
Analysis of the Application of the Ease of Administration Principle in
the Property Tax Reduction Procedure in the Fourth Industrial
Revolution: Case Study Personal Tax Payer
Elsie Sylviana Kasim
Tax Administration, Vocational Education Program, University Indonesia
Keywords: Ease of administration, Property Tax Reduction Procedure, Case Study
Abstract: The purpose of this research is to analyse the application of the ease of administration principle in property
tax reduction procedure in the fourth industrial revolution – case study personal taxpayer. This research
approach is quantitative by conducting interviews with informants as well as other supporting data. The
results of the study indicate that the principle of ease of certainty has not been fully fulfilled. The ease of
efficiency is fully fulfilled. Moreover, the ease of simplicity is fully fulfilled. This research is expected to
provide input for the government, especially Regional Tax and Retribution Agency, South Jakarta
Administrative City and also for taxpayers, as study material related to the procedure for obtaining property
tax reduction. This research is expected to provide information and be a reference material in reviewing
procedures to obtain property tax reduction and provide an overview of the application of the principle of
ease of administration.
1 INTRODUCTION
There has been an increase in the property tax
reduction procedure. One factor is the massive
changes in housing prices that have occurred over
the past decade. The increase in house prices across
the country in the early 2000s caused many owners
to apply for a reduction to their property taxes
(Doerner and Ihlanfeldt, 2014). It is because their
values rose too quickly. Residents of DKI Jakarta
also complained about by the increase in the price of
the Sales Value of Taxable Object. According to the
Head of DKI Regional Tax and Retribution Agency,
Faisal Syafruddin, the Sales Value of Taxable
Object increase varies and adjusts market prices. In
DKI Jakarta, the Average Sales Value of Taxable
Object increase is 19.54% in the 2018 period. The
adjustment is regulated in Regulation of the
Governor of the provincial district exclusive Capital
Jakarta No. 24 in 2018 on the Determination of Sale
Value of Land and Rural and Urban Land Tax
Objects in 2018.
The property tax reduction procedure gives
owners who believe that their property is overvalued
to make adjustments to its assessed value. Because
the government’s valuation system inherently
introduces some randomness in the tax burden
(Doerner and Ihlanfeldt, 2014). One of the rights of
the taxpayer is to get a reduction in Rural and Urban
Land and Building Tax. A reduction in Rural and
Urban Land and Building Tax can be given when the
amount of tax received by the taxpayer on the object
of the tax is appropriate, but the taxpayer feels
unable to pay the tax debt. This condition means that
the land and building area and the Sales Value of
Taxable Object per m
2
of tax objects (land and
building classification) are in accordance with the
field conditions. However, for the amount of tax
stipulated by the tax authorities, taxpayers feel that
they cannot pay the amount of Rural and Urban
Land and Building Tax owed. For these conditions,
taxpayers can submit a reduction in the amount of
Rural and Urban Land and Building Tax owed.
Reductions can be given based on the taxpayer’s
request. Requests can be submitted individually or
collectively (collectively). The decision is to grant a
reduction in the authority of the tax authorities
(regional head). The amount of Rural and Urban
Land and Building Tax is given is determined based
on subjective considerations of the tax authorities by
paying attention to the state of the tax object that has
to do with the tax subject.
492
Sylviana Kasim, E.
Analysis of the Application of the Ease of Administration Principle in the Property Tax Reduction Procedure in the Fourth Industrial Revolution: Case Study Personal Tax Payer.
DOI: 10.5220/0010700200002967
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE 2019) - Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable 4.0 Industry, pages 492-500
ISBN: 978-989-758-530-2; ISSN: 2184-9870
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
The complexity of the tax reduction procedure
often makes representing oneself virtually
impossible. (Tomes and Dvorak, 2014). A personal
taxpayer, in this case, is Mr X, who is a resident of
Cilandak, Lebak Bulus. Since the construction of the
mass rapid transit (MRT) phase of Lebak Bulus –
Hotel Indonesia Roundabout residents can feel
The increase in land value. However, this resulted in
an increase in Rural and Urban Land and Building
Tax in this case Property Tax through Sales Value of
Taxable Object adjustments.
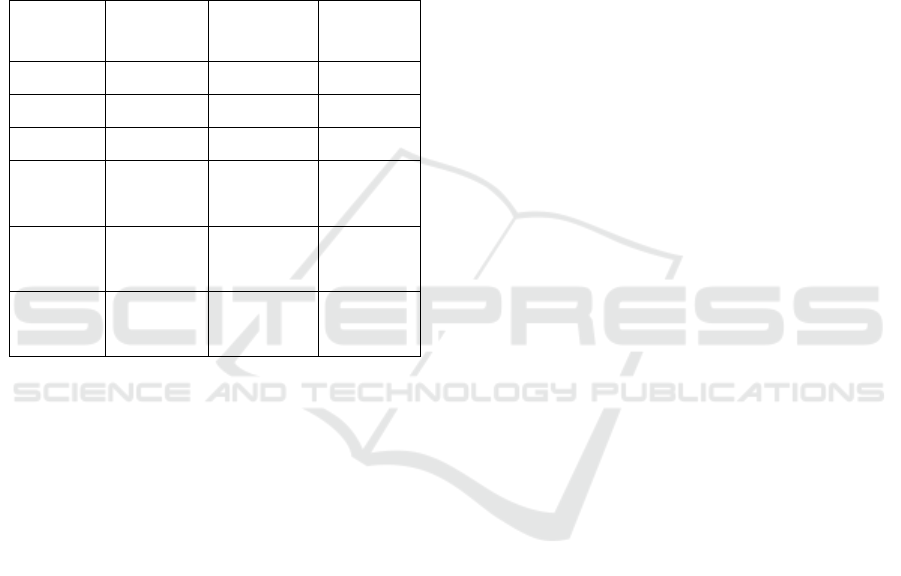
Table 1: Mr X’s Total Sales Value of Taxable Object
Yea
r
2016 2017 2018
(
R
p)
(
R
p)
(
R
p)
Lan
d
5.938.317.000
5.938.317.000
7.060.077.000
Buildin
g
2.371.500.000
2.371.500.000
2.371.500.000
Total Land
& Buildin
g
8.309.817.000
8.309.817.000
9.431.577.000
Acquisition
Value of
15.000.000
15.000.000
15.000.000
Non-Taxable
Ob
j
ect
Sales Value
of
8.294.817.000
8.294.817.000
9.416.577.000
Taxable
Ob
j
ect
Rural and
Urban Lan
d
16.589.634
16.589.634
18.833.154
and Building
Tax
Based on the table 1 above during 2016 and
2017, Mr X did not experience a rise in property tax.
However, in 2018 there was a 13.5% increase from
Rp16,589,634 to Rp18,833,154. Since 2016 Mr X
has proposed a reduction in property tax. However,
the reduction in property tax obtained by Mr X since
2016 is only 10%.
In this study, the goal is to analyse the
application of the ease of administration in Mr X
property tax reduction procedure as an input to
improve the reduction procedure system and to look
closely at the emerging technology that has enabled
online assessment appeal (OAA) systems (Brady
and Sanderson, 2017).
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
In the preparation of the study entitled “Analysis of
the Application of the Ease of Administration
Principle in Property Tax Reduction Procedure in
the Fourth Industrial Revolution - Case Study
Personal Tax Payer”, the researcher uses four other
research results that have relevance to the theme
raised by the researcher and at the same time
become a reference in the preparation of research.
The first research that became a reference is an
international journals title Munich Personal RePEc
Archive Paper year 2015 by William Doerner and
Keith Ihlanfeldt, title “An Empirical Analysis of the
Property Tax Appeals Process”. This paper
investigates the efficiency and equity of the property
tax appeals process. Regarding the efficiency of
correcting assessment error, reductions are granted
for a majority of appealing homeowners who are
overassessed but also for homeowners who are not
overassessed, leaving them under-assessed.
The secondary research that became a reference
is in an international journal entitled Munich
Personal RePEc Archive Paper year 2014 by
William Doerner and Keith Ihlanfeldt, title “ The
Role of Representative Agents in the Property Tax
Appeals Process”. This paper describes property tax
appeals to challenge their assessments and reduce
their property tax bill. Appeals are frequently filed
not by the homeowner but by a representative.
Appeals using representatives have a more
significant presence in higher-priced
neighbourhoods, which makes these homeowners
more likely to appeal than those in lower-priced
neighbourhoods.
The third research that became a reference is in
an international journal entitled Real Estate Finance
year 2014 by Johnathan P. Tomes and Richard D.
Dvorak, the title “Appeals Once and for All: In the
Matter of the Protest of Lyerla, Kathy L”. This paper
describes a recent Kansas tax case for property tax
appeals. The taxpayers believe that the assessment
on their commercial property is too high, so they
hire a tax consultant to represent them through the
property tax appeal process. The complexity of the
tax appeal process makes it virtually impossible to
represent oneself.
The fourth research that became a reference is
in an international journal entitled Journal of
property tax assessment & administration year 2017
by Michael Brady and Richard L. Sanderson, AAS,
title “The Current Environment of Online
Assessment Appeal Systems”. This paper describes
the current environment of online assessment appeal
(OAA) systems that identified as having been
implemented by assessment jurisdictions in the
United States or Canada for real property
assessments or in 2015 or earlier.
These papers offer insights on factors that effects
reduction adjustment. In the present study,
researchers tried to analyse the application of the
ease of administration principle and constraints of
Analysis of the Application of the Ease of Administration Principle in the Property Tax Reduction Procedure in the Fourth Industrial
Revolution: Case Study Personal Tax Payer
493

property tax reduction procedure in the fourth
industrial revolution - Case Study Personal Tax
Payer.
3 RESEARCH QUESTION
To determine the application of the ease of
administration in the application of property tax
reduction procedure in the fourth industrial
revolution case study personal taxpayer as stipulated
in Law No. 28 in 2009 on local tax and regional
retribution and regulation of the governor of the
provincial district exclusive Capital Jakarta No. 211
in 2012 on land tax rural and urban building
reduction.
4 RESEARCH DESIGN
4.1 Research Approaches
The author chose a quantitative approach in
analysing the implementation of the ease of
administration in the application of the property tax
reduction procedure in the fourth industrial
revolution. The research subject is the ease of
administration in the Indonesian taxation system.
While the object of research is the reduction of the
property tax as stipulated in the Law No. 28 in 2009
on local tax and regional retribution and regulation
of the governor of the provincial district exclusive
Capital Jakarta No. 211 in 2012 on land tax rural and
urban building reduction.
4.2 Types of Research
Types of research are differentiated by purpose, time
dimensions, benefits and data collection techniques.
1. Types of research by purpose
This research is descriptive research. The purpose of
using descriptive research is to describe the extent to
which the ease of administration is implemented in
the application for property tax reduction procedure
as set forth in the Law No. 28 in 2009 on local tax
and regional retribution and regulation of the
governor of the provincial district exclusive Capital
Jakarta No. 211 in 2012 on land tax rural and urban
building reduction. This research is classified as case
studies. Researchers analysed the underlying
implementation of the ease of administration of Mr
X’s property tax reduction.
2. Types of research based on the time dimension
This research included cross-sectional research
because it was implemented at a specific time from
2016 to 2018 and not carried out subsequent studies
to be compared.
3. Types of research-based benefits
The research is based on its benefits belonging to the
pure research category.
4. Types of research based on Data collection
techniques
Based on data collection techniques, this study uses
qualitative data collection techniques. Researchers
use literature studies and in-depth interviews in
conducting research.
4.3 Data Analysis Techniques
The data analysis technique used by the authors in
this research is a qualitative data analysis technique.
The authors will conduct data analysis of the
interviews and search for related data in the field to
analyse the implementation of the ease of
administration in the application of the property tax
reduction procedure.
4.4 Speaker/Informant
Mr X filed a property tax reduction from 2016 to
2018 in the Regional Tax and Retribution Agency of
South Jakarta regional administration.
4.5 Site Research
Research Site in South Jakarta Regional Tax and
Retribution Agency.
4.6 Research Constraints1
This research saw only the fulfilment of the ease of
administration elements in the application of
property tax reduction procedure Mr X from 2016 to
2018 in South Jakarta central city area.
5 RESULTS
5.1 Description of Topic
The property tax reduction can be given to taxpayers
because of certain tax object conditions that have to
do with the subject of tax and/or due to specific
other causes; and/or the condition of the tax object is
ICVHE 2019 - The International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE) “Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable
4.0 Industry”
494

exposed to natural disasters or other extraordinary
causes.
Certain tax object conditions that have to do with
the subject tax and/or due to specific other causes
are given a reduction to the individual taxpayers,
among others:
1. The object of tax that is an individual taxpayer of
veteran independence fighters, veterans defenders of
Independence, the recipient of the mark of the
service of guerrilla stars, or his widow/widower;
2. The object of tax that is an individual taxpayer of
the former president and the vice president and
former governor and deputy governor or his
widow/widower;
3. The object of tax that is an individual taxpayer of
private persons whose income is solely from retirees
so that the obligations of property tax are difficult to
fulfil;
4. The object of tax that is an individual taxpayer
who is low-income so that the property tax is
difficult to fulfil; or
5. The object of tax that is an individual taxpayer
who is low-income Sales Value of Taxable Object is
increased due to environmental change and positive
impact of development.
The property tax reduction is given to corporate
taxpayer who suffered liquidity losses and
difficulties in the previous tax year so that they
could not fulfil routine obligations. Natural disasters
are natural disasters resulting from events or a series
of events caused by nature, such as earthquakes,
tsunamis, volcanic eruptions, floods, droughts,
cyclone angina and/or landslides. Other remarkable
reasons include fire, crop outbreak and/or crop pests.
The property tax reduction can be given based on
the notification of tax due and/or the property tax
listed in the tax underpayment assessment letter.
Reductions can be administered at the highest of
50% (fifty) percent of the property tax owed.
Reductions can be provided on a taxpayer’s request
and may be individually or collectively filed.
The request for a reduction submitted
individually must meet the formal requirements:
1. 1 (one) application for 1 (one) notification of tax
due or tax underpayment assessment letter;
2. Submitted in writing in Bahasa Indonesia, stating
the magnitude of the percentage of reduction
requested by the apparent reason;
3. Submitted to the head of Regional Tax and
Retribution Agency;
4. Photocopy of notification of tax due or tax
underpayment assessment letter for reduction;
5. The taxpayer signs the application letter, and in
case the application letter signed by non-taxpayer
shall be attached with a unique authorisation letter;
6. Filed within the timeframe:
a. 3 (three) months from the date of
receipt of notification of tax due;
b. 1 (one) months is not counted as from
the date of receipt of the tax
underpayment assessment letter;
c. 1 (one) month from the date of receipt
of the objection decision letter;
d. 3 (three) months from the date of the
occurrence of natural disasters; or
e. 3 (three) months after the date of the
occurrence extraordinary cause, except
where the taxpayer may indicate that
within that period cannot be fulfilled
due to circumstances beyond its
control.
7. Have not had the arrears of the property tax year
earlier over the object of tax that is subject to
reductions, except if tax objects are exposed to
natural disasters or other extraordinary causes; or
8. For notification of tax due or tax underpayment
assessment letter the petitioned reduction has not
filed an objection, or in the event filed objection has
been issued the decision letter objection and upon
the decision, letter objection has not filed an appeal.
A reduction request that does not meet the formal
requirements is considered not an application so that
it cannot be considered. If a reduction request cannot
be considered, the head of Regional Tax and
Retribution Agency within 10 (ten) working days
from the date of the application is received, shall
provide an answer in writing by notifying the
deficiency of the terms and the underlying reasons.
Taxpayers can still apply for a reduction in return
throughout meeting requirements.
The property tax individual reduction application
in addition to fulfilling the formal requirements also
meets the following requirements:
Application for individual reductions:
1. Taxpayer independence fighter veteran,
independence defender veteran, recipient of the
service mark of the guerrilla star or his
widow/state, former president and vice
president and former governor and deputy
governor or his widow/widower:
a. Photocopy of identification card
number;
Analysis of the Application of the Ease of Administration Principle in the Property Tax Reduction Procedure in the Fourth Industrial
Revolution: Case Study Personal Tax Payer
495
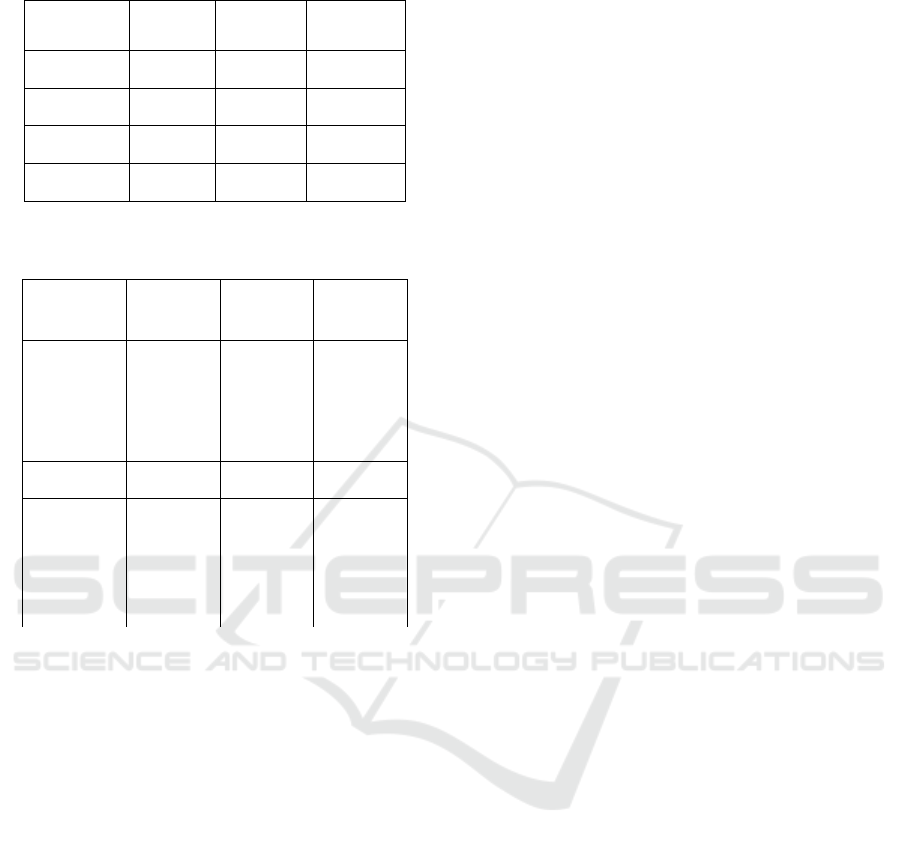
Table 2: Mr. X’s Notice of Land and Building Tax
Payable.
Yea
r
2016 2017 2018
(Rp) (Rp) (Rp)
Due of
Notice
11 Jan
2016
9 Jan
2017
4 April
2018
Due Date
31 Aug
2016
31 Aug
2017
14 Sept
2018
Application
Date
March
2016
23 March
2017
24 May
2018
Date of
Decision
14 Juni
2016
7 Aug
2017
4 Sept
2018
Table 3: The Amount of Land and Building Tax Payable
after Reduction.
Yea
r
2016 2017 2018
(Rp) (Rp) (Rp)
Rural and
Urban Land
and
Building
Tax
16.589.634 16.589.634 18.833.154
Amount of
reduction
1.658.963 1.658.963 1.883.315
Rural and
Urban Land
and
Building
Tax
after
reduction
14.930.671 14.930.671 16.949.839
b. Photocopy of a veteran member card;
c. Photocopy of a decree on the
acknowledgement, endorsement and
award of Honorary degree of a
competent officer;
d. Photocopy of Decree of appointment or
termination as President and vice
president, Governor and Deputy
governor;
e. Photocopy of the death certificate; and
f. Photocopy of property tax settlement
of the previous year.
2. Individual taxpayers whose income is solely
from retirees so that the property tax obligations
are difficult to fulfil:
a. Photocopy of identification card
number;
b. Photocopy of the family card;
c. Photocopy of pension decree;
d. Photocopy of pension slip or other
similar documents;
e. Photocopy of electricity bills, water
and/or telephone; and
f. Photocopy of property tax payment of
the previous tax year.
3. Individual taxpayers who are low-income so
that the obligations of property tax are difficult
to fulfil :
a. Photocopy of identification card
number;
b. Photocopy of the family card;
c. A taxpayer’s statement letter stating
that the taxpayer’s income is low from
the place of work, if the taxpayer is not
equipped with statement letter, a
certificate of RT/RW and known to the
local Lurah; and
d. Photocopy of property tax payment of
the previous tax year.
4. The taxpayer of a low-income personal person
whose Sales Value of Taxable Object per meter
increases due to environmental changes and the
positive impact of development:
a. Photocopy of identification card
number;
b. Photocopy of the family card;
c. A taxpayer’s statement letter stating
that the taxpayer’s income is low from
the place of work;
d. Photocopy notification of tax due the
year before;
e. Photocopy of property tax payment
previous tax year;
f. Photocopy of electricity bills, water
and/or telephone accounts; and
g. Letter from Lurah that explains the
existence of physical development by
the government of the central/regional
or commercial development that has an
impact on environmental change and
the positive impact of development.
In case the taxpayer does not attach the
document, the taxpayer’s application remains
processed as long as the formal requirements are
met.
Based on the application equipped with the
requirements, the head of Regional Tax and
Retribution Agency conducts administrative
research and if necessary, can be continued with
field research. The head of Regional Tax and
Retribution Agency within the term 6 (six) months
from the date of receipt of the reduction request,
shall give a decision on the application of reduction.
If the term has been exceeded and the decision has
not been issued, the reduction application shall be
deemed granted and further issued the decision in
ICVHE 2019 - The International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE) “Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable
4.0 Industry”
496

accordance with the taxpayer application in at least 1
(one) month since the term expires.
Discussion
Mr X applied for a reduction of property tax
from 2016 until 2018. Mr X submitted his own
application without the help of a tax consultant. Mr
X applied individually for a reason for a personal
taxpayer whose income was solely from retirees so
that the property tax obligations are difficult to fulfil.
In connection with the property tax reduction
application conducted by Mr X from 2016 to 2018,
there are 3 (three) main factors used to measure the
ease of administration, namely certainty (certainty)
in terms of the law, the efficiency of the time and
cost, and the simplicity of the taxation system and
the tax laws concerned.
1. Legal certainty
According to Mansury (2000, 12), The principle of
legal certainty is associated with 3 (three) tax
questions. It should be confident, who should be
taxed, what is the basis for taxing the tax subject,
and how much to pay based on the provisions on the
tax rate.
a. Who should be taxed
The certainty in determining who has the right to
apply for property tax reduction will affect justice.
Details on the subject refer to the section on the
application of property tax reduction, namely article
2 paragraph (1) of the Regulation of the Governor of
the provincial district exclusive Capital Jakarta No.
211 in 2012. Where in this article described the
subject that is entitled to apply for property tax
reduction is taxpayers due to certain conditions of
tax objects that have to do with the subject of tax
and/or due to specific other causes; and/or the
condition of the tax object is exposed to natural
disasters or other extraordinary causes. In article 2
paragraph (2), paragraph (3) and paragraph (4) of the
Regulation of the Governor of the provincial district
particular Capital Jakarta No. 211 in 2012 describe
what is meant by the condition of particular tax
objects that have to do with the subject of tax,
natural disasters and other remarkable reasons.
b. What is the basis for taxing the tax subject
The certainty in the essential determination to apply
for a property tax reduction refers to article 3 of the
Regulation of the Governor of the provincial district
exclusive Capital Jakarta No. 211 in 2012. Where in
this article is described the reduction awarded on the
property tax listed in the notification of tax due?
c. How much to pay based on the provisions on
the tax rate
The certainty in the determination of the number of
reductions in property tax refers to article 4
Regulation of the Governor of the provincial district
special Capital Jakarta No. 211 in 2012. Where in
this article explained reductions could be given as
large as 50% (fifty percent) of the property tax being
owed. However, for the property tax reduction
governments do not provide a specific benchmark
regarding the taxpayer’s criteria worthy of obtaining
a property tax reduction.
Here is an overview of fulfilling the fundamental
fulfilment certainty of each indicator and sub-
indicators:
Table 4: Basic Fulfillment of Certainty.
No. Indicato
r
Fulfilment Status
1 Certainty in determining
who should be taxed
Have been
fulfilled
2 Certainty in determining
what is the basis for taxing
the tax subjec
t
Have been
fulfilled
3 Certainty in determining
how much to pay
Not been fulfilled
2. Efficiency in time and cost
In connection with the property tax reduction
application, the implementation of the principle of
efficiency will determine how much it should be
incurred by the applicant’s taxpayer to obtain a
reduction for property tax. According to Rosdiana
(2012, 177), measurement of efficiency in taxation
administration can be seen from fiscal cost and time
cost. The fiscal cost, associated with the property tax
deductible application, is a cost that can be measured
by monetary value or nominal rupiah which must be
issued by the applicant taxpayer at the start of the
property tax reduction application, which can be
grouped as follows:
a. Consulting services that are hired taxpayers
who conduct assistance in managing the
property tax reduction application.
b. The transportation cost of application
management. Of property tax reduction
c. The printing fees and reproduction of
application form for property tax reduction.
As for time cost, which is the cost of intangible,
which can be the following:
Analysis of the Application of the Ease of Administration Principle in the Property Tax Reduction Procedure in the Fourth Industrial
Revolution: Case Study Personal Tax Payer
497

a. The time required to fill in the application
forms for property tax reduction.
b. The time required to discuss the tax
management and tax exposure with the tax
consultant related to property tax reduction
application.
c. The time required to wait for a decision
regarding property tax reduction application.
Here is an in-depth interview was done to Mr X for
fiscal cost and time cost.
Fiscal Cost
The fiscal fee issued by the applicant’s taxpayer has
fulfilled the efficiency.
a. A taxpayer hired tax consulting services to
conduct assistance in managing the property
tax reduction application. The cost required to
take care of property tax reduction applications
has been efficient because taxpayer applicants
do not use consulting services in managing the
property tax reduction application. It happened
because Mr X felt that the property tax
reduction application could still be handled by
himself.
b. The transportation cost of application
management of property tax reduction was
discussed. In the early stages of application of
the property tax reduction taxpayer submits the
application to Regional Tax and Retribution
Agency Cilandak office. Property tax reduction
in application management transportation costs
has been efficient due to the distance of Mr X’s
house with Cilandak Office only about 1 (one)
km.
c. Printing fees and reproduction of application
forms for property tax reduction were
determined. Referring to the regulation of the
governor of the provincial district exclusive
Capital Jakarta number 211 in 2012, eight
documents must be attached by the applicant’s
taxpayer so that the application document for
property tax reduction can be categorised as
complete. The attached documents are:
a. Photocopy of notification of tax due
b. Photocopy of identification card number;
c. Photocopy of the family card;
d. Photocopy of pension decree;
e. Photocopy of pension slip or other similar
documents;
f. Photocopy of electricity bills, water
and/or telephone accounts; and
g. Photocopy of property tax payment of the
previous tax year.
Taxpayers acknowledge that to fulfil and
complement the above data has been
streamlined because Regional Tax and
Retribution Agency only requires 1 (one)
Single document of attachment.
Time Cost
The time charge issued by the applicant taxpayer has
been efficient.
a. The time required to fill in the application
forms for property tax reduction has been
streamlined due to the application form
consisting of only 1 (one) sheet.
b. The time required to discuss tax management
and tax exposure with the tax consultant has
been efficient because the applicant’s taxpayer
does not use the tax consulting services in
managing the property tax reduction request. It
happened because Mr X felt that the property
tax subtraction application could still be
handled by himself.
c. The time required to wait for a decision
regarding property tax reduction request has
been efficient due to the application year 2016
is 106 days, in 2017 in 160 days and 2018 is
104 days. It is decided within less than 6 (six)
months from the date of receipt of the property
tax reduction.
Here is a summary of the essential fulfilment
efficiency of each indicator and sub-indicators:
Table 5: Basic Fulfillment of Efficiency
No. Indicato
r
Fulfilment Status
1 A taxpayer hired tax consulting
service to conducts assistance
in managing the property tax
reduction application
Have been
fulfilled
2 Application management for
property tax reduction fee
Have been
fulfilled
3 The cost of printing and
reproduction of application
forms for property tax
reduction
Have been
fulfilled
4 The time required to fill in the
application forms for property
tax reduction
Have been
fulfilled
5 The time to discuss tax
management and tax exposure
with tax consultants relating to
property tax reduction
applications
Have been
fulfilled
6 The time required to wait for a
decision regarding property tax
reduction application
Have been
fulfilled
ICVHE 2019 - The International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE) “Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable
4.0 Industry”
498
2. The simplicity of the taxation system
The vital issue in the arrangement of taxation
regulations and legislation is simplicity. Mansury
(2000, 23) argues that the simplicity in the
arrangement of regulation will facilitate the
understanding of the regulation and give rise to
alignment and not deviate with higher regulations.
a. The simplicity of the Regulation of the
Governor of the provincial district exclusive
Capital Jakarta No. 211 in 2012 provides an
easy understanding of the regulations.
The formulation of the Regulation of the Governor
of the provincial district exclusive Capital Jakarta
No. 211 in 2012 has given the ease of understanding
for taxpayer applicant to apply for property tax
reduction. This rule explains clearly the condition of
the object that can be granted property tax reduction.
So taxpayers can know if it can or cannot apply for a
property tax reduction. The regulation also explains
the formal requirements and materials that must be
met in filing a property tax reduction petition. With
the fulfilment of formal requirements and materials
explained in the regulation that the head of Regional
Tax and Retribution Agency within a period of 6
(six) months must give a decision to petition the
property tax reduction.
b. Position of Regulation of the Governor of the
provincial district exclusive Capital Jakarta No.
211 in 2012 against higher regulation.
When viewing from a hierarchy of regulations
governing property tax reduction, Law No. 28 on
local tax and regional retribution, Local Regulation
No. 6 in 2010 on general regional tax provisions and
Local Regulations No. 16 in 2011 on land tax on the
rural and urban building is a legal umbrella of the
Regulation of the Governor of the provincial district
exclusive Capital Jakarta No. 211 in 2012 on land
tax rural and urban building reduction. However, as
these regulations only govern widely and publicly
regarding the reduction of tax-deductible taxes, the
government publishes lower rules in its hierarchical
structure. However, it regulates more detail and
clarity on the provision of property tax reduction
such as Regulation of the Governor of the provincial
district exclusive Capital Jakarta No. 211 in 2012.
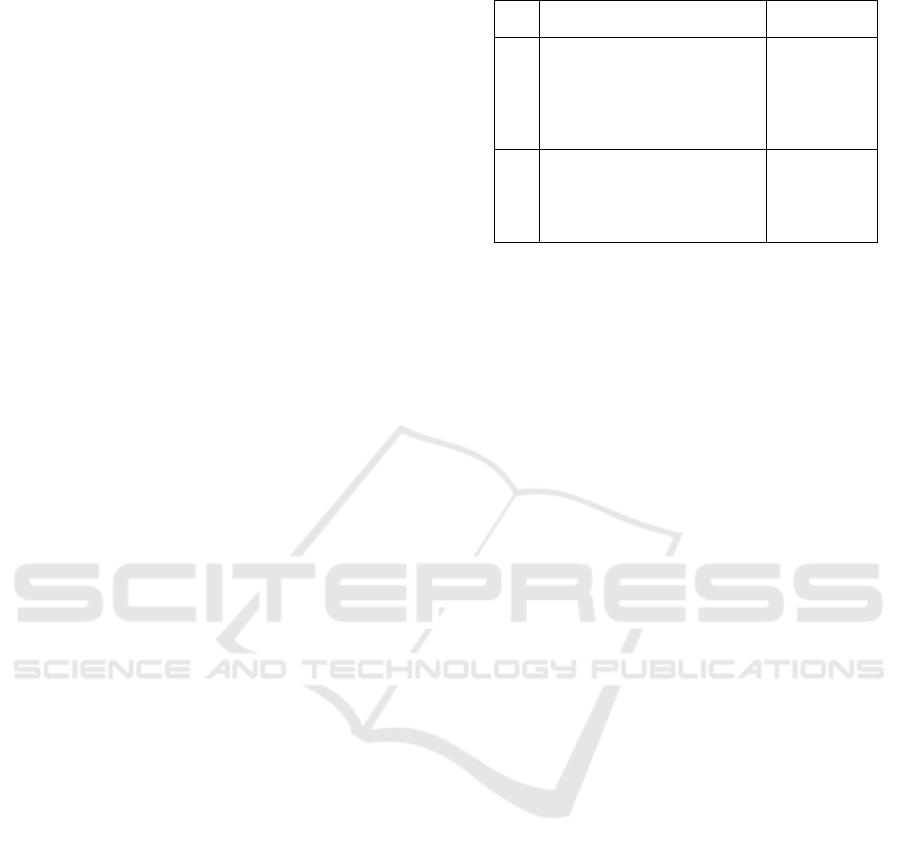
Here is a summary of the essential fulfilment
simplicity of each indicator and sub-indicators:
Table 6: Basic Fulfillment of Simplicity
No. Indicator Fulfilment
Status
1 The simplicity of the regulation
of the governor of the
provincial district exclusive
Capital Jakarta number 211 in
2012 in providing ease in
understanding the regulation
Have been
fulfilled
2 The position of regulation of
the governor of the provincial
district exclusive Capital
Jakarta number 211 in 2012 in
higher regulation
Have been
fulfilled
6 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the research that has been conducted, the
conclusion that the researcher obtained, among
others: The applying principle of certainty legally in
the application of the property tax reduction
procedure has not been fully fulfilled. This is due to
the certainty in determining how much to pay has
not been fulfilled. The applying principle of
efficiency is fully fulfilled by both fiscal and cost
time. Moreover, the applying principle of simplicity
has been fully fulfilled in terms of simplicity of
regulation and position of Regulation of the
Governor of the provincial district exclusive Capital
Jakarta No. 211 in 2012.
7 ADVICE
Here are some of the things that governments can do
to address the obstacles that the application of
property tax reduction face:
To provide standardisation regarding taxpayer
criteria for the application of property tax reduction
and to apply Online Assessment Appeal Systems
(OAA) to facilitate the application of property tax
reduction.
REFERENCES
Doerner, W., & Ihlanfeldt, K. 2014. An empirical analysis
of the property tax appeals process. Retrieved from
https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/61035
Doerner, W., & Ihlanfeldt, K. 2014. The role of
representative agents in the property tax appeals
process. Retrieved from https://mpra.ub.uni-
muenchen.de/id/eprint/61019
Analysis of the Application of the Ease of Administration Principle in the Property Tax Reduction Procedure in the Fourth Industrial
Revolution: Case Study Personal Tax Payer
499

Johanthan P. Tomes and Richard D. Dvorak. 2014.
Appeals Once and for All: In the Matter of the Protest
of Lyerla, Kathy L
Law No. 28 on local tax and regional retribution
Local Regulations No. 6 year 2010 on general regional tax
provisions
Local Regulations No. 16 year 2011 on land tax on rural
and urban building
Michael Brady and Richard L. Sanderson. (2017). The
Current Environment of Online Assessment Appeal
Systems. Retrieved from
https://researchexchange.iaao.org/jptaa/vol14/iss2/2/
Mansury, R. 2000. Kebijakan Perpajakan. Jakarta:
Yayasan Pengembangan dan Penyebaran Pengetahuan
Regulation of the Governor of the provincial district
special Capital Jakarta No. 211 year 2012 on land tax
and urban building reduction
Regulation of the Governor of the provincial district
special Capital Jakarta No. 24 year 2018 on the
Determination of Sale Value of Land and Rural and
Urban Land Tax Objects in 201
Rosdiana, Haula dan Edi Slamet Irianto. 2012. Pengantar
Ilmu Pajak: Kebijakan dan Implementasi di Indonesia
(Edisi Pertama). Jakarta: Rajawali Pers
ICVHE 2019 - The International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE) “Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable
4.0 Industry”
500
