
Measuring Global Entrepreneurship Index of Indonesia among
ASEAN 6 Countries
Elistia
1
, Suryari Purnama
1
, Nina Nurhasanah
1
and Aliaras Wahid
2
1
Economic and Bussiness Faculty, Universitas Esa Unggul, Jakarta
2
Faculty of Communication, Universitas Esa Unggul, Jakarta
Keywords: Global Entrepreneurship Index, ASEAN Economic Community, Sustainable Entrepreneurship, Economic
Growth.
Abstract: GEI (Global Entrepreneurship Index) has a contextual feature of entrepreneurship by focusing on
Entrepreneurial Attitudes (ATT), Entrepreneurial Abilities (ABT), and Entrepreneurial Aspirations (ASP).
This paper purposes in measuring Global Entrepreneurship Index of Indonesia among ASEAN 6 (six)
Countries. The implementation of the ASEAN Economic Community (AEC) 2015 will create economic
activity with very high mobility and can open business opportunities and employment, but also at the same
time become a huge challenge for countries in the ASEAN region, including Indonesia. For this reason, we
need to know how that position of Indonesia is in the Global Entrepreneurship Index (GEI) among the 6 (six)
ASEAN member countries, namely: Indonesia, Philippine, Malaysia, Singapore, Thailand and Brunei
Darussalam. From the results of the literature review of the GEI report starting from 2015 - 2017, Indonesia's
position is at the lowest rank among the 6 (six) ASEAN countries. So, answering these conditions, it is
necessary to understand what the government's efforts are in the effort to improve Sustainable Global
Entrepreneurship.To spur the development of entrepreneurship, the Indonesian government launched the
National Entrepreneurship Movement (GKN), with the aim of increasing the number of Indonesian
entrepreneurs.According to Sarkar (2014), this interest has been fuelled by the desire to understand how
entrepreneurship influences the economy of a country. Both the economists and policymakersrecognize the
effect of entrepreneurship on the economy of a country. Moreover, the research conducted by Elistia (2017)
found results that stated that the Total Entrepreneurship Activity (TEA) and Economic Growth (GDP) in
Indonesia had a strong positive correlation between TEA and GDP of 0.853 (Pearson correlation). So it can
be concluded that entrepreneurship has an impact on increasing economic growth in Indonesia, this is
expected to increase Indonesia's GEI Index ranking.
1 INTRODUCTION
Global Entrepreneurship has brought new interests
and questions from thousands of new actors to the
dynamics of the world entrepreneurial ecosystem. As
they strive to harness the power of the formation of
new companies to create jobs and innovation ahead,
we have seen a series of new accelerations,
educational programs and policy experiments -
supported by sincere interest in creating the most
powerful local enabling environment.
The purpose of writing this article is to contribute
to our understanding of economic development by
building a Global Entrepreneurship Index (GEI. The
Global Entrepreneurship and Development Institute
(GEDI Institute) is a research organization that
advances knowledge about the relationship between
entrepreneurship, economic development and
prosperity The Institute was founded by leading
entrepreneurial scholars from George Mason
University, the University of Pécs, and Imperial
College London.
GEDI captures the contextual features of
entrepreneurship by focusing on entrepreneurial
attitudes, entrepreneurial activities, and
entrepreneurial aspirations. The data and its
contribution to the business formation process are
supported by three decades of research on
entrepreneurship in some countries. The index
construction integrates 31 variables, 16 from the
Global Entrepreneurship Monitor (GEM), and 14
from other data sources, into 14 pillars, three sub-
2794
Elistia, ., Purnama, S., Nurhasanah, N. and Wahid, A.
Measuring Global Entrepreneurship Index of Indonesia among ASEAN 6 Countries.
DOI: 10.5220/0009952827942801
In Proceedings of the 1st Inter national Conference on Recent Innovations (ICRI 2018), pages 2794-2801
ISBN: 978-989-758-458-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
indices, and a 'super-index'. GEI described in this
paper is only in 6 (six) ASEAN member countries,
namely: Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Thailand,
Philippines and Brunei Darussalam.
Economic development in Indonesia cannot be
separated from the performance of entrepreneurs.
Besides that, the level of competition among
entrepreneurs in the Asian region is also getting
higher, we can take the example of GEDI rank
assessment in ASEAN member countries. The
ASEAN Economic Community (MEA) will formally
be implemented by the end of 2015 even though the
process has begun since the signing of the ASEAN
Framework Agreement on Economic Cooperation by
ASEAN leaders in 1992 (Kemenko, 2015). Thus, free
trade has actually begun to be implemented gradually
and progressively by ASEAN member countries
through the regional trade agreement (RTA) in the
form of the ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA). AEC
(ASEAN Economic Community) has a blueprint, this
is one of the most important milestones of ASEAN
economic integration. It is structured on four pillars: i)
a single market and production base; (ii) competitive
economic area; (iii) equitable economic development;
and (iv) integration into the global economy. The
work agenda starts in 2015 towards 2030, ASEAN
needs to continue to deepen regional integration by
creating a truly unlimited economic community.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
The implementation of the ASEAN Economic
Community (AEC) 2015 will create economic
activity with very high mobility and can open
business opportunities and employment, but also at
the same time become a huge challenge for countries
in the ASEAN region, including Indonesia. The
creation of the ASEAN Community implies not only
institutional/institutional reform and innovation to
build a mature and developing society, but also close
coordination in developing the three pillars of
ASEAN, namely: political-security, economic, and
socio-cultural.
The relationship between entrepreneurship and
economic growth of a country has increasingly gained
much interest from economists and policymakers
over the years. However, while some view it as a
direct relationship, others see it as an indirect kind of
relationship. According to Sarkar (2014), this interest
has been fuelled by the desire to understand how
entrepreneurship influences the economy of a
country. Both the economists and policy makers
recognize the effect of entrepreneurship on the
economy of a country.
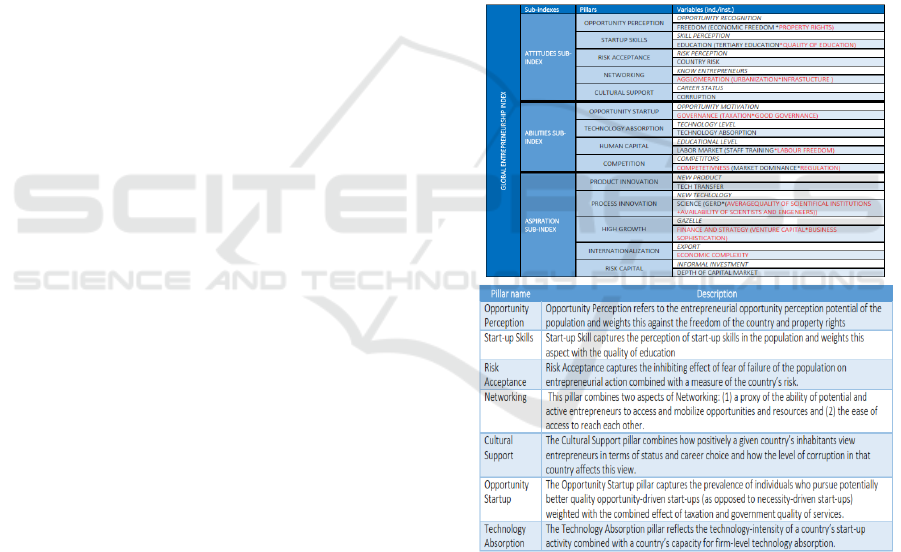
GEI consists of three components or sub-indices
3A, namely: Entrepreneurial Attitudes (ATT),
Entrepreneurial Abilities (ABT), and Entrepreneurial
Aspirations (ASP). These three sub-indices stand on
14 pillars, each of which contains an individual and
institutional variable that are compatible with the
micro and entrepreneurial aspects of the macro level.
The GEDI pillar includes individual and individual
institutional variables. This pillar is an effort to
capture the open nature of entrepreneurship;
analyzing they can provide an in-depth view of the
strengths and weaknesses listed in the index described
in the 14 entrepreneurship pillars in table 1.
Table 1: The Structure of the New Global Entrepreneurship
Index (GEI)*
Source: The GEDI 2017
*Individual variables are colored with a white
background while institutional ones with the light
blue background. Red letters show the changes in the
index structure as compared to the previous GEI
version.
According to table 1, Sub-Indexes consist of 3
aspects namely: Attitudes Sub-index, Abilities Sub-
Index, and Aspiration Sub-Index. The following is the
explanation:
Measuring Global Entrepreneurship Index of Indonesia among ASEAN 6 Countries
2795

Attitudes Sub-index is for Entrepreneurial
Attitudes (ATT). Entrepreneurial attitudes
reflect people’s attitudes toward
entrepreneurship. It involves opportunity
recognition, startup skills, risk perception,
networking, and cultural supports of
entrepreneurs. Institutional embeddingis
expressed as the property rights and economic
freedom, the quality of the education, the
riskiness of the country, the connectivity
potential, and the prevalence of corruption.
Abilities Sub-Index is for Entrepreneurial
Abilities include some important characteristics
of the entrepreneur that determine the extent to
which new startups will have potential for
growth, such as motivation based on
opportunity as opposed to necessity, the
potential technology-intensity of the startup, the
entrepreneur’s level of education, the level of
competition and digital startup capabilities.
These individual factors coincide with the
proper institutional factors of taxation and the
efficiency of government operation
(Governance), technology adsorption
capability, the freedom of the labor market and
the extent of staff training (Labor Market), and
the dominance of powerful business groups as
well as the effectiveness of antimonopoly
regulation (Regulation).
Aspiration Sub-Index is for Entrepreneurial
Aspiration refers to the distinctive, qualitative,
strategy-related nature of the entrepreneurial
activity. The individual and institutional factors
of product and process innovation such as
technology transfer, the applied research
potential of science, high growth expectations,
venture capital availability and strategy
sophistication (Finance and Strategy),
internationalization and the availability of risk
financing constitute entrepreneurial aspirations.
Based on those sub-indexes table 2 shown the
description:
Table 2: The Description of the GEI Index Pillar
Source: The GEDI 2017
3 DATA AND METHODOLOGY
This paper is based on literature review and
conceptual analysis. Literature studies and conceptual
analysis are intended to identify the value of GEI in 6
(six) ASEAN member countries in 2015, 2017. GEI
provides a detailed description of the health of the
entrepreneurial ecosystem of a country. GEI is
designed to help the government utilize
entrepreneurial power for sustainable economic
development.
Sources of data and information for this paper are
derived from the report of The GEDI Institute in the
form of an assessment of the Global Entrepreneurship
Index (GEI) in 6 (six) ASEAN member countries,
namely: Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Thailand,
Philippines and Brunei Darussalam. The data
displayed is as follows:Global Rank Global
Entrepreneurship Index (GEI)
1. Global Entrepreneurship Index (GEI) Score
2. Entrepreneurial Attitude (ATT) Score
3. Entrepreneurial Abilities (ABT) Score
4. Entrepreneurial Aspiration (ASP) Score
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The results of data processing scoring and indexing
on 6 (six) ASEAN member countries in Indonesia,
Malaysia, Singapore, Thailand, Philippines and
Brunei Darussalam are as follows:
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
2796
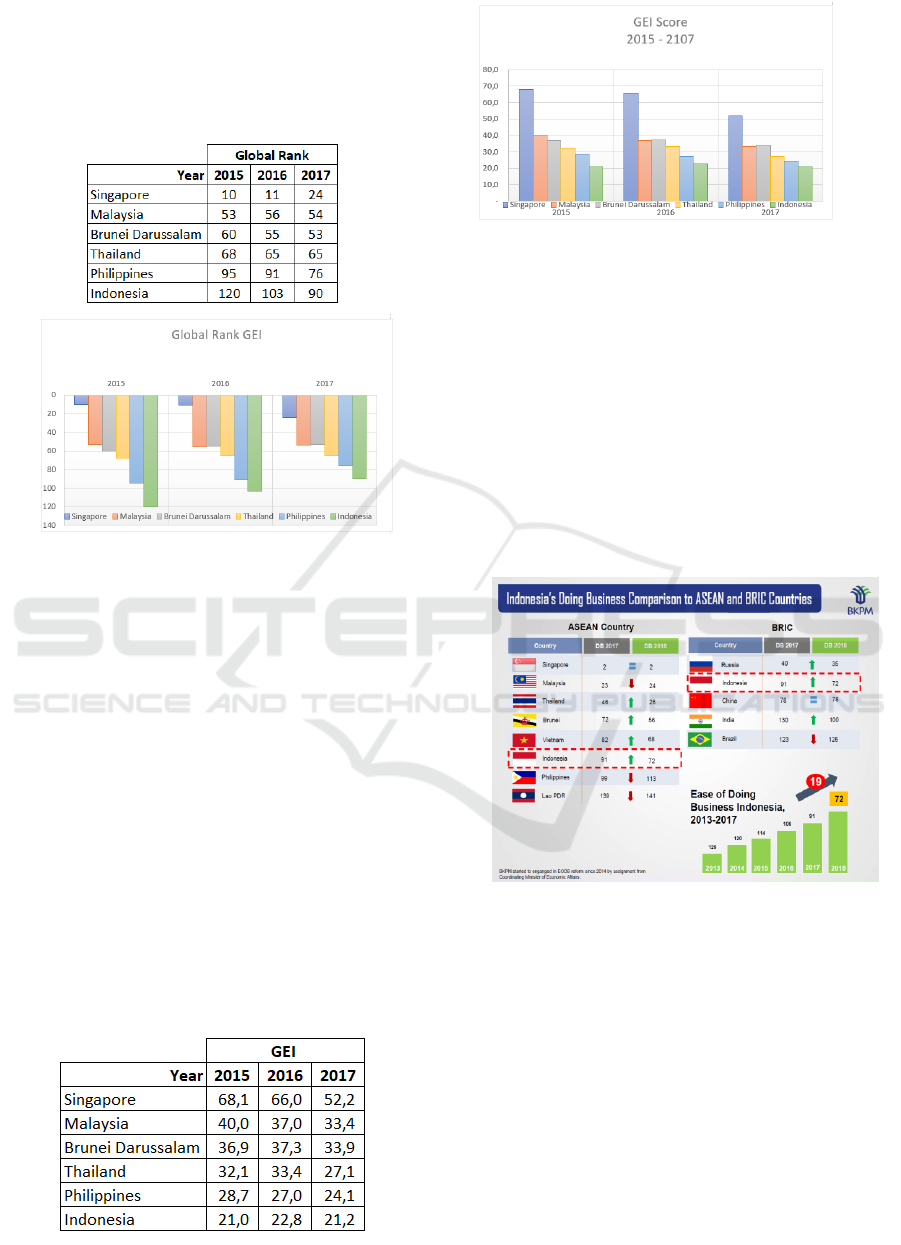
4.1 Global Rank Global
Entrepreneurship Index (GEI)
Table 3. Global GEI Rank 6 Negara ASEAN 2015 -
2017
Figure 1. Global GEI Rank 6 Negara ASEAN 2015 -
2017
Data in Table 3 and Figure 1 shows that
Indonesia, despite the lowest GEI Global Rank, is
among the 6 (six) countries, but the increase from
2015 to 2017 has increased quite well, namely an
increase of an average of 14% from the previous year.
4.2 Global Entrepreneurship Index
(GEI) Score
The following are the results of the GEI Score of
6 ASEAN countries from 2015 - 2017, which shows
that Indonesia is still in the 6th position. Therefore
Indonesia must try to improve the aspects of ATT,
ABT and ASP.
Table 4. Global Entrepreneurship Index (GEI) Score 6
Negara ASEAN 2015 - 2017
Figure 2. Global Entrepreneurship Index (GEI) Score
6 Negara ASEAN 2015 - 2017
From the data in table 4 and figure 2, GEI Score
Indonesia is the lowest position of the 6 ASEAN
countries, therefore the need for Government,
Community and Business / Industry efforts to
collaborate to improve the Global Entrepreneurship
Index (GEI) Score. An increase in the
Entrepreneurship Index can also be seen from the
Ranking of Indonesia in the Ease of Doing Business
which increases every year. The increase can be seen
in reports from the Indonesia Investment
Coordinating Board as shown in figure 3 below:
Figure 3. Indonesia’s Doing Business from 2013 –
2017
If seen in figure 3, shows that Indonesia can
compete enough among ASEAN countries, because
each year the ranking is consistently increasing.
Therefore, it is expected to be able to boost
Indonesia's GEI score.
4.3 Entrepreneurial Attitude (ATT)
Entrepreneurial attitudes are societies’ attitudes
toward entrepreneurship, which we define as a
population’s general feelings about recognizing
opportunities, knowing entrepreneurs personally,
Measuring Global Entrepreneurship Index of Indonesia among ASEAN 6 Countries
2797
endowing entrepreneurs with high status,
acceptingthe risks associated with business startups,
and having the skills to launch a business
successfully. The benchmark individuals are those
who can recognize valuable business opportunities
and have the skills to exploit them; who attach high
status to entrepreneurs; who can bear and handle
startup risks; who know other entrepreneurs
personally (i.e., have a network or role models); and
who can generate future entrepreneurial activities.
(GEDI, 2017)
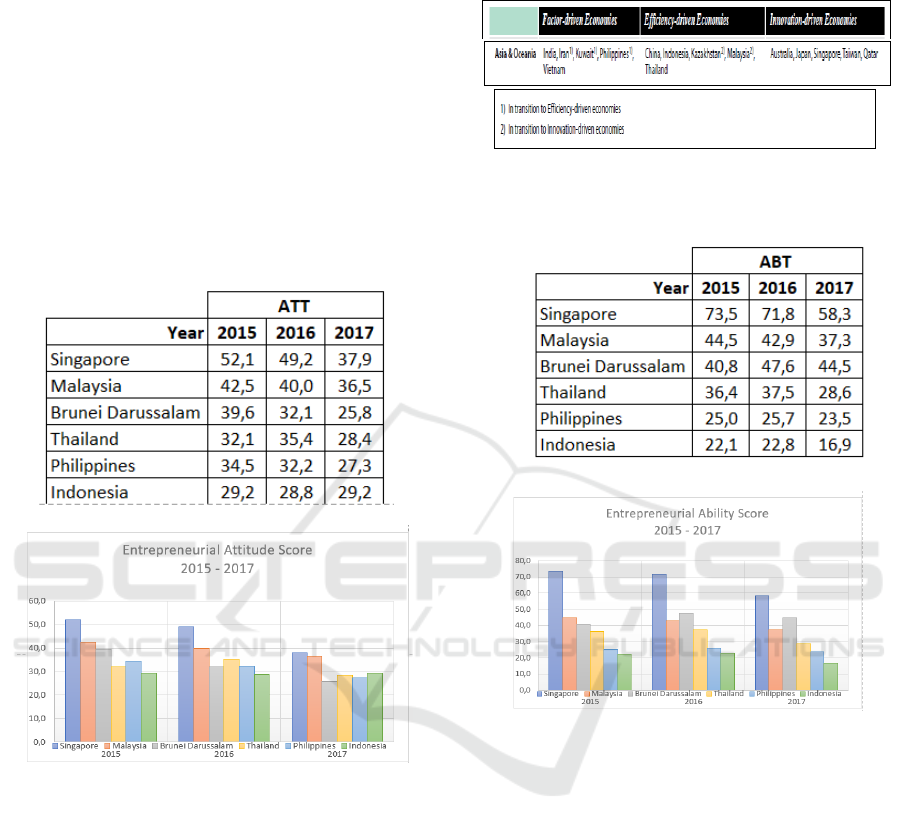
Table 5. Entrepreneurial Attitude (ATT) Score 6
Negara ASEAN 2015 - 2017
Figure 4. Entrepreneurial Attitude (ATT) Score 6
Negara ASEAN 2015 - 2017
Table 5 and Figure 4 have shown that ATT of
Indonesia can compete against Malaysia, Brunei,
Thailand and Philippines. According to the data by
GEM (General Entrepreneurship Monitor), based on
Economies Participating in the 2014 GEM Survey,
grouped by Geographic Region and Economic
Development Level in Asia & Oceania data shown,
Indonesia is in Efficiency-driven Economies, which
are consistent to increase industrialization and
economies of scale (Table 6).
Table 6. GEM Economic Development Level in ASEAN 5
Countries
Table 7. Entrepreneurial Ability Score (ABT) Score
6 Negara ASEAN 2015 - 2017
Figure 5. Entrepreneurial Abilities (ABT) Score 6
Negara ASEAN 2015 – 2017
Entrepreneurial abilities refer to the
entrepreneurs’ characteristics and those of their
businesses. Different types of entrepreneurial abilities
can be distinguished within the realm of new business
efforts. Creating businesses may vary by industry
sector, the legal form of organization, and
demographics—age, education, etc. We define
entrepreneurial abilities as startups in the medium- or
high-technology sectors that are initiated by educated
entrepreneurs and launched because of a person being
motivated by an opportunity in an environment that is
not overly competitive. In order to calculate the
opportunity startup rate, we use the GEM TEA (Total
Early Entrepreneurship) Opportunity Index. TEA
captures new startups not only as the creation of new
ventures but also as startups within existing
businesses, such as a spinoff or other entrepreneurial
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
2798
effort. Differences in the quality of startups are
quantified by the entrepreneur’s education level—
that is, if they have a postsecondary education—and
the uniqueness of the product or service as measured
by the level of competition. Moreover, it is generally
maintained that opportunity motivation is a sign of
better planning, a more sophisticated strategy, and
higher growth expectations than “necessity”
motivation in startups. (GEDI, 2017).
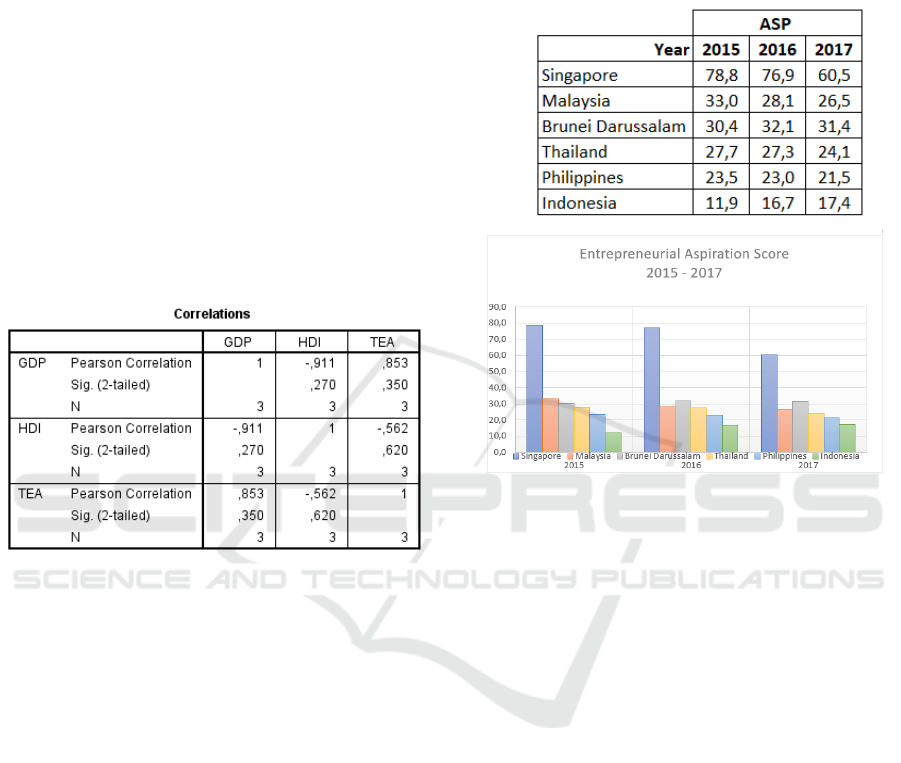
According to Elistia (2017), Indonesia has a
strong positive correlation between TEA and GDP of
0.853. While the HDI and GDP has a negative
correlation-0.911. HDI and TEA a correlation has a
negative correlation -0.562. It means that only TEA
variables are positively correlated to GDP Indonesia.
Table 8. Correlation HDI, TEA, and GDP in Indonesia
from 2013 - 2015
Source: Elistia, (2017), The Correlation of HDI
and GEI towards Economic Growth in ASEAN 5
Countries, ICSSH PROCEEDINGS, 4th Kuala
Lumpur International Conference on Social Science
& Humanities (ICSSH), ISSN 2454-5899.
4.4 Entrepreneurial Aspiration
Entrepreneurial aspiration reflects the quality aspects
of startups and new businesses. Some people just
dislike their current employment situation and want
to be their own boss, while others want to create the
next Microsoft. Entrepreneurial aspiration is defined
as the early-stage entrepreneur’s effort to introduce
new products and/or services, develop new
production processes, penetrate foreign markets,
substantially increase their company’s staff, and
finance their business with formal and/or informal
venture capital. Product and process innovation,
internationalization, and high growth are considered
the key characteristics of entrepreneurship. Here we
added a finance variable to capture the informal and
formal venture capital potential that is vital for
innovative startups and high-growth firms. (GEDI,
2017)
Table 9. Entrepreneurial Aspiration (ASP) Score 6 Negara
ASEAN 2015 - 2017
Figure 6. Entrepreneurial Aspiration (ASP) Score 6
Negara ASEAN 2015 - 2017
In terms of Ease of Doing Business, The
economies showing the most notable improvement in
performance on the Doing Business indicators in
2015/16 of ten economies are highlighted this year for
making the biggest improvements in their business
regulations—Brunei Darussalam, Kazakhstan,
Kenya, Belarus, Indonesia, Serbia, Georgia, Pakistan,
the United Arab Emirates and Bahrain. Indonesia is
one of the biggest improvements in their business
regulations. In this report tells us the following
information of 7 (seven) improvements:
4.5 Starting a Business
Indonesia made starting a business easier by creating
a single form to apply for the company registration
certificate and trading license. This reform applies to
Jakarta. Indonesia also made starting a business easier
by abolishing the minimum capital requirement for
small and medium-sized enterprises and by
encouraging the use of an online system to reserve
company names. This reform applies to both Jakarta
and Surabaya.
Measuring Global Entrepreneurship Index of Indonesia among ASEAN 6 Countries
2799

4.5.1 Getting Electricity
Indonesia made the process of getting an electricity
connection faster by reducing the time for contractors
to perform external work thanks to an increase in the
stock of electrical material supplied by the utility. In
Surabaya, getting electricity was also made easier
after the utility streamlined the process for new
connection requests.
4.5.2 Registering Property
Indonesia made it easier to register property by
digitizing its cadastral records and setting up a
geographic information system. This reform applies
to both Jakarta and Surabaya.
4.5.3 Getting Credit
Indonesia strengthened access to credit by
establishing a modern collateral registry. This reform
applies to both Jakarta and Surabaya.
4.5.4 Paying Taxes
Indonesia made paying taxes easier by introducing an
online system for filing and paying health
contributions. Indonesia also made paying taxes more
costly by levying a new pension contribution at a rate
of 2% paid by employers. These reforms apply to
both Jakarta and Surabaya.
4.5.5 Trading across Borders
Indonesia made exporting and importing easier by
improving the customs services and document
submission functions of the single national window.
This reform applies to both Jakarta and Surabaya.
4.5.6 Enforcing Contracts
Indonesia made enforcing contracts easier by
introducing a dedicated procedure for small claims
that allows for parties’ self-representation. This
reform applies to both Jakarta and Surabaya.
5 CONCLUSION
An effort to maintain and enhance the entrepreneurial
position that has been achieved at this time, the
entrepreneurial practitioners should build sustainable
entrepreneurship to create entrepreneurship that is
strong, sustainable and mutually supportive and
sustainable, by utilizing the synergy of various
elements of society. With the creation of sustainable
entrepreneurship, sustainable competitiveness at the
national and global levels can be realized. Sustainable
entrepreneurship focuses on the skills of
entrepreneurs to realize their success through social
and environmental change or social innovation.
Entrepreneurship no longer only produces
economic success, but sustainable entrepreneurs can
manage the "triple bottom line" (corporate
profitability, potential benefits for the environment,
as well as potential benefits for the community) by
balancing economic health, social justice and
environmental resilience through their
entrepreneurial behavior. Lately, there have been
many scientific discussions about entrepreneurial
theory and practices related to sustainable
entrepreneurship that is oriented towards the
community, ethical, economic and ecological goals.
In fact, entrepreneurship has been considered as
the engine of economic growth,and it has come to be
perceived as a catalytic agent for expansion and
promotion of productive activities in every sphere of
economic life all over the world. The role and
significance of entrepreneurship development in
numerous nations worldwide were quite significant.
Furthermore, the research of Jeanel Dominique et al.
(2017) showed there was a positive relationship
between entrepreneurship and economic
development. And, the research of Omoruyi et al.
(2017) found that innovation, entrepreneurship
curriculum training and education, individual
entrepreneurial characteristics, the participation of
micro, small and medium enterprises, youth
empowerment, the collaboration of government-
university-industry are the key tool for
entrepreneurship development which is stimulating
employment are eventually alleviating poverty.
The government effort through the National
Entrepreneurship Movement (GKN) is a movement
that grows from the bottom, so it has a strong
foundation to develop. This condition can increase
the ratio of Indonesian entrepreneurs who in
2013/2014 were still 1.67 percent, this year based on
BPS data it has risen to 3.1 percent (Ministry of
Cooperatives and SMEs, 2017).
So it can be concluded that to realize Indonesia
which is more competitive through the development
of entrepreneurship and the digital sector, it takes
cooperation from all parties. Not only the
government, but also the business world, academics,
and the wider community to create a conducive
entrepreneurial ecosystem.
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
2800

REFERENCES
Acs, Zoltán J. & László Szerb, 2010, “The Global
Entrepreneurship and Development Index (GEDI)”,
Summer Conference 2010 on "Opening Up Innovation
: Strategy, Organization and Technology" at Imperial
College London Business School, June 16 - 18, 2010.
Amorós, José Ernesto., Cristóbal Fernández &Juan Tapia,
2011, “Quantifying the Relationship Between
Entrepreneurship and Competitiveness Development
Stages in Latin America”, The International
Entrepreneurship and Management Journal (IEMJ,
DOI 10.1007/s11365-0100165-9).
Basu, A., Asbjorn Osland, & Michael Solt, 2009, A New
Course on Sustainability Entrepreneurship (Working
Paper), San Jose State University & National
Collegiate Inventors and Innovators Alliance,
http://nciia.org/basu1 (Diakses 28 Maret 2014).
Batra, Surinder., 2012, “Sustainable Entrepreneurship and
Knowledge Based Development”, The 11th
International Entrepreneurship Forum Kuala Lumpur,
Malaysia, 3-6 September, 2012.
Carree, M., Van Stel, A., Thurik, R., & Wennekers, S.,
2007, “The Relationship Between Economic
Development and Business Ownership : Revisited”,
Entrepreneurship and Regional Development, Vol.19,
No. 3, pp 281–291.
GEDI (Global Entrepreneurship and Development Index),
2015 – 2017
Elistia,. 2017, The Correlation of HDI and GEI towards
Economic Growth in ASEAN 5 Countries, ICSSH
PROCEEDINGS, 4th Kuala Lumpur International
Conference on Social Science & Humanities (ICSSH),
ISSN 2454-5899.
Jeanel D.M. Bonito, Felbien J.A. Daantos, Jesi C.A. Mateo,
Marie Antoinette L.Rosete, M.D.E. (2017). Do
Entrepreneurship and Economic Growth Affect
Poverty, Income Inequality and Economic
Development?. Review of Integrative Business and
Economics Research, Vol. 6, no. 1, pp.33-43, January
2017.
Sarkar S (2014), International Journal of Finance and
Policy Analysis. London: Universal Publishers, UK.
Omoruyi EMM, Olamide KS, Gomolemo G and Donath
OA. (2017). Entrepreneurship and Economic Growth:
Does Entrepreneurship Bolster Economic Expansion in
Africa? Journal of Socialomics. ISSN: 2167-0358.
Volume 6, Issue 4.
Global Entreprenuership Monitor.
https://gemconsortium.org/report
https://www.ekon.go.id/press/view/siaran-pers-ekonomi-
digital.3016.html
http://www.depkop.go.id/content/read/ratio-wirausaha-
indonesia-naik-jadi-31-persen/
Measuring Global Entrepreneurship Index of Indonesia among ASEAN 6 Countries
2801
