
Relationship of Tobacco Weight in Commercial Cigarettes to
Nicotine Levels
Mariany Razali
1
, Muhammad Taufik
2
, Evi Dayatul Atiqah
3
, Rid Wanto
3
, Anny Sartika Daulay
3
,
Desi Ardilla
4
, Endang Susilawati
5
and Afniwati
5
1
Department of Pharmacy, Universitas Tjut Nyak Dhien, Medan, Indonesia
2
Department of Chemistry, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
3
Department of Pharmacy, Universitas Muslim Nusantara Al Washliyah, Medan, Indonesia
4
Department of Agricultural Technology, Universitas Muhammadiyah Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
5
Department of Nursing, Poltekkes Kemenkes, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Nicotine, Cigarettes, Electrosynthesis, Paper Chromatography, UV Spectrophotometer.
Abstract: Nicotine is a substance contained in tobacco leaves which is used for the manufacture of cigarette raw
materials. Nicotine will come out of tobacco in the process of smoking or inhaling second hand smoke. In
cigarettes the nicotine content should not exceed 1.5 mg. Nicotine is very dangerous for health and is
addictive. This study aims to determine the effect of tobacco weight on nicotine levels and to analyse the
nicotine contained in commercial cigarettes by applying the paper chromatography method and UV-Vis
spectrophotometry. In this study, an experimental method was used, the experimental method was
developed on electro synthetic coupling maceration with variations in sample weights of 0.3, 0.6, 0.9, 0.12,
and 0.15 grams. The qualitative test results obtained in the Paper Chromatography method were nicotine
positive because the Rf value of the sample was close to the Rf value of the standard solution and was
reddish yellow, using electro synthetic coupling maceration with qualitative tests with Cyanogen bromide,
the best results were marked by abundant greenish yellow colour . Using the UV-Vis spectrophotometry
method, it was obtained that in each increase of 0.3 to 1.5 grams of tobacco, the concentration would
increase by 0.4 ppm. Paper Chromatography Methods and UV-Vis Spectrophotometry can be used to
analyse nicotine and produce the best results.
1 INTRODUCTION
Tobacco leaves contain the alkaloid nicotine, a type
of neurotoxin (Baranska, Kaczor, and Chruszcz-
lipska 2012). This substance is often considered evil,
which makes tobacco products banned. Nicotine will
come out of tobacco in the process of smoking or
inhaling secondhand smoke or chewing (Rahmat
Nur Hidayat, Adam M. Ramadhan 2016). In pristine
leaves, nicotine is bound to organic acids and
remains bound to acids when the leaves are slowly
dried. Tobacco is deadly when consumed 60 mg at a
time. It is the same as when the body receives water
consumption that exceeds the capacity that is usually
tolerated. In the case of cigarettes, the nicotine
absorbed in the body is 10% of the nicotine content
in a cigarette. If the weight of tobacco in a cigarette
is 0.76 g, with 2% nicotine content in tobacco
leaves, then the cigarette contains 15 mg of nicotine
and 10% is absorbed by the body or the equivalent
of 1.5 mg (Solarino et al. 2009).
Nicotine is the main pharmacologically active
component of tobacco, and is also found in large
quantities in other species in the Solanaceae family
(Wiencek et al. 2019). At low concentrations
nicotine is a stimulant, namely nicotine increases
activity, alertness, and memory. This is one of the
factors that contribute to the dependence on tobacco
smoking. Nicotine can increase heart rate, blood
pressure, and reduce appetite. At high doses,
nicotine acts as a depressant or suppressant (Rahmat
Nur Hidayat, Adam M. Ramadhan 2016).
Cigarettes are one of the tobacco products that
are intended to be burned, smoked or inhaled,
including clove cigarettes, white cigarettes, cigars or
other forms produced from the nicotiana tabacum,
nicotiana rustica, and other species or synthetics
whose smoke contains nicotine and tar. , with or
Razali, M., Taufik, M., Atiqah, E., Wanto, R., Daulay, A., Ardilla, D., Susilawati, E. and Afniwati, .
Relationship of Tobacco Weight in Commercial Cigarettes to Nicotine Levels.
DOI: 10.5220/0010614800002775
In Proceedings of the 1st International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath 2019), pages 621-625
ISBN: 978-989-758-556-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
621

without additives (Fidrianny 2004). Cigarettes are
usually cylindrical of paper with a length of between
70 and 120 mm (varies by country) with a diameter
of about 10 mm which contains chopped tobacco
leaves (Hamdan 2018).
Extraction is the process of separating
materials from the mixture using a suitable solvent
(Gupta and Kothari 2014). The extraction process is
stopped when an equilibrium is reached between the
concentration of the compound in the solvent and
the concentration in plant cells. After the extraction
process, the solvent is separated from the sample by
filtration (Rusevska and Zdravkovski 2011). The
initial extract is difficult to separate through a single
separation technique to isolate a single compound.
Therefore, the initial extract needs to be separated
into fractions that have the same polarity and
molecular size (Jahed, Hamidi, and Galehassadi
2020).
Nicotine extraction from cigarettes can be done
in several ways, namely maceration extraction,
reflux, and distillation. Extraction by maceration
provides the advantage of undamaged samples and
more yields (Rusevska and Zdravkovski 2011).
Maceration is a simple method of extraction.
Maceration is done by soaking the simplicia powder
in a liquid filter. The fluid will penetrate the cell
wall and enter the cell cavity containing the active
substance, the active substance will dissolve because
of the difference in concentration between the active
substance solution in the cell and the one outside the
cell, the concentrated solution is pushed out. These
events are repeated so that there is a balance of
concentration between the solution outside the cell
and inside the cell (M Taufik et al. 2018).
The extraction of nicotine from cigarettes can
be done by means of electrosynthetic maceration
because it is a way to synthesize or produce a
substance which is based on electrochemical
techniques (Muhammad Taufik et al. 2021). In this
method, there is a change in the element or chemical
compound into the desired compound (Taufik,
2016).
Hidayat (2016) has analyzed nicotine using the
ultraviolet spectrophotometric method, where the
extraction of cigarettes is carried out with methanol
which is then stirred for 30 minutes. Then add 2M of
NaOH and aquadest then stir again for 5-10 minutes
on the hotplate with a temperature of 700C. Add
zinc acetate and potassium ferro cyanide before
being centrifuged for 10 minutes at a speed of 3000
rpm. The supernatant obtained is added with
petroleum ether and separated using a separating
funnel and the fraction of petroleum ether is
extracted. The determination of the nicotine content
of cigarette samples was carried out by ultraviolet
spectrophotometry at a wavelength of 262 nm with
different concentrations of 20,40,60,80,100, 120 and
the absorbance of 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5 in order to
obtain the equation regression y = 0.019 + 0.067 at a
price of R2 = 0.983 (Rahmat Nur Hidayat, Adam
M. Ramadhan 2016).
Hidayat (2015) has reported that accurate
information is obtained regarding the nicotine
content of herbal cigarettes, a research on the
identification of secondary metabolites and analysis
of nicotine levels in herbal cigarettes was carried out
using the UV-Vis spectrophotometer method at a
wavelength of 262 nm. The materials used in this
study included samples of herbal and conventional
cigarettes, methanol, aquadest, petroleum ether, 2 M
NaOH, zinc acetate, and potassium. Cigarette
extraction was carried out with methanol plus 2 M
NaOH and aquadest on a hotplate with a temperature
of 70°C. Zinc acetate and potassium ferrocyanide
were added before being centrifuged for 10 minutes
at 3000 rpm. The supernatant obtained was added
with petroleum ether and separated using a
separating funnel and the petroleum ether fraction
was taken. The results obtained by herbal cigarettes
have a higher nicotine content than conventional
cigarettes. Even though the nicotine levels listed on
the herbal cigarette packaging are very low, even
close to 0 (Hidayat, Siradj, and Selatan 2015)
Commercial cigarettes are cigarettes that are
sold in the market. This cigarette product is a
cigarette product that is in great demand by the
public. Due to advertising promotions that do not
explicitly invite or persuade someone to smoke.
Thus increasing the target consumer to have
smoking behavior. The tendency of society to
understand that commercial cigarettes are no more
dangerous. Actually, commercial cigarettes are the
same as other cigarettes, only differentiating the way
of promoting these cigarettes (Muhammad Taufik et
al. 2017).
The effect of nicotine levels in tobacco found in
cigarettes greatly affects health, so it must be known
the levels contained in each gram of tobacco weight
in cigarettes. This study aims to determine the effect
of tobacco weight on commercial cigarettes on the
levels of nicotine produced, to analyze the
qualitative nicotine in commercial cigarettes using
the Paper Chromatography method, and to analyze
the nicotine contained in cigarettes using the UV-Vis
Spectrophotometric method.
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
622

2 METHODS
Analysis of nicotine in cigarettes using experimental
methods. The experimental method was carried out
using electro synthesis with a time of 15 minutes and
using variations in sample weight successively 0.3 g,
0.6 g, 0.9 g, 0.12 g and 0.15 g. Samples were
analyzed qualitatively using Cyanogen bromide until
a greenish yellow color was obtained and tested
using the paper chromatography method. The
quantitative test was carried out using the UV
spectrophotometer method.
2.1 Materials
The materials used in this study were filter
cigarettes, reagent pH, methanol, chloroform,
aquadest, dragendroff reagent, aluminum foil, filter
paper, and paper chromatography. The tools used in
this research are glass tools in the laboratory such as
measuring cups, beaker glass, test tubes, petri dishes,
Erlenmeyer, a set of electro synthetic tools, a set of
paper chromatography tools and a UV-Vis
spectrophotometer.
2.2 Collecting Sample
Samples were collected used purposive sampling
method, it was carried out deliberately by directly
selecting researchers who met the sample criteria.
The part of the cigarette that is taken is the cigarette
part of the filter
2.3 Preparation
2.5 grams of nicotine standard solution is put into a
1000 ml measuring flask. Gradually dissolve with
methanol while shaking, until it reaches the marking
line. From this solution, a dilution is made with a
concentration of 0.5 ppm, 1 ppm, 1.5 ppm, 2 ppm
and 2.5 ppm.
2.4 Extraction
Filter cigarettes as samples were weighed with
successive variations of 0.3 g, 0.6 g, 0.9 g, 1.2 g, and
1.5 g, put the sample into a 100 ml glass beaker plus
methanol solvent macerated electro synthesis with a
time of 15 minute. The results of electro synthetic
coupling maceration were filtered with filter paper
and then put into a petri dish, allowed to evaporate
until the nicotine was obtained. The nicotine
obtained was dissolved with 20 ml of methanol and
then measured the pH (pH 9).
2.5 Paper Chromatography
Chromatography paper is made horizontal lines on
the bottom edge of 2 cm and the top edge of 3 cm.
Creepage distance is 10 cm. The standard solution
(nicotine) and the test solution were spotted on the
chromatography paper that had been activated
beforehand. The marking is carried out on a
horizontal line on the bottom edge of the paper
chromatography with a spacing of 2 cm. The volume
of the solution is 5 µl, the diameter of the dots
should not be more than 0.5 cm. Then insert the
chromatography paper into the chamber, and closed.
Mobile phase: methanol: chloroform (50: 50). Left
and observed until the spot rises and the solvent
surface reaches the 10 cm limit mark. Then remove
the chromatography paper plate and dry it. Observed
the appearance of spots on paper chromatography
using dragendroff reagent. The colored spots give a
reddish yellow color, then the spots are marked from
the standard solution and the test solution. The Rf
value is calculated based on existing data.
2.6 UV Spectroscopy Analysis
The sample of filter cigarettes as a result of electro
synthetic coupling maceration was analyzed
quantitatively using UV-Vis spectrophotometry.
Where the working conditions in spectrophotometric
analysis are as follows:
1. The cuvette used was a glass cuvette with a
thickness of 10 mm in a square shape.
3. The wavelength used in nicotine analysis is 262
nm.
4. The cuvette containing methanol is inserted into
the spectrophotometer and press the blank button
with a wavelength of 262 nm.
5. The cuvette containing methanol was replaced
with a sample of the nicotine solution from the
maceration results.
6. Wait for the absorbance reading on the
spectrophotometer to stop and show a fixed
number.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Preparation
The standard solution used is a solution containing
the precisely known concentration of the element.
The process of making standard solutions is carried
out by diluting with five concentrations, namely 0.5,
1.0, 1.5, 2.0, and 2.5 ppm.
Relationship of Tobacco Weight in Commercial Cigarettes to Nicotine Levels
623
3.2 Preparation
Smoker's saliva preparation was carried out in the
laboratory of the University of North Sumatra,
Medan. The samples used were 10 ml of active
smoker's saliva with the addition of chloroform
solvent, in the smoker's saliva there is a nicotine
compound that comes from cigarette consumption,
which is directly exposed to cigarettes and cigarette
smoke through the mouth where saliva is contained.
Smoker's saliva has 2 layers perfectly where the
bottom layer of nicotine and the top layer of the
saliva remains. Non-smoker's saliva does not have a
perfect 2-layer separation so it takes 5 minutes to let
the saliva and solvent split into two layers.
3.3 Extraction
The extraction process by means of electro synthetic
coupling maceration has a very important role in the
compounds contained in the filter cigarette sample.
Optimization is carried out through continuous
observation of the aspects that affect the inclusion of
active compounds in the sample to be analyzed. In
this method, the electro synthetic coupling
maceration takes 15 minutes for the maceration
process.
In this electro synthetic coupling maceration
extraction method, a chemical element or compound
changes into the desired compound. The use of
methods in synthesizing materials is based on the
various advantages offered such as the equipment
required is very simple, which consists of two or
three electrode rods connected to an electric current
source.
3.4 Paper Chromatography
Paper chromatography is an analytical method used
to separate colored chemicals, especially pigments.
Apart from being easy and cheap, chromatography
also has the advantage that the resulting spots appear
directly on the chromatography paper. Spraying is
done using dragendroff so that the spots are clearer.
In this study, the results of the paper
chromatography test were used to identify the Rf
value of the test sample, where the sample was said
to be positive for nicotine, if the Rf value of the
sample was the same or close to and the Rf value of
the standard solution. In addition, it is said to be
positive for nicotine when the spots are reddish
yellow. This can be seen in the following Figure
3.1. :
Figure 3.1: The results of the analysis used paper
chromatography.
Figure 3.1 shows that the Rf value in the standard
solution is 0.84 and in samples with 5 variations in
sample weight, namely the sample 0.3 with an Rf
value of 0.76, for a sample 0.6 with an Rf value of
0.77, for a sample 0.9 for an Rf value of 0.8 , sample
1.2 Rf value 0.81, sample 1.5 Rf value 0.83 and the
average Rf value obtained is 0.80. From these data it
can be said to be positive for nicotine because the Rf
value of the standard solution is close to the Rf value
of the sample solution. In addition, the resulting spot
color is orange.
3.5 UV Spectroscopy Analysis
Tthe wavelength at a concentration of 2 ppm and an
absorbance of 1.046 with a wavelength of 262 nm.
In this study, the calculation of the concentration
of quantitative analysis by UV-Vis spectro-
photometry was carried out using the regression
method, namely by using a regression equation based
on the standard concentration of nicotine and the
absorption rate. The results of the regression equation
can be seen in Figure 3.2. the following:
Figure 3.2: The regression equation in nicotine cigarettes
analysis.
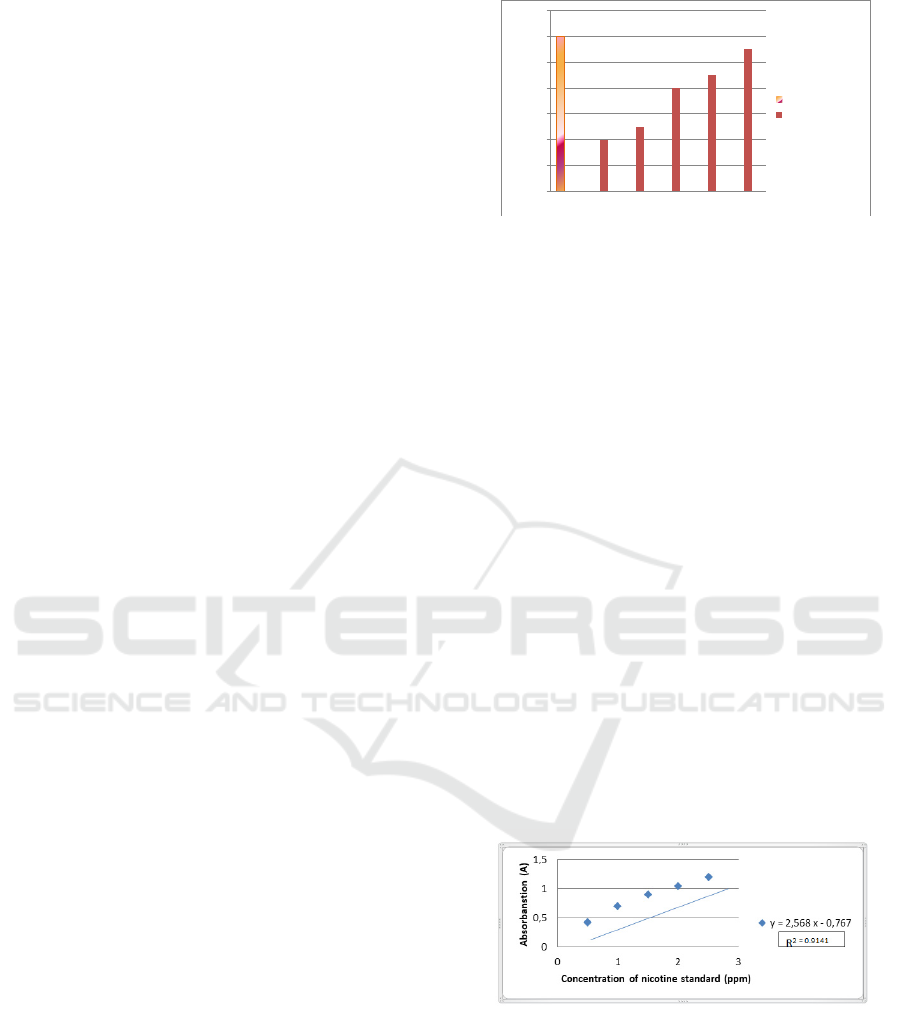
Figure 3.2. shows that the regression equation for
filter cigarettes and non-filter cigarettes is Y =
2.568x - 0.767 and R2 = 0.9141. The regression
equation can be used to calculate the nicotine
concentration in filter cigarettes. The results of the
sample concentration can be seen in Figure 3.3 the
following:
0,72
0,74
0,76
0,78
0,8
0,82
0,84
0,86
LB 0,3 0,6 0,9 0,12 0,15
RfValue
comparisonsample
Sample
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
624
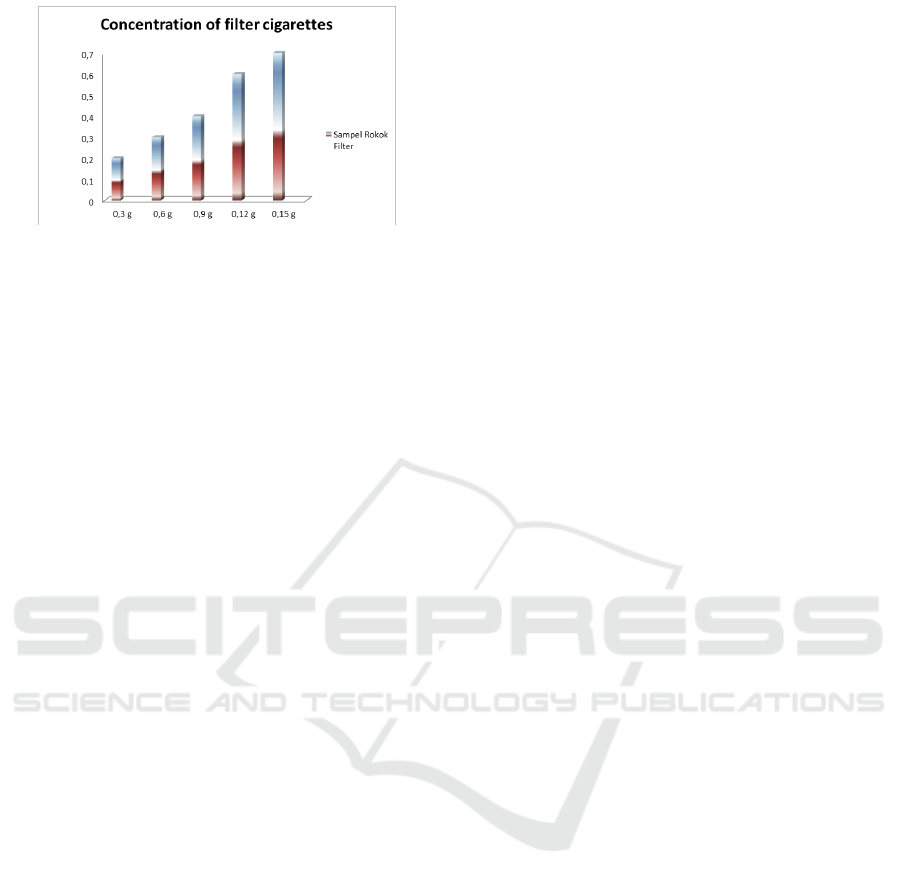
Figure 3.3. The concentration of the filter cigarette
sample.
Figure 3.3. shows that the heavier the sample the
heavier the nicotine concentration and each gram of
the sample has a different nicotine concentration.
Therefore, every tobacco that is in a cigarette has a
different nicotine content. Nicotine levels in
cigarettes have a very negative impact on health and
can become addictive. From these data shows the
highest yield of nicotine at a sample weight of 0.15
g, obtained by the micro synthetic coupling
maceration method with a concentration of 0.7 ppm.
However, in this study, we obtained a model on a
lab scale that in each increase of 0.3 to 1.5 grams of
tobacco, the concentration will increase by 0.4 ppm.
4 CONCLUSION
Preparation and extraction of nicotine in cigarettes
using the electro synthetic coupling maceration
method with time variations and methanol solvent
produced nicotine compounds with a positive
greenish yellow color in the qualitative test of
cyanogen bromide. The Paper Chromatography
method can be used to analyze nicotine with positive
results for the presence of nicotine because the Rf
value of the standard solution is close to the Rf value
of the sample besides the resulting spot color is
orange. However, UV spectroscopy can be used to
analyze nicotine with the result that each increase of
0.3-0.15g of tobacco yields a concentration of 0.4
ppm using the Y = 2.568x - 0.767 line.
REFERENCES
Baranska, M., Kaczor A., Chruszcz-lipska K. 2012.
Tobacco Alkaloids Analyzed by Raman Spectroscopy
and DFT Calculations. Journal of Raman Spectroscopy
43 (December 2019): 1065–73.
https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.3127.
Fidrianny, I. 2004. Analisis Nikotin Dalam Beberapa
Organ Mencit Jantan Yang Telah Menghirup Asap
Rokok Analysis of Nicotine in Various Organs of Male
Mice after Inhalation of Cigarette Smoke. Majalah
Farmasi Indonesia 15 (4): 207–10.
Gupta, A., Kothari V. 2014. Modern Extraction Methods
for Preparation of Bioactive Plant Extracts.
International Journal of Applied and Natural Science s
(IJANS) 1 (1): 8–26.
Hamdan, S.R. 2018. Pengaruh Peringatan Bahaya Rokok
Bergambar Pada Intensi Berhenti Merokok. Mimbar 31
(June 2015): 241–50. https://doi.org/
10.29313/mimbar.v31i1.1323.
Hidayat, A.S., Siradj M. 2015. Sertifikasi Halal Dan
Sertifikasi Non Halal Pada Produk Pangan Industri.”
Ahkam XV (2): 1–12.
Jahed, F.S., Hamidi S., Galehassadi. M. 2020. Dispersive
Micro-Solid Phase Extraction for Sensitive
Determination of Methotrexate from Human Saliva
Followed by Spectrophotometric Method. Research
Article 21 (1): 1531–38.
https://doi.org/10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.6.1531.
Rahmat N.H., Adam M.R, Rolan R. 2016. Analisis Kadar
Nikotin Rokok Herbal Indonesia. Prosiding Seminar
Nasional Kefarmasian Ke-3, 1:20–21.
Rusevska, K., Zdravkovski Z. 2011. Simple Extraction
Method For Detecting Exogenous Substances In Scalp
Hair By Gc-Ms. Journal of Hygienic Engineering and
Design 3: 1–9.
Solarino, B., Rosenbaum F., Rießelmann B., T Buschmann
C.T., Tsokos M. 2009. Death Due to Ingestion of
Nicotine-Containing Solution : Case Report and
Review of the Literature. Forensic Science
International 195 (November): 18–22. https://doi.org/
10.1016/j.forsciint.2009.11.003.
Taufik, M, D Ardila, M Razali, and A Ghozali. 2018.
Physical Properties of Lard in Tuna Processed Products
in Order to Oncrease Halal Food Safety. Proceeding
International Conference of Sustainable Agriculture
and Natural Resources Management 2 (1): 10–15.
Taufik, M., Ardilla D., Daulay A., Wanto R., Rahmawati
E, Alfian Z, Cahyady B., Razali M.. 2021.
Exploration of Maceration Methods for Extracting of
Lard from Industrial Food Products Exploration of
Maceration Methods for Extracting of Lard from
Industrial Food Products. AIP Conference Proceedings
020006 (April): 1–6.
Taufik, M., Wanto R.,, Cibro S.R., Ardilla D., Razali M,
Tarigan D.M. 2017. Studi Pendahuluan Maserasi
Coupling Elektosintesis Dalam Mengekstraksi Nikotin
Yang Terkandung Dalam Puntung Rokok. Prosiding
Seminar Nasional Kimia Unmul, 182–90.
Wiencek, J.R., Gehrie G.A, Keiser A.M., Penny C.,
Johnson-davis K.L., Booth G.S.. 2019. Detection of
Nicotine and Nicotine Metabolites in Units of Banked
Blood. AJCP 1 (1): 516–21. https://doi.org/
10.1093/AJCP/AQY176.
Relationship of Tobacco Weight in Commercial Cigarettes to Nicotine Levels
625
