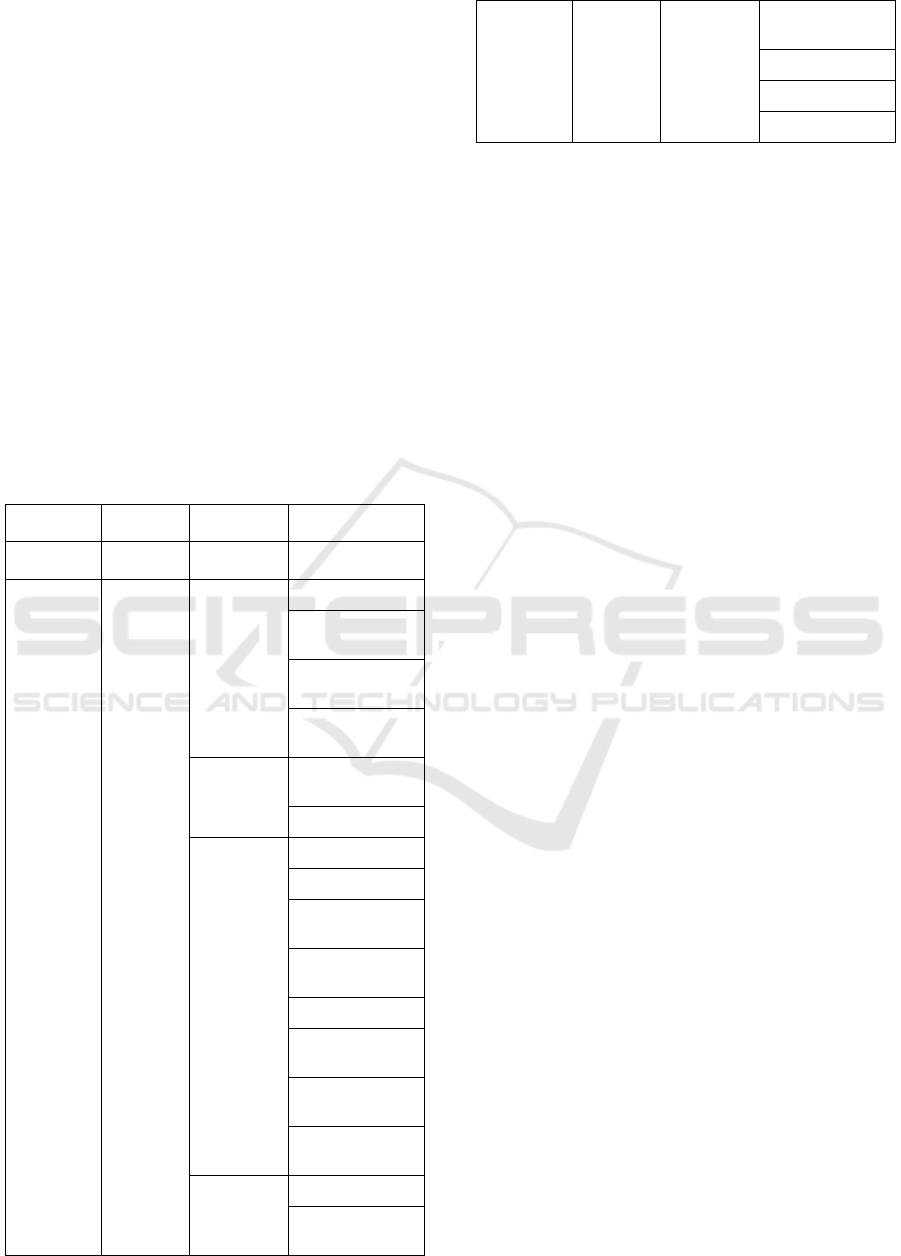
Table 1: Work Breakdown Structure Level 1-4.
Project Name Work
Section
Work Type Work Package
Level 1 WBS Level 2
WBS
Level 3 WBS Level 4 WBS
Maintenance
and
Treatment
Work of
University of
Indonesia
Buildings and
Area
Electrical
Electrical
Sources
Power house
Backup Power
Generator
Renewable Power
Uniterruptable
Power Supply
Distribution
System
LVMDB Panel
MV Panel
Electrical
Load
Load Panel
Cable
Lightning Control
System
Lightning
Protection
Lightning
Grounding System
Receptacle and
Switch
Under Floor Duct
Electronics
CCTV System
Fire Alarm and
Detector
Internet and
Computer
Signal Repeater
Sound System
Telephone
From table 1, there are 4 components at WBS
level 3 and 19 components on WBS level 4.
Furthermore the work package will be more detailed
in alternative designs / methods and activities. The
implementation of the work package can be a
control account. Control accounts are a control point
for management where scope, budget, and schedule
are compared with earned values for performance
measurement.
5.2 Alternatives Design/Method and
Level 5 WBS
To get the results in the second phase, the researcher
used Ministry Regulation of PUPR no.24 of 2008,
electrical WBS, and literature study for inputs. Then
for the analysis, I used the delphi method to collect
opinions from several experts using questionnaires.
The list of alternative design / method in table 2
covers all the scope of the work package in electrical
work. Then each alternative design / method is
implemented into more specific activities which
consist of inspection, maintenance, treatment, and
testing.
Inspection is cover surveillence and monitoring
the device to find a defect or anomaly during normal
operation. Maintenance work includes several
activities such as cleaning, tidying, inspecting,
testing, repairing, and replacing building materials
or equipment. While the treatment is an activity
building treatment and / or replace parts of
buildings, components, construction materials, and /
or infrastructure and facilities in order to remain
eligible buildings function. Testing is a process that
aims to ascertain whether all devices functions work
properly and look for errors that might occur in the
system.
From table 2, there are 41 components in
alternative designs/methods and 61 components in
activities. Furthermore, alternative designs/methods
will be more detailed in the resources. The
implementation of alternative designs/methods is a
method used to select alternative types of use of
work functions such as transformers, diesel
generators, and solar panels.
Development of Implementation Guidelines for Maintenance and Treatment Work of Electrical Components in University of Indonesia
Buildings and Area based on Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
169
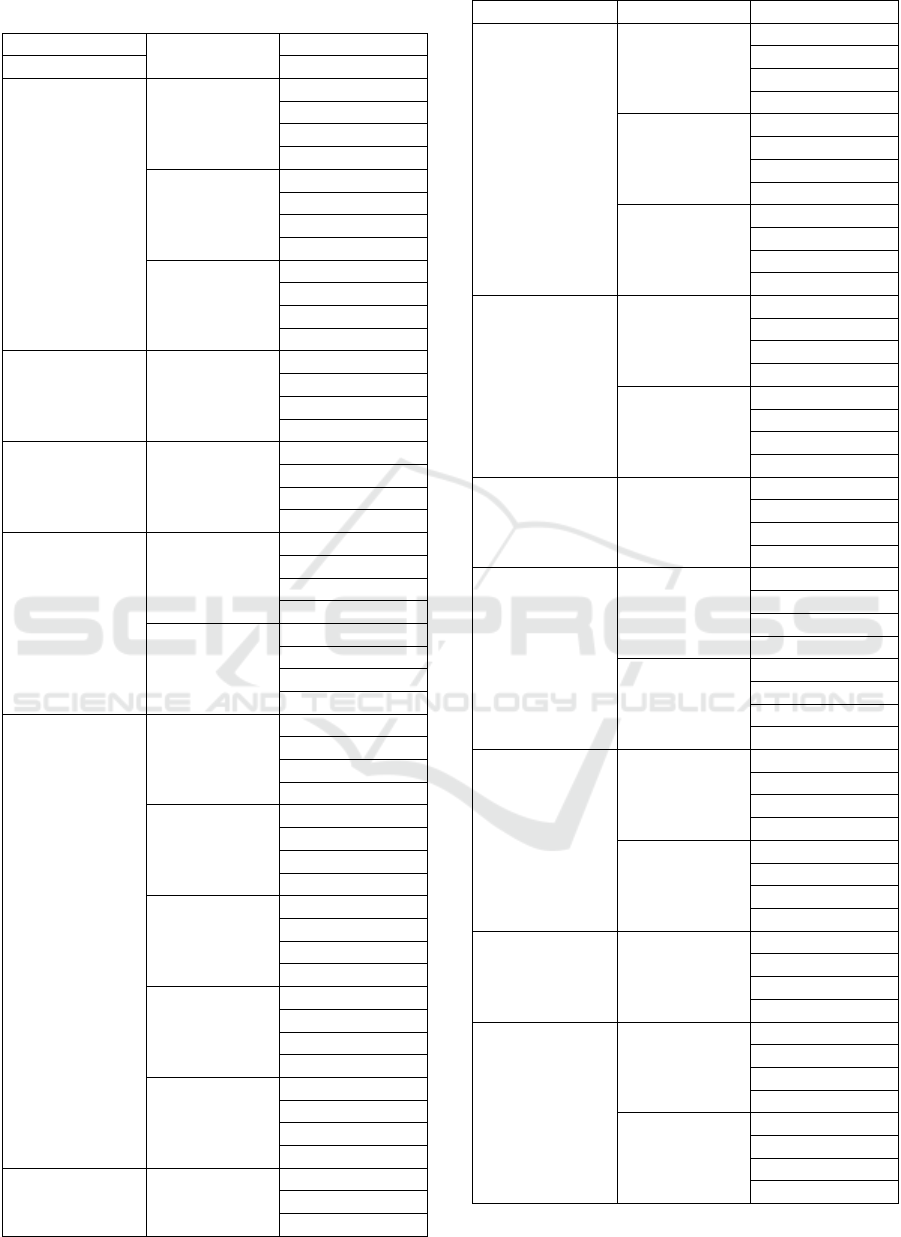
Table 2: Alternatives Design / Method.
Work Package
Alternative Design /
Method
Activity
WBS Level 4 WBS Level 5
Power House
MV Cubicle
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
LVMDB
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Transformer
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Backup Power Generator Diesel Generator
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Renewable Energy Solar Panel
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Uniterruptable Power
Supply
UPS Central
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
UPS Lokal
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
LVMDB Panel
LVMDB
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Sub Distribution Panel
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Connecting Board
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Mini Circuit Breaker
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Molded Case Circuit
Breaker
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
MV Panel
Vaccum Circuit
Breaker
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Load Panel
AC Panel
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Lighting Panel
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Utility Panel
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Cable
Medium Voltage
Cable
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Low Voltage Cable
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Lightning Control
System
Time Sensor
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Lightning Protection
Lightning Rod -
Tight Wire
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Lightning Rod -
Meshed Cage
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Lightning
LED Lamp
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Fluorescent Lamp
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Grounding System Solid Grounding
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Receptacle and Switch
Switch
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Receptacle
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
ICIB 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World
170
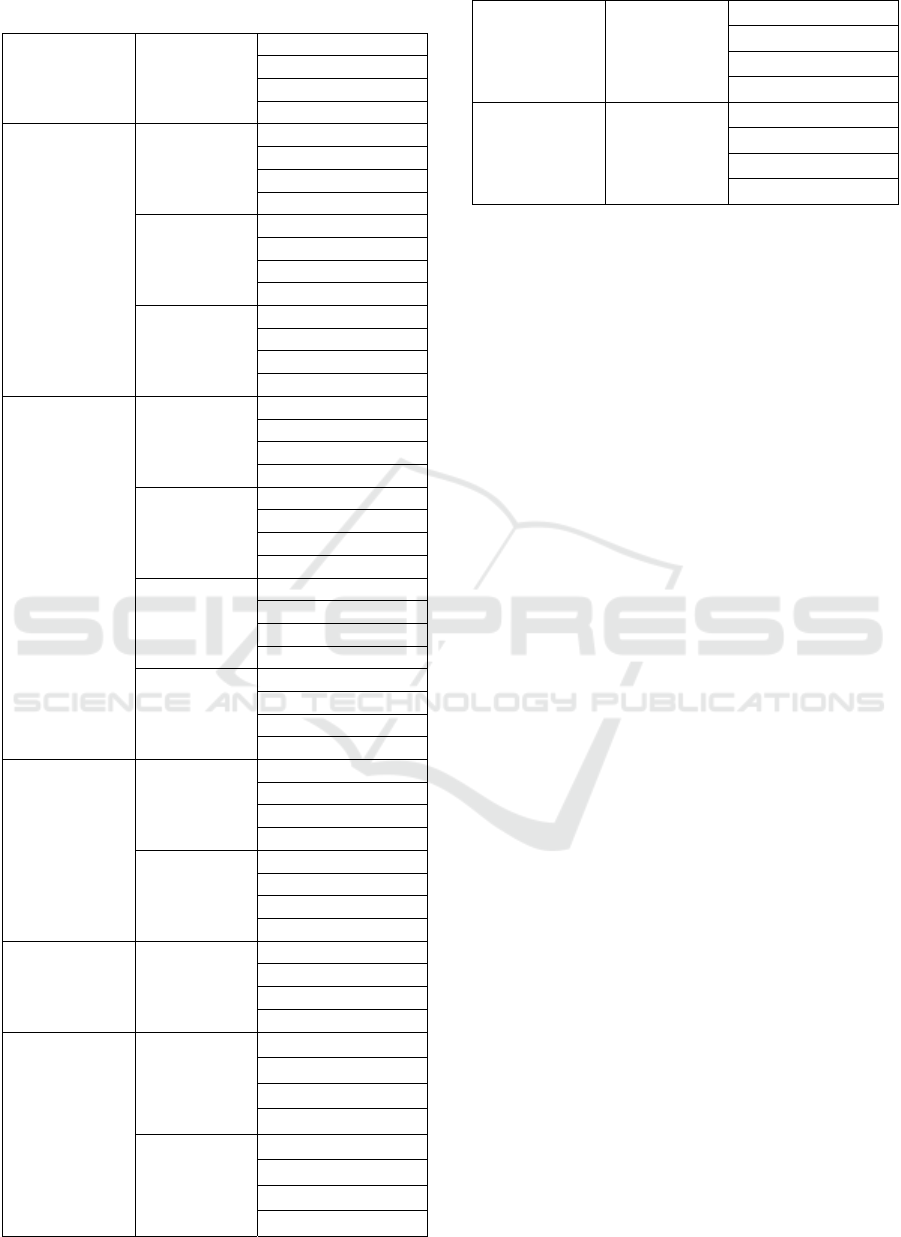
Table 2: Alternatives Design / Method. (cont.)
Under Floor Duct Under Floor Duct
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
CCTV System
DVR
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
CCTV Camera
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Recorder
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Fire and Alarme
Detector
Smoke Detector
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Heat Detector
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Fire Panel
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Fire Alarm
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Internet and Computer
Ethernet Server
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Wifi
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Signal Repeater
Telephone Signal
Repeater
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Sound System
Mic
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Speaker
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Tape Recorder
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
Telephone PABX
Inspection
Maintenance
Treatment
Testing
While the implementation of activities is to
identify and document specific actions that will be
carried out to produce a deliverable project. The
main benefit of this process is the decomposition of
work packages into activity schedules that provide
the basis for estimating, scheduling, implementing,
monitoring and controlling project work. This
process is carried out throughout the project.
5.3 Level 6 WBS
To get the results in the third phasethe, the
researcher used Ministry Regulation of PUPR no.24
of 2008, PUIL documents about Electrical
Instalation, and Standard for Maintenance Testing
Spesification for inputs. Then for the analysis, I used
the the delphi method to collect opinions from
several experts using questionnaires. Every
maintenance and treatment activity requires
resources to complete its objectives. Resources
consist of materials, equipment, and men. In this
case, the researcher took the example of the work
package and transformer alternative design.
The implementation of good resource planning is
in accordance with the logical needs of the project
that will help achieve project suggestions and
objectives maximally.
5.4 Technical Specification
To get the results in the fourth phase, the researcher
used Ministry Regulation of PUPR no.24 of 2008,
PUIL documents about Electrical Instalation, and
Standard for Maintenance Testing Spesification for
inputs. Then for the analysis, I used the the delphi
method to collect opinions from several experts
using questionnaires. Technical specifications are
needed so that all materials used in maintenance and
treatment work are of equal quality. This makes it
easy for workers to choose the material used.
Technical specifications can also be used as
inspection activities and tested back to initial
performance.
Development of Implementation Guidelines for Maintenance and Treatment Work of Electrical Components in University of Indonesia
Buildings and Area based on Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
171
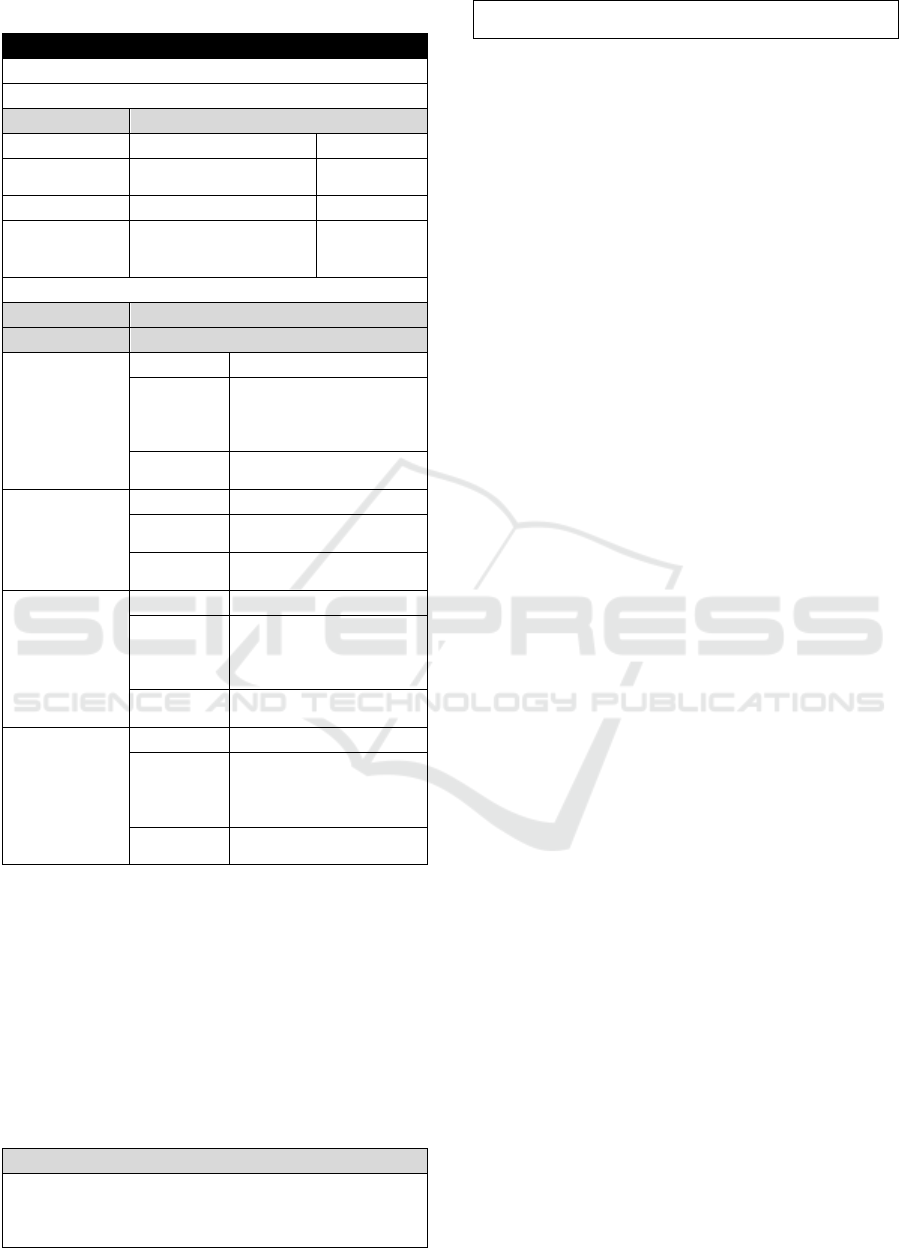
Table 3: Work Breakdown Structure Level 5 & 6.
POWER HOUSE
TRANSFORMER
CODE DESCRIPTION
WBS LEVEL 2 WORK SECTION Electrical
WBS LEVEL 3 WORK TYPE
Electrical
Sources
WBS LEVEL 4 WORK PACKAGE Power House
DESIGN
ALTENATIVES/METH
OD
Transformer
LEVEL 5 WBS LEVEL 6 WBS
ACTIVITIES RESOURCES
Inspection
Materials -
Equipments
Personal protective
equipment, multimeter,
torque wrench, light tools,
temperature gun
Man
Electrical technician,
superviso
r
Maintenance
Materials Patchwork
Equipments
Personal protective
equipmen
t
Man
Electrical technician,
superviso
r
Treatment
Materials Spare parts
Equipments
Personal protective
equipment, multimeter,
torque wrench, special
tools
Man
Electrical technician,
superviso
r
Testing
Materials -
Equipments
Personal protective
equipment, multimeter,
torque wrench, special
tools
Man
Electrical technician,
superviso
r
The implementation of technical specifications is
to ensure the accuracy of measurement results
obtained in accordance with what has been
determined. In addition, the specifications are also
arranged in a complete and clear manner
regarding items, methods or final results of work
that can be purchased, built or developed by other
workers so that it can fulfill the wishes of all
stakeholders involved.
Table 4: Technical Specification.
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION
1. Meets the SNI 0225: 2011 standards or the latest on
"General Requirements for Electrical Installations"
2. Meets the SNI IEC 60076: 2012 standards or most
recently on "Power Transformers"
3. Meets the ISO 14001: 2015 standards or the latest on
"Environmental Management"
5.5 Guideline Development
To get the results in the fifth phase, the researcher
used the previous project name, work section, work
package, work type, alternative design/method,
activity, resources, and technical spesification for
inputs. Then for the analysis, I used the delphi
method to get experts approval using questionnaires.
Then after expert validation on how to develop
guidelines based on the WBS (Work Breakdown
Structure) for maintenance and treatment work of
electrical components in buildings and areas at the
University of Indonesia, there are seven stages in
developing implementation guidelines. Starting from
knowing the project name, work section, work type,
work package, alternative design / method,
resources, and technical specifications.
With the development of WBS-based guidelines,
these guidelines become structured, measurable,
scheduled, and complete as well as to avoid the
failure to fulfill all components of maintenance and
treatment of electrical components because all
building facilities are supported by these
components. The use of electrical components can
be harmful to humans and the environment if not
done carefully so that these electrical components
must be safe and in their use must be in accordance
with the applicable provisions and standards so that
no damage can endanger the user (Suyono, et al.,
2011).
6 CONCLUSION
WBS-based guidelines of maintenance and treatment
electrical work are structured, complete, and can
avoid the mistakes of all work components so it can
make easier for users to easier and better understand
the steps of each process, so the process can be more
effective and efficient.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The Authors would like to thank the financial
support provided by the University of Indonesia
through PIT 9 funding scheme under Grant number
NKB-0087/UN2.R3.1/HKP.05.00/2019 managed by
the Directorate for Research and Public Services
(DRPM) University of Indonesia.
ICIB 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World
172
REFERENCES
Achmada, A., 2013. Manajemen Perawatan dan
Perbaikan Bangunan Gedung Utama Rumah Sakit
Umum Daerah (RSUD). Pekanbaru: Titoti Press.
Arikunto, S., 2000. Manajemen Penelitian Jakarta.
Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Au-Yong, C., 2014. Preventive Maintenance
Characteristics Towards Optimal Maintenance
Performance: A Case Study of Office Buildings. Kuala
Lumpur: University of Malaya.
BPMA, 2007. Penjaminan Mutu Akademik Universitas
Indonesia. Depok: BPMA.
B. & S., 2012. Memahami Penelitian Kualitatif. Jakarta:
Rineka Cipta.
Direktorat Jenderal Cipta Karya, 2008. Peraturan Menteri
Pekerjaan Umum Nomor 24 Tahun 2008 Tentang
Pedoman Pemeliharaan dan Perawatan Bangunan
Gedung. Jakarta: Departemen Pekerjaan Umum.
Foley, R., 1972. Dairy Cattle Principles, Practices,
Problems, Profit.. Philadelphia: LEA & Febiger.
Hills, K. & Fowles, J., 1975. The Methodological Worth
of The Delphi Forecasting Technique Technological.
Technological Forecasting and Social Change, pp.
179-192.
Kerlinger, F., 1973. Foundations of Behavioural
Research. 2nd penyunt. New York: Holt, Rinehart, &
Winston.
Plavina, B. & Geipele, I., 2013. Chances For The
Development of Multiapartment Dwelling Houses'
Policy in Latvia. Latvia, Jelgava, LLU, EF, pp. 43-47.
Prayitno, B., 2018. Kepala Pengelolaan Penghematan
Energi Berkelanjutan Universitas Indonesia
[Wawancara] (4 October 2018).
Project Management Institute, 2013. Project Management
Body of Knowledge. Fifth penyunt. Pennsylvania:
Project Management Institute, Inc..
Republik Indonesia, 2002. Undang - Undang Nomor 28
Tahun 2002 tentang Bangunan Gedung. Jakarta:
Sekretariat Negara.
Son, L. & Yuen, G., 2002. Building Maintenance
Technology. London: Palgrave.
Sugiyono, 2006. Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif, Kualitatif,
dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Suyono; Prasetyo, M.T.; Assafat, L, 2011. Tingkat
Keandalan Utilitas Kelistrikan Bangunan Gedung
Bertingkat di Kota Semarang. Semarang: Media
Elektrika.
Yin, R., 2013. Case Study Research. 4th penyunt. London:
SAGE.
APPENDIX
Indicators for Each Construct:
I
nspection
Get a permit and work permit related to the activities that
will be carried out
Conduct risk studies to find out the dangers that might occu
r
Use personal protective equipment according to the type of
wor
k
Check physical and mechanical conditions
Check anchorage, alignment and grounding
Check the condition of equipment parameters
Check the electrical bolt connection using a low-impeded
ohmeter, torque-wrench and / or conduct a thermographic
survey
Check the operation of the cooling fan
Check the surge arrestor condition
Check the condition of the alarm, function of the dick, trip
from the observer / protection equipmen
t
Record all findings and anomalies as further maintenance
activities
M
aintenance
Get a permit and work permit related to activities that will be
carried out
Conduct risk studies to find out the dangers that might occu
r
Use personal protective equipment according to the type of
wor
k
Secure equipment, turn off equipment or use LOTO
Clean the outside of the transformer (body and floor) from
dus
t
Adjust the temperature and air condition of the transformer
room
Tighten all cable strings on the terminal in the correct and
strong position
Perform calibration of measuring and protection devices
Record all the troubles or anomalies as further treatment
activities
Treatmen
t
Get a permit and work permit related to the activities that
will be carried out
Conduct risk studies to find out the dangers that might occu
r
Use personal protective equipment according to the type of
wor
k
Prepare all parts and materials needed
Secure equipment, turn off equipment or use LOTO
Replace parts (electrical, mechanical, measuring, and
protective equipment) that are damaged, obsolete or expired
Conduct testing activities to ensure that the installed parts
have the desired performance
Testing
Get a permit and work permit related to the activities that
will be carried out
Conduct risk studies
t
o find out the dangers that might occu
r
Use personal protective equipment according to the type of
wor
k
Measure resistance through the condition of a low-impeded
ohmeter bolt
Test coil insulation to coils and coils to groun
d
Get a permit and work permit related to the activities that
will be carried out
Conduct risk studies to find out the dangers that might occu
r
Use personal protective equipment according to the type of
wor
k
Perform turn-ratio tests at each tap position
Exitation-current test on each phase
Test the surge arresters
Record all test results and plan maintenance and
maintenance activities if there are inappropriate results.
Development of Implementation Guidelines for Maintenance and Treatment Work of Electrical Components in University of Indonesia
Buildings and Area based on Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
173
