
Merger & Acquisition: A Comparative Integration Analysis of Third
World Country
Zaib Maroof and Muhammad Jawad
Department of Leadership & Management Studies, National Defence University Islamabad, Pakistan
Lahore Business School, University of Lahore Islamabad, Pakistan
muhammad.jawad@lbs.uol.edu.pk
Keywords: Merger & Acquisition, Horizontal Mergers, Vertical & Conglomerate Mergers, Financial Analysis.
Abstract: After globalization, an upsurge in Merger & Acquisition (M&A) activities has been observed all over the
globe especially in last decade, as same contributed towards the economic wellbeing of any country.
Companies adopted different Integration Strategies (Vertical, Horizontal & Conglomerate) to undergo the
merger deals and accordingly their post merger financial performance analysis was documented for future
reference. On the contrary, comparatively inadequate evidence is accessible to appreciate the outcome of
this activity in Pakistan, which cannot be taken as reference for future M&A deals. Therefore, the present
research investigate in a decent way the impact of various M&A Integration Strategies on the financial
performance of the merged firms in Pakistan, with an aim to identify the best suited M&A Integration
Strategy in own environment. Available data from pre and post merger financial Statements of 36 merger
events categorized broadly into three Integration Strategies (year 2000 to 2010) had been examined using
paired sample T-test for difference of means of ratio categorized on four basis i.e. Liquidity Ratio,
Profitability Ratio, Operating Expense Ratio & Financial Leverage Ratio. Plausible recommendations were
solicited for the benefit of the investors, financial analysts, advisory firms and investment banks.
1 INTRODUCTION
The advancement in the field of information
technology has transformed the business markets
and have increased competition to manifolds
Companies have expanded their operation across the
international boundaries and in order to achieve
growth and expansion of products and services,
businesses use diverse strategies depending on their
business environment and the degree of competition
prevailing in the markets. Literature narrated that in
order to meet competition different integration
strategies are used by firms all across the globe.
David (2000) discussed in his book “Strategic
Management concepts and cases” that different
Integration strategies were adopted by firms at
domestic and International level according to the
circumstances. Among all the integration strategies
the most widely used included vertical integration
strategies, diversification strategies and defensive
strategies however, the type and mean of adopting
and implementing a strategy depends on the
circumstances faced by the firms (David, 2000).
Literature infers that firms used different means for
growth and expansion of the businesses which
mainly included collaboration with the competitors,
joint ventures, Merger & Acquisition (M&A) and
Outsourcing, strategic alliances and internal
development etc. (Santos et al., 2011).
Literature evidenced that among all the means to
achieve expansion M&A activity is the most widely
used across the globe and has witnessed an upward
trend especially in developed countries due to their
contributing role in bringing structural economic
changes in any country (Santos et al., 2011).The
growth of M&A activity had made it an area of
interest for large group of investors which can be
witnessed with the approximate financial statistics of
M&A activities in USA, which is equal to US $ 2.1
trillion in the last one decade (Bashir et al., 201l).
Estimates have also showed that more than 1500
M&A cases have been reported in the USA markets
in last decade (Hoang et al., 2007). Researchers have
verified that generally the objective of the M&A
activity is to expand the customer base, risk
minimization, increased possession of distribution
78
Maroof, Z. and Jawad, M.
Merger Acquisition: A Comparative Integration Analysis of Third World Country.
DOI: 10.5220/0007761000780085
In International Conference on Finance, Economics, Management and IT Business (FEMIB 2019), pages 78-85
ISBN: 978-989-758-370-4
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

channels and to acquire the assets of the target
company which is sometime impossible to acquire
through other alternative strategy (Zappa, 2008).
Bashir et al., (201l) further argued that integration
of firms through M&A activity is backed by
different motives, of which the two most prominent
are value maximization and non value maximization.
M&A activity implied that on the basis of the
Integration Strategies there are three types of
mergers namely vertical mergers, Conglomerate
mergers (diversification) and horizontal mergers
(Robert et al., 2012). Vertical mergers have further
been categorized into two more types forward
(combination with distributors) and backward
integration (combination with supplier). However,
Horizontal mergers include incorporation of
organizations involved in similar business and
conglomerate mergers include incorporation of
organizations involved in dissimilar business
(Robert et al., 2012).
Studies have investigated the M&A activity from
different perspective including strategic, financial,
accounting, marketing and management. Despite this
fact that M&A activity has increased considerably
across the globe very little evidence have been found
about the M&A activity in Pakistan. Numerous
studies have been conducted across the globe that
investigated the post merger financial performance
and the impact of merger deals on the share holder’s
wealth patterns. Despite this fact, in Pakistan almost
negligible researches have been reported in this area
and a very few studies have been found on the
subject under study (Bashir et al., 201l). Apropos in
view, a need is identified to carry out an in-depth
comprehensive analysis of the impact of M&A on
the financial performance of the merged firms in
Pakistan with an aim to analyze the pre merger &
post merger financial statements of all the merged
firms in all sector from time period 2000 to 2010
and then identify whether mergers in Pakistan are
contributing significantly to financial growth of the
companies or not. This study adopted a different
methodology to investigate the issue. The review of
the literature has evidenced that not a single study
has been conducted in Pakistan that investigate the
financial performance of the merged companies
from the strategic perspective. All the companies
that merged during time period 2000 to 2010
adopted certain integration strategy for merging with
the target company. Some of the companies merge
through vertical integration, some adopt horizontal
integration strategy and some merged through
conglomerate integration strategy. The current study
investigates this issue and analyzed 3 to 5 yrs
premerger and post merger financial performance of
the companies merged through vertical, horizontal
and conglomerate integration strategies separately,
with an aim to examine and compare the financial
performance of different types of merger deals held
in Pakistan and suggesting the way forward to the
advisory firms and investment banks.
1.1 Study Objectives
Does adopting Horizontal, Vertical and
Conglomerate integration strategies have any
effect on the financial performance of merged
companies in Pakistan or not?
Does financial performance of the Horizontally,
Vertically and Conglomerate merged enhanced
in Pakistan from the time period 2000 to 2010
as per 3 to 5 yrs premerger and post merger
financial data or not?
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Fan and Goyal (2002) revealed that vertical mergers
contributes positively towards the wealth creation of
the merged companies and significantly impact the
performance of the company. Coontz (2004)
discovered significant role of mergers in reducing
systematic risk of the companies while horizontal
and conglomerate mergers does not. Chang and
Thomas (1989) concluded that risk and return of the
merged firms is more closely associated with the
structural factors related to markets and business
than with the diversification strategy used for the
mergers. Hitt et al., (1990) revealed that Merger and
Acquisition activity is positively related to the
managerial commitment and innovation. Sinha et al.,
(2010) investigated the impact of merger and
acquisition on the financial efficiency of the
financial institutions in India and showed that M&A
activity significantly improved the financial
performance of financial institutions in India (Sinha
et al., 2010). Selcuk and Kiymaz (2013)
demonstrated that the returns of the acquiring firms
decreased as a result of the merger and further the
smaller firms reported more abnormal returns as
compared to the larger firms. Ramswamy (1997)
concluded that the banks merged through horizontal
integration strategy showed an improved financial
performance after the merger as compared to those
merging with the strategically dissimilar banks.
Studies further measured the impact of strategic
similarities between the bidder and the target firms
Merger Acquisition: A Comparative Integration Analysis of Third World Country
79

on the financial performance of the merged banks in
European Union. The results revealed that the
financial performance of the merged banks has
improved as a result of the Merger and Acquisition
activity (Altunba and Ibanez, 2004). Coontz (2004);
Kashiramka and Rao (2013); Natarajan and
Kalaichelvan (2011) explored the shareholders
wealth effects of mergers & acquisitions and
reported the gains of shareholder of the target as
well as acquirer firms irrespective of the deal
announcement period. Liargovas and Repousis
(2011) further examined the impact of the merger
and acquisition on the performance of the Greek
Banking Sector. Event study methodology was used
to analyze the data and overall results indicated that
Mergers and acquisitions held in Greek banking
sector have no impact on their financial performance
and also do not create shareholders wealth
(Liargovas and Repousis, 2011).
Bashir et al., (2007) investigated the performance
record of forty five Mergers and acquisitions (M&A)
that took place during 2004 to 2010 in various
sectors of Pakistan and proved that the M&A
activity has no influence on the wealth
maximization of the merged companies in Pakistan,
contradictory to the literature and finding of the
global researches. Kemal (2011) further analyzed the
four years financial statements (2006-2009) of the
Royal Bank of Scotland (RBS) to measure its Post-
Merger Profitability. The results revealed that the
profitability, cash flows, liquidity, leverage and
assets management of the RBS has been relatively
reasonable previous to the merger agreement but
after the merger the financial performance of RBS
decreased so the deal failed to improve the
profitability of RBS. Arshad (2012) analyzed the
post merger performance of Standard Chartered
bank Pakistan. Results revealed that the financial
performance of the Standard Charter bank also
decreased after the merger. Usman et al., (2008)
investigated the Operating and financial
Performance of Merged Companies in Textile Sector
of Pakistan from time period 2001 to 2005. The
results revealed that the post merger operating
performance of the firms in textile sectors also
decreased as compared to the pre merger financial
performance. Afza and Yusuf (2011) examined the
impact of mergers on efficiency of conventional
banks in Pakistan. The results revealed that the
mergers held in banking sector reported
improvement in the cost efficiency of in Pakistan
from 93.83% to 94.15%. Kouser and Saba (2011)
examined the impact of M&A activity on the
profitability of the merged banks in Pakistan. The
six financial ratios i.e. profitability ratio, return to
net worth ratio, invested capital ratio and debt to
equity ratio were analyzed using paired sample t-test
and the findings evidenced decreased financial
performance of commercial banks after the mergers
(Kouser and Saba, 2011).
Ramaswamy (1997) investigated efficiency gains
from Banks in Pakistan. Findings revealed that
efficiency effect is marginal and pre merger
efficiency of acquirer didn’t contribute anything in
efficiency gains (Ramaswamy, 1997). Usman et al.,
(2010) investigated the impact of Scale Efficiency in
Banking Sector of Pakistan. For analytical purpose
banks were divided into three categories: domestic
private banks, state owned Banks, and foreign
owned banks. Foreign owned banks reported more
efficiency, followed by state owned banks and
domestic private banks (Usman et al., 2010).
Kayani et al.,(2013) examined the impact of merger
and acquisition on operating performance and
shareholder wealth in Pakistan banking sector and
showed that the operating performance &
shareholder wealth of the banks decreased after the
merger (Kayani et al., 2013).Hence, from the
extensive review of the literature we can conclude
that the researchers across the globe have studied the
M&A activity from different perspectives and
investigated the diversified issues encountered by
the merged firms concerning the HR, Marketing and
finance. Some studies investigated the
organizational differences among the acquired and
target firms and further investigated the cross
country determinants, HR Practices and
organizational structure of merged firms around the
globe. Researchers also examined the impact of
Merger and Acquisition on the post merger financial
performance, Share holder wealth maximization,
Operating financial performance and profitability of
the merged firms in different countries by adopting
different methodologies i.e. event study
methodology, financial ratio analysis technique etc.
Apropos in view, no study have been found in the
literature that investigates the impact of mergers and
acquisition on the financial output of all the merged
companies in Pakistan from the time span 2000 to
2010. The contribution of the current research is that
it investigates the influence of different integration
strategies (Vertical, Horizontal & Conglomerate)
upon financial output of the merged companies. It
distinguish the Merger deals held from 2000 to 2010
on the basis of Integration strategies (Vertical,
Horizontal & Conglomerate) and then evaluates
financial output through financial ratio system by
using their yearly financial declaration with an idea
FEMIB 2019 - International Conference on Finance, Economics, Management and IT Business
80
to categorize that whether implementing diverse
integration strategies have some influence on the
financial output of the merged companies or not.
Further it also categorize and advocate the best
integration strategy to Investors, MNCs, advisory
firms and Investment Banks for the future merger
deals in Pakistan.
2.1 Horizontal/ Vertical/ Conglomerate
Mergers
There is a significant difference between the Pre-
Merger and Post-Merger means of
H1:H8:H15 Current Ratio of Horizontal,
Vertical and Conglomerate Mergers.
H2:H9:H16 Sales Growth Ratio of Horizontal,
Vertical and Conglomerate Mergers.
H
3
:H
10
:H17
NPM of Horizontal, Vertical and
Conglomerate Mergers.
H4:H11:H18 ROE of Horizontal, Vertical and
Conglomerate Mergers
H5:H12:H19 Interest coverage Ratio of
Horizontal, Vertical and
Conglomerate Mergers
H6:H13:H20 Operating Expense Ratio of
Horizontal, Vertical and
Conglomerate Mergers
H7:H14:H21 Debt to Equity Ratio of Horizontal,
Vertical and Conglomerate Mergers
U
1
≠U
2
H
0
: There is no significant difference between the
Pre Merger and Post Merger means Current
Ratio, Sales Growth Ratio, NPM, ROE,
Interest Coverage Ratio, Operating Expense
Ratio and Debt to Equity Ratio Horizontal,
Vertical and Conglomerate Mergers
U1=U2
3 METHODOLOGY: STUDY
VARIABLES
Liquidity situation of the company is calculated
through Current ratio, Profitability of the firms is
calculated through Net Profit Margin & Return on
Equity, Operating expense ratio is used to measure
Operating efficiency of the company and Debt to
equity & Interest coverage ratio is used to measure
financial Leverage of the firms.
3.1 Population/Sample Size
For the purpose of current study initially 60 Merger
events were observed from the time period 2000 to
2010 based on three Integration Strategies i.e.
Horizontal, Vertical and Conglomerate mergers.
However 24 merger deals were excluded later on the
basis of non accessibility of the financial statistics.
Therefore, final sample comprises of 36 merger
deals which were analyzed separately after
distinguishing them on the basis of three integration
strategy. Almost 17 of the total merger
transactions/deals were integrated through vertical
strategy about 9 were merged through horizontal
strategy and 10 were merged through Conglomerate
strategy.
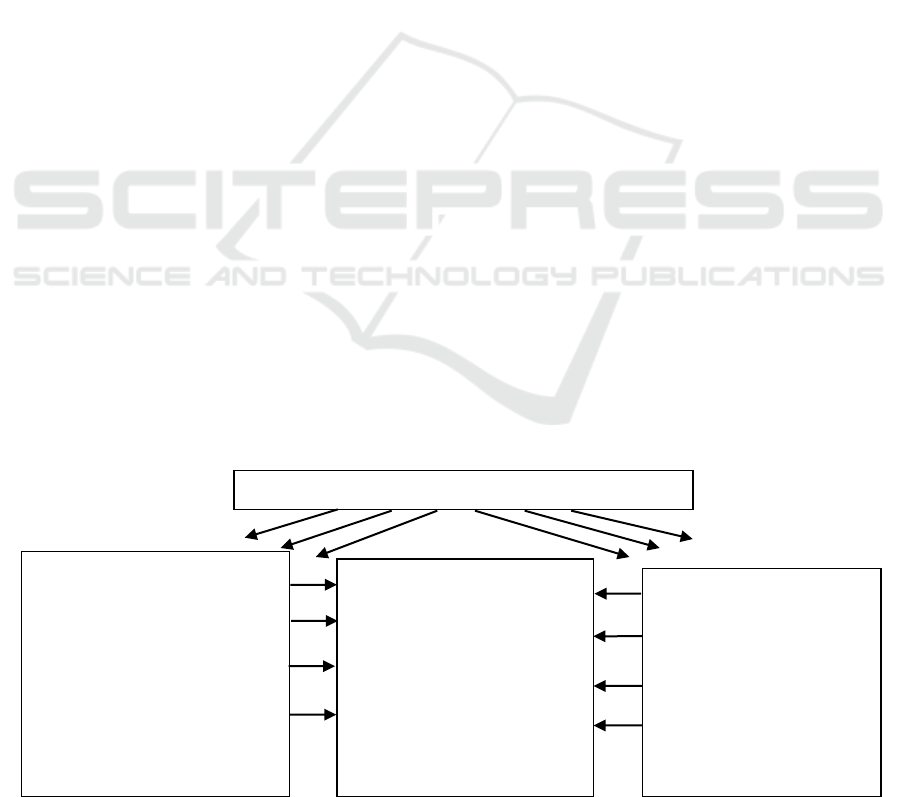
Theoretical Framework of the Study
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of the study.
Merger Types: Horizontal, Vertical and Conglomerate
Pre-Merger
Liquidity ratio
Current Ratio
Profitability Ratio
NPM
ROE/SG
Efficiency Ratio
Operating Expense
Interest Coverage
Leverage Ratio
Debt/Equity Ratio
Difference of Mean-
Application of Paired Sample
T –test
Pre-Merger
Liquidity ratio
Current Ratio
Profitability Ratio
NPM
ROE/SG
Efficiency Ratio
Operating Expense
Interest Coverage
Leverage Ratio
Debt/Equity Ratio
Merger Acquisition: A Comparative Integration Analysis of Third World Country
81
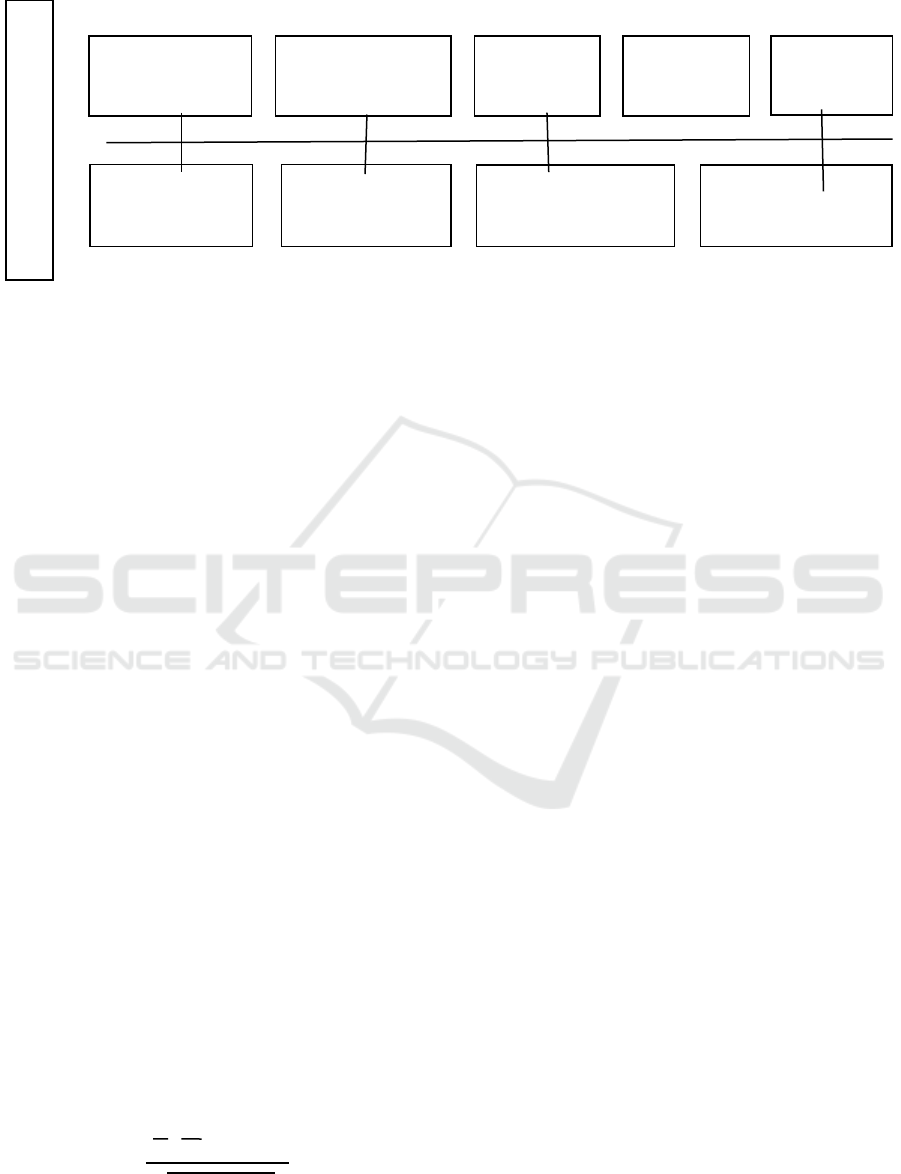
Research Design
Figure 2: Diagrammatic representation of study research design.
3.2 Statistical Analysis
The financial declaration of every merger events are
subsequently evaluated by financial ratio
examination. Entire seven ratios used in the study
included Current Ratio, Sales Growth ratio, Net
profit margin ratio, Return on equity, Operating
expense ratio, Interest coverage ratio and Debt to
equity ratio to measure the Liquidity, Profitability,
Operating Efficiency and financial Leverage of the
merged firms.
3.3 Financial Ratio Examination
A technique employed to examine the current,
previous and predictable financial output of the
companies (Tugas and CPA, 2012). Firstly, for pre-
merger period, each variable i.e. Current Ratio, Sales
Growth Ratio, NPM Ratio, ROE, Operating
efficiency Ratio, Interest coverage Ratio and Debt to
Equity Ratio is calculated for each of the three to
five years (-5,-4-3,-2,-1) independently for mutually
the acquirers’ and the target companies in the
sample. Likewise, the variables under study are then
evaluated for the acquiring companies merely for
three to five years post merger era (+1, +2, +3, +4,
+5). A combined mean for three years pre and
combined mean for three years post-merger period is
then computed. The difference between the mean
output measure of the pre and post-merger years is
then studies. To verify the outcome and significant
differences in the output during the pre and post
merger era Paired sample t-test was used in the
current study.
(x
1
– x
2
) – (µ
1
-µ
2
)
√s
2
1/
n
1 +
s
2
2 /
n
2
Where; X1=Target firm, X2=Acquirer firm,
μ1=Population of Target firm, μ2=Population of
Acquirer firm, S1=variance of target firm,
S2=Variance of acquirer firm, n1=Sample of target
firm, n2=Sample of Acquirer firm.
4 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
o Horizontal Mergers
The findings of horizontal mergers evidenced that
the liquidity position, Sales Growth and profitability
of the horizontally merged firms deteriorated after
the merger while the Operating efficiency increased,
interest coverage Ratio declined and financial
leverage/Risk of the horizontally merged firms
decreased after the mergers.
o Conglomerate Mergers
The comprehensive analysis of the data revealed that
the liquidity position and the sales growth of the
firms merged through conglomerate integration
strategy decreased after the merger while the
profitability in some cases improved and in some
cases deteriorated after the mergers. The findings
further evidence that the operating efficiency
improved after the merger while leverage ratio
remained insignificant during post merger period.
o Vertical Mergers
Comprehensively, we can conclude that the liquidity
position, Sales growth, profitability and Operating
efficiency of the vertically merged firms increased
after the merger while the risk/leverage of the
vertically merged firms decreased during the post
merger period.
Data collection
Secondary
Secondary
Sampling design
Convenient sampling
Time Horizon
Longitudinal
Unit of Analysis
Organization
Purpose of Study
Hypothses testing
Type of investigation
Differentials
Researchers
Interferences
Minimal
Study setting
Non-contrived
Measurement
Financial Ratio
P
R
O
B
L
E
M
S
T
M
E
N
T
FEMIB 2019 - International Conference on Finance, Economics, Management and IT Business
82
5 DISCUSSION
Financial and economic state of Pakistan has
encountered numerous challenges among which the
predominant is to generate prospects for the
investment in Pakistan. Furthermore, from the
literature safely accomplished that M&A is
considered as an important means to enhance the
economic expansion of any country and are
frequently performed with an aim to progress the
financial output of any industry. On the contrary, in
case of Pakistan, same has been proved otherwise.
So the current study investigated the issue in
Pakistan and explores the impact of different
integration strategies (Horizontal, Vertical &
Conglomerate) on the financial output of the merged
companies in Pakistan. The study differentiated the
Merger deals held from 2000 to 2010 on the basis of
Integration strategies (Vertical, Horizontal &
Conglomerate) and then measured their financial
performance through financial ratio technique and
OLS Regression. The results of the financial ratio
analysis demonstrated that vertical integration
strategy is the most effective among the three
Integration strategies adopted by the firms for
conducting merger deals in Pakistan from time
period 2000 to 2010. The findings further revealed
that the firms that adopted vertical integration
strategy for merging reported improvement in
liquidity position, profitability, Operating efficiency
and improved financial leverage during the post
merger period and hence is identified as a most
effective integration strategy among the three under
study.
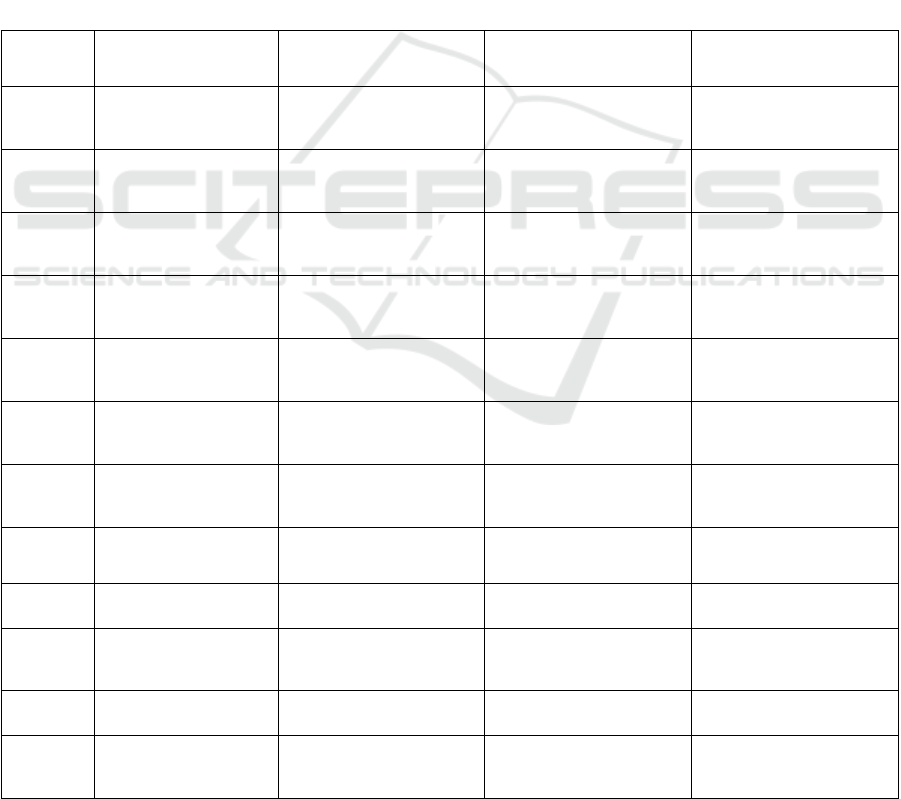
Table 1: Comparative Analysis of Financial Ratio.
Ser no.
Ratio
Horizontal Merger
Vertical Merger
Conglomerate Merger
1
Current Ratio
Deteriorated
(Accepted H1)
Improved
(Accepted H8)
Deteriorated
(Accepted H15)
2
Sales Growth Ratio
Deteriorated
(Accepted H2)
Improved
(Accepted H9)
Deteriorated
(Accepted H16)
3
NPM
Deteriorated
(Accepted H3)
Improved
(Accepted H10)
Improved
(Accepted H17)
4
ROE
Deteriorated
(Accepted H4)
Improved
(Accepted H11)
Deteriorated
(Accepted H18)
5
Operating Expense
Ratio
Deteriorated
(Accepted H5)
Deteriorated
(Accepted H12)
Deteriorated
(Accepted H19)
6
Interest Coverage
Ratio
Deteriorated
(Accepted H6)
Improved
(Accepted H13)
Improved
(Accepted H20)
7
Debt to Equity
Deteriorated
(Accepted H7)
Deteriorated
(Accepted H14)
Insignificant
(Accepted H0)
Ser no.
Ratio
Horizontal Merger
Vertical Merger
Conglomerate Merger
1
Liquidity position
Declined
Improved
Declined
2
Profitability
Declined
Improved
In some cases improved
/Declined /insig
3
Operating Efficiency
Improved
Improved
Improved
4
Financial Leverage
Declined
Declined
Insignificant neither
Improved/ Declined
Note: Comparative analysis of Vertical, Horizontal and Conglomerate Mergers (FY2000-FY2010).
Merger Acquisition: A Comparative Integration Analysis of Third World Country
83

Lastly, the results verified that the adopting different
integration strategies for conducting merger deals
have significant impact on the Liquidity position,
Profitability, Operating Efficiency and Financial
Leverage of the merged firms and suggests that
Vertical Integration strategy is the most favorable
among the three in Pakistani environment and hence
recommends Investors, MNCs, advisory firms, and
Investment Banks to adopt vertical integration
strategy for conducting future merger deals in
Pakistan and suggest the best M&A value chain
strategy to their clients in merger deals. Further the
study recommends that the Planning commission of
Pakistan should formulate a proper mechanism for
selecting a suitable integration strategy after proper
analyzing the previous trends and financial facts in
the industry. Lastly the study wills also assists policy
making organizations in increasing the volume of
merger activity in Pakistan by uprooting the factors
responsible for failure of mergers in Pakistan and
formulating a strategy that can increase the success
ratio of merger activity in term of financial
performance as it can contribute significantly in
improving the economic well of Pakistan.
Moreover, other developing and developed
economies should also consider the importance of
supply chain strategies i.e. Horizontal, Vertical and
Conglomerate strategies before making the merger
deals to maximize the shareholder’s wealth. The
adoption of appropriate strategy of supply chain
would also facilitate economies to expand their
customer base, minimize risk, increase possession of
distribution channels and acquire the assets of the
target company which is sometime impossible to
acquire through other alternative collaborating
strategies like joint venture or franchises etc
REFERENCES
David, F. R., 1999. Strategic Management Concepts Cases
Set. Prentice Hall.
Carvalho Santos, J., Ferreira, M. P., Reis, N. R. and Serra,
F., 2010. Mergers & acquisitions research: a
bibliometric study of top strategy journals, 2000-2009.
Bashir, A., Sajid, M. R. and Sheikh, S., 2011. The impact
of mergers and acquisitions on shareholders wealth:
evidence from Pakistan. Journal of Scientific
Research, 8(1), pp.261-264.
Hoang, T. V. N. and Lapumnuaypon, K., 2008. Critical
success factors in merger & acquisition projects: A
study from the perspectives of advisory firms.
Zappa, M., 2008. The Fundamentals of Strategic Logic
and Integration for Merger and Acquisition Projects.
Management, Economics and Technology, pp.42-61.
Roberts, A., Wallace, W. and Moles, P., 2012. Mergers
and Acquisitions, United Kingdom, Edinburg Business
School. Retrieved on, 10.
Chang, Y. and Thomas, H., 1989. The impact of
diversification strategy on risk‐ return performance.
Strategic Management Journal, 10(3), pp.271-284.
Fan, J. P. and Goyal, V. K., 2006. On the patterns and
wealth effects of vertical mergers. The Journal of
Business, 79(2), pp.877-902.
Hitt, M. A., Hoskisson, R. E. and Ireland, R. D., 1990.
Mergers and acquisitions and managerial commitment
to innovation in M-form firms. Strategic Management
Journal, pp.29-47.
Sinha, N., Kaushik, K. P. and Chaudhary, T., 2010.
Measuring post merger and acquisition performance:
An investigation of select financial sector
organizations in India. International Journal of
Economics and Finance, 2(4), pp.190-200.
Selcuk, E.A. and Kiymaz, H., 2013. The impact of
diversifying acquisitions on shareholders' wealth.
Ramaswamy, K., 1997. The performance impact of
strategic similarity in horizontal mergers: Evidence
from the US banking industry. Academy of
Management Journal, 40(3), pp.697-715.
Coontz, G., 2004. Economic impact of corporate mergers
and acquisitions on acquiring firm shareholder wealth.
The Park Place Economist, 12(1), pp.62-70.
Altunbaş, Y. and Marqués, D., 2008. Mergers and
acquisitions and bank performance in Europe: The role
of strategic similarities. Journal of economics and
business, 60(3), pp.204-222.
Kashiramka, S. and Rao, N.M., 2013. Shareholders wealth
effects of mergers & acquisitions in different deal
activity periods in India. European Journal of
Business and Management, 5(4), pp.116-129.
Natarajan. P. and Kalaichelvan., 2011. Stock Price
Reaction of The Merged Banks-An Event Study
Approach. International Journal of Research in
Commerce & Management, 2(4).
Liargovas, P. and Repousis, S., 2011. The impact of
mergers and acquisitions on the performance of the
Greek banking sector: An event study approach.
International Journal of Economics and Finance, 3(2),
pp.89-100.
Kemal, M. U., 2011. Post-merger profitability: A case of
Royal Bank of Scotland (RBS). International Journal
of Business and Social Science, 2(5), pp.157-162.
Afza, T. and Yusuf, M.U., 2012. The impact of mergers
on efficiency of banks in Pakistan. Elixir International
Journal: Finance Management, 48, pp.9158-9163.
Kouser, R. and Saba, I., 2011. Effects Of business
combination on financial performance: Evidence from
Pakistan's banking sector. Australian Journal of
Business and Management Research, 1(8), p.54.
Usman, A., Khan, M.K., Wajid, A. and Malik, M.I., 2012.
Investigating the operating performance of merged
companies in textile sector of Pakistan. Asian Journal
of Business and Management Sciences, 1(10), pp.11-
16.
FEMIB 2019 - International Conference on Finance, Economics, Management and IT Business
84

Kayani, A. J., Javed, B., Majeed, A. and Shaukat, A.,
2013. Impact of merger and acquisition on operating
performance and shareholder wealth in Pakistan
banking sector. Interdisciplinary Journal of
Contemporary Research In Business, 5(6), pp.385-
391.
Tugas, F. C., 2012. A Comparative Analysis of the
Financial Ratios of Listed Firms Belonging to the
Education Subsector in the Philippines for the Years
2009-2011. International Journal of Business and
Social Science, 3(21).
Merger Acquisition: A Comparative Integration Analysis of Third World Country
85
