
Improving the National Internship Certified Program based on
Examination from Vocational Education Program (University of
Indonesia) Students Experience
Mila Viendyasari
Program Pendidikan Vokasi, Universitas Indonesia, Jl. Kalibata Tengah No. 29, Jakarta 12740, Indonesia
Keywords: Human Capital, Vocational Education, Competency, Industry 4.0
Abstract: This article aims to deliver recommendations based on the research as a result of student experiences and to
provide recommendations for improving the implementation of the nationally certified internship program.
Method uses an analytical method with a quantitative approach, the research design used in this study is Cross-
Sectional. The study was conducted by survey method on samples in a population using a questionnaire as a
method of data collection. This research indicates that the implementation of nationally certified internships
able to broaden the insight and skills of the students but needs to be improved the readiness of the company
for day to day implementation. Several recommendations for nationally certified internship program
improvement, based on student's experience regarding the assignment orientation given, mentor guidance and
working environment conditions as long as they take part in a certified internship program. This study expands
the exciting literature on the national internship program by providing theoretical support focusing on
vocational education.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the year of 2018, the Ministry of BUMN along with
Forum Human Capital Indonesia initiated the
National Internship Certified Program. This program
has a strategic goal of optimizing human resources in
order to develop vocational education based on
competency that is connected to industrial needs.
Certified Internship model grows more
importantly when industrial landscape evolved
compare to previous few decades ago; even more,
since the term of IT-based industrial revolution 4.0
term appeared. There are growing concerns that in the
near future IT will replace human capital in the
industry. These risks must be anticipated, despite the
notion that whether or not these concerns
materialized. Nonetheless, industrial 4.0 should
become an indicator of early warning to improve the
quality of human capital. By then, only the most
improved human capital will win the competition in
the future.
An internship is a unique educational program
with the purpose of integrating research with planned
experiences and related performance. It is designed
for the most commonly unemployed freshly graduate
students and postgraduate students all around the
world who have completed 14 to 16 educational
years. The main objectives of the internship program
are to develop and to strengthen student’s abilities
and to prepare them for the profession. (Parveen,
2012)
By definition, nowadays, an internship is defined
as a part-time job for a certain period of time, with or
without pay, where interns gain knowledge while at
the same time making a contribution to the
organization. For students, an internship provides a
better understanding of the reality of business
situation under supervisions and supports (Batool,
2012)
Entering industrial era 4.0, most scholars
especially undergraduates must prepare themselves
optimally and be ready to show uniqueness or
distinction and their added value. Inside the Industrial
revolution 4.0, there are automatic systems and
internet integration (combining digital automation
with cyber technology). With this industrial
revolution, the job competitions are getting much
tougher. Vocational education program is
implementing a few things to prepare their students
for the upcoming industrial revolution 4.0, these may
84
Viendyasari, M.
Improving the National Internship Certified Program based on Examination from Vocational Education Program (University of Indonesia) Students Experience.
DOI: 10.5220/0010030800002967
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE 2019) - Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable 4.0 Industry, pages 84-90
ISBN: 978-989-758-530-2; ISSN: 2184-9870
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

include: replacing the term Internship program with
undergraduates’ internships program, strengthening
cooperation with the world of industry, campus that
cooperates with world of industry must prepare their
undergraduates’ competencies, by cooperating with
the industry playmaker, students clearly have more
added values to the industries demand once they
graduate, foreign language implementation ,
cooperation with local campuses as well as foreign
industries.
According to the Research, Technology and
Higher Education Ministerial regulation number 44
the year 2015 article 11, the learning process
characteristics consist of these values: interactive,
holistic, scientific, thematic, effective, collaborative
which centered with the students themselves.
Industrial revolution era 4.0 triggers the promotion of
higher education level 4.0, where universities have
the obligation to provide their students and graduates
to grasp the technology literation, data and people,
and the implementation of lifelong learning
education. The Ministry of Research, Technology and
Higher Education (KEMRISTEKDIKTI) has put a lot
of effort in increasing access, relevance, and quality
of higher education in the industrial revolution era 4.0
through co-operative learning and work-integrated
learning/Co-operative education or Co-op which
objectives are to increase leadership competencies,
teamwork and Higher Order of Thinking Skills
(HOTS) for higher education graduates.
Internships provide real-world experience for
those who want to explore or gain the relevant
knowledge and skills needed for a specific field of
work. Internships are relatively short with the primary
focus getting into the job training, taking what is
learned at the university and applying it into the real
world. Internships generally have supervisors who
assign specific tasks and evaluate the intern’s
performance. (Mung'atu, 2016)
A good internship program is not merely
duplicating documents or making coffee for the
superior. Effective and structured internships play an
important key role in maximizing the students’
potentials and guiding them in order to make
significant contributions to the institution.
An effective internship experience is mutually
beneficial for both apprentices and the institutions.
Students are faced with best practices, effective
management and a good understanding of the skills
and applications needed to be successful in the
transition into productive contributors. Business
benefits by providing structures and guidelines for the
students by helping them understand the
opportunities in their organizations, industry, and
business. (Natarajarathinam, 2014)
Facing the industrial revolution 4.0 is certainly
not an easy thing. There are several things needed to
be prepared, for instance, converting the learning
method in the world of education that exists today.
The very fundamental thing is to change the nature
and students’ mindset. According to the
Kemenristekdikti version, to counter this industrial
revolution 4.0 is by building a more innovative
learning system, institutional policy reconstruction,
improving the quality of lecturers and research
breakthroughs. Therefore, in this era, educational
institutions must have cross-sector collaboration, all
of which must be involved, including government,
scholars and industry players so that the impact of this
industrial revolution 4.0 can truly benefit all levels of
society.
Internships can also develop partnerships
between educational institutions, companies,
businesses, and industries. Internships create positive
attitudes toward the business community while at the
same time business may be taking part in student
education.
Local businesses also can take part by offering
internship programs according to their business
discipline or technical field. (Merritt, 2018)
A well-planned internship program will include
the following functions: (Parveen, 2012)
• Understanding the target profession and
prospects for future working conditions.
• Providing valuable exposure to work
• Developing professional skills and attitudes
• Building a network of people with a similar
profession.
By participating in an internship program,
students get a chance to do the job and interact with
other professionals in the same field for some time,
which can be their field of interest. Internships
provide students with opportunities to gain
knowledge about their prospective careers in
industry, identify general preferences related to the
job, and develop profound vocational interests.
Internship students will learn what they like or dislike
from one job, and this can be identified early in the
process of their job search, it has more advantages
compared to students who do not take part in the
internship. One of the competitive advantages for
apprentice workers is that they have an early head
start to the career because of the knowledge and
experience gained during the internship program,
therefore there is no need for trial and error in their
field of interest. (Maertz Jr, 2013)
Improving the National Internship Certified Program based on Examination from Vocational Education Program (University of Indonesia)
Students Experience
85

Internships can empower students and help them
improve their professionalism. Apprentices who
participate in this program appreciate that by
participating in the internship programs they can
prepare themselves better for important career skills
including problem-solving, job interviews,
networking, resume writing, oral presentations,
interpersonal communication, and written
communication. (James, 2018)
To take part in this certified internship program,
prospective apprentices also attend a recruitment
process organized by each institution, such as BUMN
employees’ recruitment. Prospective apprentices are
asked to make job applications, CVs, take interviews
and also undergo the tests requested by the company.
A certified internship program involving the
Ministry of BUMN in Indonesia was recently
implemented in 2018, so there are still many things
can be done in the future in order to make the
internship program functions optimally. With this
research, it is hopeful that we found solutions that can
improve the implementation of certified internships
program through interns’ experiences during the 6-
month internship at a state-owned enterprise
(BUMN), therefore the implementation of the
internship can run effectively and achieve its main
objectives.
2 DATA AND METHODOLOGY
2.1 Research Approach
The approach used by the author in carrying out this
research is a quantitative research approach. The
quantitative research approach is research conducted
by calculating numbers statistically based on
hypothesis testing, analyzing and interpreting the
results that answer the research objectives.
Quantitative research according to Sudjan (2005),
measurements based on the form of numbers,
numbers or direct observations that can produce a
measurable result from the object or variable to be
measured.
According to the development model or growth
model, this type of research approach is known as a
cross-sectional model. The cross-sectional model is a
way of obtaining complete data which is done
quickly, while at the same time can predict
developmental stages of individuals in a certain
growth period. The quantitative approach is a relation
that will be calculated statistically through variables
involved, which are the independent and dependent
variables. The quantitative approach can decipher all
the explanations in the operational definition such as
describing the purpose of measuring a measuring
instrument, measuring method and measuring the
scale and not deviating from the objectives and
formulating the research problem (Arikunto, 2010).
The method used in data collection is the survey
method. Survey research is the way research is carried
out by directly coming to the location that will be used
as an object by making observations or conducting
data collection according to existing problems
(Singarimbun, 2008). One of these types is
characterized by the distribution of questionnaires in
a place with the number of respondents adjusted.
2.2 Research Data Sources
Data collection is carried out by stages of process
based on the procedures in the field and the selection
of data collection techniques is precisely picked
through the nature, character, and frequency of
respondents sampled. The process of retrieving data
from primary data, known as the distribution of
questionnaires or conducting in-depth and second
interviews using secondary data taken from the
previously generated reports from research or
previous records. Sources of data or information
include primary data and secondary data.
a. Primary data is data obtained directly as a result
of questionnaires distribution with subjects about
evaluating the implementation of work internships in
state-owned enterprises (BUMN) that are influenced
by independent variables such as work environment,
mentor role, and task orientation
b. Secondary data is data that the author obtained
through literary studies by studying literature,
scientific writing, legislation and documents obtained
by the related agency of which the research objectives
and the issues raised.
2.3 Population and Sample
The population in this study were Vocational
Education Program students who participated in a
certified internship training at BUMN companies as
many as 75 people. The sampling technique used in
this study was a total sampling of 75 people.
2.4 Research Instrument
A research instrument is a tool selected and used by
researchers in their activities to collect the data
needed in their research so that the activity becomes
systematic and puts the author at ease in doing this
research. In quantitative research, the instrument
ICVHE 2019 - The International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE) “Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable
4.0 Industry”
86

must be created and become an "independent" tool
apart from the researcher.
The variable and indicator are :
1. Evaluation :
a. Recommendation
b. According to needs
c. According to abilities
d. Comfortability
2. Role of mentor :
a. Discussion
b. Directing
c. Responsibility
3. Working Environment :
a. Work Relation
b. Communication
c. Directing
d. Responsibility
4. Task Orientation :
a. According to competency
b. Increasing knowledge
c. Increasing skill
2.5 Data Collection and Technique
Sambas and Maman (2009) explain that data
collection techniques are ways that can be used to
collect data. In research with this quantitative
approach data collection techniques used are
questionnaires. As mentioned in Sugiyono (2009)
that questionnaires are instruments used to explore
information relating to statements or theories
presented through the respondent's answers according
to their views when filling out.
The technique that I use to collect data in this
study is by distributing questionnaires to respondents
using a Likert scale. Likert scale is used to measure
the attitude, and perceptions of people or groups of
people about a social phenomenon (Sugiyono, 2014).
Respondents will choose one of the available options,
usually, five scale options will be provided with the
following format:
1. = Strongly Disagree (SD)
2. = Disagree (D)
3. = Neutral (N)
4. = Agree (A)
5. = Strongly Agree (SA)
In the questionnaire used in this research, there
are also included open sentences in each statement
that will be answered by the respondent. According to
Mas'ud (2004), the implementation of the method of
data collection in this research is administered by
using surveys in groups. Respondents are collected in
a certain place, then explained the purpose, and how
to answer the questionnaire. After filling out the
questionnaire, the respondent then returned the
questionnaire.
The methodology adopted for conducting the
research was a questionnaire. A questionnaire is often
used in quantitative marketing research and social
research. This method is a valuable method for
gathering information from a large number of
individuals. Zamara Batool (2012), in her research,
has taken samples of students who have been part of
a national internship program in the Punjab region -
India. We have taken their views on the program and
its continuation. (Batool, 2012)
2.6 Descriptive Statistic
Descriptive statistical analysis is used to determine
the description criteria of each variable studied and
the characteristics of the respondents. Descriptive
analysis is a quantitative analysis that is used to
explain more deeply the results of the analysis and
able to provide more detailed information (Umar,
2010).
Descriptive analysis in this study is used to
quantify work environment factors, the role of
mentors and task orientation towards evaluating the
implementation of work apprenticeship programs in
state-owned enterprises (BUMN) and describe
descriptions of research variables based on the
answers to each questionnaire by giving scores to
each answer. The analysis then uses the average value
and percentage of the respondent's answer scores.
The collected data are classified into two groups
of data, namely quantitative data in the form of
numbers and qualitative data in the form of words or
symbols. Qualitative data in the process is
temporarily set aside because it will be used to
accompany and complete the picture obtained from
quantitative analysis. Quantitative data are summed
or grouped according to the shape of the instrument
used.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The results of the study were arranged systematically
beginning with a description of univariate analysis
which objective was to obtain an overview of the
distribution of respondents or variations of the
variables studied. This analysis was used to describe
the variables studied by making a frequency
distribution table, and the data was presented in the
form of a percentage. Then, at the end of this study,
an SEM (Structural Equation Modeling) analysis was
provided to explain the complex relationship between
Improving the National Internship Certified Program based on Examination from Vocational Education Program (University of Indonesia)
Students Experience
87
some of the variables tested in this study. The number
of samples in this study was 75 respondents.
3.1 Characteristics of Respondents
The number of questionnaires distributed was 75
questionnaires to vocational program students as
primary respondents who took a certified
apprenticeship program at state-owned enterprises
(BUMN). The characteristics of respondents in this
study were divided into 3 (three) categories, which
consisted of gender, age, and interests of the chosen
profession. The study on the characteristics of
respondents based on these categories was carried out
to provide an overview of the identity of respondents,
as shown in the pie chart. Based on the results of data
processing, a frequency distribution can be arranged
to exhibit the characteristics of respondents as shown
at the following:
1. Gender
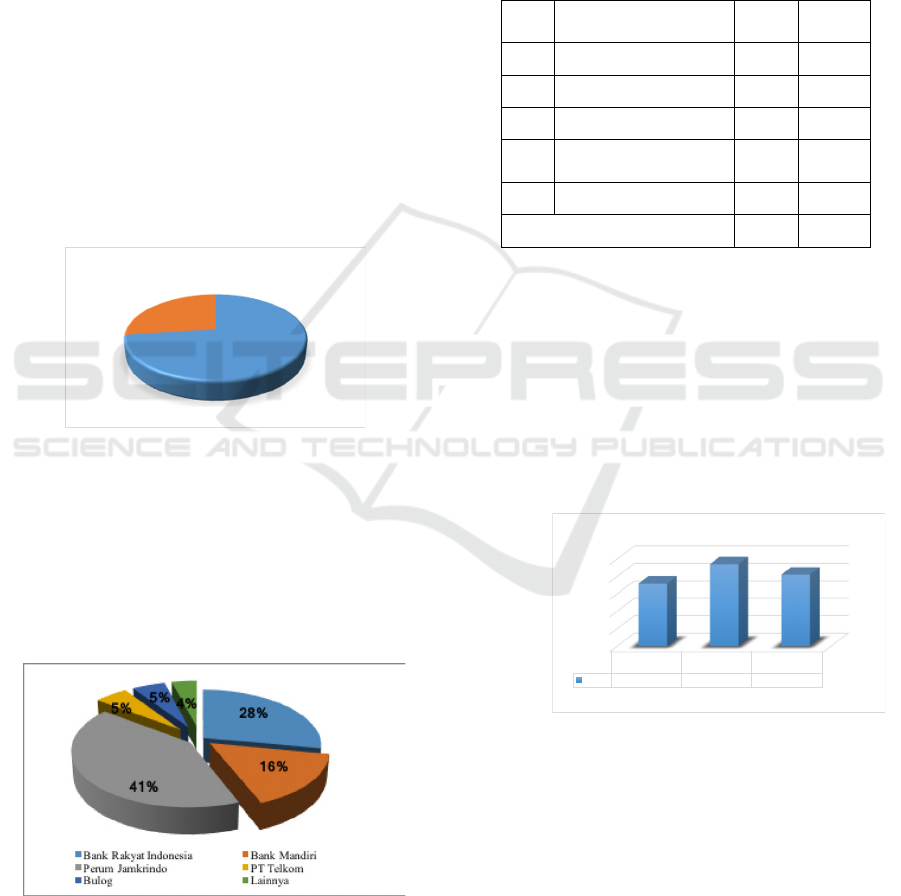
Figure 1: Respondents Data by Gender (n = 75)
Data on the frequency distribution of respondents
in figure 4.1 shows that based on gender, most of the
samples in this study were 55 women (73%) and 20
men (27%).
2. Internship Placement by State-owned
enterprises (BUMN)
Figure 2: Respondents Data by State-owned enterprises
(BUMN) internship placement
Data on the frequency distribution of
respondents’ characteristics in figure 4.2, shows that
based on the company internship placement, most of
the apprentices work at Perum Jamkrindo (41%),
Bank Rakyat Indonesia (28%), Bank Mandiri (16%),
Bulog and PT Telkom respectively 5% each as well
as other companies 4%.
3. Career Interest
Table 1. Characteristics of Respondents by Career Interest
No Career Interest
Qty
(n)
%
1
Retail
8
11%
2
Government
22
29%
3
Finance
18
24%
4IT/
Telecommunication
6
8%
5
Others
21
28%
Total
75
100%
Based on career interests, most of the respondents
interested in a career in government (29%), others
such as consultants, education and culinary (38%),
finance (24%), retail (11%) and IT
/Telecommunication (8%). Thus, the respondents
interested in a career in the government sector are
much larger than respondents with other career
interests.
Categories of characteristics of respondents by
variables can be exhibited in the form of a histogram
as follows:
Figure 3: Frequency of Working Environment Score in
Histogram (n = 75)
Figure 4.3 above shows that the largest dimension
in terms of establishing a working environment in
BUMN companies is communication (4.7) compared
to comfort (4.1) and working relations (3.6). Based on
vocational program students’ perception, there are
statements that communication is the highest
dimension which establishes the highest working
environment, among others:
Woman
73%
Man
27%
GENDER
Series1
0
1
2
3
4
5
Working
Relation
Communication Convertability
Series1
3.6 4.7 4.1
ICVHE 2019 - The International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE) “Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable
4.0 Industry”
88
1. Good communication relationships with
colleagues or employees around the working
environment
2. Do not experience communication barrier
with fellow colleagues
3. It is free to express opinions at the working
environment
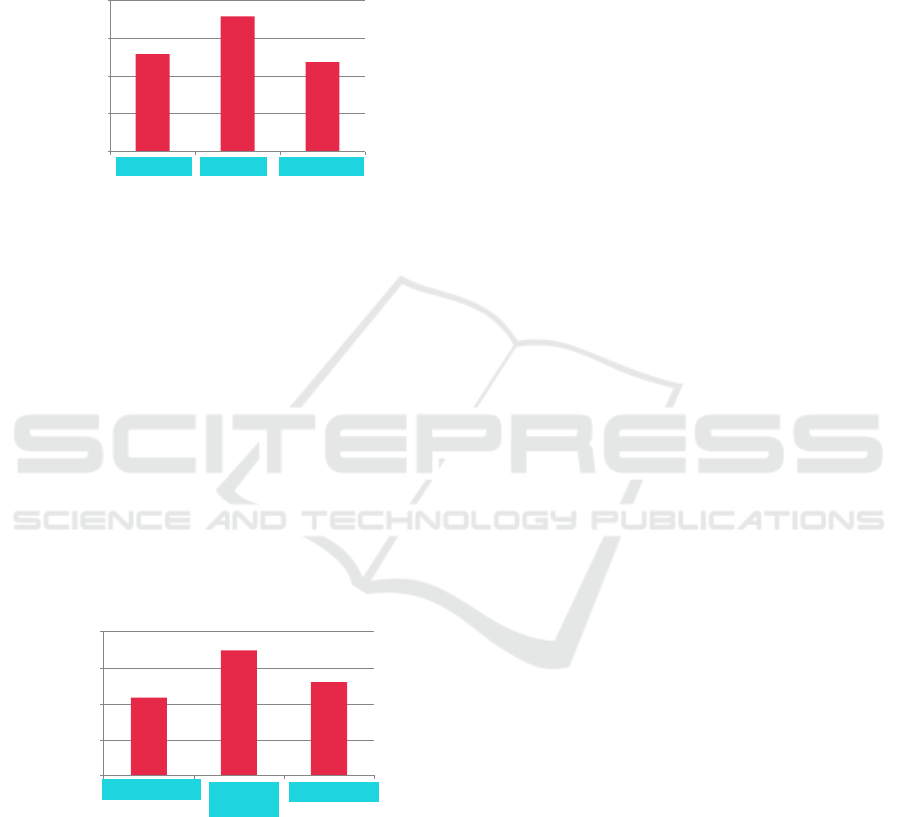
Figure 4: Frequency of Mentor Role Score in Histogram (n
= 75)
Figure 4.4 above shows that the largest dimension
establishes the role of a mentor in a BUMN company
is the directing dimension (4.6) compared to the
discussion dimension (3.6) and responsibility (3.4).
Based on vocational program students’ perception,
there are statements that directing is the highest
dimension which establishes the highest role of
mentor, among others:
1. The mentors provide me with detailed
instructions on how to do the assignment
2. The mentors provide guidance related to
working internships in state-owned
enterprises (BUMN)
3. The mentors provide an explanation to
apprentices on how to start and end a task.
Figure 5: Frequency of Task Orientation Score Histogram
(n = 75)
Figure 4.5 above shows that the largest dimension
which establishes the task orientation in BUMN
companies is the dimension of increasing knowledge
(4.5) compared to the dimension of adding skills (3.6)
and competency (3.2). Based on the vocational
program students’ perception, there are statements
that increasing knowledge is the highest dimension
that establishes the highest task orientation, among
others:
1. Tasks given can increase knowledge and
experience at work
2. Technical obstacles in carrying out a task
that is highly important
3. Explanation about all I need in this
company comes very late
4 CONCLUSION AND
RECOMMENDATION
Based on the results of research and discussion also
analysis that have been done in the previous chapter,
then this chapter concludes the following research:
4.1 Descriptive Variable
The biggest dimension forming a working
environment in implementing a certified
apprenticeship program in state-owned enterprises
(BUMN) is the communication dimension
The biggest dimension forming the role of a
mentor in implementing a certified apprenticeship
program in state-owned enterprises (BUMN) is the
directing dimension
The biggest dimension forming the task
orientation in implementing a certified apprenticeship
program in state-owned enterprises (BUMN) is the
dimension of knowledge
4.2 The Evaluation of the
Implementation of a Certified
Internship Program
There is a direct influence between the work
environment on the evaluation of the implementation
of the work apprenticeship program in SOEs with a P
value (0,000) <alpha value. Thus the better the work
environment factors will improve the implementation
of work apprenticeship programs in state-owned
enterprises (BUMN)
There is a direct correlation between a mentor role
towards implementation evaluation of the internships
program in state-owned enterprises (BUMN) with P
value (0,000) < alpha value. Therefore the better a
mentor role in state-owned enterprises (BUMN) will
increase the implementation of internship programs
in state-owned enterprises (BUMN).
There is a direct correlation between task
orientation towards the implementation evaluation of
the internships program in state-owned enterprises
3.6
4.6
3.4
1.0
2.0
3.0
4.0
5.0
Berdiskusi Mengarahkan Tanggung Jawab
Discussion Directing Responsible
3.2
4.5
3.6
1.0
2.0
3.0
4.0
5.0
Sesuai Kompetensi Menambah
Pengetahuan
Menambah Skill
As competency
Increase
knowledge
add skill
Improving the National Internship Certified Program based on Examination from Vocational Education Program (University of Indonesia)
Students Experience
89

(BUMN) with P value (0,000) < alpha value.
Therefore the better the task assignments will
increase the implementation of the internship
program in state-owned enterprises (BUMN).
4.3 Recommendation
This research shows that the working environment,
mentor roles, and task orientation become important
aspects of the implementation evaluation of the
internship program of state-owned enterprises
(BUMN). Therefore, there are some
recommendations made as follows:
This program should be continued, the internship
program not only giving benefits to all the
students but also strengthening the relationship
between the higher education system and state-
owned enterprises (BUMN). Therefore,
combining roles, skills, and knowledge from the
higher educations systems with the industry
becomes a way of improving the quality of
vocational program graduates.
The educational institution needs to direct and
communicate with the participants of the
internship program in terms of work at the state-
owned enterprises (BUMN) by giving
assignments that match their skills.
Education institution together with companies
should prepare standard internship guidance and
socialized to the mentors or users. In some case
we have found that some mentors did not
understand so well regarding this program.
Companies should be more seriously doing the
program, specialy in facilities and working
equipment and also companies should prepare
more budget for extra works, because the
internship program applied for six months
minimum, so the company may maximize the
students contribution but they should pay
attention to student benefit.
REFERENCES
Parveen, Dr. Saleha., 2012 Associate Professor. “Internship
Program in Education: Effectiveness, Problems and
Prospects”. Department of Curriculum & Special
Education, Faculty of Education, University of Sindh,
Sindh, Pakistan.International Journal of Learning &
Development ISSN 2164-4063, Vol. 2, No. 1
Murasira, Gerard, Dr. Joseph ,Kyalo Mung'atu., 2016.
“Effectiveness Analysis of Internship Program in
Rwanda from July 2014 to June 2015: Kaplan Meier
and Cox Regression Models” , International Journal of
Social Science and Humanities Research ISSN 2348-
3164 (online) Vol.4, Issue 2, pp: (257-272), Month:
April - June 2016, Department of Statistics & Actuarial
Science, Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and
Technology
Natarajarathinam, Dr. Malini., 2014 How to structure an
internship that is great for the intern and the manager?,
Texas A&M University, , Texas A&M University.
R. D. Merritt, Ph.D., 2018 Student Internships.
Carl P. Maertz Jr, Philipp A. Stoeberl and Jill Marks., 2013
Building successful internships: lessons from the
research for interns, schools, and employers. John
Cook School of Business, St Louis University, St Louis,
Missouri, USA.
Ann James, Elizabeth, Lexington, Dr. Jeff Bieber., 2018 A
Qualitative and Quantitative Study of Required
Internship: The Student’s Perspective, Educational
Policy Studies and Evaluation Lexington, Kentucky.
Batool, Zamara., 2012. ”National Internship Programme
and Its Evaluation: A Case Study of Punjab Region”.
Department of Economics, Foundation University,
Islamabad, PAKISTAN. Academic Research
International, ISSN-L: 2223-9553, ISSN: 2223-9944,
Vol. 2, No. 2, March.
Andrew ,Vladimirovich., 2001. Dissertation. Perceived
impact of internship and practical training programs
on professional and personal growth: implications to
agricultural and extension education.
Chan, H. M-Y., Mui. K.W., Wong, L.T., 2005. The impact
of industrial placements on student’s learning
experiences, World Transactions on Engineering and
Technology Education, UICEE, Vol. 4 No. 1.
Ellis, N., 2000. Developing graduate sales professionals
through co-operative education and work placements:
a relationship marketing approach, Journal of
European Industial Training 24/1.
Ghazali, Imam.,2011. Model Persamaan Struktural Konsep
dan Aplikasi dengan Program PLS Ver 3.0.
Harsuko, Rosda.,2011. Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia
Perusahaan, Jakarta.
Leena Toivonen, Sari Pitkakoski, Pirjo Hynninen., 2017.
Mentoring LIS Students During Their Internships: Case
Study. the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0
International License.
Sugiyono., 2014. Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif Kualitatif
dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Sutrisno, Edy., 2013. Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia,
cetakan ke-5, Jakarta: Kencana Prenada Media Group.
Widagdo, B. dan Widayat., 2011.
Pemodelan Persamaan
Struktural : Aplikasi dalam Penelitian Manajemen,
Malang: UMM Press.
ICVHE 2019 - The International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE) “Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable
4.0 Industry”
90
