
Technical and Economic Analysis Repair of the Wooden Boat using
Fiberglass Laminates on Fishing Boats in Lamongan District
Mohammad Sholikhan Arif
1 a
, Heri Supomo, Hasanuddin, Sri Rejeki Wahyu Pribadi,
Wing Hendro Prasetyo Akbar Putra, Dedi Budi Purwanto, Sufian Imam Wahidi,
Ahmad Nasiruddin, and Chandra Ariesta
1
Department of Naval Architecture, Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember, Indonesia
Keywords: Boat Repair, Fibreglass Laminates, Fishing Boat, Lamongan District, Wooden Boat.
Abstract: In 2016 there are 3,263 vessels fishing boats in Lamongan, and 90 percent uses wood as the primary material
for fishing vessels. The wooden boat repair activities in the Lamongan Regency are very high, considering
the wooden vessels repaired regularly so that the vessels' condition remains suitable for fishing activities in
fishing. At present, repairing wooden vessels still uses conventional methods, such as attaching the skin of
the boat with fiber or cloth axis and replacing damaged wood with new ones. Conventional methods are
inefficient and ineffective because it has checked periodically and it is expensive to buy new wood,
considering the price of wood is increasingly expensive because of the difficulty of finding wood material.
One new method in repairing damage to new boats by using FRP (Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic) lamination.
In this research, tensile testing carried out on several fibreglass layers on wood to obtain the most significant
strength. Furthermore, we have an economic analysis to get the cheapest variations of fibreglass lamination.
1 INTRODUCTION
Lamongan Regency located on 6
o
51 '- 7
o
23' South
Latitude and 112
o
33 '- 112
o
34 East Longitude.
Lamongan Regency has approximately 1,812.8 km2
or ± 3.78% of the total area of East Java Province.
With a length of 47 km, the sea area of Lamongan
Regency is 902.4 km2, if calculated 12 miles from sea
level (Norromadani, 2016).
According to data from the Central Statistics
Agency of Lamongan Regency in 2008, fish
production in Lamongan District amounted to 61,436
tons, Lamongan with the most significant amount of
fish production in East Java, it also had an impact on
the lives of the community, where most of the
Lamongan community utilize resources fisheries as
their livelihood or work as fishermen, both permanent
fishermen. With the most significant amount of fish
production in East Java, resulting in the number of
fishers in Lamongan because of the many fishermen,
Lamongan Regency become the highest number of
fishers (Utami, 2016).
Maintenance of wooden boats used to catch fish is
needed to keep the boat in good condition, and repairs
are needed if damage occurs. In general, a wooden
boat maintenance and repair must be done on regular
basis, and if not done properly and adequately, it will
result in high costs for the boat repair process. (Arif,
2018) The process carried out in repairing the damage
uses several conventional methods, including using
natural fibres and fabric wicks to patch the boundaries
between the wood. From a technical perspective. this
is obviously lacking and needs to be done both
technically and economically. As a result, one method
of repairing a wooden boat using fibreglass
lamination exist.
This study aims to conduct a technical and
economic analysis of wooden boat repairs using
fibreglass laminates application methods on existing
boat objects in the coastal fishing community of
Lamongan. The technical analysis carried out is to
obtain the number of fibreglass layers that will be
applied to the repair of wooden boats that meet the
classification requirements, and economic analysis to
get the cost of repairing wooden boats using
fibreglass laminates.
128
Arif, M., Supomo, H., Hasanuddin, ., Pribadi, S., Putra, W., Purwanto, D., Wahidi, S., Nasiruddin, A. and Ariesta, C.
Technical and Economic Analysis Repair of the Wooden Boat using Fiberglass Laminates on Fishing Boats in Lamongan District.
DOI: 10.5220/0010856000003261
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Marine Technology (senta 2019) - Transforming Maritime Technology for Fair and Sustainable Development in the Era of Industrial
Revolution 4.0, pages 128-135
ISBN: 978-989-758-557-9; ISSN: 2795-4579
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Damage to Wooden Boat
There are several types of damage to wooden hulls as
follows:
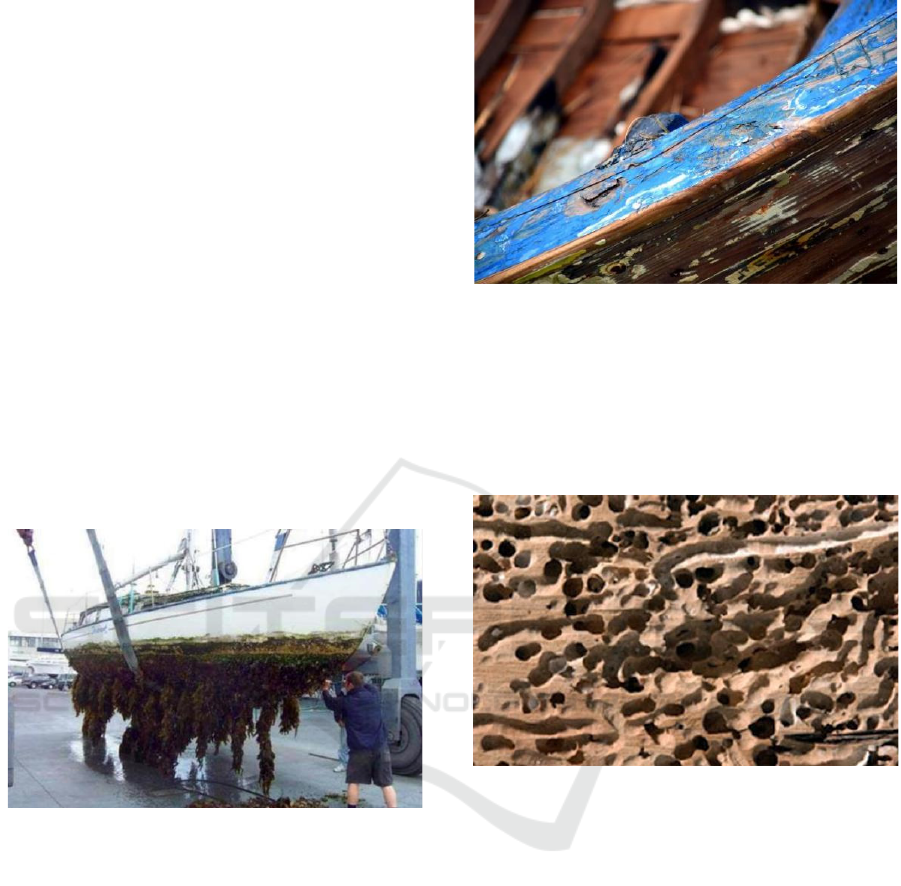
2.1.1 Marine Growth
Marine growth is a various species of marine
animals/plants that grow and colonize the surface of
buildings/structures in the sea, where temperature,
food/nutrition, pH (acidity) factors, and other
environmental conditions are suitable for their
growth. The growth of marine growth on the surface
of this building may cause various problems. Marine
growth that grows on wooden boats will cause the
boat's weight to increase, causing additional
resistance to the boat. In addition, marine growth on
fishing boats will increase the boat's resistance when
moving because the surface of the boat's skin
becomes rough.
Figure 1: Marine growth.
2.1.2 Wood Weathering
Wood Weathering occurs in the natural process of the
wood itself, also caused by destructive marine
animals such as moulds and barnacles attached to the
body of the boat and microbes in the form of mould
mildew. During this time, the process of
drying/preservation of material carried out at the
Boatyard naturally and takes up to one month, which
will affect the strength of fishing vessels.
Weathering on wooden boats will cause damage
to the boat hull in the form of leakage or reduced
strength of the boat when receiving loads, both
internal and external.
Figure 2: Wood weathering.
2.1.3 Leaks (holes)
Leakage on the hull is one of the results of several
previous events, such as the condition of weathered
wood and the presence of sea animals that enter the
construction of the wooden hull (Greene, 2016).
Figure 3: Leakage because of sea animals.
2.1.4 Crack
Crack damage on wooden boats occurs due to several
possibilities such as collisions with objects, collisions
on the hull of the boat and in the form of collisions
with fellow boats or collisions between boats with
objects in the water such as rocks, buoys, beams, logs,
chunks of ice or collisions with other boats with
objects in the water such as rocks, buoys, beams, logs,
chunks of ice and others.
Collision with objects on the edge of the land,
such as jetty and breakwater, occurs when they jutting
into the water. Another possible cause of cracking is
the damage associated with wave propagation to the
hull of the boat due to the vibration of the propulsion
engine and the other engines as well as the impact of
the waves on the hull of both waves from the outside
and waves that arise due to the spinning of the
propeller engine and the other engines as the impact
Technical and Economic Analysis Repair of the Wooden Boat using Fiberglass Laminates on Fishing Boats in Lamongan District
129

of the waves on the hull of both waves from the
outside and waves that arise due to the spinning of the
propeller engine and the other engines as with the
waters when the boat is operated in the construction
of the boat and damaged due to excessive vibration
caused by faults in the design of construction where
the vibration is not channelled correctly so that the
construction experiences a cracking and release of
welding from certain parts of the construction caused
by defects in the design of construction where the
vibration is not appropriately channelled so that the
construction experiences a cracking and release of
welding from certain parts of the construction due to
other defects in the design of construction where the
vibration is not appropriately channelled. Propeller
leaf damage.
Figure 4: Crack on the wooden boat.
2.2 The Material Used for Wooden
Boat Repair using Fiberglass
Materials used in boat repair using fiberglass
lamination are (Baskoro, 2018):
2.2.1 Resin
Resin is a binder used to support fiberglass so that the
fiberglass stays in place. The resin consists of three
main components, glycol, organic acids, and active
thinners (usually styrene). Resins that used are
polyester resins, vinyl ester resins, and epoxy resins
(Bader, 2002).
2.2.2 CSM (Chopped Strand Mat)
Chopped Strand Mat (CSM) is a type of fiberglass
made of glass fiber placed and arranged randomly
between one another. CSM Fiberglass is
distinguished by weight per square meter. For
example, CSM 300 means that each square meter of
fiberglass weighs 300 grams.
2.2.3 WR (Woven Roving)
Woven Roving (WR) is fiberglass made of glass fiber
woven in two directions continuously at an angle of
90°. Fiberglass WR is the reinforcement material
most often used for the construction of marine
structures.
2.2.4 Catalyst
The catalyst has the function of accelerating the
curing and polymerization between resin and
fiberglass.
2.2.5 Talc
Talc serves as a mixture of fiberglass dough to make
it rigid and somewhat flexible; as the name suggests,
this material is white powder-like sago.
2.2.6 Gelcoat
Gelcoat is a layer made of resin, aerosol, and cobalt
(accelerator). In making Gelcoat, the three materials
mixed evenly. When the gel coat has cured, the gel-
coat will have a shiny and smooth surface. Therefore
the gel coat is generally applied as the outermost layer
of the laminate after the release agent layer.
The method used in this boat repair process is by
direct application (Boat Structure Committee, 1990).
Fiberglass is applied to damaged wooden fishing
boats using the multi-layered (3-layer) method and
then analyse economic feasibility calculations with
the repair method compared to traditional wooden-
boat repair.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Technical Method
The material, tensile, and compressive testing are
carried out to find out the strength of the tensile and
compressive. There are five variations of material to
be used as shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Variations and lamination schedule.
Name Lamination Schedule
1
st
Variation Wood
(
reference material
)
2
nd
Variation Wood + CSM300 +WR600 + CSM300
3
rd
Variation Wood + CSM450 +WR600+ CSM300
4
th
Variation Wood + WR600 + CSM450 +CSM300
5
th
Variation Wood + WR600+ CSM300 + CSM300
senta 2019 - The International Conference on Marine Technology (SENTA)
130
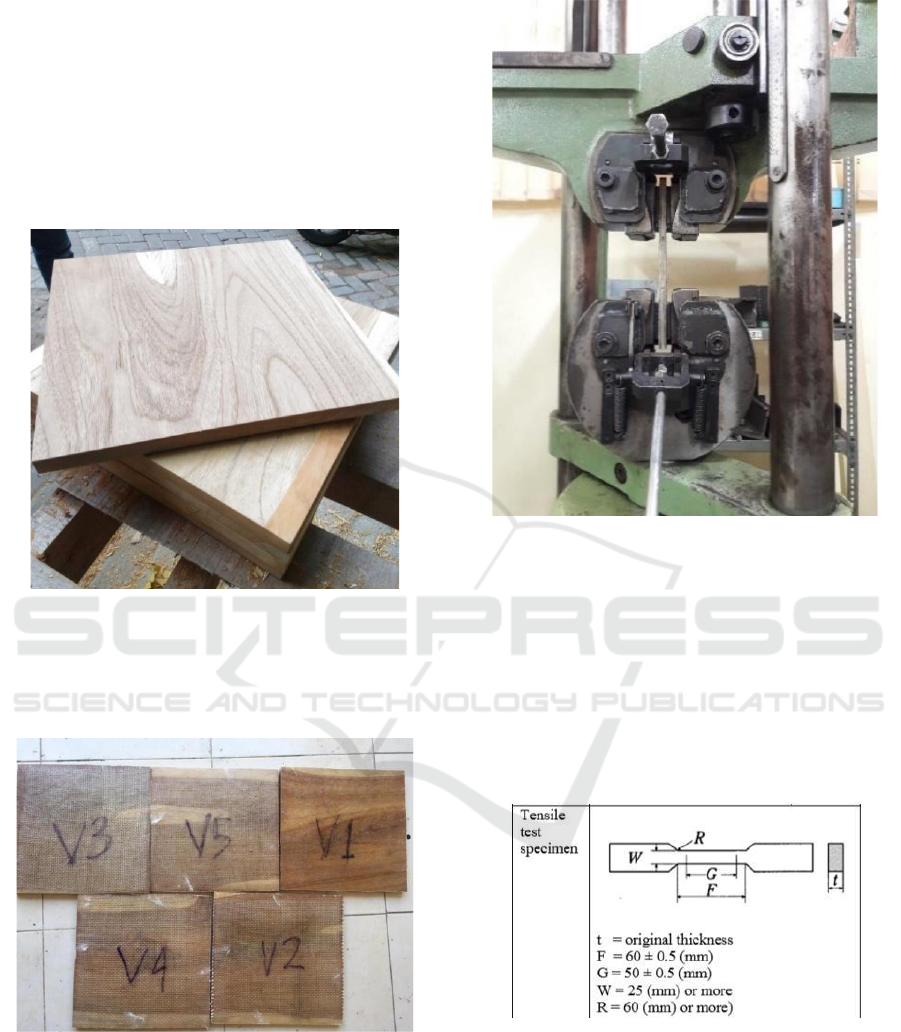

After determining the Variation of material to be
tested, the next step is making the material, while the
stages in making the material are as follows:
• Prepare five pieces of teak wood material with
dimensions of 30 cm x 30 cm x 2 cm.
• Preparing the resin that will be used for the
material and mixed with a catalyst that functions
to dry the resin, the ratio of catalysts and resins is
1: 100.
Figure 5: Wood as a primary material.
• Coating wood with resin and fiberglass fibers by
the lamination schedule using a roll and brush to
avoid air bubbles that enter during the lamination
because it will reduce the laminate's strength.
Figure 6: laminated wood with fiberglass.
Before testing and pulling, the first thing to do is
to prepare the test material. Test materials are
numbered in accordance with variations so that it is
accessible when recording test results. In tensile
testing, the engine used is Universal Testing Machine
MFL/UFD 2.0.
Figure 7: Universal testing machine MFL / UFD 2.0.
The width size for tensile and bending specimens
is determined by the laminated material thickness,
while the length of the specimen is free as long as it
exceeds 20 times the thickness of the material. The
size of tensile and compressed specimens is
determined by the size of fiberglass material
specimens determined in the 2016 Indonesian
Classification Bureau annex, Rules for Fiberglass
Reinforced Plastic Boats.
Figure 8: BKI Tensile Specimen Standard.
Technical and Economic Analysis Repair of the Wooden Boat using Fiberglass Laminates on Fishing Boats in Lamongan District
131
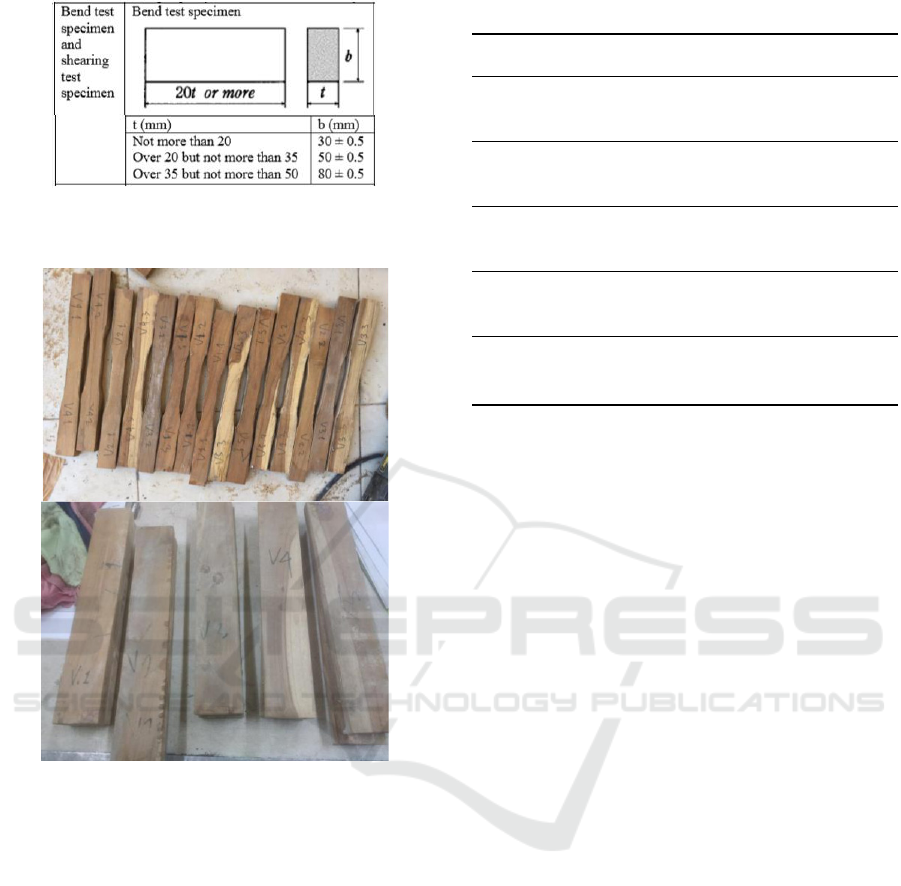
Figure 9: BKI Bending Specimen Standard.
Figure 10: Specimen of tensile and bending test.
Then the test specimen is made following the
provisions of predetermined standards.
3.2 Economic Method
Economic analysis is carried out after technical
analysis. Repair of wooden boats using the fiberglass
lamination method adjusts to technical aspects,
including the number of layers of fiberglass laminate
according to the Variation of specimens that have
been made. The cost components calculated are as
follows:
3.2.1 Material Cost
To calculate the cost of repairing wooden boats using
the fiberglass lamination method, it is necessary to
know the price of the material used in the boat repair
process, including the price of resin, the price of
mat/CSM, catalyst, nails used per m
2
.
3.2.2 Labor Cost
Labour costs are calculated to determine how much
these costs are used to repair wooden boats using the
fiberglass lamination method per m
2
.
3.2.3 Total Cost
The total cost is calculated by adding the material cost
and labour costs together.
4 ANALYSIS OF RESULTS
The results of the tensile test are tabulated in Table 2.
It can be seen that the third variation has the highest
average tensile test results, which are equal to 47.87
MPa. Whereas the results of the compressive test can
be seen in Table 3.
From the bend test results table above, we can see
the most significant buckling test results is the third
Variation that is equal to 4.20 MPa.
For economic analysis, we do the following
calculations. In Table 4 we can see that the material
costs in variations 2 and 5 are the same, Rp 284,537
while variations 3 and 4 have the same material cost,
Rp. 317,056. This difference is due to the different
thickness of the woven roving, and the CSM used.
Meanwhile, the labour cost for each m2 is Rp
208,907, so that we can see economically that
variations 2 and 5 have the advantage of being
cheaper than variations 3 and 4.
Table 2: Tensile strength result and stress calculation.
Code Fu (kN)
Stress
(Mpa)
Average Stress
(M
p
a)
V1.1
14 29.41
27.11
V1.2
13 27.18
V1.3
17 24.75
V2.1
18 34.71
32.99
V2.2
15.5 33.73
V2.3
13.5 30.52
V3.1
21 47.23
47.87
V3.2
23 52.66
V3.3
18 43.71
V4.1
15.5 38.88
39.82
V4.2
15 41.63
V4.3
15 38.94
V5.1
19.5 45.27
44.59
V5.2
17.5 42.14
V5.3
20 46.34
senta 2019 - The International Conference on Marine Technology (SENTA)
132

Table 4: Cost calculation.
Code
Material Cost
(Rp)
Labour Cost
(Rp)
Total Cost
(Rp)
2
nd
Variation
284,537 208,907 493,444
3
rd
Variation
317,056 208,907 525,963
4
th
Variation
317,056 208,907 525,963
5
th
Variation
284,537 208,907 493,444
5 APPLICATION
Fiberglass lamination on a wooden boat is the process
of repairing a wooden boat using fiberglass coating to
a wooden boat by attaching fiberglass fibres to the
damaged or in need of repair part of the boat or the
entire body of the boat. Repair purposes replace the
damaged part of the boat and protect the hull from
leaks and strengthen the hull's construction.
Fiberglass lamination can increase the thickness of
the hull between 0.5-1 centimetre.
The steps in the process of repairing wooden
vessels using fiberglass lamination are explained as
follows:
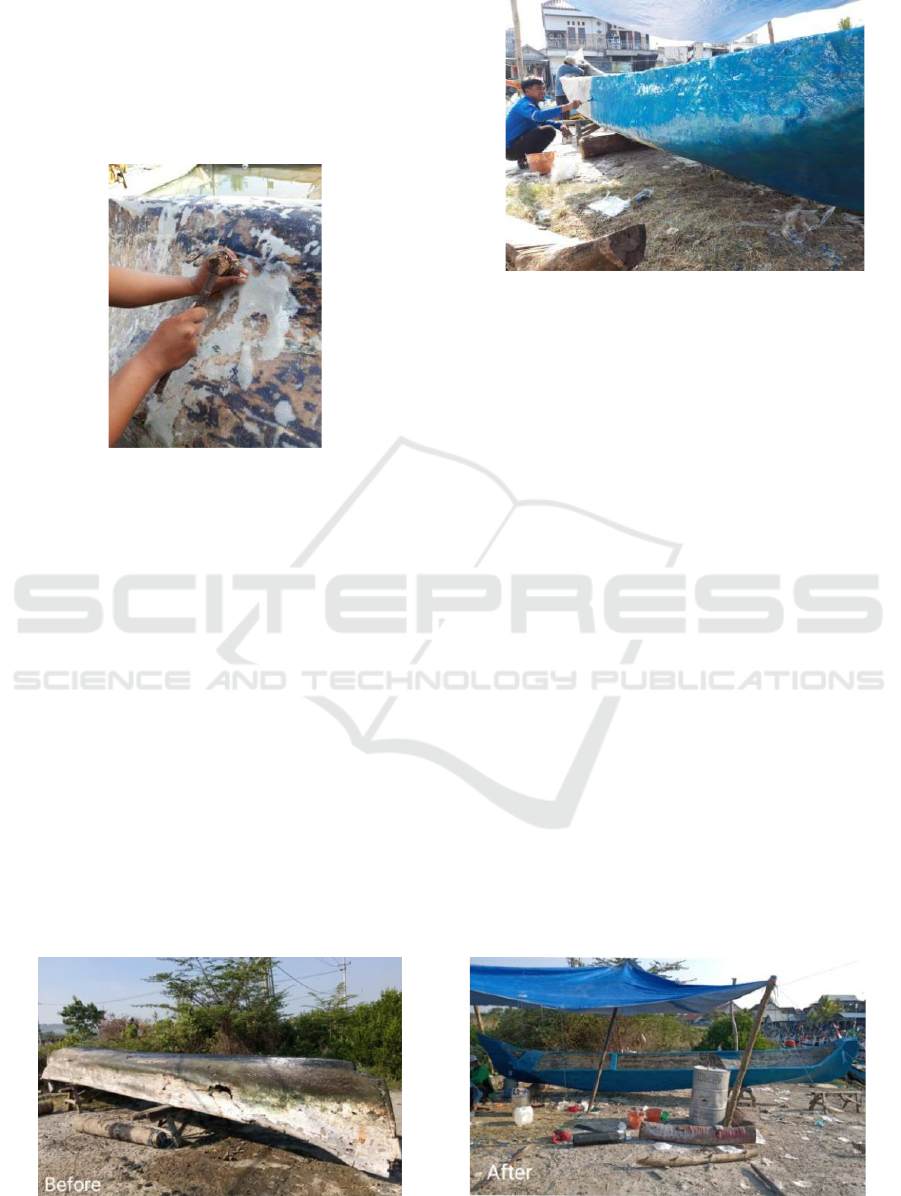
5.1 Drying the Boat
Wooden vessels to be laminated must be dried before
starting to make repairs. The purpose of this drying is
to avoid water content into the wood, which would
damage the fiberglass layer, which will would
otherwise adhere tightly to the hull of the boat. Resin,
fiberglass, and wood cannot bond effectively if
exposed to water, even in minimal amounts (Sunardi,
2018).
Figure 11: Boat drying process.
5.2 Cleaning the Hull
After the wooden boat underwent a process of drying,
the boat first cleaned all parts using a grinder and
sandpaper. It aims to remove the rest of the paint,
putty or dirt that still attached to the boat's hull and
the remnants of marine plants connected to the boat.
5.3 Installation of Fiberglass
After the boat undergoes a drying and cleaning
process, the next step of the boat is ready to be
repaired by the fiberglass lamination method.
Fiberglass laminates are used in 3 layers (Wood +
CSM450 +WR600+ CSM300). This laminate will
add a thickness of 5-10 mm.
Figure 12: Installation of fiberglass fiber.
The installation of fiberglass lamination will
make the hull of the boat impermeable and not leak
so that the boat will avoid the entry of seawater. Boat
construction will also be stronger, and weathering in
wood, which usually occurs due to seawater, will be
avoided.
Table 3: Bend test result.
Code
Fu (kN)
Deflection
(
mm
)
Stress
(
MPa
)
Average
Stress
(
MPa
)
V1.1
2.6 11 2.74
2.71
V1.2
2.55 12 2.68
V2.1
2.7 13 3.00
2.97
V2.2
2.8 13 2.95
V3.1
4.15 11 4.15
4.20
V3.2
4.25 10 4.25
V4.1
3.6 13 3.79
3.53
V4.2
3.1 13 3.26
V5.1
3 12 3.33
3.28
V5.2
2.9 12 3.22
Technical and Economic Analysis Repair of the Wooden Boat using Fiberglass Laminates on Fishing Boats in Lamongan District
133

5.4 Fiberglass Lamination Nailing
Strengthening of the laminate with anti-rust nails
measuring 3 cm at 20-30 cm. The purpose of nailing
is to strengthen the fiberglass layer attached to the
hull, so there is no possibility of the fiberglass
separated layer from the hull.
Figure 13: Nailing on the fiberglass layer.
5.5 Retardation and Refinement
After the layers have been installed, the heating
process is carried out. The putty used is made up of
talc and resin with a catalyst added. After stirring,
putty is applied to the hull of the boat. Once it has dry,
mashed the putty using sandpaper.
6 PAINTING AND FINISHING
After all the processes are done, the last step is to
apply unique paint with colour pigments. This colour
pigment is mixed with resin and addictive to make the
surface of the boat more glossy and not easy to get
dirty. This paint can also avoid the sticking of sea
animals or dirt that usually attached to the hull of the
boat.
Figure 14: Painting on the hull of a boat.
The economic benefits of fiberglass lamination
for wooden boat repair compared to traditional boat
repair explained as follows:
1. Repair and maintenance with fiberglass
lamination can reduce maintenance in cleaning
marine growth because, in fiberglass, marine
growth cannot eat the fiberglass material
differently.
2. Repair and maintenance in a conventional way
need more time than the fiberglass method,
fiberglass method faster 50% than the
conventional way.
Fiberglass lamination on wooden boat repair will
offer the following benefits:
1. Damages that occur on a wooden boat can be
overcome by doing fiberglass lamination, which
prevent wooden boats leaks.
2. Fiberglass laminated material, which marine
animals and plants do not eat, allows the boat's life
to be longer.
3. Facilitate the cleaning of the hull so that
maintenance costs are lower compared to wooden
boats.
a. Before
b
. Afte
r
Fi
g
ure 15: Boat Re
p
air Before and After Results.
senta 2019 - The International Conference on Marine Technology (SENTA)
134

4. With fiberglass lamination, the boat repair process
will become more comfortable and lighter in
terms of price.
7 CONCLUSIONS
Fiberglass lamination on wooden boat repair can
increase the strength of the hull construction and
prevent leakage in the boat. Repairs using fiberglass
lamination benefit fishers because it can save
maintenance costs and repair boats. The boat's
lifespan is also longer because maintenance can be
more routine.
From the tensile and bending tests that have been
carried out on five variations, with the highest value
is obtained in the 3rd Variation of the tensile strength
of 47.87 MPa and the bending strength of 4.20 MPa.
The cheapest boat repair cost is obtained for
variations 2 and 5, which is Rp.493,444 / m2
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We gratefully thank for Institut Teknologi Sepuluh
Nopember Surabaya for financial support, we thank
to PT. Justus Kimia Raya to support the material of
Fiberglass and Resin. We also thank the reviewer for
the constructive comments and suggestions that
substantially improved the paper.
REFERENCES
Arif, M., Pribadi, S., Prasetyo, W., Purwanto, D.,
Ahadyanti, G., Utama, D., & Ariesta, R. (2020). Design
and Production of FRP Catamaran Boat for Better River
Transportation in Randuboto Village, Sedayu District,
Gresik Regency.
https://doi.org/10.5220/0008375000820086
Bader, S. (2002). Composites Handbook. Wollaston: Scott
Bader Company Ltd.
Baskoro, A. (2018). Analisa Teknis dan Ekonomis
Pembangunan Kapal Ikan Ukuran 10-20GT
Konstruksi Fibreglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Sesuai
Standar Biro Klasifikasi Indonesia. Surabaya: ITS.
Greene, E. (2006). Composite Boat Repair: Part One,
Damage Assessment. Maryland: Eric Greene
Associate.
Lamongan, K. (2018, 02 19). Kabupaten Lamongan.
Retrieved from Kabupaten Lamongan:
https://lamongankab.go.id/paciran/potensi-perikanan-
kelautan
Munawaroh, S., Adrianto, A., & Suwarno. (2017). Perahu
Tradisional Ijon-Ijon di Desa Semangkon Lamongan.
Yogyakarta: BPNB.
Norromadani Y, R. (2016). Pemetaan Perikanan Laut
Kabupaten / Kota Jawa Timur dengan Metode Fuzzy K-
Means Clustering. Seminar Nasional Maritim, Sains,
dan Teknologi Terapan , 14-21.
Boat Structure Committee. (1990). Use of Fiber Reinforced
Plastics In The Marine Industry.
Washington DC: Boat Structure Committee.
Sunardi, S. B. (2018). Laminasi Fiberglass untuk
Memperbaiki Kapal Ikan Kayu di Kecamatan Lekok,
Kabupaten Pasuruan, Jawa Timur. Jurnal
Pengabdian Masyarakat J-DINAMIKA, Vol. 3 No. 1,15.
Utami, I. D. (2016). Perkembangan Perikanan Lamongan
Tahun 1998 - 2008. Avatara, e-Journal Pendidikan
Sejarah , 832-842.
Technical and Economic Analysis Repair of the Wooden Boat using Fiberglass Laminates on Fishing Boats in Lamongan District
135
