
The
R
epresentations of Informative Function in Handling Food
Service at Restaurant
Denok Lestari
1
1
Dept. of Hotel Management, Sekolah Tinggi Pariwisata Bali Internasional, Denpasar, Indonesia
Keywords: English for Specific Purposes, Informative Function, Language Functions, Tourism.
Abstract: Tourism is the worldwide fast-growing industry which directly affects various fields of life. Tourism study
does not stand by itself, but is supported by other social sciences, specifically language education. This paper,
based on a research in language functions, aimed to identify the use of informative functions in handling food
service at the restaurant. Categorized as a study of English for Specific Purposes (ESP), this paper described
language variations to provide preliminary analysis of needs in tourism and hospitality context. The research
methods were qualitative, using observation and recording technique. The data were in the form of transcribed
utterances between guests and waiters at the restaurant. The result of the analysis showed that informative
functions were represented through micro functions, namely ‘asking’, ‘explaining’, ‘stating’, and
‘confirming’.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the benefits of tourism is to expand
employment and improve living standards of local
people. The rapid development of the hospitality
industry can directly affect language needs (Lin, Wu,
and Huang, 2013). As tourism growth in line with
hospitality industries, the ability to speak foreign
languages, especially English, is increasingly
becoming a necessity and the main requirement for
achieving the desired profession. To practitioners
involved in the industry, especially those who have
direct contact with guests, such as front office staff
and waiters at restaurants, English is very important
as a media for revealing product knowledge and
services. Therefore, those who work in the tourism
sector must improve communication skills, as well as
fluency in language (Zahedpisheh, et al. 2017). The
sparks of language research in tourism have attracted
attention due to high mobility of international tourists
in the non-English speaking countries. English, which
is the most widely used language as a medium of
interaction, has a major role in delivering quality of
services. Employees working in the tourism and
hospitality industry are fully aware of the importance
of good English competence to carry out their roles.
Given the importance of language support in the
development of tourism, this article highlights the use
of language functions used in restaurant service.
Although language learning currently tends to be
communicative, linguistic knowledge is still needed
to improve understanding of the target language
(Lestari, 2013). Discussing the function of language
is equal to discussing language use because the
language will not be meaningful if it is not used or
functioned (Luardini, 2009). Language function
refers to the use of language by speaking, writing,
reading, and listening to achieve communication
goals (Halliday and Hasan, 1985: 17). The word
'function' can be seen as the equivalent of the word
'use' so that the function of language cannot be
separated from the situational and cultural context
behind the language.
'Functions' from a pragmatic point of view tend to
focus more on the purpose of the speaker than the
effect on the listener (Cook, 1994). Function involves
two things: the purpose of the language in general –
referred to as a macro function, and the action carried
out by speech specifically – referred to as a micro
function (Cook, 1994). For example, 'explaining' is
included in the micro function, while 'informative' is
categorized as a macro function. The function of
language is basically the goal achieved by language,
for example stating, asking, responding, greeting,
saying farewell words, and so on (Brown, 2007: 245).
Leech (1974: 47-50) divides the communicative
functions of language into five, such as: 1)
Informational functions to convey information; 2)
2050
Lestari, D.
The Representations of Informative Function in Handling Food Service at Restaurant.
DOI: 10.5220/0009939120502056
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Recent Innovations (ICRI 2018), pages 2050-2056
ISBN: 978-989-758-458-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Expressive functions to express the feelings and
attitudes of speakers; 3) Directive functions are used
to influence the behavior and attitudes of others; 4)
Aesthetic functions, the use of language for the sake
of the work itself without hidden intentions, for
example in poetry; 5) Phatic function, oriented to
means of communication with the aim of keeping the
lines of communication open and to maintain good
relations in society. Four of the five language
functions proposed by Leech (1974) are very suitable
to be used as an analytical knife to identify the
representation of language functions in the field of
food service, namely informational, directive,
expressive, and phatic functions, while an aesthetic
function (which tends to be poetic) may not be
suitable to be applied in the language variation in
restaurants which are mostly informative.
Meanwhile, Halliday (1973: 22-26) divided
language functions into seven categories described as
follows (1973: 22-26): An instrumental function is
the function of language to manipulate the
environment, and to create certain situations or
events; 2) Regulatory functions, namely the function
of language in controlling circumstances or events; 3)
Representational functions, namely the function of
language to make statements, convey facts and
knowledge, explain or bring back reality as people see
it; 4) Interactional function, which is a language
function that refers to its function as an interacting
tool; 5) Personal function, which is a language
function that implies the meaning that language is
a tool to identify oneself; 6) Heuristic function,
which is used to obtain knowledge; and 7)
Imaginative functions, which can be used to imagine
or create ideas. The most appropriate with the
objective of this research is the fourth function,
namely interactional functions that mainly aim to
interact. This function requires a speaker to
understand cultural values including politeness that
applies in certain language.
Previously, Bühler (1965) argued that language
could fulfill three functions: i.e. representational
functions, conative functions, and expressive
functions. 1) Representational functions are carried
out by signs of language, e.g. text, utterances,
sentences, etc.; 2) The conative function will be
fulfilled when the text asks the reader or listener to do
something, mentally, emotionally or physically, and
influences their behavior, and 3) Expressive function
will be achieved when the text is able to express the
inner state of the writer or speaker. Whereas Jacobson
(1960) divided language functions into six, namely:
1) Emotive function, used in human feelings as a tool
to express themselves; 2) Conative function, used to
motivate others to behave or do something; 3)
Referential function, used to discuss a problem with
a particular topic; 4) Poetic function, used to convey
a specific message or message; 5) Phatic function,
used to greet each other simply to make contact with
others; and 6) Metalingual functions, used to discuss
language problems with certain language.
The four theories of language function were then
reformulated in Lestari (2017) which was adjusted to
the use of language in the restaurant, called the food
service, which was described as follows: 1)
Informative function is used to exchange information
represented in the function 'explain', 'state' , and 'ask';
2) The directive 'ordering' function is refined to
'invite' or 'ask'; 3) The interactive function is identical
with the effort to create as well as to maintain
harmonious and communicative interactions between
participants, which is represented in the function of
'greeting', and “chit-chatting’. 4) Indicative functions
are used as markers in a conversation, which are
realized in the function of 'thanking' and
'apologizing'; 5) Persuasive functions are used when
offering and providing alternatives to guests with the
aim of selling restaurant products; and 6) Permissive
functions to create comfort and smoothness in a
speech event. The use of non-standard English that
remains acceptable, the use of intonation, and the use
of passive forms is the representation of permissive
functions.
The taxonomy in table 1 shows that the extended
study of language functions is getting more
interesting to discuss, especially if it is associated
with studies outside the language, such as tourism and
hospitality. In food service, the language function
mostly used is the informative function, that is, when
the waiter provides information to guests about the
menu or facilities available. Therefore, the problem
raised in this study is: how is the function of
informative language represented in the expressions
of language used in restaurants? The findings in this
study can be used as a needs analysis and
contribute to the preparation of ESP learning
materials, especially in the field of tourism and
hospitality.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
This research was carried out at Mamasan
Restaurant, located on Jalan Kerobokan No 135,
Kuta-Badung. Qualitative data were in the forms of
recorded conversations between waitresses and
guests, and also the results of interviews of 25 waiters
and waitresses. The data were secondary as taken
The Representations of Informative Function in Handling Food Service at Restaurant
2051
from a dissertation on language functions (Lestari,
2017). In qualitative research, the researcher can be
the main instrument (Creswell, 2010). The
instruments used were a recorder, observation sheet,
and a semi-structured interview sheet, in addition to
the researcher herself. The findings were then
presented informally using narrative descriptions.
The analysis method used is the taxonomy of
language functions.
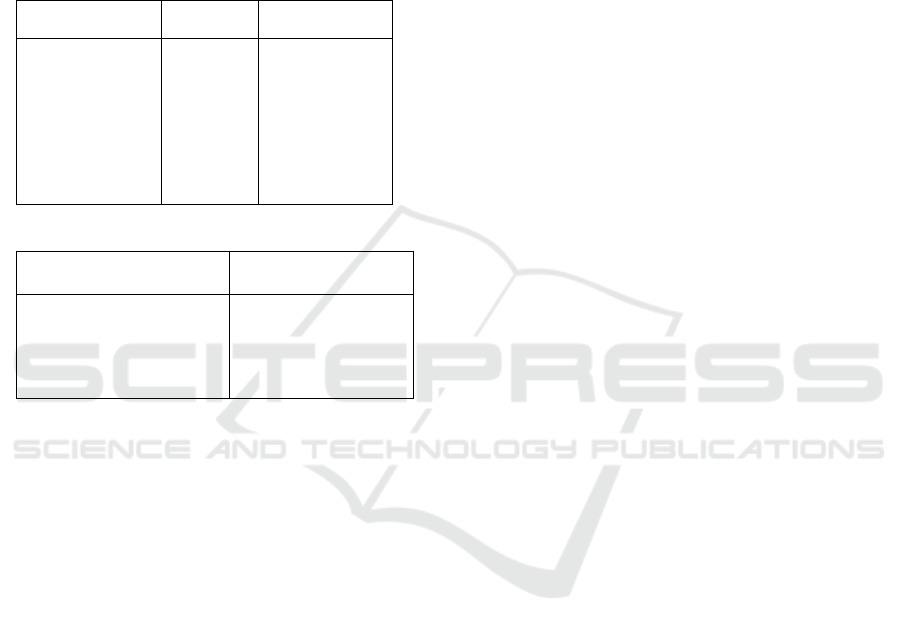
Table 1: Taxonomy of Language Functions (1)
Bühler
(1965)
Jacobson
(1960)
Lestari
(2017)
Representational
Conative
Expressive
Referential
Conative
Phatic
Emotive
Poetic
Metalingua
l
Informative
Directive
Interactive
Indicative
-
-
-
Persuasive
Permissive
Table 2: Taxonomy of Language Functions (2)
Leech
(1974)
Halliday
(1973)
Informational Directive
Phatic
Expressive Aesthetic
Representational
Instrumental
Interactional Personal
Imaginative
Regulatory Heuristic
3 FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS
The verbal transcription indicated that informative
function tends to be used by waiters when explaining
menu to guests at the restaurant. This informative
function is represented in a number of micro
functions, including 'explaining', 'asking', and
'confirming'. The following is a more detailed
description of the informative function and its
representations.
3.1 ‘Explaining’ Function
Waitress: Good evening, ma’am, sir. Have you been
here before?
Guest: No, it’s our first time.
Waitress: So, we will explain the Mamasan concept,
please. Our concept here is family dining,
like a family self. So, we put the food in
the middle, you can share between you like
the starter or the main course. But for the
entrée, start from the Grilled Scallops until
the Chicken Betel Leaf is come one pieces,
and the rest you can share in the middle.
And this is good come with the side dishes
like the Naan or some rice. And ... are you
OK with the spicy or you have any allergy,
please?
Conversation above, is the 1
st
experiment.
Mamasan Restaurant is unique in that it serves a large
portion of food so that it can be enjoyed together. To
first-time visitors, the waitress is obliged to explain
this concept. As shown in the 1
st
data, waitress used
the interrogative "Have you been here before?" to find
out whether or not the guest has ever visited the
restaurant. The purpose of this question was to
determine if the waitress needed to explain the
concept of the restaurant, because the unique concept
must be explained to each guest who first came to the
restaurant. This is to avoid mistakes in ordering food
that might lead to problems or complaints from
guests.
The waitress's question was responded by the
guest, indicating that they were first-time guests.
Knowing this, she immediately decided to give an
explanation about the restaurant concept, by starting
with a statement "Our concept here is family dining".
The waitress then explained at length what is meant
by the concept of family dining, i.e. dishes were
served in large portions so that they could be shared
in group. The waitress also informed that there were
several menus which were served in small portions.
When the guest asked a second time, the waitress
immediately explained and described the name of the
food in question complete with the accompanying
dish. Thus, in a speech, the waitress used the function
‘explaining’ together with ‘describing’.
Unlike the previous interrogative, the following
questions "Do you have any food allergy?" And "Do
you have any problem with spicy?" gave clues on
what foods might be recommended to guests or, on
the contrary, should be avoided. This certainly aimed
to prevent the emergence of complaints or unwanted
problems. Thus, the function 'asking' is often a trigger
for statements, explanations, as well as determining
the next response. For example, it is necessary to
explain the concept of a restaurant, as shown in the
previous conversation. This conclusion is reinforced
by the following data:
Guest: What’s different for entrée and starter?
Waitress: So entrée are mostly smaller like
individual portion, and starter are
bigger...like salad. You can check all in
the menu.
Guest: Great. And what is Pork Belly?
Waitress: Pork Belly is a type of cube pork belly, it
comes with the tamarind sauce and the
other side is dipping sauce, the Naan pan
sauce. It’s a bigger portion.
Conversation above, is the 2
nd
experiment. In data
above, guests asked about Pork Belly, one of the top
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
2052

dishes in the restaurant. This question was then
answered by the waitress with a description of
the dish. This, again, confirmed the previous
conclusion that in the function of 'asking' related also
the function 'explaining' or 'describing'.
Waitress: Do you have any food allergy?
Guest: Actually, I’m allergic to shell fish.
Waitress: I see. Do you have any problem with
spicy? Guest : Not too spicy, maybe.
Waitress: Alright. Because mostly our food here is
spicy, so I’m gonna tell you if you order
for something that is really spicy. Please
have a look first, let me know if you are
ready to order.
Conversation above, is the 3
rd
experiment.
Different from the previous one, the interrogative
sentence used by waitress in the data (3) serves to find
out whether guests have allergies to certain types of
food, so they can avoid food poisoning or other
unwanted problems. Every waiter / waitress at
Mamasan Restaurant had gone through training on
the menu and the ingredients contained in it.
Therefore, they must always ask about food allergy to
each guest so they can help when explaining and
providing food recommendations. In addition to
asking about food allergies, the waiter / waitress also
has to make sure that guests do not have a problem
with spicy taste because the dishes in the restaurant
tend to be spicy, especially for Europeans.
When recommending food and drinks to guests,
of course the waiter must provide an explanation of
these products. For example, a brief description of the
taste of food (flavor), how to make it (method of
cooking), or ingredients (ingredients) contained in it.
In addition to explaining the menu, the waiter also
needs to ask whether guests have allergies to a type
of food and whether guests like the spicy taste or not.
The 'explaining' and 'asking' functions are the micro
functions of the informative.
3.2 ‘Confirming’
When a guest orders food in a restaurant, of
course he needs some information related to the food
he will order. Questions that arise in the food
ordering process aim to ensure the information
needed so that guests avoid dissatisfaction with the
food and drinks ordered. The following data
contained the ‘confirming’ function, which was
closely related to other informative functions, namely
'asking', and 'explaining' function.
Waitress: What kind of starter would you like,
madam?
Guest: I’ll have this Snapper umplings, this
one... and then for the salad I can take the
Salmon Salad,... is it nice?
Waitress: Yes, but this is spicy. Are you ok for
spicy?
Guest: It’s ok, no problem. ... and for the main,
I can take this Masaman Curry Chicken,
and the side crispy thing I take the
Chinese Style Pork Belly, and then for
the side I take one Jasmine Rice and one
stir fried Asian Grill. That’s it.
Waitress : I’ll just inform you, madam. Are you ok
with the fat? Because the Pork Belly here
is come with the fat.
Conversation above, is the 4
th
experiment. In data
above, the waitress used the function ‘asking' and
'explaining' in response to the 'ordering' function used
by guests. After deciding which food, he wanted to
order, the guest again confirmed that the food would
taste delicious by saying "Is it nice?". The waitress
knew that the food was one of the foods with a spicy
taste then tried to inform the guest and ensured that
the guest would not have a problem with it. The
interrogative form "Are you OK for spicy" in this case
was crucial to avoid guest complaints if the food did
not match their taste.
The same thing was done by the waitress when
guests ordered Pork Belly which contained high fat.
The waitress again ensured that guests would not
have problems with fatty foods by asking "Are you
OK with the fat?" which is then followed by a brief
description of the food ordered.
Waiter: What would you like to drink,
madam?
Female Guest: I think I’ll have Two Islands, please.
Waiter: Two Islands, by the glass?
Female Guest: Yes.
Male Guest: Do you want it by the glass? Just one
glass?
Female Guest: Yes. One glass... Two Islands, please.
Male Guest: Can I have Ginger Ale, please?
Waiter: Ginger Ale with ice, sir?
Male Guest: Uhm.. Yes... Oh .. No!... No ice,
please.
Waiter: Let me repeat your order, one glass of
Two Islands and one Ginger Ale
without ice.
Male Guest: Yes. Thank you.
Waiter: Thank you.
Conversation above, is the 5
th
experiment. Data
above, also showed the use of informative functions
represented in the function of 'asking' and
'confirming' when ordering drinks. Hearing guests
order Two Islands drinks, the waiter immediately
asked if guests wanted to order one glass or one bottle
of the drink. Not only waiters, but also the male guest
ensured if the female guest intended to order only one
drink. When male guest ordered drinks, the waiter
asked if the guest wanted ice in the drink. All waiter’s
questions when taking food and beverage orders were
The Representations of Informative Function in Handling Food Service at Restaurant
2053

aimed to ensure orders as desired by guests in order
to avoid complaints. The guest orders were then
repeated for this purpose using the phrase "Let me
repeat your order ...".
Female Guest: How about the snapper, is it fillet? No
bones?
Waiter: Yes.
Female Guest: OK, I’ll have the Snapper. One fillet
Snapper, please.
Male Guest: Uhm.. Could we order the Grilled
Vegetable Salad, please? How long
will it take?
Waiter: More or less may be five minutes.
Male Guest: OK thank you.
Conversation above, is the 6
th
experiment. In data
above, the function 'asking' in the phrase "Is it fillet?
No bones?" was used by female guest before ordering
food. This aimed to ensure that the fish menu ordered
according to the tastes of guests. After confirming
this, the guest immediately decided the choice of
food. While male guest used the function 'asking' in
the phrase "Could we order ...?". The guest asked how
long it would take to prepare the food ordered in the
sentence "How long will it take?"
Based on the description above it can be said that
the function 'explaining' is often a response to the
function 'asking'. The use of the 'asking’ function is
not only intended to request information, but can also
be to 'offer' something or 'persuade' the listener to try
or do something, or also to 'confirm' information
previously obtained. The function ‘asking' can also be
used to give choices to the listener as shown in the
following data.
Waitress: We have Indonesian food in our buffet.
If you need anything else, we will
prepare for you.
Guest: Yes, can I have some eggs, please?
Waitress: Yes, of course. Please looking our buffet.
Maybe you want to take another food,
and I’ll prepare for your eggs. What
would you like to have for your eggs, sir?
Guest: Omelette, please.
Waitress: One omelette... Mix, Cheese, or
Mushroom omelette? What would you
like to have?
Guest: Uhm... Mix Omelette.
Waitress: Mix Omelette, served with some bacon
or sausages?
Guest: uhm... bacon, please.
Conversation above, is the 7
th
experiment. Data
above, occurred at breakfast, when the guest wanted
an egg dish that was not available at the buffet table
so it had to be prepared specifically on request. The
waitress must obtain detailed information about the
type of dish desired, so she asked some questions that
are actually an option. In general, there are two types
of breakfast provided for hotel guests, namely
Continental Breakfast (consisting of cereals, bread,
juice, tea / coffee) and American Breakfast
(consisting of hot dishes namely egg dishes, toast,
juice and tea / coffee). Egg dishes can be served with
a variety of choices, such as sunny side up, turn over,
omelette, scrambled, poached, soft boiled and hard
boiled. When guests order omelette, the waitress had
to ask again what filler material was desired because
the restaurant provides various choices such as mix,
cheese, and Mushroom. Mix Omelette was still
divided into bacon and sausages. Thus, the function
of 'asking' can also be used to inform the choices
available to guests so that they can more freely
determine choices when ordering food.
The following data strengthened the function of
'asking' which was used to give consideration about
menus in restaurants.
From the data, occurred at breakfast, when the
guest wanted an egg dish that was not available at the
buffet table so it had to be prepared specifically on
request. The waitress must obtain detailed
information about the type of dish desired, so she
asked some questions that are actually an option. In
general, there are two types of breakfast provided for
hotel guests, namely Continental Breakfast
(consisting of cereals, bread, juice, tea / coffee) and
American Breakfast (consisting of hot dishes namely
egg dishes, toast, juice and tea / coffee). Egg dishes
can be served with a variety of choices, such as sunny
side up, turn over, omelette, scrambled, poached, soft
boiled and hard boiled. When guests order omelette,
the waitress had to ask again what filler material was
desired because the restaurant provides various
choices such as mix, cheese, and Mushroom. Mix
Omelette was still divided into bacon and sausages.
Thus, the function of 'asking' can also be used to
inform the choices available to guests so that they can
more freely determine choices when ordering food.
The following data strengthened the function of
'asking' which was used to give consideration about
menus in restaurants.
Waitress: Excuse me, would you like to order now,
sir?
Guest: Yes, please. maybe I’ll try the steak...
Tell me, is the beef imported?
Waitress: yes, sir. Our steak is imported from
Australia.
Guest: Well, I guess I want to try the Rib eye
steak. How big is it?
Waitress: It’s about 200 grams, sir. But I need to
inform you that the rib eye steak is greasy
and fatty because it contains a lot of fat.
Guest: Oh really? Well. how about the sirloin
steak?
Waitress: The sirloin is cut from the back part
which is less tender, sir.
Guest: So, which one do you recommend?
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
2054

Waitress: Well, I suggest you try our tenderloin
steak. It’s the most tender part of the
beef, and not too fatty
.
Guest: alright, maybe I’ll have that, please.
Waitress: Of course, sir. How would you like it
done, rare, medium, or well done?
Guest: Medium well, please.
Waitress: And what would you like to come with
it? baked potatoes or french fries?
Guest: Baked potatoes, please.
Conversation above, is the 8
th
experiment. Data
above, was a conversation about ordering steak, when
the guest asked a few questions that the waitress
immediately responded to. Here, it was clearly seen
the use of informative functions that were full of
information from waitresses to guests. The implicit
information included steak meat imported from
Australia so of course the quality of meat was better
than local meat. Waitress also gave a brief explanation
about the parts of beef with the aim of helping guests
in choosing the type of steak they want.
The questions posed by the waitress could also
function as a 'bait' to sell products with more leverage.
For example, in a sentence when a waitress offers
vegetables, "And what would you like to come with
it? baked potatoes or French fries? ", the guest who
initially did not intend to order finally agreed and
chose baked potatoes as a complement to the dish.
Based on the description above, it can be said that the
‘confirming’ function is closely attached to the
function of 'explaining' and 'asking' as an informative
function. The ‘confirming’ function is also used when
ordering food as shown in the data below.
Waitress: What kind of starter would you like,
madam?
Guest: I’ll have this Snapper Dumplings, this
one... and then for the salad I can take the
Salmon Salad, is it nice?
Waitress: Yes, but this is spicy. Are you OK for
spicy?
Guest: It’s ok, no problem. ... and for the main,
I can take this Masaman Curry Chicken,
and the side crispy thing I take the
Chinese Style Pork Belly, and then for
the side I take one Jasmine Rice and one
stir fried Asian Grill. That’s it.
Waitress: I’ll just inform you, madam. Are you ok
with the fat? Because the Pork Belly here
is come with the fat.
Guest: It’s ok. I want to try it.
Waitress: May I repeat for your order? For the
starter it’s a Snapper Dumplings, and a
Salmon Salad, for the main course it’s a
Masaman Curry and the Chinese Style
Pork Belly, and a Jasmine Rice.
Guest: Ok. Is that enough for two people?
Waitress: Yes, it’s enough for two people.
Guest: Alright.
Conversation above, is the 9
th
experiment. In data
above, the function of ‘confirming’ was more widely
used by waitresses to ask whether or not guests have
problems with spicy and fatty foods. The
‘confirming’ function was also used by the guest who
once again ask whether the portion of food ordered is
enough for two people. Later, the waitress repeated
all food orders by saying "May I repeat your order?"
This question-like sentence form actually aimed to
ensure and check that there were no orders left behind
or wrong. Based on the data analysis above, it could
be said that the ‘confirming’ function was used to
confirm the message so that errors do not occur. This
function also aimed to prevent potential problems or
complaints.
Data below presented how the waitress explained
the menu and persuaded the guests to place more
orders at the same time.
Waitress : Excuse me, Ma’am. Are you ready to
order?
Guest: I don’t know ... I cannot decide, so do you
have recommendation?
Waitress : Certainly, Ma’am.... The normally for the
entrée and the starter you can keep two
different things from the starter, I
recommend you for the Scallops and then
Pork Belly so you can share together with
your friends, and for the main course you
can keep two different things from the
main course, I recommend you for the Pork
Vindaloo, and then the Crispy Whole Fish,
that’s very popular food in our restaurant
and very tasty, Madam.
Guest: The Crispy Whole Fish, does it come in big
portion?
Waitress : Ehm.... that’s... ehm.... that’s only five
hundred grams of the Snapper, deep fried
of a Snapper with chilly jam sauce, and the
taste is a bit spicy, sweet and spicy.
Guest: Oh, the fish itself is already spicy?
Waitress : Yes, Madam.
Guest: And is it big? No, it’s not too big?
Waitress : No, not too big.
Guest: We can share?
Waitress : Because it comes with the bones, so I think
the meat is not too much.
Conversation above, is the 10
th
experiment. The
waitress in data above, at first used the informative
function in explaining portions of Pork Belly and the
scallops. Later, she tried to make the guest order
something more, such as the pork vindaloo and crispy
whole fish, using the persuasive function. The aim was
to offer or persuade the guest. This showed that
informative function was closely related to persuasive
function when dealing with order taking at the
restaurant.
The Representations of Informative Function in Handling Food Service at Restaurant
2055

4 CONCLUSION
The informative function in this study, similar to the
informational function (Leech, 1974), has the
function to exchange information. The function of
this language is represented in the function of
'explaining', 'stating’, and ‘asking'. The function
‘stating’ aims to convey the intention or desire of the
speaker which is generally represented in declarative
form, as in the sentence "I think I'll have Two Islands,
please". However, the function of 'stating' can also be
represented in the form of interrogations, for example
"Can I have Ginger Ale, please?" The interrogative
form "Can I ...", might also be used to express the
wishes of the speaker.
The 1
st
experiment shows that the waitress's
question was responded by the guest, indicating that
they were first-time guests. Knowing this, she
immediately decided to give an explanation about the
restaurant concept, by starting with a statement "Our
concept here is family dining". Meanwhile, the 2
nd
experiment shows that guests asked about Pork Belly,
one of the top dishes in the restaurant. This question
was then answered by the waitress with a
description of the dish. This, again, confirmed the
previous conclusion that in the function of 'asking'
related also the function 'explaining' or 'describing'.
The 4
th
to the 10
th
experiment show that Waitress
also gave a brief explanation about the parts of beef
with the aim of helping guests in choosing the type of
steak they want. It can be said that the ‘confirming’
function is closely attached to the function of
'explaining' and 'asking' as an informative function.
The function ‘asking’ can be used to inform
choices available so that guests can more freely
decide when ordering food. For example, "What
would you like for the vegetables? We have salad and
steamed vegetables." This kind of question can lead
to further products selling. The function of
‘confirming’ also aims to avoid errors or the
emergence of problems later, such as errors in
recording food orders. Therefore, restaurant staff
must always repeat or reconfirm every message
received from guests.
Based on the data discussed above, it can be seen
that the interaction takes place in two directions,
namely the guest uses the 'asking' function while the
waitress uses the 'explaining' and ‘confirming’
functions, both of which fall into the category of
informative functions. Thus, it is clear that the
informative function is represented in the function of
'asking,' explaining ', and ‘confirming' at restaurant
service.
REFERENCES
Brown, H. Douglas. 2007. Principles of Language
Learning and Teaching (5th Edition). San Francisco:
Longman..
Bühler, K. (1965). Theory of language: the
representational function of language. Amsterdam,
Holanda: John Benjamins Publishing Company.
Cook, Guy. 1994. Discourse and Literature. Oxford:
Oxford University Press.
Creswell, John W. 2010. Designing and Conducting Mixed
Methods Research (2nd Edition). New York: SAGE
Publications, Inc.
Halliday, MAK dan Hasan, Ruqaiyah. 1985. Language,
context, and text: Aspect of language in a social-
semiotic perspective. Victoria: Deakin University Press
Halliday, M.A.K. 1973. Explorations in the Function of
Language. London: Edward Arnold. Leech, Geoffrey.
1974. Semantics. England: Penguin Books.
Leech, Geoffrey. 1974. Semantics. England: Penguin
Books.
Lestari, Denok et al. 2017. Developing A Method of
Learning English Speaking Skills Based on the
Language Functions Used in the Food and Beverage
Service. e-Journal of Linguistics, [S.l.], p. 70-79,
jan. 2017. ISSN 2442-7586. Available at:
<https://ojs.unud.ac.id/index.php/eol/article/view/2646
8>. Date accessed: 20 july 2018. doi:
https://doi.org/10.24843/eJL.2017.v11.i01.p05.
Lestari, Denok. 2015. Developing Communicative
Competence of the Students at The Bali Hotel School by
Implementing Instructional Role Play. Journal of
Business on Hospitality and Tourism, 1 (1)
https://jbhost.org/jbhost/index.php/jbhost/article/view/
31
Lestari, Denok. 2013. The Role of Articulatory Phonetics in
Improving Listening for the First- Year Students of
English at STIBA Saraswati Denpasar. Prosiding
International Conference ICEL 2013, p.258-264.
http://artikel.ubl.ac.id/index.php/icel/article/viewFile/2
07/745
Lin, Chia-Hui., Wu, Wen-Chih., & Huang, Yin-Tsuo. 2013.
English for Specific Purposes (ESP) for Hospitality
College Students and Hotel Employees in Taiwan.
International Journal of Education and Research Vol.
1 No 8, August 2013, p. 1-14.
Luardini, Maria Arina. 2009. Fungsi Bahasa dalam
Legenda Rakyat Kalimantan Tengah. Jurnal
Linguistika Vol. 16 No. 30. 2009). Denpasar:
Universitas Udayana.
Jacobson, Robert. 1960. Closing Statement: Linguistics and
Poetics. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Zahedpisheh, N., Abu bakar, Z., & Saffari, N. 2017. English
for Tourism and Hospitality Purposes (ETP). English
Language Teaching; Vol. 10, No. 9; 2017, p.86-94.
URL: http://doi.org/10.5539/elt.v10n9p86
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
2056
