
Business Model as a Cloud Services-based Movility Strategy That
Allows to Diminish the Number of PYMES Closures in Ecuador
Cristina Pesántez, Freddy Tapia and Jorge Edison Lascano
Department of Computer Science, Universidad de las Fuerzas Armadas ESPE, Sangolqui, Ecuador
Keywords: Business Model, Small and Medium Enterprises SME, Innovation and SMEs’ Mortality.
Abstract: Nowadays, enterprises face big problems in a global market, especially small and medium-sized enterprises
(PYMES), they are required to innovate the way they offer their products/services, without affecting their
limited financial resources. In consequence they need to find new business opportunities, also cloud services
trend could complement the business models promoted by PYMES, providing them competitive advantages.
Here we propose the development of a business model based on data mobility and ease of access. This model
contributes to reduce PYMES mortality causes, and at the same time to increase their growth projection rates.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the intention of having competitive and
innovative advantages when enterprises offer and
acquire products or services, they are adapting their
traditional business models to a different model that
focuses on the optimization of technological
resources (Sánchez and González, 2017), this model
would simplify timely and adequate decision making,
allowing continuing innovation new business
opportunities discovery (Burgos and Herrera, 2018).
Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMES) in
Latin America are part of the involution, mainly at
internal and external level regulations, and to certain
technical flaws that prevent their development. This
causes that many of them have a very short life time
(Cardoza et al., 2016).
The average life time of a SME is approximately
five years, depending on the structural and political
conditions of a country in terms of financing
resources.
According to data provided by the National
Institute of Statistics and Geography and Informatics
(INEGI) of Mexico, in 2014 a large percentage of
enterprises considered SMEs were developed in low
productivity sectors and value added (Sánchez and
Vargas, 2018).
Small businesses’ mortality rate is presented in
terms of the ease or difficulty of overcoming
obstacles such as: Level of competence, technology,
market knowledge (saturation or not, market
dispersion), production capacity (excess or full),
variety of products, and levels of service (Zaridis and
Mousiolis, 2014)
In Ecuador, SMEs are very important for its
productive sector, specially because of the
employment generation. According to the National
Economic Census of 2010 issued by the National
Institute of Statistics and Census of Ecuador (INEC),
three out of four positions jobs, were generated by
SMEs (Chávez, 2016).
Nowadays, enterprises are in need of having valid
information in real time, receiving analysis results,
notifications, projections, share data, among others;
not only among their executives, but also among
employees from different areas. New trends help
reach these targets of increasing productivity and
facilitating proper decision making, one of these
trends is Cloud Services.
The present research work was guided by the
design science research methodology, which will
display techniques such as: An exploratory and
descriptive study that focuses on the development of
a model that optimizes its scope or business
strategies, then surveys will help discover results and
possible real benefits from implementing this
business model proposal. In section 2, we explain the
research methodology. Section 3 explains the
development of the business model, and section 4
presents conclusions, specifically from the survey
answers.
596
Pesántez, C., Tapia, F. and Lascano, J.
Business Model as a Cloud Services-based Movility Strategy That Allows to Diminish the Number of PYMES Closures in Ecuador.
DOI: 10.5220/0007727305960603
In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2019), pages 596-603
ISBN: 978-989-758-372-8
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
As mentioned before, this study uses the design
science research methodology. It presents the design
process as a fundamental part and defines it by means
of a sequence of logical activities that generate a
product (result): here are the steps revised for our case
study
Knowing the Problem: It is essential to detail and
determine the problem that is going to be
investigated, to establish the causes and guidelines of
possible solutions. This is detailed in the introduction.
Suggestion: Based on a literature review, it identifies
what the main technological trends are. They can be
used to propose a business model or technological
trends according to the case study and place it as the
main strategy within the model.
Development: A business model based on
technological trends extracted in the previous phase
is proposed. It provides support for stakeholders. It
will also be necessary to investigate and identify the
main causes of mortality of SMEs in Ecuador,
hereafter it is possible to develop a business model
that is articulated altogether with the technological
section, allowing to contribute with the reduction of
SMEs mortality in Ecuador.
Evaluation: A case study will be used to verify the
results of the proposed model; surveys are used as
validation techniques.
Conclusions: The contribution provided by the
proposed business model for SMEs in Ecuador will
be detailed and alternatives for technological
solutions will be proposed.
As part of the initial phase of the research project,
the following questions were proposed:
What type of studies do contribute in the selection
of a technological trend as a business strategy?
(¿Qué tipo de estudios aportan en la selección de
una tendencia tecnológica como estrategia de
negocios?)
What are the characteristics of the technological
trends that could be used as a business strategy in
SMEs? (¿Cuáles son las características de las
tendencias tecnológicas que podrían ser usadas
como estrategia de negocios en las PYMES?)
What is the selected technological trend and what
are the characteristics that motivated its selection?
(¿Cuál es la Tendencia Tecnológica seleccionada
y cuáles son las características que motivaron la
selección de la misma?)
Is it possible to leverage a business model with the
selected technological trend? and does that allow
to assist and / or diminish the main causes of
SMEs mortality? (¿Es posible apalancar un
Modelo de Negocios con la Tendencia
Tecnológica seleccionada y que permitan atender
y/o disminuir las causas principales de mortalidad
de las PYMES?
Is it possible to validate the proposed business
model by studying a case? (¿Es posible validar el
Modelo de Negocios propuesto mediante el
estudio de un caso?)
2.1 Literature Review
To continue with the research methodology, the
sustainability or suggestion phase is developed
through a Systematic Literature Mapping (SLM),
following the next activities:
2.1.1 Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Inclusion criteria:
Works from 2012 and beyond.
Books, journals, and articles, that are available
and indexed.
Works related to technology and business models.
Exclusion criteria
Works that are written in languages different than
English or Spanish.
Blogs.
2.1.2 Search Strategy
Within this section, it is necessary to develop other
stages such as: Search for candidate studies,
conformation of the search chain and selection of
primary studies, i.e., the selection of studies that are
going to be used to answer the research questions.
Search for candidate studies: The search for
books, journals and scientific articles published in
databases such as Springer, ACM, IEEE, Science
Direct, and Google Scholar is performed. They must
meet the inclusion and exclusion criteria described
above. To facilitate this search, some terms were used
according to the research questions and the objectives
of this project, finally, we obtained a list of 36
candidate studies. From the search chain and after the
necessary cross validations were executed, 8 studies
were selected. They are listed in table1.
After attaining the primary studies, it is possible
to answer the three research questions determined in
the initial literature review, as follows:
What type of studies do contribute in the selection of
a technological trend as a business strategy?
The selected studies include researches of the
technological situation in different countries, the
same studies that have been analyzed and compared
Business Model as a Cloud Services-based Movility Strategy That Allows to Diminish the Number of PYMES Closures in Ecuador
597
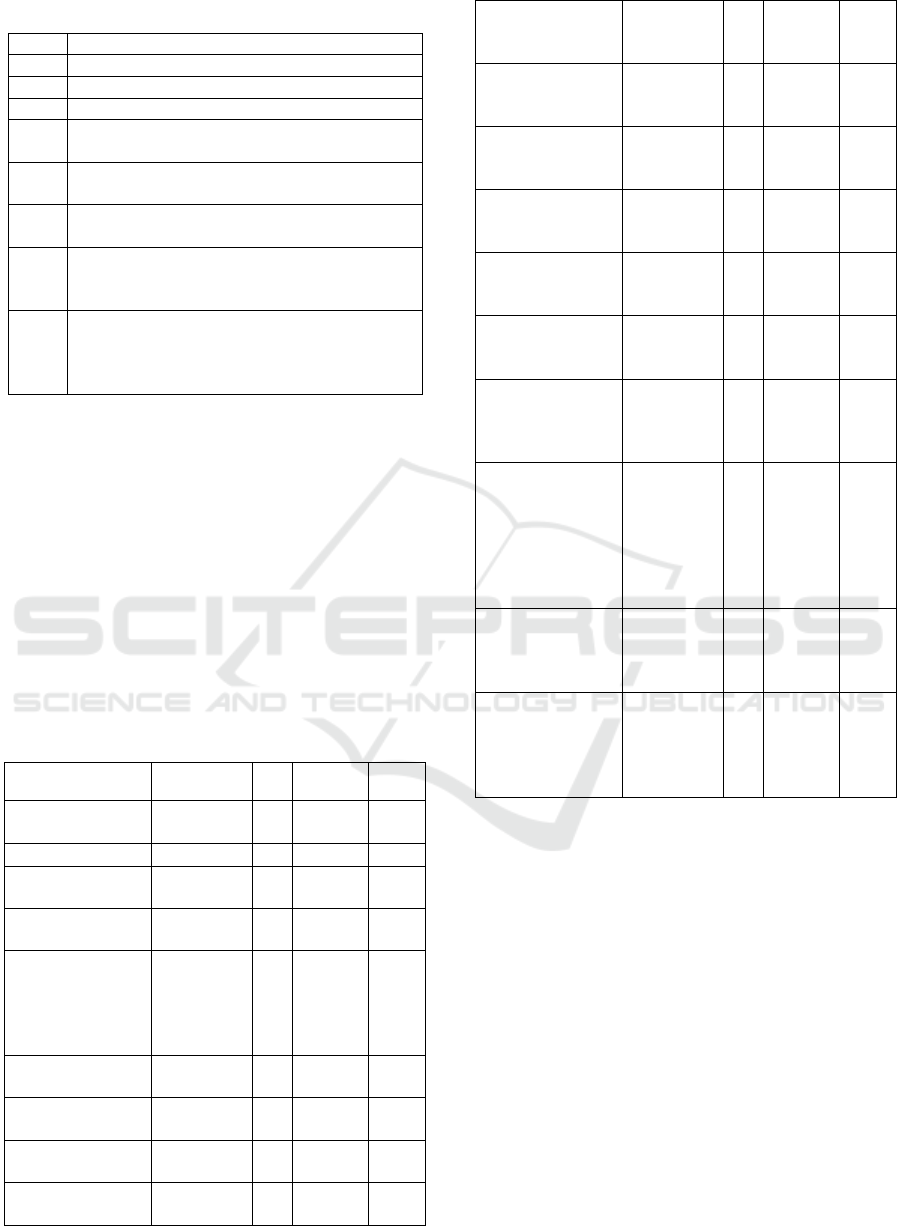
Table 1: Primary studies list.
Item
Selected study
1
How Hybrid IT Is Transforming Enterprises.
2
Top five trends for cloud computing in 2017.
3
Business Intelligence Solutions for SME's
4
Contextualizing BYOD in SMEs in
developing countries.
5
Mobile business intelligence adoption (case
of croatian SMEs).
6
Mobile Adoption in Collaborating Supply
Chains: A Study of Indian Auto SMEs.
7
Influence of the computing cloud on the
economic development of SMEs in El
Salvador.
8
La implementación del Cloud computing y
Big data como herramienta para incrementar
la productividad de las Empresas en él
Ecuador.
with Ecuador reality. In addition, we extracted
recommendations related to innovation and the use of
technology as support in SMEs.
What are the characteristics of the technological
trends that could be used as a business strategy in
SMEs?
After each primary study analysis (See Table 1), we
present a summary and comparative table of the
influential technological trends useful in a business
model, they are based on the reality that Ecuador is
experiencing and they are compared with the success
cases from other countries with similar characteristics
(See Table 2):
Table 2: Characteristics of selected technology trends.
Item
Cloud
services
BI
BYOD
MBI
Implementation
costs decrease
x
More efficiency
x
x
x
x
More
performance
x
x
x
x
Add value to the
business
x
x
x
x
Processing,
storage and
distribution of
big amounts of
data
x
x
x
x
Increase
productivity
x
x
x
x
Help in customer
loyalty
x
x
x
x
Flexibility and
scalability
x
Improves
decisions making
x
x
x
x
Generation of
facts-based
reports
x
x
x
x
Generation of
real time data
reports
x
x
x
x
Analysis and
visualization of
real time data
x
x
x
x
Reduction of
decisions making
costs
x
x
Accessibility
independent of
time and place
x
x
x
x
Offer
competitive
advantages
x
x
x
x
Use of mobile
devices for
working
activities
x
x
x
x
Employees
workflow is done
within the
comfort,
flexibility and
portability of
their devices
x
x
x
x
Access to
organization
resources from
anywhere
x
x
x
x
Acquisition and
interchange of
knowledge
among
employees
x
x
x
x
After reviewing the characteristics of each
technological trend that could be used as a business
strategy, according to what has been presented in the
primary studies (See Table 1) and taking it to the
reality of Ecuador, we conclude that:
The use of cloud services, if applicable in
Ecuador, can be used as a technology strategy,
according to the results gotten in countries with
similar SME’s, such is the case of El Salvador
(Cerritos, 2015).
The last research question about the technological
trend:
What is the selected technological trend and what
are the characteristics that motivated the its
selection?
Enterprises face a very common problem, which is,
insufficiency of resources in terms of technology,
finance and knowledge. Technologies and
information systems can help overcome this problem
ICEIS 2019 - 21st International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
598
by providing better communication and a
collaborative environments for their users. Exchange
of information in real time further improves the
performance and efficiency of their processes.
For the proposed business model development,
we selected cloud services as a strategy according to
the analysis performed on each technological trend
(see Table 2). The following are the characteristics
that motivated that selection:
Cloud Services help enterprises manage large
amounts of data through a shared infrastructure,
acquiring in this way, advantages such as: Cost
reduction, scalability and flexibility in terms of
implementation and technology, as well as
improving data production and ease of access. To
achieve the success of an organization, you need
a combination of services that adapt to the
changing needs of enterprises. This adaptability is
due to the need for greater efficiency and lower
cost.
Cloud Services, also have the potential to allow
improved and more effective communication
environments with its partners, and better access
to useful and necessary information in real time,
thus improving the scope and collaborative work.
3 BUSINESS MODEL
DEVELOPMENT
In this phase, we develop a business model as a
mobility strategy based on cloud services, this model
offers an alternative solution to the high number of
SMEs closures. For this purpose, we need a detailed
current situation of Ecuador’s PYMES.
3.1 Current Situation of PYMES in
Ecuador
EKOS magazine, in one of its publications, using
information provided by the Superintendencia de
Companías, and Security and Insurance agencies,
presents a summary of the evolution of small
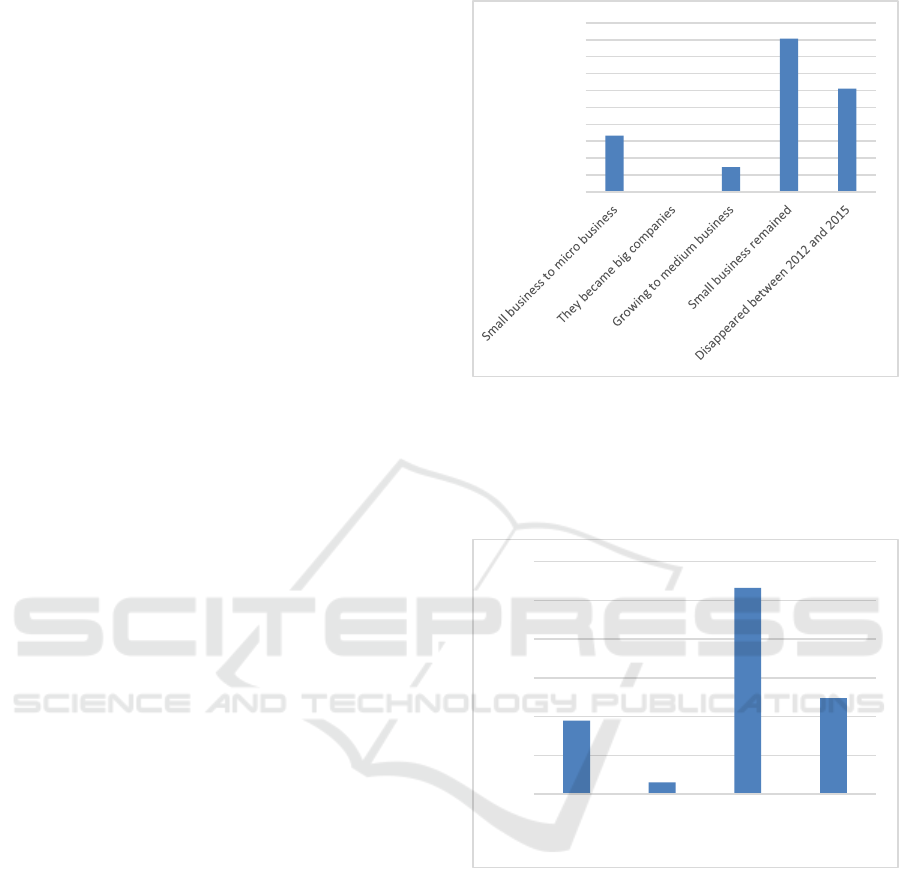
businesses (See Figure 1). They identified that
30.56% of the enterprises had disappeared. It is also
worth to note that 16.66% of these enterprises stopped
being small enterprises and became micro businesses,
also 7.38% of small enterprises managed to ascend to
medium or large enterprises (EKOS, 2017).
Furthermore, EKOS magazine presented an
analysis of medium-sized enterprises from 2012 to
Figure 1: Evolution of small enterprises: 2012–2016.
2016 (See Figure 2), it can be seen that 24.75% of the
enterprises constituted in this interval were closured,
3.04% of them grew and 18.98% became small or
micro enterprises.
Figure 2: Evolution of SEMs 2012–2016.
According to analyzes presented by EKOS
magazine and the National Institute of Statistics and
Census - INEC (Labor and Business Panorama of
Ecuador 2017) (INEC, 2017), maintaining a SME in
Ecuador is a complex task, which depends on many
factors, most of which have to do with the operation
environment and market.
According to the Global Entrepreneurship
Monitor database (GEM 2017), the main causes for
enterprise closures since 2016 are: "Business was not
lucrative and had financing problems" (Global
Entrepreneurship Monitor, 2017).
Also, GEM 2017 highlights that behind these
causes are found 14 pillars that offer a broader
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
Down to small
or micro
enterprise
Growing to
large business
Medium
business
remained
Disappeared
between 2012
and 2015
Business Model as a Cloud Services-based Movility Strategy That Allows to Diminish the Number of PYMES Closures in Ecuador
599

analysis of the Quality of Entrepreneurship and its
Ecosystem. To find those pillars that would help
reduce the causes for enterprises closure, they
identified those reasons, that managed in a suitable
way, will allow a business to improve its production,
offer innovative products / services, be more
competitive, digitize its internal processes, allow
businesses to develop in a highly competitive market.
4 out of 14 causes were selected due to the following
analyzes based on the studies conducted by GEM
2017 (Global Entrepreneurship Monitor, 2017):
Technology Absorption: this pillar is under
development in Ecuador. According to GEM2017
statistics, it represents 21% of consideration in the
enterprises and place itself in position 8 in 2018 and
in position 11 in 2017 (1 is the lowest value, and 14
the highest), this points out that its application
decreased.
Competition: this pillar has not been fully exploited
by the enterprises, it takes third place, besides
representing 29% of application in the enterprises.
Product Innovation: this pillar is key when
encouraging a SME to be more competitive,
encouraging it to focus on delivering a product with
value added to its customers, however it is ranked 4,
this means that its implementation is scarce and has
29% of attention in enterprises.
Process Innovation: according to GEM 2017 studies,
most enterprises still perform their processes
manually, this pillar is placed 9th, and has a 19%
application in enterprises.
Based on these 4 pillars, the present business
model proposes the bases on which an SME should
be directed to create, provide and capture value in the
market. For this, it is necessary to guide their
strategies towards the mobility offered by cloud
services.
Continuing with the resolution to the research
questions proposed above, we proceed to analyze the
following question:
Is it possible to leverage a business model with the
selected technological trend? and does that allow to
assist and / or diminish the main causes of SMEs
mortality?
After the previous analysis, it was determined that the
technological trend to be used is Cloud Services,
based on it, a business model is designed.
The business model based on cloud services will
address the 4 pillars: Technological absorption,
competition, product innovation, and process
innovation. Thus, it becomes a fundamental part of
the strategy for an enterprise to excel, achieving a
reduction in the causes of business closures. This will
contribute to have quality, innovative, and
competitive businesses that will be on par of
technological advances.
The use of cloud services within the business
model becomes the new ally or strategic partner to
drive innovation at the enterprise level, mainly
offering cost reduction in information technology
(IT) resources and ease of data access, helping
managers take the right decisions in the right time and
with real time information.
3.2 Business Model
Our study is also based in Hamels’ proposal (Hamel,
2000), whose model is focused on one strategy, that
in our case is data mobility.
The business model based on cloud services is
composed by four elements:
3.2.1 Basic Strategy
It is essential to align the IT area with business
objectives, to specify this component, some questions
must be asked, they will define what the current
situation is and where you want to go, with this in
mind, the competency pillar will be developed. Some
of the questions that should be asked are:
How big is the identified market segment?
How will the offered product/service be?
What clients’ problems will be solved with my
product/service?
Where (geographic area) will my business be
developed?
What makes my product different from others that
offer the same product?
What is the proposal of value added that I offer to
my clients?
Can the competency imitate my value added
proposal?
3.2.2 Strategy Resources
Once business strategies are identified, it is necessary
to recognize the areas of the SME in which it is
necessary to intervene: streamline processes,
production, corporate image, decision-making,
obtaining data of current situation in real time, etc.;
here it is needed to create and identify competitive
advantages, exploiting the pillars of: technological
absorption, product innovation and process
innovation.
An IT elements inventory of the SME must be
made, whether they are hardware, software or
network connections.
ICEIS 2019 - 21st International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
600

3.2.3 Interface with the Client
It represents the way the SME will enter the market,
what services it will use to reach customers, and the
channels that it will use looking for a different
distribution chain. Within this component, several
alternatives for the use of cloud services are
presented.
For correct operation of services in the cloud, it is
necessary to have internet connectivity, for which the
Ley Orgánica de Telecomunicaicones (LOT)
promulgated in 2015, considers Internet access as a
basic service. With this, the Ministry of
Telecommunications and Information Society
(MINTEL) has among its objectives the plan of
connectivity 2016 - 2021 to prioritize the deployment
of infrastructure that offers connectivity to most of
the population. According to surveys by MINTEL, 8
out of 10 SMEs use Internet, this data favors and
drives the implementation of this business model.
The services in the cloud have 3 different options,
everything depends on the business of the SME, its
budget and its competitive strategy, below are the
main cloud service options:
IaaS Infrastructure as a service,
SaaS Software as a service,
PaaS Platform as a service,
3.2.4 Value Network
For the definition of this component, it is necessary to
identify the suppliers with whom we are going to work,
they will be the strategic partners. In addition, it will be
possible to carry out coalitions with competitors with
common interests, although this may represent risks, it
is part of the innovation of the SME.
Regarding technology service providers, below are
some providers that stand out among others for certain
characteristics of the technological services they offer,
which also include those that will allow an adequate
Internet connectivity according to the proposed
strategy.
For Internet connection providers, there is a wide
range of different plans for SMEs starting at $ 35 per
month.
A number of international enterprises offer services
in the cloud: IBM, Microsoft, Google, Amazon. In
addition, there are other providers that offer specific
services.
After proposing a business model based on cloud
services, the last research question is opened:
Is it possible to validate the proposed business model
through a case study?
To validate the proposed business model, two case
studies exist, we verified that the model represents an
improvement in SMEs competitiveness within its
environment using the survey technique (detailed in
Appendix A), the results are synthesized as follows:
We got a perspective that enterprises, even if
they have a great trajectory at some point, had a crisis
that forced their managers to look for alternatives to
stay in the market and not closure.
It was possible to corroborate that the pillars that
were taken into account influenced determinately on
closure of SMEs and that the proposed business
model can help them successfully pass this type of
crisis.
It was confirmed that knowledge and application
of these services are gradually increasing.
It was possible to determine that most
enterprises make use of cloud services despite not
having solid knowledge in this type of technology.
There is evidence that the more knowledge you
have of the services in the cloud, the more th
application of them increases the benefit to the
enterprise.
It is evident, with the results, that nowadays
people in charge of enterprises have an open mind
ready for change to empower themselves in their
markets.
We could conclude that the service level
agreements between the client and the provider
should be able to increase user confidence in cloud
services.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Once our research is complete, we can conclude that
the first three months after the creation of an
enterprise are critical and therefore must be well
founded with solid grounds such as structure
organization and planning, allowing to redirect all its
resources to meet every objective, and even going
beyond the level of competitiveness in the market
they work.
Through a business model, it is possible to assist each
of the pillars that determine the quality of enterprises,
this allows to reduce enterprise mortality causes. In
the present study, the proposed model is mainly based
on the following pillars: technological absorption,
competition, product innovation and process
innovation, making them a fundamental part of the
proposed strategy, in this way we will get a quality,
innovative and competitive business that will be on a
par with technological advances.
The use of cloud services within a business model
becomes the ally to drive innovation at the enterprise
level, offering IT cost reduction and data ease of
Business Model as a Cloud Services-based Movility Strategy That Allows to Diminish the Number of PYMES Closures in Ecuador
601
access, supporting managers in the decision-making
process. Right decisions at the right time and with
real-time information.
According to the interviews with executives of
two Ecuadorian SMEs, we learned that there is a lack
of knowledge about cloud services, their benefits,
advantages and applications within an enterprise, all
that can contribute to improve their productivity,
innovation and competitiveness as well as keeping
them at the technological forefront.
The proposed business model will transform the
current way of managing SMEs, it highlights the use
of technology to turn it into a competitive and
innovative enterprise, thus decreasing the main
causes of mortality of SMEs.
REFERENCES
Burgos, M., Herrera, J. (2018, Febrero). Investigación
cualitativa para establecer las principales causas que
limitan el crecimiento de las PYMES. Retrieved from
Universidad de Guayaquil:
http://repositorio.ug.edu.ec/bitstream/redug/29422/1/In
v.%20Cuali.%20Factores%20que%20Limitan%20el%
20Crecimiento%20de%20las%20Pymes.pdf
Cardoza, G., Fornes, G., Farber, V., Gonzalez, R., Ruiz, J.
(2016). Barriers and public policies affecting the
international expansion of Latin American SMEs:
Evidence from Brazil, Colombia, and Peru. Journal of
Business Research , 2030-2039.
Cerritos, V. (2015, Marzo). Anuario de Investigación
Universidad Católica de El Salvador. Retrieved from
Influencia de la nube de cómputo en el desarrollo
económico de las PYMES en El Salvador:
http://repositoriounicaes.catolica.edu.sv/bitstream/123
456789/104/1/24CloudAnVol4.pdf
Chávez, D. (2016). Repositorio Universidad Simón Bolívar.
Retrieved from Diseño de un modelo de gestión para la
aplicación del cloud computing enfocado a la
productividad de las PYME ecuatorianas:
http://repositorio.uasb.edu.ec/bitstream/10644/5686/1/
T-2326-MBA-Chavez-Dise%C3%B1o.pdf
EKOS. (2017, Octubre 17). EKOS NEGOCIOS. Retrieved
from
http://www.ekosnegocios.com/negocios/verArticuloC
ontenido.aspx?idArt=9813
Global Entrepreneurship Monitor. (2017). ESPAE -
Graduate School of Management ESPOL. Retrieved
from http://espae.espol.edu.ec/wp-
content/uploads/documentos/GemEcuador2017.pdf
Hamel, G. (2000). Liderando la Revolución. Bogotá:
Ediciones Gestión 2000.
INEC. (2017). Ecuador en Cifras. Retrieved from
http://www.ecuadorencifras.gob.ec/documentos/web-
inec/Bibliotecas/Libros/Panorama%20Laboral%20201
7.pdf
Osterwalder, A., Pigneur, Y. (2010). Business Model
Generation. España: Centro Libros PAPF, S. L. U.
Sánchez, C., Vargas, J. (2018). Crecimiento en PYMES en
base a sus recursos: Caso Gasticom. Revista de la
Agrupación Joven Iberoamericana de Contabilidad y
Administración de Empresas (AJOICA) , 33-45.
Sánchez, J., González, G. (2017). Estrategias de Comercio
Electrónico para Implantar un Modelo de Marketing
por Internet. Revista Mercados y Negocios por
Departamento Mercadotecnia y Negocios
Internacionales - Universidad de Guadalajara , 32-41.
Zaridis, A., Mousiolis, D. (2014). Entrepreneurship and
SME's Organizational Structure - Elements of a
successful Business. Procedia - Social and Behavioral
Sciences , 463-467.
APPENDIX A
Survey to measure the contribution of using a business
model as mobility strategy based on cloud services
Estimado empresario, la información proporcionada en la
presente encuesta tiene fines estrictamente académicos, la
cual permitirá recabar información que permita evaluar el
aporte de un Modelo de Negocios basado en Servicios en la
Nube para el desarrollo de las PYMES en el Ecuador.
DATOS INFORMATIVOS:
Nombre de la empresa: ______________________
Nombre del encuestado: ______________________
Puesto que ocupa en la empresa: ________________
Número aproximado de empleados: _____________
PREGUNTAS:
Seleccione la respuesta que más se ajusta a la realidad de su
empresa.
1. ¿Su empresa ha presentado por lo menos una crisis que
le haya hecho pensar en cesar sus actividades?
SI
NO
2. Si su respuesta anterior fue afirmativa. ¿La crisis por la
que atravesó su empresa tuvo que ver con alguno de los
siguientes aspectos: i) Tecnología Obsoleta; ii)
Competitividad; iii) Falta de Innovación de un
producto/servicio o falta de innovación en los procesos
internos?
SI
NO
3. ¿Qué nivel de conocimientos tiene sobre los
servicios en la nube?
MUCHO
POCO
NADA
4. ¿Su empresa ha utilizado o está utilizando algún
servicio en la nube?
SI
NO
ICEIS 2019 - 21st International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
602
5. Si su respuesta anterior fue afirmativa. ¿Qué
servicio está utilizando?
Infraestructura como Servicio (Ejemplo:
servidores virtualizados o centro de datos)
Software como Servicio (Ejemplo: correo
electrónico, sistema de facturación, ERP, CRM,
etc.)
Plataforma como Servicio (Ejemplo: plataforma
que le permita desarrollar aplicaciones como
Zimbra)
6. ¿Sabía que el uso de servicios en la nube puede
ayudarle a reducir costos en tecnología, además de
permitir a su empresa innovar y ser más competitiva?
SI
NO
7. ¿Sabía que su empresa puede mantenerse a la
vanguardia tecnológica, acceder a aplicaciones que le
permiten fidelizar a sus clientes, digitalizar sus
procesos internos, entre otros beneficios haciendo uso
de los servicios en la nube y pagando de acuerdo a sus
necesidades?
SI
NO
8. ¿Su empresa cuenta con un Modelo de Negocio,
es decir tiene una estrategia planteada que le permite
cumplir los objetivos de su negocio?
SI
NO
9. ¿Estaría dispuesto a implementar un Modelo de
Negocio basado en servicios en la nube dentro de su
empresa, si este le ofrece: modernizar su tecnología,
ser más competitivo, innovar su producto/servicio e
innovar sus procesos internos?
SI
NO
10. Si su respuesta anterior fue afirmativa. ¿Cuál
sería su principal preocupación sobre la
implementación del Modelo de Negocios planteado?
La seguridad y confidencialidad de los datos.
Pérdida de control.
Dependencia de un proveedor.
__________________________
Firma
Business Model as a Cloud Services-based Movility Strategy That Allows to Diminish the Number of PYMES Closures in Ecuador
603
