
Lifestyle of Chronic Kidney Failure Patients before Undergoing
Hemodialysis in Medan, Indonesia
Cholina Trisa Siregar
1
, Novi Yulisa Harahap
1
, Siti Zahara Nasution
1
, Zulkarnain
2
,
M. Pahala Hanafi Harahap
3
and Muhammad Taufik
4
1
Faculty of Nursing, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
2
Faculty of Psychology, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
3
Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
4
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Healthy lifestyle, Renal dialysis, Habits, Humans
Abstract: Changes in a person's lifestyle or habits can result in changes in body rhythm and can cause balance
disorders, resulting in a decrease in bodily functions. The aim of the study was to describe the habits of the
patients before chronic kidney failure. Design with sampling using purposive sampling. The inclusion
criteria of this study were chronic kidney failure patients who underwent hemodialysis for less than 6
months, had chronic kidney failure not due to diabetes mellitus and hypertension. The number of samples is
50 respondents. Data collection tools using questionnaires made based on the literature Result: The study
obtained data on the lifestyle of patients before suffering from chronic kidney failure that is an unhealthy
lifestyle as many as 44 people (88%). This lifestyle is judged by 4 habits, namely the habit of consuming
food that is not good as many as 45 people (90%), amounting to 45 people (90%) lack of physical activity,
bad daily life of 40 people (80%) and resting less by 37 people (74%). A healthy lifestyle requires the
attention of health workers, especially for patients who are at risk of decreased organ function.
1 INTRODUCTION
Changes in the body's homeostasis can be caused by
a decrease in kidney function, a continued decline in
kidney function resulting in chronic kidney failure
that is at risk of causing a high rate of morbidity and
mortality. Decreased kidney function requires
permanent kidney replacement therapy, namely
dialysis or kidney transplantation (Gansevoort et al.,
2013). Chronic kidney failure has increased and is
becoming a very serious health problem in the
world. Chronic renal failure caused the death of the
27th sequence in the world in 1990 and increased to
18th in 2010 (Mills et al., 2015). Chronic kidney
failure sufferers who undergo dialysis therapy or
kidney transplantation are more than 2 million and
only around 10% experience it routinely, so that
millions of people die every year because they don't
have access to treatment (Ri, 2018). Basic health
data (Kesehatan, 2018) patients with chronic failure
based on the most age is 65-74 years, the most sex is
Male (4.17%). According to the Indonesian Minister
of Health that risk factors for chronic kidney failure
can be caused by hypertension (25.8%), obesity
(5.40%), diabetes mellitus (2.3%)(Ri, 2018).
Indonesian Renal Registry (IRR), 2015 data on risk
factors for chronic kidney failure that occur in young
adults is caused by Diabetes Mellitus, hypertension,
smoking habits and consumption of supplement
drinks.
Chronic kidney failure can be caused by changes
in modern lifestyle that do not pay attention to health
such as lack of activity, consuming unhealthy eating
and drinking (Susanto, 2003). Changes in lifestyle of
patients with chronic kidney failure are caused by a
lot of the wrong lifestyle by consuming energy
drinks, lack of rest, consuming excessive
supplement drinks and foods containing
preservatives consuming fast food, stressful
busyness, sitting all day in the office, often drinking
coffee, energy drinks, rarely consuming water is a
bad habit is a risk factor for kidney damage (White
et al., 2009). The economic level can affect the
pattern or type of food consumed, changes in
lifestyle or habits of a person must be able to change
the way of thinking by changing one's paradigm
138
Trisa Siregar, C., Yulisa Harahap, N., Zahara Nasution, S., Zulkarnain, ., Pahala Hanafi Harahap, M. and Taufik, M.
Lifestyle of Chronic Kidney Failure Patients before Undergoing Hemodialysis in Medan, Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0010137600002775
In Proceedings of the 1st International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath 2019), pages 138-142
ISBN: 978-989-758-556-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

(Suhardjo, 2008).
This habit change resulted in a decrease in
kidney function and increased mortality and
morbidity in the world (Howden et al., 2013).
Chronic kidney failure has a risk of 3 to 4
contracting infectious diseases such as influenza,
pneumococcal pneumonia, hepatitis and other
diseases due to decreased immune system (Naqvi &
Collins, 2006). (Levey & Coresh, 2012) said the
decline in the ability of the kidneys to perform their
functions causes a high risk of complications such as
cardiovascular, acute kidney injury, infection,
cognitive impairment, and impaired physical
function . Complications can occur at any stage of
decline in kidney function and cause death.
Chronic kidney disease in addition to causing
physiological changes also affects psychological and
social changes in patients such as the addition of
funds for hemodialysis actions that patients undergo
(Muehrer et al., 2011). Increasing the number of
hemodialysis patients each year also causes many
complications such as increased interdialytic weight
gain, nutrition, skin problems, and insomnia during
or after undergoing hemodialysis sessions. Other
complications experienced by patients when
undergoing hemodialysis are interradial
hypertension, hypotension, muscle cramps, access
problems, chills, headaches, nausea and vomiting,
itching, and others. This condition can result in a
decrease in the quality of life of the patient.
Hemodialysis therapy indirectly affects the quality
of life of patients, such as physical, psychological,
spiritual health, socioeconomic status and changes in
the functioning of family (Cavalli, et al., 2010).
2 METHODS
The design used in this research is exploratory
descriptive with a retrospective approach. This study
aims to explore information about the lifestyle of the
patient before undergoing chronic kidney failure.
Sampling using a purposive sampling method
involving 50 respondents. Criteria for inclusion are
chronic kidney failure patients who have just
undergone 6 months of hemodialysis, the cause of
chronic kidney failure due to diabetes mellitus and
hypertension. This research was conducted from
March to July 2019. The instrument used was a
questionnaire consisting of data on the
characteristics of respondents and the lifestyle of
patients before experiencing chronic kidney failure.
The research questionnaire uses the Guttman scale,
the statement yes given a score of 1 and given a
value of 0 for no. Rating categories consisting of
nutrients are stated in statements number 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
and 6; bad habits statements number 7, 8, 9, 10, 11,
12 and 13; physical activity statements number 14
and 15; Ability to break statement number 16.
The research instrument was based on a literature
review and validation was tested with the CVI
(Content Validity Index). The CVI result of the
instrument is 1.00 so that the patient's lifestyle
questionnaire before experiencing conic kidney
failure is declared valid and can be used for
research. The reliability test of the lifestyle
instrument of the patient used KR 21 involving 30
people who had the same criteria as this study. If the
KR 21 test results are obtained by 0.90 or more, then
the lifestyle instrument is declared reliable for this
study. Data collection was carried out when the
respondent was undergoing hemodialysis therapy
and respondents who were unwilling were not
included in the study sample. Data analysis uses a
frequency distribution to see the highest data that
causes kidney function decline. The data submitted
by the patient is kept confidential and this study has
received ethical tests from the Faculty of Nursing,
University of North Sumatra.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Characteristics of Respondents
Table 1 depicts the highest age data for middle adult
as many as 37 (74%) respondents, 14 majority
respondents with no work status as many as 35
(70%), most male sex as much as 32 (64%).
Table 1. Characteristics of respondents in the hemodialysis
room in Medan City in 2019
Characteristics respondent f %
Age:
Teena
g
a
r
6 12
Youn
g
Adul
t
7 14
Middle Adul
t
37 74
Occupation
Wor
k
15 30
Does not wor
k
35 70
Gender:
Female 18 36
Male 32 64
Table 1 shows the majority of male respondents as
many as 64 people (54.7%), age range 41-60 years
as many as 66 people (56.4%), 53 senior high school
Lifestyle of Chronic Kidney Failure Patients before Undergoing Hemodialysis in Medan, Indonesia
139
education (45.3%), 48 self-employed (41%), the
married status of 108 people (92.3%).
3.2 Patient's Lifestyle before
Experiencing Chronic Kidney
Failure.
Table 2 Ilustrates the lifestyle of respondents before
experiencing the highest chronic kidney failure,
which is a bad lifestyle of 44 people (88%).
Table 2. Lifestyle of patients before chronic renal failure
Medan City in 2019
Lifestyle f %
Well
Not Good
6
44
12
88
Table 3. Lifestyle categories of patients before
experiencing chronic kidney failure in Medan City in 2019
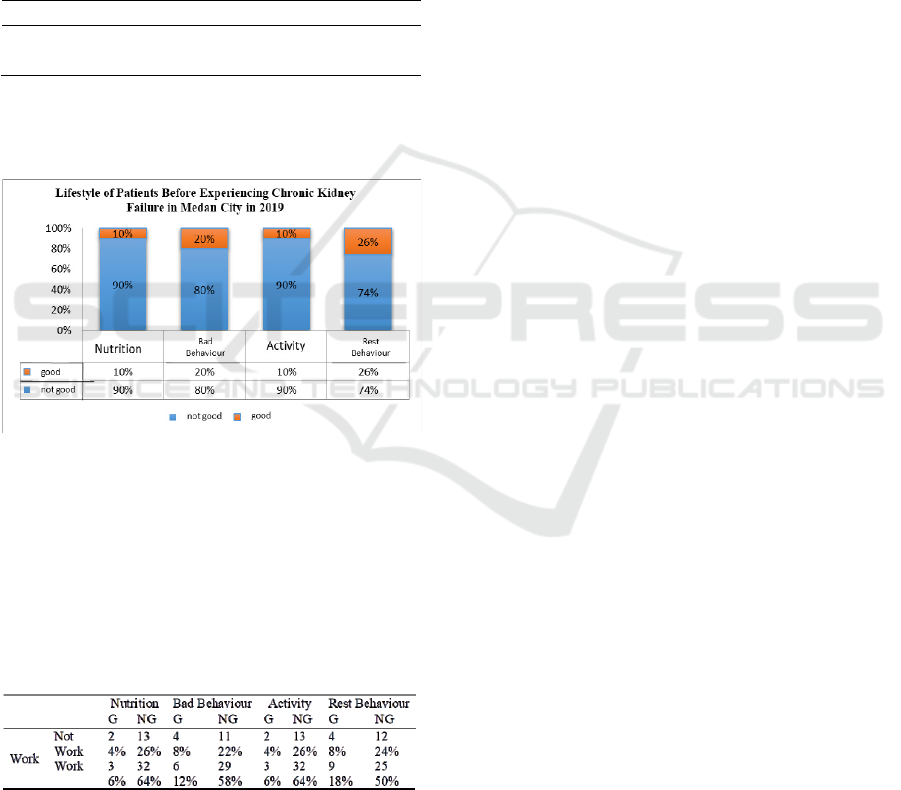
Table 3 illustrates 4 lifestyle categories of
patients before experiencing chronic kidney failure,
namely Nutrition 90% is not good and 10% is good,
Bad Habits 80% is not good and 20% is good,
Physical Activity 90% is not good and 10% is good,
Resting Habits 74% not good and 26% good.
Table 4. Data on cross-tabulation of patient lifestyle
before experiencing chronic kidney failure in Medan City
in 2019
G = good
NG = Not good
Table 4 illustrates the cross table data between work
and 4 aspects of the patient's lifestyle. based on 4
aspects. The results of cross-tabulation of jobs with
the highest nutritional value that is not working with
aspects of poor nutrition that is equal to 32 (64%);
the results of the work of cross-tabulation of jobs
with bad habits the highest value is work and bad
habits that are not good is 29 (58%); cross-tabulation
of the highest value of work with physical activity is
32 (64%; the highest value of cross-tabulation
between work with the habit of resting the highest
value is working with bad rest habits that are 25
(50%).
4 DISCUSSION
The results of this study obtained patient lifestyle
data before experiencing chronic kidney failure
which was studied as many as 50 patients with 4
lifestyle factors of patients before experiencing
chronic kidney failures such as Nutrition, Bad
Habits, Physical Activity, and resting habits. Patients
with chronic kidney failure mostly have a history of
bad lifestyle. The results of this study are similar to
Dewi’s research, from 40 patients who were
examined from 3 lifestyle factors of chronic kidney
failure such as Physical Activity, Substance Use, and
Diet Patterns, having 23 patients (57.5%) having
unhealthy lifestyles before undergoing hemodialysis
therapy (Publikasi, 2018) .
Consuming bad nutrients is influenced by the
work environment that makes them not care about
good nutrition patterns, eating fast food such as
canned foods, fried foods, packaged rice and
everyday cooking using flavoring. Modern lifestyles
change lifestyles such as eating fast food, canned
foods, bottled chili sauce, canned drinks, fruits and
vegetables that use preservatives, foods rich in fat,
foods rich in cholesterol. People who do not pay
attention to the composition of nutrients contained in
daily food will be more susceptible to disease than
those who are careful in consuming food. Foods that
contain high carbohydrate content but lack of fiber
such as fast food, accelerate the accumulation of fat
in the body that triggers obesity. Obese individuals
are prone to type 2 diabetes mellitus and
cardiovascular disease. Fat accumulation in the
abdominal area is one of the risk factors that trigger
diabetes mellitus. An increase in diabetics will
increase the number of people with kidney disease
due to complications from diabetes, namely diabetes
nephropathy (Ortiz et al., 2014).
Bad habits are carried out such as drinking
alcohol from family and environmental factors that
make them try to drink alcohol and wine so that it is
addictive. Promotions and invitations of friends to
try herbal medicines such as body administrators,
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
140

body massagers, to cure diseases and beautify
themselves and types of herbal medicines that are
often consumed, supplement drinks consumed by
male patients work as drivers and consume water
that does not meet the body's needs
Environmental factors including exposure to
heavy metals such as lead, cadmium, arsenic, use of
chemicals for plants (agrochemicals) and some
Chinese herbal medicines, use of nonsteroidal anti-
inflammatory drugs, and infectious diseases
leptospirosis, hantavirus, leprosy, and malaria are
endemic diseases in Indonesia. a cause of chronic
kidney failure (Soderland, et al., 2010). The
statement of Bruno & Langford that a bad lifestyle
is seen from the use of substances is risky behavior
such as smoking, using drugs not in accordance with
the rules that have been given, the use of chemicals
that are harmful to the body (Stack & Murthy,
2010). This behavior, if carried out by individuals in
the long term, can result in disruption of kidney
work that ends with chronic kidney failure. The
results of this study indicate that people who take
herbal medicines are 11.76 times more at risk of
developing chronic kidney failure compared to those
who do not consume herbal medicines (Gluba-brz, et
al., 2017). Previous studies also mentioned that
consumption of herbal medicines is a risk factor for
kidney failure. The results of research on the
majority of patients before experiencing chronic
kidney failure are the physical activity of patients is
not good because of the work factors that make them
unable to do exercise every day and work at home.
The results of this study are similar to Dewi's
research, from 40 patients examined in 19 patients
whose physical activity was 47.5% and 21 patients
whose physical activity was not good, 52.5%.
Individuals who have low physical activity are at
risk of experiencing various diseases such as
diabetes, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and obesity
(Publikasi, 2018).
Adequate rest is needed by our body. Lack of
sleep can cause the body limp, no enthusiasm,
irritability, and stress. Prolonged stress can result in
a persistent increase in blood pressure (Sorat, 2019).
Factor research results that resulted in respondents
not paying attention to resting habits due to factors
working and often out at night with friends so that
the decreasing sleep act does not meet the body's
needs.
5 CONCLUSION
A healthy lifestyle is important to prevent a decline
in organs. Unhealthy lifestyles such as the intake of
nutrients that do not fit the body's needs, poor
abusive habits, lack of physical activity and resting
habits that do not meet the body's needs are the
cause of chronic kidney failure.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors thank the Ministry of Research,
Technology, and Higher Education, the Republic of
Indonesia for funding this research through Research
Grant in 2019
REFERENCES
Cavalli, A., Vecchio, L. D. E. L., Manzoni, C., &
Locatelli, F. (2010). HEMODIALYSIS : REVIEWS
E, 62(1), 1–12.
Gansevoort, R. T., Correa-rotter, R., Hemmelgarn, B. R.,
Jafar, T. H., Heerspink, H. J. L., & Mann, J. F. (2013).
Globa Kidney Disease 5 Chronic kidney disease and
cardiovascular risk : epidemiology , mechanisms , and
prevention. The Lancet, 382(9889), 339–352.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60595-4
Gluba-brz, A., Franczyk, B., & Rysz, J. (2017).
Vegetarian Diet in Chronic Kidney Disease — A
Friend or Foe, 1–16.
https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9040374
Howden, E. J., Leano, R., Petchey, W., Coombes, J. S.,
Isbel, N. M., & Marwick, T. H. (2013). Article Effects
of Exercise and Lifestyle Intervention on
Cardiovascular Function in CKD, 8.
https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.10141012
Kesehatan, K. (2018). HASIL UTAMA RISKESDAS
2018.
Levey, A. S., & Coresh, J. (2012). Chronic kidney disease.
The Lancet, 379(9811), 165–180.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60178-5
Mills, K. T., Xu, Y., Zhang, W., Bundy, J. D., Chen, C.,
Kelly, T. N., … He, J. (2015). A systematic analysis of
worldwide population-based data on the global burden
of chronic kidney disease in 2010, 950–957.
https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2015.230
Muehrer, R. J., Schatell, D., Witten, B., Gangnon, R.,
Becker, B. N., & Hofmann, R. M. (2011). Factors
Affecting Employment at Initiation of Dialysis, 489–
496. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.02550310
Naqvi, S. B., & Collins, A. J. (2006). Infectious
Complications in Chronic Kidney Disease, 13(3),
199–204. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ackd.2006.04.004
Ortiz, A., Covic, A., Fliser, D., Fouque, D., Goldsmith, D.,
Kanbay, M., … Lyon, D. (2014). Kidney disease 1
Lifestyle of Chronic Kidney Failure Patients before Undergoing Hemodialysis in Medan, Indonesia
141

Epidemiology , contributors to , and clinical trials of
mortality risk in chronic kidney failure, 1831–1843.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60384-6
Publikasi, N. (2018). Hubungan gaya hidup dengan
kejadian gagal ginjal kronik di rumah sakit pku
muhammadiyah yogyakarta naskah publikasi.
Ri, M. K. (2018). Nila F Moeloek.
Soderland, P., Lovekar, S., Weiner, D. E., Brooks, D. R.,
& Kaufman, J. S. (2010). Chronic Kidney Disease
Associated With Environmental Toxins and
Exposures. Advances in Chronic Kidney Disease,
17(3), 254–264.
https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ackd.2010.03.011
Sorat, W. (2019). PREDICTORS OF QUALITY OF LIFE
IN THAI ADULTS WITH EARLY-STAGE
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE.
Stack, A. G., & Murthy, B. V. R. (2010). Cigarette Use
and Cardiovascular Risk in Chronic Kidney Disease :
An Unappreciated Modifiable Lifestyle Risk Factor,
23(3), 298–305. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-
139X.2010.00728.x
Susanto, A. S. (2003). MEMBUAT SEGMENTASI
BERDASARKAN LIFE STYLE ( GAYA HIDUP ),
1–6.
White, S. L., Polkinghorne, K. R., Cass, A., Shaw, J. E.,
Atkins, R. C., & Chadban, S. J. (2009). Alcohol
consumption and 5-year onset of chronic kidney
disease : the AusDiab study, (March), 2464–2472.
https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfp114
Tim Indonesian Renal Registry. (2015). 8th Report of
Indonesian Renal Registry
Suhardjo. (2008). Perencanaan Pangan Dan Gizi. Jakarta:
Bumi Aksara.
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
142
