
Insurance Agents in Indonesia in the Era of Industrial Revolution 4.0
Fia Fridayanti Adam
Vocational Education Program, Universitas Indonesia, Indonesia
Keywords: General insurance, distribution channel, insurance agents, competency
Abstract: In the current era of industrial revolution 4.0, insurance companies can sell insurance products by
combining their distribution channels. This distribution channel includes through the internet or website,
direct sales by companies, bank assurance, and sales through agents. For motor vehicle insurance, data in
2018 shows that only nine general insurance companies provide online applications to purchase motor
vehicle insurance products which indicate that the utilization of the company’s official website is not
optimal. In general, insurance companies still rely on agents as marketers of their products. To improve the
ability of agents, insurance agents must be competent. For this reason, insurance agents must take the
certification exam held by the Indonesian General Insurance Association (AAUI). This study aims to
provide an overview of general insurance agents in Indonesia that have been certified. Data sourced from
the Financial Services Authority (OJK) and AAUI shows that there are still many general insurance agents
that have not met these competencies. To make it easier for insurance agents to take a certification exam,
AAUI has issued an e-certificate.
1 INTRODUCTION
At present, the world is facing a 4.0 industrial
revolution. In this era, there was a massive change in
all fields. Changes that occur are not only digital
changes, but also there are developments in
innovations that are rapidly spreading and the
emergence of platforms that can unite several fields
at once as stated by Roblek et al., (2016) that the era
of industrial revolution 4.0 is characterized by the
process of digitization and automation, and the use
of electronic devices and information technology in
the process of making and servicing a product. The
world of insurance is also not spared from the 4.0
industrial revolution. Eling and Lehmann (2018)
analyzed what technologies affect the insurance
sector. While in Klapkiv and Kalpkiv (2017) stated
that the main factors that determine the emergence
of new technologies in the insurance sector are
asymmetry information, increasingly fierce
competition, changing generations and social norms,
growth of technology and computer capabilities,
economic crisis and reduced premiums insurance.
The insurance industry in Indonesia is growing
every year. In Rahim (2013), the results of the
analysis of various data and predictions of the
growth of the insurance industry explained that the
insurance industry in Indonesia is experiencing a
significant development from year to year. However,
the industry must be improved because the
penetration is still low. Given the size of Indonesia’s
population, the insurance market in Indonesia is still
quite large. So that many efforts have been made to
increase the number of insurance participants in
Indonesia.
In general, the efforts made by insurance
companies to increase the number of customers are
carried out through distribution channels. In Dumm,
R. E., & Hoyt, R. E. (2003) described a variety of
distribution channels commonly used to increase
insurance sales, namely distribution channels carried
out by companies themselves, agents, banks, and the
internet. In this industrial revolution era 4.0, the
distribution channel that is more widely used is the
internet. However, in the study of Adam and
Hikmah (2018), it was found that only nine general
insurance companies in Indonesia provided online
applications to purchase motor vehicle insurance
products. This condition shows that the utilization of
the company’s official website in Indonesia is not
optimal. Many general insurance companies choose
to use other distribution channels, especially using
insurance agents. Insurance agents can be called the
spearhead of insurance marketing. In deciding
Fridayanti Adam, F.
Insurance Agents in Indonesia in the Era of Industrial Revolution 4.0.
DOI: 10.5220/0010674100002967
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE 2019) - Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable 4.0 Industry, pages 277-282
ISBN: 978-989-758-530-2; ISSN: 2184-9870
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
277

insurance sales to prospective customers or their
customers representing insurance companies. Those
who know, serve, and master customer portfolios.
For example, insurance agents that insurance
products for the market motor vehicle. They must be
able to explain the definition of motor vehicle
insurance, the type of motor vehicle insurance
coverage, how benefits will be received, and others.
By definition, insurance agents are
entrepreneurs who carry out agency activities under
the agency contract stated by the insurance company
and included in the insurance agent list (Andrzej,
2015). Besides, insurance agents must be
professional. The study conducted by Tseng et al.,
(2016) states the extent to which the attitude of
insurance agents in recommending an inappropriate
insurance product can increase sales of insurance
products that do not meet customer needs.
Meanwhile, the era of the industrial revolution
4.0 despite having many opportunities, also further
complicates the problem of competition. This fact is
because organizations no longer compete with local
brands; instead, they compete with brands from all
over the world. This situation means that every
organization must be prepared, not only to build its
business with global standards but also to try to
outperform the global competition. To be able to
achieve success, the industry focuses on people who
have a higher level of individual competence
(Amodu et al., 2017). Similarly, the insurance agent
profession, in addition to being a professional, the
insurance agent must also be competent or certified.
Like the insurance industry, insurance agents are
also divided into general insurance agents and life
insurance agents.
OJK Regulation Number 69 / POJK.05 / 2016 /
states that insurance agents must be registered with
OJK and have agency certificates following their
business fields. While based on Law No. 40 of 2014
concerning insurance states that OJK gives authority
to associations to certify agency, AAUI as the
association that oversees general insurance in
Indonesia, has taken several steps to improve the
competence of general insurance agents in
Indonesia. This study will provide an overview, the
extent to which general insurance agents fulfil these
requirements and what efforts are made by AAUI to
increase the number of certified general insurance
agents.
2 LITERATURE STUDY
2.1 Definition of Insurance
Based on Law No. 40 of 2014 concerning Insurance,
insurance is an agreement between two parties,
namely an insurance company and policyholder,
which is the basis for receiving premiums by
insurance companies in return for:
a. Provide replacement to the insured or
policyholder due to losses, damages, costs incurred,
loss of profits, or legal liability to third parties. They
may be suffered by the insured or policyholder due
to an uncertain event, or provide payments based on
the death of the insured or payment. Based on the
life of the insured, the benefit of the amount
determined and /or based on the results of the
management of funds.
The above definition implies that there are two types
of insurance, namely life insurance and general
insurance. Life Insurance Business is a business that
carries out risk management services that provide
payments to policyholders, insured, or other parties
who are entitled in the event the insured dies or
remains alive, or other payments to policyholders,
insured, or other parties entitled at certain times
regulated in the agreement, the amount of which has
been determined and/or based on the results of the
management of funds. While the General Insurance
Business is a risk insurance service business that
provides compensation to the insured or
policyholder due to losses, damages, costs incurred,
loss of profits, or legal responsibility to third parties
that may be suffered by the insured or policyholder
due to an uncertain event. Ayat (2012) states that in
general insurance there are 13 types of insurance
products commonly marketed, namely insurance
transportation, ship frame insurance, shipbuilding
insurance, property insurance, motor vehicle
insurance, guarantee insurance, various insurance,
engineering insurance, satellite insurance, aviation
insurance, energy insurance, credit insurance, and
liability insurance.
2.2 Definition of Insurance Agents
All types of general insurance products require a
marketing process to reach consumers. In marketing
terms, it is known as a distribution channel, which is
a path that must be traversed by the flow of goods
from producers to agents or intermediaries or large
traders to users, in this case consumers. Distribution
channels can be also defined as marketing channels
or market channels. A distribution channel is a group
ICVHE 2019 - The International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE) “Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable
4.0 Industry”
278

of dependent on each other organization units, which
are taking part in process of flow of products or
services form producers to buyers (Szopa and
Pękała, 2012).
In Dumm, R. E., & Hoyt, R. E. (2003)
described a variety of distribution channels
commonly used to increase insurance sales, namely
distribution channels carried out by companies
themselves, agents, banks, and the internet. If
marketing is carried out by the insurance company
itself, whether through company sales staff, home
service agents, or the internet, the sales are
categorized as direct marketing channels.
Conversely, if marketing is done by agents, brokers,
or banks, it is called an indirect marketing channel.
From various known distribution channels,
insurance agents play an essential role in insurance
sales. According to Law No. 40 of 2014, insurance
agents are people who work alone or work for a
business entity, who act for and on behalf of an
Insurance Company or Sharia Insurance Company
and fulfill the requirements to represent an Insurance
Company or Sharia Insurance Company to market
insurance products or products sharia insurance.
In addition, an insurance agent is an agent
engaged for an insurance company based on the
requirements specified by the insurance company
where the insurance agent works. Furthermore, it
can be found in the Financial Services Authority
Regulation Number 23 / POJK.05 / 2015 concerning
Insurance Products and Insurance Product Marketing
Article 45 said that “Insurance companies can only
market insurance products through marketing
channels, one of which is mentioned by insurance
agents, which meet the provisions statutory
regulations regarding insurance agents “. Along with
the task of the agent as a liaison between the insured
and the insurer, then in this case the agent is also
required to recognize an insurance company where
the insurance agent works which aims to provide
information to the insurer that will be obtained from
having an insurance product based on the premium
amount paid by the insured. Insurance agents can
also be intermediaries between the insured party and
the insurer to make insurance premium payments
and also the process of filing claims against
insurance customers who experience a loss as stated
in the insurance policy. To become an insurance
agent who carries out work as a liaison between the
insured party and the guarantor, it must go through
procedures that have been determined by the
insurance company.
According to the Financial Services Authority
Regulation Number 69 / POJK.05 / 2016, individual
insurance agents and Legal Entity insurance agents
can conduct agency cooperation with 1 (one)
General Insurance Company, 1 (one) Islamic
General Insurance Company, 1 (one) Insurance
Company Life and 1 (one) Sharia Life Insurance
Company. Thus, Insurance Agents are prohibited
from conducting agency cooperation with more than
similar Insurance Companies. To be able to carry out
consultancy activities on insurance needs and / or
mediation of insurance closure to prospective
policyholders and to be able to place insurance with
insurance companies according to the needs of
prospective policyholders, a Legal Insurance agent
can apply for a business license as an Insurance
Brokerage Company.
Every insurance agent must be registered with
the Financial Services Authority (OJK) and must
have sufficient knowledge and ability and have a
good reputation. According to Article 31 of Law No.
40 of 2014 Insurance Agents, Insurance Brokers,
Reinsurance Brokers, and Insurance Companies are
required to apply all their expertise, attention, and
accuracy in serving or transacting with
Policyholders, Insured, or Participants. In other
words, an insurance agent must have good
competence in carrying out their work or in other
words, a right insurance agent is a certified agent.
2.3 Definition of AAUI
AAUI or the Indonesian General Insurance
Association is a forum where general insurance
companies work together in the same vision and
mission, with one of its functions being a forum for
unity and deliberation for the benefit of the general
insurance industry. In article 68 of Law No. 40 of
2014, each insurance company is required to become
a member of one of the insurance business
associations in accordance with the type of business.
For general insurance companies, the association in
question is AAUI.
As seen on its website, www.aaui.or.id, AAUI
currently has 84 members, consisting of general
insurance / loss companies and reinsurance
companies (78 Insurance Companies & 6 reinsurance
companies), and 27 branches spread throughout the
region. in Indonesia. AAUI is an organization that
runs all of its business in a non-profit nature and by
always adhering to all applicable legal provisions.
AAUI’s financial resources originate from
membership fees consisting of base fees for new
members and annual contributions consisting of basic
contributions and tiered contributions from AAUI
members whose amount is stipulated in the general
Insurance Agents in Indonesia in the Era of Industrial Revolution 4.0
279
meeting of members, other legitimate businesses and
receipts that are not contrary to the intent and the
purpose of AAUI.
3 DATA AND METHODS
This research is a descriptive study that provides an
overview of how many general insurance agents
meet the competency standards set by AAUI.
Secondary data is obtained from OJK through
www.ojk.go.id , from AAUI at www.aaui.or.id, and
the results of written interviews with AAUI
administrators. The object of research is the number
of general insurance agents working to market
general insurance products in all conventional
general insurance companies registered with the
OJK until 2019. The steps taken are:
1. Check the number of insurance companies in
Indonesia.
2. Check the number of general insurance agents in
Indonesia.
3. Check the number of certified general insurance
agents in Indonesia.
4. Explain the AAUI E-certification.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
As explained earlier, AAUI has 84 members,
consisting of 78 insurance companies and six
reinsurance companies. However, OJK data per May
2019 only has 75 general insurance companies and
six reinsurance companies registered. In general,
there are a total of 151 insurance companies,
including well-known insurance companies and
sharia. Table 1 below explains the number of
insurance firms in Indonesia based on data from the
Financial Services Authority of May 2019. Table 1
shows that insurance companies are divided into life
insurance companies, general insurance, reinsurance
companies, mandatory insurance, and social.
Table 1: Number of the insurance company in Indonesia.
Component May 2019 Total
Conventional
Sharia*
Insurance
139
13
151
Life Insurance
53
7
60
General
Insurance
75
5
80
Reinsurance
6
1
7
Mandatory
Insurance
3
-
3
Social
Insurance
(
BPJS
)
2
-
2
From Table 1, there are quite a several
insurance companies in Indonesia, so that the need
for insurance marketers or insurance agents,
including general insurance agents is still
substantial. Table 2 explains the number of general
insurance agents in Indonesia from 2013 to 2018
sourced from www.ojk.go.id.
Table 2: Number of Indonesian general insurance agents.
Year National
Compan
y
Joint
Venture
Total
2013 8131 11074 19205
2014 7016 17288 24304
2015 9336 6402 15738
2016 8874 7757 16631
2017 12011 6060 18071
2018 13435 5904 18529
From Table 2, it can be seen that the number of
general insurance agents in Indonesia fluctuated
from year to year, with a tendency to increase the
number of general insurance agents in Indonesia.
However, it is not seen whether the number of
agents mentioned is already certified or not. OJK
Regulation Number 69 / POJK.05 / 2016 / states that
insurance agents must be registered with OJK and
have agency certificates in accordance with their
business fields. While according to Law Number 40
of 2014 concerning Insurance states that OJK grants
authority to associations to carry out agency
certification, in this case the general insurance
agency certificate is issued by AAUI.
To get agency certification, AAUI holds
special exams for general insurance agents. Initially,
AAUI developed a certification system with a half-
ICVHE 2019 - The International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE) “Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable
4.0 Industry”
280
day workshop model with two main topics. The
prospective insurance market agents are crammed
with topics about insurance sales salesmanship and
the concept of risk management which covers the
principles of insurance. After the workshop, a
written test in the form of multiple-choice was held
with 100 questions in 60 minutes. The certification
is held once a month. More detailed information
about the number of insurance agents that have been
certified through the exam can be seen in the
following Table 3:
Table 3: Certified Agent.
Year Agent
2013 2351
2014 4900
2015 3556
2106 2396
2017 5948
2018 6838
When compared with the number of agents, as
shown in Table 2, until 2016, the number of certified
agents is still very small. In 2016, for example, only
around 12.5% of the agents had competency
certificates issued by AAUI. This shows that the
number of insurance agents who have the
certification is still lacking. But along with the
issuance of OJK Regulation Number 69 / POJK.05 /
2016 / which states that insurance agents must be
registered with the OJK and have an agency
certificate in accordance with their line of business,
in 2017 the number of certified agents becomes
5958 people, increasing by 3552 people. However,
when compared to the number of agents, only about
33% of agents are certified. To increase this number,
the AAUI issued a new strategy by utilizing
information technology.
In May 2018, AAUI issued a new scheme,
namely an E-certification or electronic-based
certification. Android-based E-certification platform
that can be downloaded at Google Playstore, so that
it can help agents to be able to carry out exams
anytime and anywhere as long as there is internet
access, the E-certification has also been equipped
with standardized material with the aim of insurance
agents being able to explain products that are offered
and understood general insurance principles and
products. In addition, this application is also
equipped with an exercise program so that agents
can carry out exam exercises before carrying out the
exam itself.
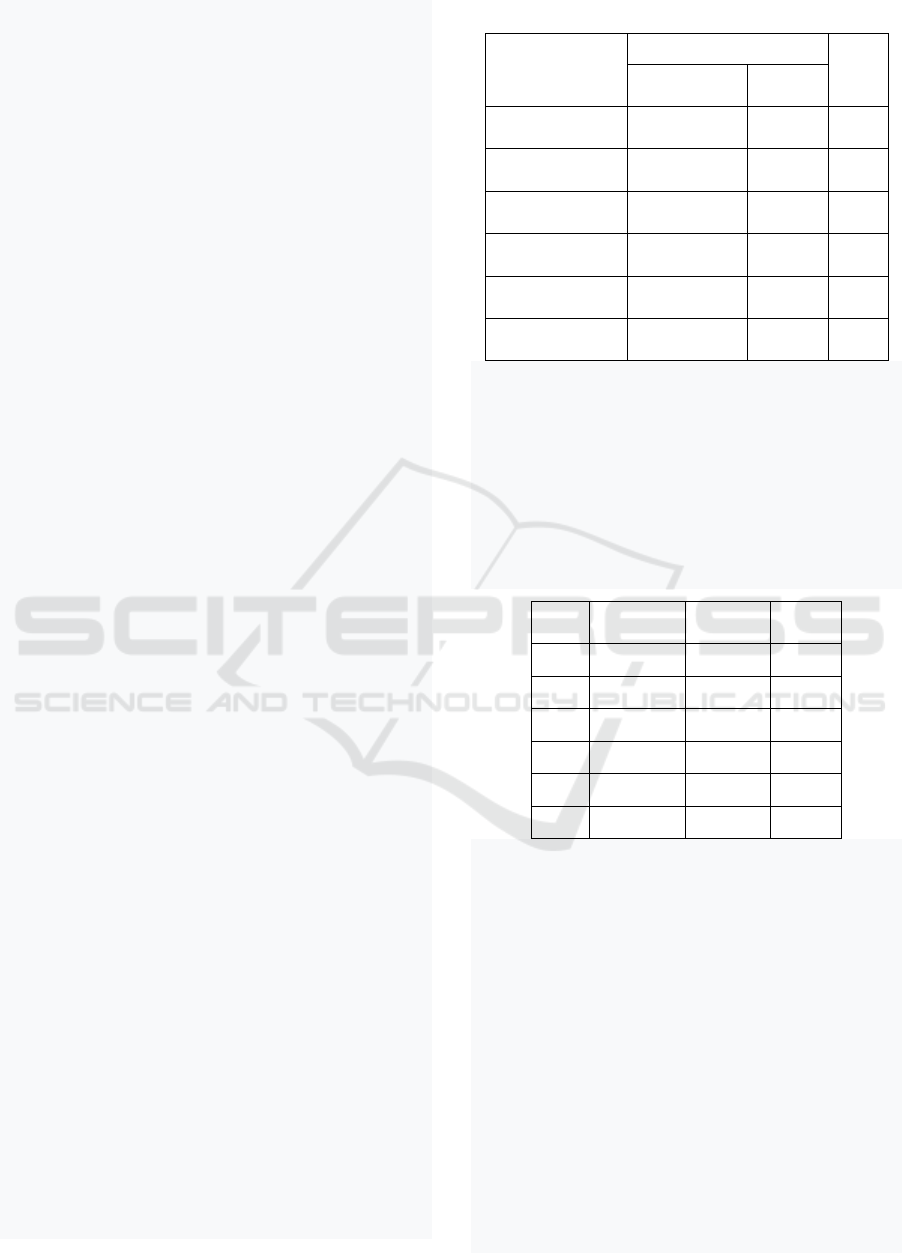
Figure 1: E-certification AAUI.
In Figure 1, you can see an e-certification
screenshot that includes test material and practice.
Materials include insurance law, insurance products,
risk recognition and insurance principles.
Prospective examinees can do the exercises before
taking the exam. Thus E certification is carried out
very effectively and efficiently without reducing the
quality of the agent.
Since the launch of the E-certification, the
number of certified agents in 2018 is 6,838, or there
has been an increase of 14.9%. In general, the
development of the number of certified general
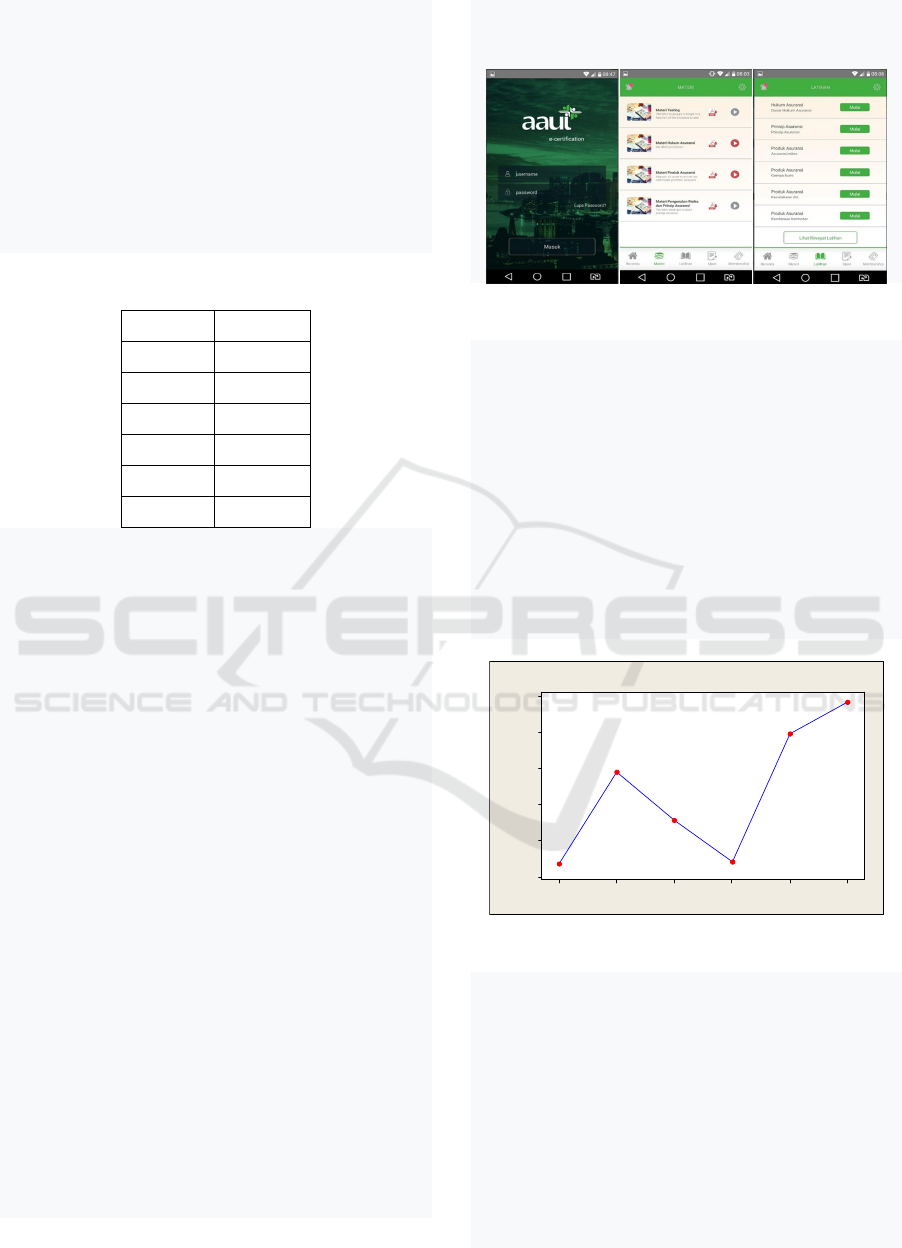
insurance agents can be seen in Figure 2 below:
201820172016201520142013
7000
6000
5000
4000
3000
2000
Year
Agent
The Development of Agent
Figure 2: The Development of Certified Agent.
From Figure 2, it can be seen that in 2016 there
was a decrease in the number of certified agents, but
since 2017 there has been an increase in the number
of certified agents in line with the FSA regulation
No. 69 / pojk.05 / 2016. Then it will increase in
2018 along with the E-certification, although the
increase is still 14.9%. This relatively small increase
shows that AAUI has not carried out effective
socialization. The socialization carried out by AAUI
has actually arrived at the process and practice of
implementing the exam by using an E-certification
to all AAUI Members represented by the agency
Insurance Agents in Indonesia in the Era of Industrial Revolution 4.0
281

coordinators of each company on the 26th February
2018 at the AAUI secretariat in Jakarta with the
hope that the agent coordinator will notify the
insurance agent in the area about this E-certification.
But it seems that it is not as effective as socializing
With the rapid development of information
technology in the current era of the industrial
revolution 4.0 it is hoped that socialization can be
intensively carried out so that more and more
general insurance agents can reach E-certification
and insurance agents in remote areas can reach E-
certification.
5 CONCLUSION
The insurance agent becomes an intermediary
between the insured party and the guarantor to pay
insurance premiums and also the process of filing
claims against insurance customers who experience
a loss as stated in the insurance policy. OJK
Regulation Number 69 / POJK.05 / 2016 / states that
insurance agents must be registered with OJK and
have an agency certificate in accordance with their
line of business. In other words, insurance agents
must be professional and competent. To achieve this
competency, OJK gives authority to associations to
carry out agency certification, in this case the
general insurance agency certificate issued by
AAUI. To get agency certification, AAUI holds
special examinations for general insurance agents.
Manual exams only produced 5958 certified agents
in 2017. Since the launch of E-certification in 2018,
the number of certified agents in 2018 was 6,838
people or an increase of 14.9% compared to 2017.
With the rapid development of information
technology in the era of the industrial revolution 4.0
is expected that more general insurance agents can
reach E-certification and insurance agents in remote
areas can reach E-certification.
REFERENCES
Adam FF, Hikmah Y. 2018. Analysis Web Site Utilization
of General Insurance Company in Selling Motor
Vehicle Insurance. Proceeding of the 3th ICVHE;
Batam, 2-4 August 2018. ISBN No 9786925252402.
Amodu, L., Alege, P., Oluwatobi, S., & Ekanem, T.
(2017). The Effect of Human Capital Development on
Employees ’ Attitude to Work in Insurance Industry in
Nigeria, 2017. https://doi.org/10.5171/2017.
Andrzej, J. 2015. The future of insurance agent as a
partner in a company’s operating
Activity. Scientific Journal (ScienceRise) No 2/3 (7). DOI:
10.15587/2313- 8416.2015.36928
Ayat S. Pengantar Asuransi. STMA Trisakti. Jakarta.
2012
Dumm, R. E., & Hoyt, R. E. (2003). Insurance distribution
channels: Markets in transition. Journal of Insurance
Regulation, 22(1), 27–47.
Eling, M., & Lehmann, M. (2018). The Impact of
Digitalization on the Insurance Value Chain and the
Insurability of Risks. The Geneva Papers on Risk and
Insurance - Issues and Practice, 43(3), 359–396.
https://doi.org/10.1057/s41288-017-0073-0
Klapkiv L., & Kalpkiv J. 2017. Technological innovations
in the insurance industry. Journal of Insurance,
Financial Markets and Consumer Protection 26: 67-
78.
Law No. 40 of 2014 concerning Insurance.
OJK Regulation Number 23 / POJK.05 / 2015 concerning
Insurance Products and I nsurance Product
Marketing
OJK Regulation Number 69 / POJK.05 / 2016 /
concerning the Operation of Insurance Companies,
Sharia Insurance Companies, Reinsurance Companies,
and Sharia Reinsurance Companies
Rahim, H. (2013). Optimisme Pertumbuhan Asuransi
Indonesia : Proyeksi Perkembangan Lima Tahun
(2014-2018). Jurnal Asuransi dan Manajemen Risiko
Vol 1 No. 2.
Roblek, V., Meško, M., & Krapež, A. (2016). A Complex
View of Industry 4.0. SAGE Open, 6(2).
https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244016653987
Szopa P., & Pekala W. 2012. Distribution channels and
their roles In the enterprise. Polish journal of
management studies.
Tseng, L. M., Kang, Y. M., & Chung, C. E. (2016). The
insurance agents’ intention to make inappropriate
product recommendations: Some observations from
Taiwan life insurance industry. Journal of Financial
Regulation and Compliance, 24(3), 230–247.
https://doi.org/10.1108/JFRC-03-2015-0014.
ICVHE 2019 - The International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE) “Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable
4.0 Industry”
282
