
A Performance Analysis Study of a Single Slope Solar Still with
Integrating Fins and Nanofluid for Productivity Enhancement
H. Hafs, A. Zaaoumi, Z. Bouramdane, O. Ansari, A. Bah, M. Asbik
and M. Malha
1
Research Team in Thermal and Energy, ENSET, Mohammed V University Rabat, Morocco
o.ansari@um5s.net.ma, a.bah@um5s.net.ma, mohamed.asbik@um5.ac.ma, malha102@yahoo.fr
Keywords: Desalination, Solar Still, Nanofluid, Fins, Productivity.
Abstract: The present paper deals with the thermal performance of solar desalination system. The mean objective of
this work is to enhance the productivity of fresh water by integrating fins in basin liner and using Cu
2
O
nanoparticles in the base fluid, based on the experimental data (solar radiation and ambient temperature) (lat
34°00′47″ N, Rabat). A finite element based 3D mathematical model has been developed using COMSOL
Multiphysics 5.2a.the numerical results showed that the daily productivity increase by20% for the finned
basin liner with nanofluid (Brackish water/Cu
2
O) and by 12.6% for the finned basin liner with base fluid
compared to the conventional solar still.
1 INTRODUCTION
Solar desalination is one of various technologies
developed for water purification; it is an effective
and an ecological technology, but the low
productivity of freshwater is the mean and essential
problem to solve for solar stills.
A lot of research works are developed to
improve the productivity of solar stills desalination
systems. (Tiwari and Tiwari, 2007) highlighted the
effect of different parameters such as water depths
and ambient air velocities on the productivity of
solar still, in their others works (Sahota and
Tiwari,2016) studied impacts of different
concentrations of Al
2
O
3
nanoparticles on thermal
properties of the passive double slope solar still
(DSSS) with 35kg and 80kg of basefluid, Moreover,
they investigated the effect of three different
nanoparticles (Al
2
O
3
,TiO
2
and CuO)on the
performance of passive double slope solar still, this
study showed that the thermal energy efficiency was
higher for nanofluids compared to basefluid. Also,
incorporation of AL
2
O
3
nanoparticles in saline water
(Water/Al
2
O
3
) gives more productivity than others
nanofluids (Water/TiO
2
and Water/CuO). (Rabhi et
al, 2017) developed experimentally a modified
single basin solar still with pin fins absorber and
external condenser. It can be concluded from the
results that using solar still with pin fins enhance the
productivity of fresh water by 32.18% compared to
the conventional still. Other experimental work
highlighted graphite and copper oxide effects as new
nanoparticles on the still yield. Also different basin
water depths and different film cooling flow rates is
experimentally investigated. The obtained results
showed that the solar still productivity increase by
about 44.91% and 53.95% using the copper oxide
and graphite, respectively, compared with the
conventional solar still, however by adding the glass
cooling the daily efficiency is 47.80% and 57.60%
using copper oxide and graphite, respectively
(Sharshir et al, 2017).
(El Sebaii et al, 2009) studied experimentally
and numerically the performance of a single solar
still with PCM (Stearic Acid) during charging and
discharging periods. It was founded that the daily
productivity is doubled by using 3.3cm of PCM
compared to conventional solar still. Moreover, they
investigated the effect of fin configuration
parameters (El Sebaii et al, 2015) (El Sebaii and
El-
Naggar, 2017) such as numbers of fins, thickness and
height, also by using different materials (aluminum,
iron, copper, stainless steel).It was concluded that
productivity increase by 13.7% using seven fins with
a thickness and height of 0.001m and 0.04m
respectively.(Ansari et al, 2013) Conducted a
342
Hafs, H., Zaaoumi, A., Bouramdane, Z., Ansari, O., Bah, A., Asbik, M. and Malha, M.
A Performance Analysis Study of a Single Slope Solar Still withIntegrating Fins and Nanofluid for Productivity Enhancement.
DOI: 10.5220/0009773203420348
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference of Computer Science and Renewable Energies (ICCSRE 2018), pages 342-348
ISBN: 978-989-758-431-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
numerical study which highlighted the improvement
of passive solar still performances by using
separately three kinds of phase change materials
(Paraffine C18, Paraffin52–54, Paraffin wax) as a
storage medium. They reported that using heat
energy storage enhances both the productivity and
the efficiency of the distillation system.
Furthermore, this last research work was
undertaken by (Asbik et al, 2016) to determine the
exergy losses during the charging/discharging
periods. They deduced that the use of the latent heat
storage process allows the increasing of the water
productivity but it also reduces the exergy efficiency
of the system. For the same goals mentioned above.
(Ragupathy and Velraj, 2018
) Studied
experimentally the effect of floating absorbers acted
as storage material and bubble-wrap (BW) insulation
on the single slope solar still (SSSS).the results
showed that the daily productivity increase to
3.1l/m².day compared with 1.9 l/m².day for the
Conventional solar still. (Kabeel et al, 2011)
fabricated three solar still designed with a same
construction, the first one is a conventional type, the
second is a finned still and the third one is a
corrugated still. They compared the performance of
both stills with the conventional one, it was
concluded that integrating nineteen fins on the
bottom of solar still increase the amount of distillate
water by 40%; however an amount of 21% is
measured for a corrugated still.
The mean objective of this paper is enhancing
the rate of heat transfer between basin liner and
brackish water by integrating fins in the basin liner.
Moreover, improving the productivity by using
Cu
2
O nanoparticles in the base fluid (Brackish
Water).
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 System Description
The geometry configuration used in this study is
shown in Figure.1. The single basin desalination
system is constructed with a basin area of 1m².Based
on the results of (El Sebaii et al, 2015). The absorber
plat is integrated with seven fins where the thickness
and the height are 0.001m, 0.04m respectively.
Cuprous oxide nanoparticles (Cu
2
O) have been
added to the saline water (40kg) to obtain a
nanofluid whose thermal and optical properties will
be enhanced (Table.1). The whole system is
insulated by the Foam layer (5cm of thickness) to
minimized heat losses between the system and
ambient area; also it is covered by a transparent
glass with a thickness of 3mm and inclination angle
of 34°. The solar still is south facing in order to have
a maximum solar radiation.
The weather data (ambient temperature and solar
radiation) were measured in the “Ecole Normale
Superieure de l’Enseignement Technique-ENSET”
localized at Rabat city (Morocco) whose
geographical coordinates are: Latitude: 34°00′47″
N, Longitude: 6°49′57″ W. On a typical day of
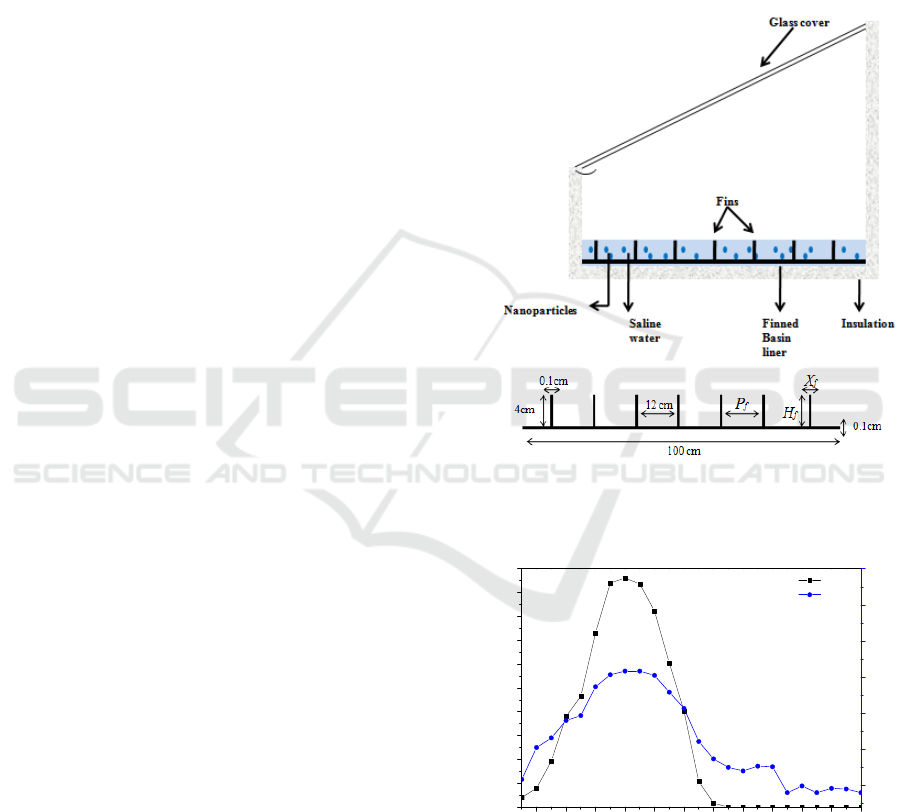
26/05/2018 (Figure.2).
Figure.1: A Schematic diagram of desalination system
with finned basin liner with nanofluid (Brackish
Water/Cu
2
O).
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
1000
G (t)
Ta (t)
Time(hr)
G(W/m²)
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
Ta,°C
26-05-2018
Figure.2: Hourly variation of solar radiation and ambient
temperature for 26-05-2018
A Performance Analysis Study of a Single Slope Solar Still withIntegrating Fins and Nanofluid for Productivity Enhancement
343

2.2 Numerical Model
In order to define the thermal energy process
through different components of the system, three
physical processes are simulated in this study: heat
transfer by conduction, convection and radiation.
2.2.1 Heat Transfer: Conduction
Heat transfer in solid region like glass, finned
absorber and insulated material is by conduction
only. The heat equation to solve is
.
.
.
,
,
,
Where T is the temperature,
, Cp and k are the
density, the specific heat and the thermal
conductivity of the material.
i: glass/finned absorber/insulation.
2.2.2 Heat Transfer: Convection
Heat transfer from finned basin liner to brackish
water happens by convection .In this case, the
energy equation between solid fluid interfaces is
defined as
.
.
.
T
2.2.3 Heat Transfer: Radiation in
Participating Media
The glass cover is exposed to solar radiation
intensity. Qr(t) is the heat flux radiation defined as
Where the solar absorption coefficient
(Table.2) and I (t) is the solar radiation intensity.
Table.1: Thermophysical properties of nanofluid (Brackish
Water/Cu
2
O).
Correlat
ions
Expressions
(Taylor
et al, 2013)
nf
=(1-
p
).
bf
+
p
.
p
(Taylor
et al, 2013)
Cp
nf
=[(1-
p
).Cp
bf
+
p
.Cp
p
]/(
bf
)
(Alawi
et al,2018)
k
nf
=k
bf
.[1+1.0112.
p
+2.4375.
p
.(47/d
p
)-0.0248.
p
.(k
p
/0.613)]
(Kabeel
et al, 2017)
µ
nf
=µ
bf
.(1+2.5
p
)
2.2.4 Boundaries Conditions
The governing equations of thermal model are
developed and written using the following initial and
boundary conditions:
Initially (t=0), all the domains of the system
are at constant temperature (T
ini
=288.95K).
The external surface of the desalination
system exchanged energy by convection with
the ambient area (Ta (t)).
.
.
Were T
ext
=Ta (t) and h is the heat
transfer coefficient.
No slip at the solid-liquid interfaces.
Water layer is supposed to be an isothermal
domain.
2.3 Mesh Generation
Free tetrahedral mesh has been used (Figure.3), to be
sure that smaller geometries are discretized with
232468 numbers of elements.
Figure.3: Meshed solar still desalination
geometry.
Table.2: Technical specifications and numerical constants
of the developed solar still (Sahota and Tiwari, 2016;
Ansari et al, 2013; Kabeel et al, 2017)
Thermal
Properties
value Numerical
constants
value
Glass
g
g
Cp
g
0.78(W/m
.K)
2800(kg/
x
g
x
b
x
ins
g
0.003(
m)
0.002(
m)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(1)
ICCSRE 2018 - International Conference of Computer Science and Renewable Energies
344
g
Water
bf
bf
Cp
bf
bf
Absorber
b
b
Cp
b
Cu
2
O
p
Cp
p
p
m
3
)
840(J/kg.°
C)
0.88
0.64(W/m
.K)
1000(kg/
m
3
)
4190(J/kg.
°C)
0.9
73(W/m.K
)
7897(kg/
m
3
)
452(J/kg.°
C)
6320
(kg/m
3
)
550
(J/kg.°C)
76.5
(W/m.K)
τ
g
Ag
w
b
bf
d
p
L
bf
0.05(
m)
0.05
0.09
1(m²)
0.05
0.9
0.469.10
-3
(N.s/m
2
)
20(nm)
2350(kJ/k
g.K)
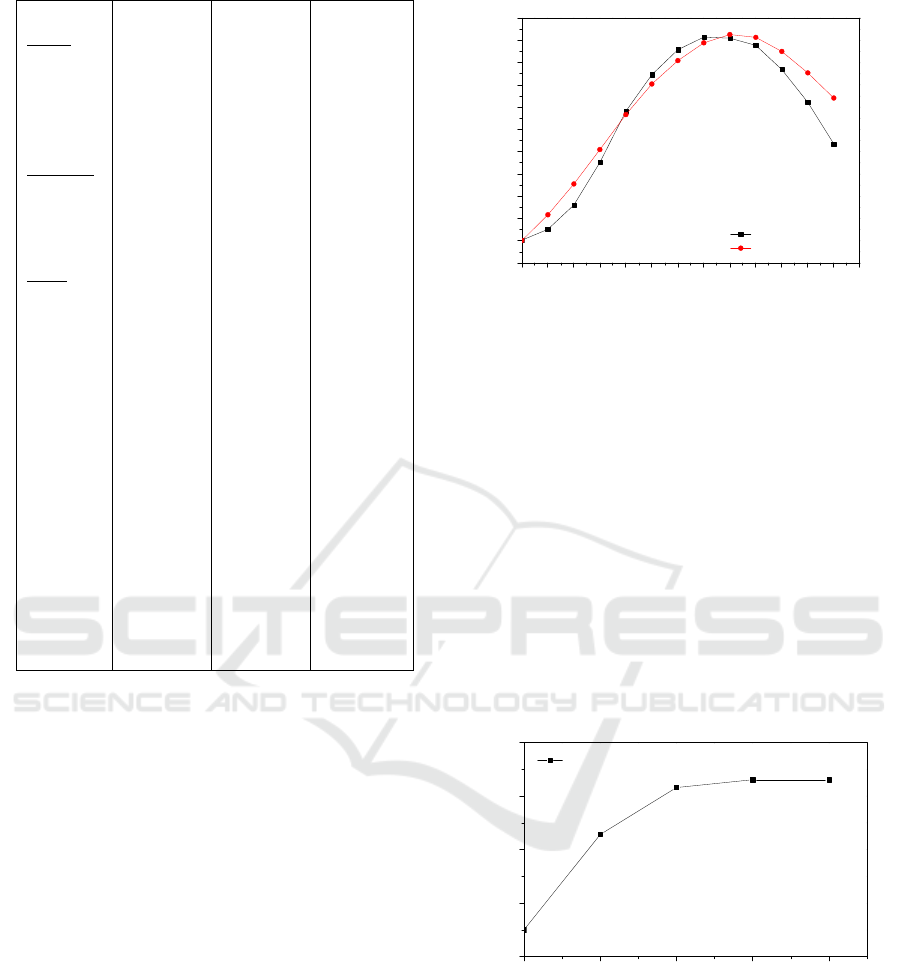
2.4 Validation Model
In order to validate the current model, a numerical
simulation has been carried out using COMSOL
Multiphysics and taking into account the initial and
boundaries conditions defined in section (2.2.4).
A comparison with experimental results of (El
Sebaii et al, 2015) has been done. It is clear from the
results of figure.4, that the current model showed
good agreement with those reported in the reference
(El Sebaii et al, 2015).
1234567891011121314
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
75
Experimental
Numerical Simulation
T
w
,°C
Time (hr)
06-08-2014
Figure.4: Experimental and numerical Hourly
temperature variation of brackish water
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Numerical simulations have been carried out for
modified solar still by using the nanofluid based on
cuprous oxide (Cu
2
O) nanoparticles with integrating
fins in the basin liner.
It can be observed from Figure.5 that the
maximum average temperature (T
nf
-T
bf
) of 4.6°C
occurred when using Cu
2
O concentration of
0.25%.thermal conductivity of nanofluid plays a
vital role in enhancing productivity of the system. It
is the most significant property. So, by applying this
conditions thermal properties of the system
enhanced.
0,10 0,15 0,20 0,25 0,30
3,0
3,5
4,0
4,5
5,0
Cu
2
O
(
T
nf
-T
bf
)
avg
, °C
Concentration, %
Figure.5: Average temperature variation between
nanofluid (Brackish water/Cu
2
O) and base fluid for
different concentration
Figure.6 highlights variations of temperature
during time for different components (finned basin
liner, nanofluid and glass cover). The solar radiation
absorbed by basin liner is transferred by convection
to the brackish water. It is generally observed that
the temperature of nanofluid increases with
A Performance Analysis Study of a Single Slope Solar Still withIntegrating Fins and Nanofluid for Productivity Enhancement
345
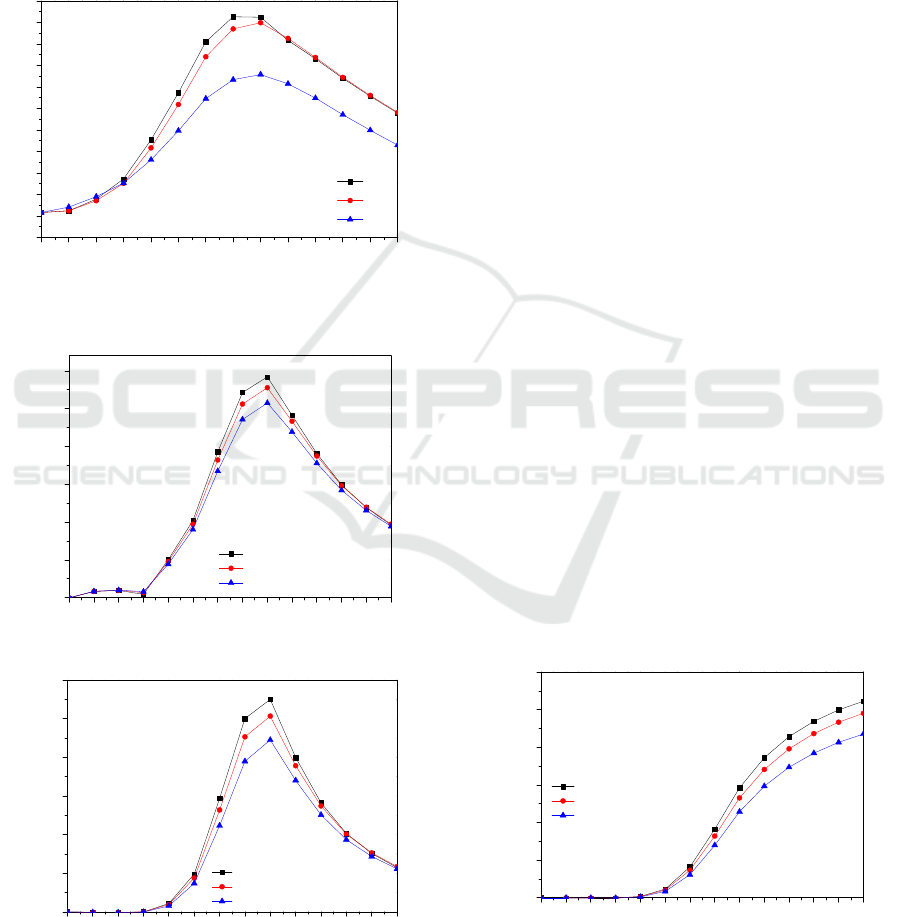
nanoparticles concentration (=0.25%) and by using
finned basin liner.
The viscosity correlation (see Table 1), as
known, is a function of volume fraction and
therefore the Nusselt number vary with this
parameter. Also, it had been inferred that the
nanofluid’s temperature increases due to the energy
received from finned basin liner and cuprous oxide
nanoparticles.
1234567891011121314
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
65
T
p
T
w
T
g
T,(°C)
Time(hr)
26-05-2018
m
w
= 40kg
np
= 0,25%
Figure.6: Hourly temperature variation for modified solar
still with integrating fins and nanofluid (Brackish
water/Cu
2
O)
1234567891011121314
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
With find and nanofluid
With fins
CS
h
evap
,(W/m².k)
Time (hr)
26-05-2018
m
w
=40kg
Figure.7: Evaporative heat transfer coefficient.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
0,0
0,1
0,2
0,3
0,4
0,5
0,6
with fins and nanofluid
with fins
CS
P
h
,(kg/m².hr)
Time(hr)
m
w
=40kg
26/05/2018
Figure.8: Variation of hourly freshwater productivity for
developed solar still and conventional solar still,
26-05-2018.
Three modes of heat transfers occurred between
base fluid and the bottom surface of the glass cover,
by radiation, convection and evaporation. Figure.7
illustrates a significant increase of h
evap
for finned
basin liner with nanofluid where the maximum value
is (29W/m².k), during the sunny period of the
specific day, compared to the conventional solar still
(h
evap
=26 W/m².k).
Besides, the hourly and daily productivity are
defined using the following equations (Ansari et al,
2013)
P
h
= (Q
e,f-g
.3600)/L
f
P
d
=
t
P
h
(t)
From the results of Figure.8, it has been found
that the hourly variations of the yield increase over
time as solar radiation increase. It is due to the
coefficient of evaporation enhanced by the effect of
nanofluid and fins compared to the conventional
solar still.
It has also obvious that the daily productivity of
the conventional solar still , the SSSS integrating
fins in the basin liner with nanofluid ,and the SSSS
with only integrating fins are 2.17 kg/m².day, 2.45
kg/m².day and 2.61 kg/m².day, respectively
(Figure.9). Moreover, the equation used to define the
overall thermal efficiency is:
= (L
f
.
t
P
h
(t))/A
g
.
t
G(t)
So, it is the report between evaporative heat flux
(Q
e,f-g
)and total solar radiation incident (G(t)).
Figure.10 illustrates these variations, where we show
the significant increase for the developed SSSS with
fins and nanofluid of 25% compared to 20% for the
single slope solar still (SSSS) without fins and
nanofluid.
1234567891011121314
0,0
0,5
1,0
1,5
2,0
2,5
3,0
With fins and nanofluid
With fins
CS
P
d
,(Kg/m²)
Time(hr)
26/05/2018
m
w
=40kg
Figure.9: Accumulated daily productivity on a typical day
of 26-05-2018
(7)
(5)
(6)
ICCSRE 2018 - International Conference of Computer Science and Renewable Energies
346
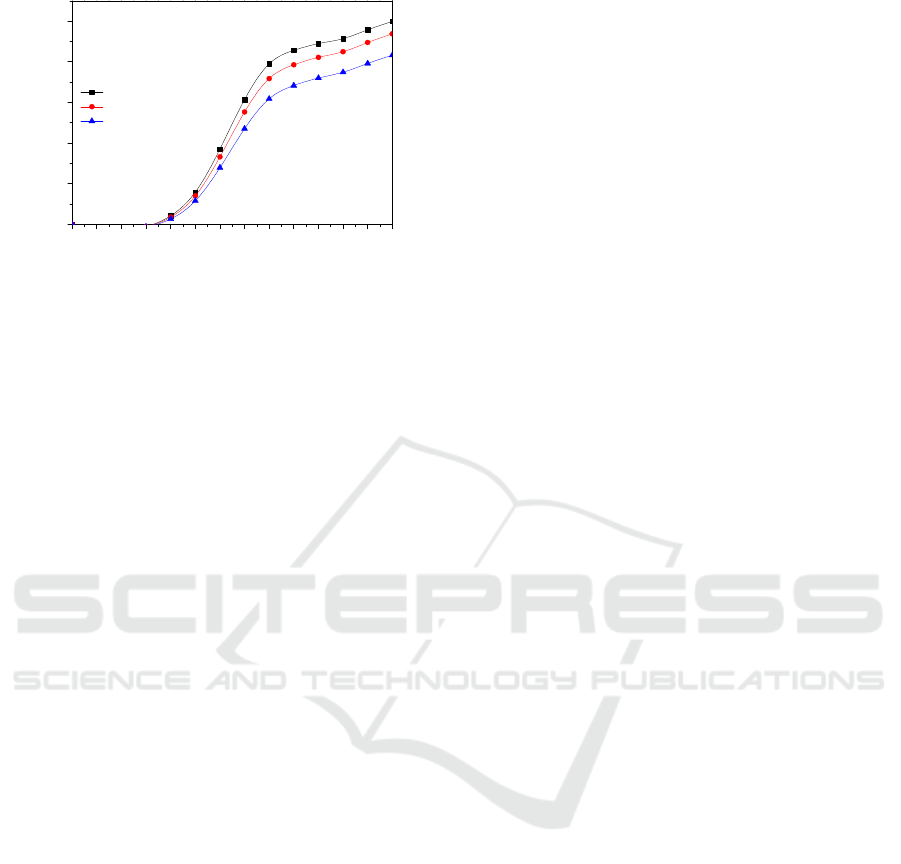
1234567891011121314
0,00
0,05
0,10
0,15
0,20
0,25
With fins and nanofluid
With fins
CS
Time(hr)
26/05/2018
m
w
=40kg
Figure.10: Overall thermal efficiency of developed solar
still with fins and nanofluid, only with fins and for the
conventional solar still
4 CONCLUSION
In this work, the effect of nanofuid based cuprous
oxide nanoparticles (Cu
2
O) with integrated fins has
been studied for the single slope solar still (SSSS)
under real climatic conditions of Rabat city
Morocco. Moreover, the physical processes
encountered in the heat transfer by conduction,
convection and radiation can be developed
numerically using COMSOL Multiphysics.
The results showed that the daily productivity
registered for modified SSSS with fins and nanofluid
(Brackish water/Cu
2
O), for modified SSSS only with
fins and for conventional solar still are 2.61
kg/m².day, 2.45kg/m².day and 2.17 kg/m².day
respectively.
NOMENCLATURE
A Surface Area, m²
Cp Specific heat, J/Kg. °K
h Heat transfer coefficient, W m
−2
K
−1
H
f
height of fins, m
G Incident solar power, W m
−2
L Latent heat, J/Kg
m Masse, Kg
P
h
Distillation mass flow rate, Kg/m².h
P
f
Distance between two fins, m
Q Heat flux, W/m²
T Temperature, °C
t Time, hour
X
f
Thickness of fins, m
GREEK LETTERS
Thermal conductivity, W/m. K
Viscosity, N.s/m
2
Density, Kg/m
3
Emissivity
Nanoparticles concentration
Absoptivity
Thermal expansion coefficient of nanoparticle, K
-1
SUBSCRIPTS
a Ambient
b, abs Absorber
bf Base fluid
d Daily
e Evaporation
g Glass
h Hourly
nf nanofluid
r Radiation
w Water
REFERENCES
A. K. Tiwari and G. N. Tiwari, “Thermal modeling based
on solar fraction and experimental study of the annual
and seasonal performance of a single slope passive
solar still: The effect of water depths,” Desalination,
vol. 207, no. 1–3, pp. 184–204, 2007.
L. Sahota and G. N. Tiwari, “ScienceDirect Effect of Al 2
O 3 nanoparticles on the performance of passive
double slope solar still,” Sol. ENERGY, vol. 130, pp.
260–272, 2016.
L. Sahota and G. N. Tiwari, “Effect of nano fl uids on the
performance of passive double slope solar still : A
comparative study using characteristic curve,”
Desalination, vol. 388, pp. 9–21, 2016.
K. Rabhi, R. Nciri, F. Nasri, C. Ali, and H. Ben Bacha,
“Experimental performance analysis of a modified
single-basin single-slope solar still with pin fins
absorber and condenser,” Desalination, vol. 416, no.
January, pp. 86–93, 2017.
S.W. Sharshir, Guilong Peng, Lirong Wu, Nuo Yang ,
F.A. Essa, A.H. Elsheikh, Showgi I.T. Mohamed, A.E.
Kabeel “Enhancing the solar still performance using
nanofluids and glass cover cooling: Experimental
study”, Applied Thermal Engineering, vol.113,
pp.684–693, 2017.
A. A. El-Sebaii, A. A. Al-Ghamdi, F. S. Al-Hazmi, and A.
S. Faidah, “Thermal performance of a single basin
solar still with PCM as a storage medium,” Appl.
Energy, vol. 86, no. 7–8, pp. 1187–1195, 2009.
A Performance Analysis Study of a Single Slope Solar Still withIntegrating Fins and Nanofluid for Productivity Enhancement
347

A.A. El-Sebaii, M.R.I. Ramadan, S. Aboul-Enein, M. El-
Naggar, “Effect of fi n con fi guration parameters on
single basin solar still performance,” Desalination,
vol. 365, pp. 15–24, 2015.
A.A. El-Sebaii, M. El-Naggar. Engineering, “Year round
performance and cost analysis of a finned single basin
solar still,” Appl. Therm. Eng., vol. 110, no. January,
pp. 787–794, 2017.
O. Ansari, M. Asbik, A. Bah, A. Arbaoui, and A. Khmou,
“Desalination of the brackish water using a passive
solar still with a heat energy storage system,”
Desalination, vol. 324, pp. 10–20, 2013.
M. Asbik, O. Ansari, A. Bah, N. Zari, A. Mimet, and H.
El-ghetany, “Exergy analysis of solar desalination still
combined with heat storage system using phase
change material ( PCM ),” Desalination, vol. 381, pp.
26–37, 2016.
P. Ragupathy and R. Velraj, “Productivity enhancement of
solar still by using porous absorber with bubble-wrap
insulation,” J. Clean. Prod., 2018.
Z. M. Omara, M. H. Hamed, and A. E. Kabeel,
“Performance of finned and corrugated absorbers solar
stills under Egyptian conditions,” Desalination, vol.
277, no. 1–3, pp. 281–287, 2011.
P. Taylor, “Experimental Heat Transfer : A Journal of
Thermal Energy Generation, Transport , Storage , and
Conversion HYDRODYNAMIC AND HEAT
TRANSFER STUDY OF DISPERSED FLUIDS
WITH SUBMICRON METALLIC OXIDE,” no.
January 2013, pp. 37–41.
O. A. Alawi, N. Azwadi, C. Sidik, H. Wei, T. Hao, and S.
N. Kazi, “International Journal of Heat and Mass
Transfer Thermal conductivity and viscosity models of
metallic oxides nanofluids,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transf.,
vol. 116, pp. 1314–1325, 2018.
A. E. Kabeel, Z. M. Omara, and F. A. Essa, “nanofluids
and external condenser,” J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng.,
vol. 0, pp. 1–10, 2017.
ICCSRE 2018 - International Conference of Computer Science and Renewable Energies
348
