
Motivation vs. Demotivation of Employees Work: An Empirical
Study Post Organizational Changes
Fatimah Malini Lubis
1
, Moch. Asmawi
1
and Billy Tunas
1
1
Post Graduated Students, Universitas Negeri Jakarta, Jakarta -Indonesia
Keywords: Motivation, Demotivation, Organization Changes
Abstract: President election is an activity which is held by all democratic countries. The post president election of
2014, Indonesia faces the era of changes in the aspect of economy, social, politics and government
bureaucracy. Jakarta as the capital government holds the important role to support the government program
and become a success factor indicator of the government. To support this, it is needed the government
employee which has motivation and able to anticipate all organization changes such as performance
demotivation as an impact of organization changes. This research used qualitative case study approach by
snowball and purposive sampling with the informant number of 300 State Civilian Apparatus (SCA).
Novelty of this research is finding out the factors that increase the performance motivation through career
opportunities and organizational development, increased income, new challenges, solid teamwork and a
positive work atmosphere. And the cause of performance demotivation post organizational changes in the
government organization environment including: organizational change factors, work environment,
workload, placement, rotation and diversity.
1 INTRODUCTION
Indonesia is a country that adheres to democratic
system which means the election comes from and
for the people. The president election process
becomes a routine agenda which is participated by
all Indonesian who has required for the public
election. The result of president election in 2014
gives an impact in the aspect of economy, social,
politics and government bureaucracy management.
This is a new thing for government organization to
do the change which is based on the president’s
visions and missions. Jakarta as the capital
government becomes the area which holds important
role of the government success in this ongoing
government. Government changes which include a
policy and the change of working plan become a
characteristic in each era which has the organization
changes. State Civilian Apparatus (SCA) as an
execution subject of the changes becomes the main
character in performing and accepting the raised
changes. One of the raised changes impact of
organization changes is an increase in performance
motivation and demotivation of SCA employee in
respond to the changes where the SCA works. This
research aims to investigate the factors which is
affected the performance motivation and
demotivation of SCA performance that works in
Jakarta in respond to organizational changes.
Organizational changes are certain activity that is
done by the organization in respond to the
organization challenges either in the side of
organization performance increase or keep the
company sustainability.
Many studies have been done by the researcher
about the motivation such as: Barney and Steven
Elias (2010) found that with extrinsic motivation
there exists a significant interaction between job
stress, flex time, and country of residence.
Panagiotakopoulos (2013) concluded that factors
affecting staff motivation at a period where the
financial rewards are kept to the least leads to
stimulate employee performance. So, management
personnel’s responsibility to motivate their
employees to work as per the expectation to enhance
the organization’s performance. The employee
characteristics which are motivated are the high-
spirited, high performance discipline and enthusiasm
employee in facing the changes. While the
616
Lubis, F., Asmawi, M. and Tunas, B.
Motivation vs. Demotivation of Employees Work: An Empirical Study Post Organizational Changes.
DOI: 10.5220/0009509606160622
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 616-622
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

characteristic of employee with demotivation is
always rejecting every change, lacking spirit in
performance, often absent and ignoring task that
been given to them.
2 THEORICAL FRAMEWORK
Bangun (2012 said motivation comes from the word
motive (motive), which means encouragement or
being because someone does an action / activity that
takes place consciously. Leaders know that at the
heart of every productive and successful business
lies a thriving organizational culture and
hardworking people collaborate passionately to
produce great results (Gignac and Palmer, 2011).
Robbins in Sentot Imam Wahyono (2010) argues
that motivation is the willingness to issue a high
level of effort for organizational goals that is
conditioned by the ability of that effort to meet some
individual needs. This means that someone needs to
strive with maximum effort in achieving its goals
that will contribute to the organization.
Chandra Sekhar et.al (2013) said motivation to
work as a support person to provide work to the
organization to be able to improve individual and
organizational performance even in a better way
than they usually do. Vuori and Okkonen (2012)
stated that motivation can be useful for providing
knowledge through an intra-organizational social
media platform to help the organization to achieve
its goals.
Research conducted by DeCenzo & Robin
(2010) states two types of awards, both financial and
non-financial rewards for job satisfaction and
employee motivation.
According to Hasibuan (2003), it was stated that
position rotation is a change in the place or position
of an employee but still in the same rank within the
organization, terms that are the same as rotating
positions are moving, assignment and transfers.
As per Yamamoto (2013) employees assume that
they will get awards for well-done work and
guarantees of the work and will have an automatic
impact on performance. Similarly, Zhang and Wu
(2004) provide the fact that with work problems,
employees will trust themselves with the future of
their work will also provide the best business
according to the goals of the organization.
Therefore, it can reduce job satisfaction given
motivation that contributes to employees to ensure
their performance and the achievement of
organizational goals and maximize company profits.
According to Candi et al. (2013), a recognition of
innovation through staging experience. Mahazril et
al. (2012) concluded that several ways to motivated
employee are rewards, recognition and
communication. Increasing levels of productivity
and job performance can be shown in the first
performance or progressively to strengthen
employee behavior through recognition.
In (2012), Jung and Kim stated job satisfaction
and an employee organizational commitment
increase due to good work environment and good
work conditions. Thus, employees will work
optimally to get good employee work performance.
Similarly, Cheng et al. (2013) found that there were
evidences associations between psychosocial work
conditions and health in moderating effects of age.
At present the need for working conditions and
physical environment is very important for
employees. With poor working conditions will have
a negative impact on performance, because it will
result in a decrease in mental and physical health of
employees. For this reason, employees need good
working conditions.
A study by Garc ́ıa et al. (2012) identified that
organizational justice and job satisfaction
perceptions influenced of promotion systems affect.
Likewise, Koch and Nafziger (2012) promotion is
something that is desired by most employees to
compensate them for providing harder work.
Promotion within a regular time period will provide
an optimistic approach behind and employees are
given promotions as psychological requirements in
an organization
The work of Hunter et al. (2012) defines that
achievement is form of organizational performance
which unique and special. As per Satyawadi and
Ghosh (2012), employees who are more motivated
are caused by good achievement and mature self-
control. Understood together that an employee who
is motivated to pursue achievement, looking for
goals that are realistic but challenging and continue
to make improvements in the work. There is hope
that feedback from company leaders will be given
and the need for a sense of achievement.
In (2011), Parvin and Kabir conduct studies and
tests on factors that influence job satisfaction in
pharmaceutical companies and provide an overview
of satisfaction through the views of employees on
their work and view job satisfaction that is different
from their motivations, although clearly related.
Wickramasinghe (2009) conducted an investigation
that gender and working period are important factors
in measuring employee job satisfaction. It can be
said that one's job satisfaction is determined by the
results expected to exceed the target or expectation.
For example, a good work environment and
supportive working conditions can improve
employee job satisfaction, therefore employees will
make the best contribution in improving their
Motivation vs. Demotivation of Employees Work: An Empirical Study Post Organizational Changes
617

performance. Williams et al. (2003) said that job
satisfaction brings a good working relationship
between employees and leaders, maintaining good
rest periods, maximizing existing resources and
providing flexibility for employees within the
organization. Job satisfaction leads to someone who
enjoys doing his job and is rewarded for his
achievements. This is the main basis for recognition,
promotion, income and other achievements in order
to meet the expected goals and objectives. (Kaliski,
2007).
As summarized by Park (2010), monetary
incentive as a trigger for greater action and high
enthusiasm and enthusiasm for the work of
employees, this will be an aid in recognizing
employee performance. Likewise, Beretti et al.
(2013) reviewing monetary incentives used in order
to build a positive work environment and maintain
work morale, this is consistent with employees who
will encourage employees to produce better
performance. Therefore, monetary incentives can
motivate employees and increase employee
commitment to produce company performance,
psychologically able to provide satisfaction to
someone and become job satisfaction in the form of
behavior or views of employees towards work in the
organization.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This research is a qualitative case study research
approach, which conducted learn a real case context
phenomenon in the capital city of Jakarta that occur
post organization change. The method and procedure
employed in this study is case study research design
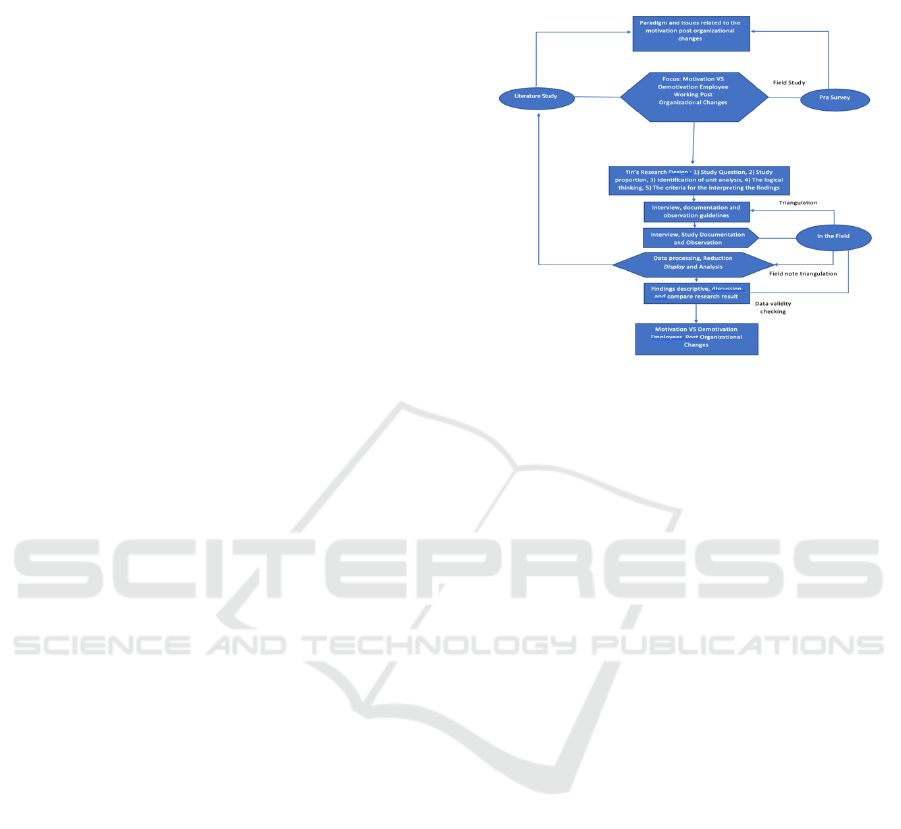
by Yin (2012), with the following stages:
(1) Research questions; before making a series of
questions, the researcher began by conducting a
literature review by reading journals related to
performance motivation, demotivation, leadership
and organizational change both the civil service and
employees in the private sector. The researcher did
this because he wanted to know the previous similar
research methods and their relation to the research
being carried out so that it would be easier for
researchers to bring up research questions and show
when there was a development of new knowledge.
As stated by Neuman, a good review showed a
relevance to the existing body of knowledge and at
the same time can create coherence and summarize
"what is known in an area". Literature reviews
obtained from relevant journal studies make it easier
for researchers to group and synthesize different
research results. The results showed what has been
done and what has not been done. The results of the
review helped the researchers to tell something that
has been found, so that researchers benefit from
what others have done. By completing the two
stages of the process, the researcher had defined and
carried out the research design. The results of the
literature review, documentation, observation, and
initial interviews were used by researchers to make
interview guidelines. This interview guide was used
by researchers when interviewing informants.
(2) Research theorem or theoretical framework
(proportion of studies); Researchers study, collect,
and analyze the data related to government
employees and how the employee motivation and
causes of employee demotivation is. Researchers
also study the legal basis of government employees
(3) Unit identification analysis; the next stage,
the researcher made preliminary observations with
government officials. To add some accurate
information and more than one source, researchers
also conducted observations in the government
office and talked with informants. In addition of a
party and the affected by organizational changes was
observed, researchers also observed the real
situation. This is done to get the results of
observations, their experiences and opinions on
organizational changes that occur. The results of
information and discussions with various internal
parties become the data, hence will be a multi-source
document for researchers. To get direction and
sharpness on these problems, researchers conducted
discussions with human resource practitioners who
had conducted research with case studies, promoters
and co-promoters to get insight into the research and
agreement on employee motivation problems of post
organization changes to be used as research material.
(4) The logical relations of data with theorem or
theoretical (logical relation); The researcher made a
research proposition and set out the analysis units
from the start which had been chosen by the
researcher as a case study. Then, the researcher also
assembled the logic by the research question,
proposition, and analysis units. Propositions were
necessary to identify the relevant information related
to the problems of employee’s performance
motivation of post organization changes. If the
researcher did not make a proposition, the researcher
would be easily tempted to collect everything that
was not needed. At this stage, the researcher made
the questions point to the case of demotivation of
employees beginning with giving an overview
related to employee motivation prior and post
organization changes in order to provide answers to
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
618
what causes demotivation of employees, how
committed they are within organization and how to
foster their performance motivation of post
organization changes.
(5) Criteria to interpret the findings; the
researcher conducted the data collection and
analysis. In this activity, researchers prepare time,
mentally and practice skills to foster good relations
with related parties and improve the ability to obtain
information through the interview process. This
interview process requires skills to listen, ask
questions, read the body language of the informants
and conclude the results of interviews. Because the
research profession was not in the world of human
resource, then the researcher invited the other
researchers with management backgrounds
knowledge and had carried out the interview process
to participate in the interview process. This is done
to provide input during interviews and provide
scientific opinions related to the interview process
that has been conducted. After completing the
interview process, the researcher also discussed with
other researchers' friends to make sure the results of
the interview could be used as a reference in making
interview transcripts. Other preparations are a set of
interview guides and media to make it easier for
researchers to conduct interviews such as recorders,
cameras, mobile phones, pens, memos, and other
supporting tools. During conducting research, in
addition to the informant's expressions summarized
from the body language of the informant also the
complements of the analyzed information. In this
process, researchers observed things visually so that
the research was better to understand the full context
of the information conveyed by informants. The task
of the researcher is to collect data and present it in
written form that can provide life and in-depth
information on the research.
This research was conducted with 300
informants who worked in central government
employees in DKI Jakarta who experienced
organizational changes. The data collection
techniques used observation, interviews,
documentation and audio material. In the process of
data analysis techniques, the researchers used the
Miles & Huberman approach, namely the procedure
of analyzing qualitative data with data reduction,
data presentation and conclusion / verification. The
validity check of the data utilizing Moleong's
opinion with four criteria for data validity checks,
namely credibility, transferability, dependability,
and conformability. The research process carried out
by the researchers can be described in figure 1 as
follows:
Figure 1: Frame of Research Methodology
4 RESEARCH FINDING AND
DISCUSSION
Based on the observation results, interviews and
literature studies that have been conducted, it was
found that there was a performance demotivation of
government employees of post organization
changes. This is indicated by the decrease of work
discipline and work ethic which has significant
changes. This work motivation can be seen from two
sides, namely from internal organization and
external organization. Sahar F. Abu-Jaraour
examines the demotivation of someone in the life of
an organization which states that demotivation can
be caused by inside and outside factors of the
organization; the factors cover the financial aspects
obtained by employees, besides that slow
development also causes demotivation; external
factors include the achievement of work life and
social life; thus, the lower achievement will trigger
demotivation (Sahar, 2014).
a. Internal Factors
Internal factor is a factor which comes from the
inside of the organization as dimensions that arise in
post organization changes. This factor includes:
organizational change, work environment, workload,
placement and diversity.
Changes made post organizational changes are
things that must be accepted by government
Motivation vs. Demotivation of Employees Work: An Empirical Study Post Organizational Changes
619
employees. This change should be done in good
manner to achieve the goals of the change itself. The
success of organizational change depends on the
actors of change, namely human resources. If
changes are made without seeing the situation of the
human resources, then these changes will not work
properly.
Working environment is a factor that create
demotivation of employee’s performance in post
organization changes. In this case, the working
environment will experience some significant
changes because by these changes, it will change the
existing work environment. Changes in the work
environment include physical work environments
such as working facilities, work tools while non-
physical work environments such as relationships
between superiors and subordinates.
Workload is a causal factor for employee’s
demotivation. In the post organization changes, the
workload is still not in a normal state as proper as
the position. Thus, the workload will tend to
demotivate employees because the employees must
experience an increase in workload.
Placement is one of the factors that cause
demotivation of employees. Most employees feel
that the placement of employees does not match the
passion and background of Education. This becomes
a challenge for the organization in placing
employees in the right place. In this case, the term
man in the right place is very appropriate for the
organization in placing its employees according to
the needs of the organization.
Indonesia as a country that has high diversity is
certain that the employees in each organization will
have diversity such as religion, race, ethnicity and
culture. Diversity can be demotivating when
organizations do not instill a culture of tolerance and
respect the diversity that exists. So, when the
organization does not find diversity management
that can be applied in the government, this diversity
will have an impact on the demotivation of
employees.
b. External Factors
External factors are factors that come from outside
of the organization, namely factors from individual
employees themselves. These individual factors
come from the personality and daily environment of
the employee. Although the admission process has
been carried out through several existing standards,
the personality of the employee can still be affected
by the environment around the employee. So that
over time organizational changes will have an
impact on the employee itself.
To confirm the results of this study, especially on
the dimensions that affect the demotivation of
government employees, the researchers take
measurements using a table which is specifically
designed by the researchers to empirically produce
results on these indicators. The following are the
results of measurements using 11 (eleven)
dimensions of motivation according to Chandra et.al
(2013). Each informant responds positively or
negatively to their attitude towards these dimensions
with the following results in table 1 below:
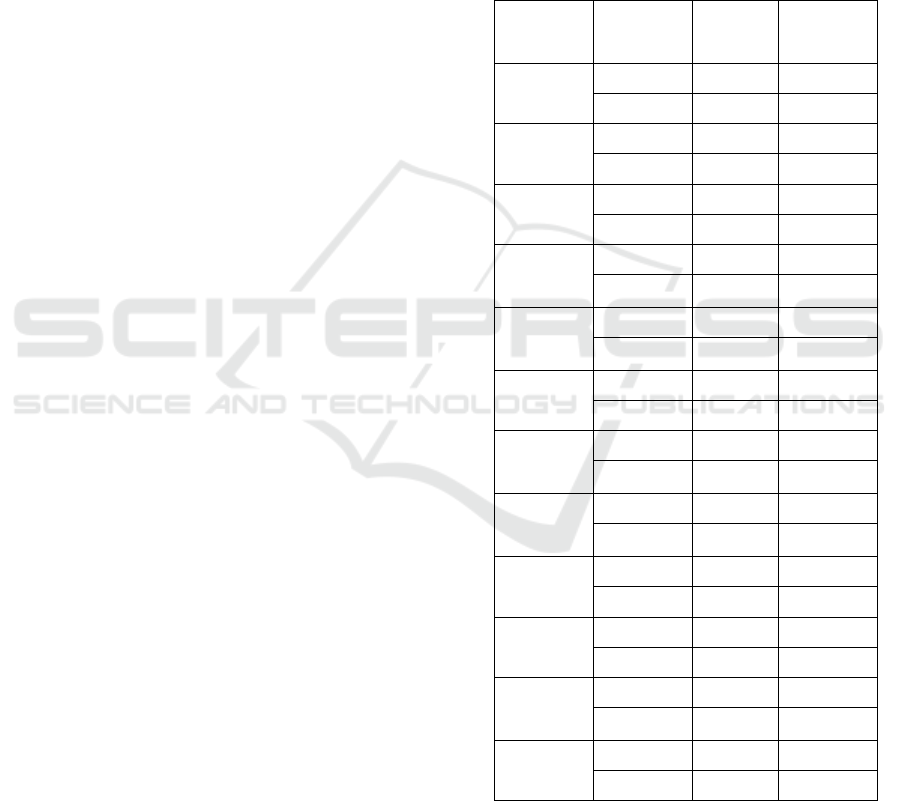
Table 1: FML Motivation Measurement
Indicator
Response
Count
(Employ
ee)
Percentag
e
Monetary
Incentives
-
74
25%
+
226
75%
Training
-
76
25%
+
224
75%
Job
Security
-
90
30%
+
210
70%
Recogniti
on
-
120
40%
+
180
60%
Appreciati
on
-
68
23%
+
232
77%
Job
Transfer
-
90
30%
+
210
70%
Working
Condition
s
-
86
29%
+
214
71%
Job
Satisfactio
n
-
89
30%
+
211
70%
Achievem
ent
-
162
54%
+
138
46%
Promotion
-
47
16%
+
253
84%
Social
Opportuni
ties
-
77
26%
+
223
74%
Motivatio
n
-
159
53%
+
141
47%
Monetary incentives are indicators that show the
importance of financial incentives for employees to
support motivation. There were 75% (224 people) of
the total informants said that they felt that financial
incentive factors were a supporting factor in
increasing motivation after organizational change.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
620

As stated by Wiley (1997) which is concluded that
good pay is an important motivator regardless of
age. This shows that a good salary will be a good
motivator for all working ages.
Training is the second indicator that has affected
the motivation. From the informant's response, there
were about 75% of the total 300 informants who
stated that training was a support for motivation
after organizational change while 25% said training
caused a decrease in work motivation.
Job Security is an indicator that supports
motivation. There are 70% of the 300 informants
who convey job security which increases
performance motivation and 30% states that the
indicator is a cause of decreased work motivation.
Recognition is one of the factors which
supporting motivation in post organization changes.
There are 60% of 300 informants stating that the
recognition has an impact on work motivation after
organizational change. While 40% said that
recognition did not make a positive contribution to
motivation.
Appreciation is something that has an impact on
motivation. 77% of the informants said they were
motivated because of the appreciation given after
organizational change. While 23% of informants
said appreciation was a factor that caused a decrease
in work motivation.
Job transfer is an indicator that shows 70% of
300 informants who convey job transfers are things
that make work motivation increase while 30% of
informants state that job transfer is a factor that
causes a decrease in work motivation.
Working conditions are factors that greatly
influence employee motivation. There were 71% of
300 informants stating that working conditions were
factors that were able to increase employee
motivation, while 29% of informants stated that
working conditions had an effect on decreasing work
motivation.
Job Satisfaction from informants shows that 70%
of informants are satisfied with their work. Even
though, the work done is in the form of routines that
are carried out every day with minimal variations in
work. While 30% of informants stated that job
satisfaction does not have a positive impact on
motivation.
Achievement is an indicator that shows the
response of informants by 46% giving an increase in
employee motivation, but there are 54% who say
achievement is not a positive factor in work
motivation.
Promotion is an indicator that has a big influence
on work motivation. Based on the informant's
response, 84% of informants stated that promotion
provided an increase in work motivation, but 26% of
informants stated that they did not have a positive
influence on work motivation.
Social Opportunities are the biggest factor of
several indicators mentioned above. There were 74%
of informants giving a positive response to the social
opportunities indicators, while 26% said this
indicator did not have a positive impact on
increasing motivation.
This research is a follow-up research from a
previous research which produced dimension of
motivation and implement to SCA post
organizational changes.
5 CONCLUSION
Based on the results of the research and literature
review it can be concluded that: first, factors that can
increase employee motivation in post organization
changes are career opportunities and organizational
development, increased income, new challenges,
solid teamwork and a positive work atmosphere.
These factors are able to provide new enthusiasm of
the employees in accepting and implementing
organizational changes. Second, based on the results
of the research that has been conducted, there are
several factors that make employees demotivated,
including: organizational change factors, work
environment, workload, placement, rotation and
diversity.
REFERENCES
Bangun, Wilson, Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia
(Jakarta: Erlangga, 2012), p. 312.
Barney, E. C., & Steven Elias, M. S. (2010). Flex-time as
a moderator of the job stress-work motivation
relationship: A three nation investigation.
Personnel Review, 39(4), 487–502.
Beretti, A., Figuie`res, C., & Grolleau, G. (2013). Using
money to motivate both ‘saints’ and ‘sinners’: A
field experiment on motivational crowding-out.
Kyklos, 66(1), 63–77.
Candi, M., Beltagui, A., & Riedel, J. C. K. H. (2013).
Innovation through experience staging: Motives
and outcomes. Journal of Product Innovation
Management, 30(2), 279–297.
Motivation vs. Demotivation of Employees Work: An Empirical Study Post Organizational Changes
621

Chandra Sekhar, Manoj Patwardhan, Rohit Kr. Singh
(2013). A literature review on motivation.
International Network of Business and
Management, Glob Bus Perspect, 1:471–487.
Cheng, Y., Chen, I.-S., Chen, C.-J., Burr, H., &
Hasselhorn, H. M. (2013). The influence of age on
the distribution of self-rated health, burnout and
their associations with psychosocial work
conditions. Journal of Psychosomatic Research,
74(3), 213–220.
DeCenzo, D. A. and Robbins S. P.(2010),
Fundamentals of Human Resource
Management .10th ed., Hoboken, NJ: John
Wiley & Sons, Inc.,.
Gignac, G. E., & Palmer, B. R. (2011). The genos
employee motivation assessment. Industrial and
Commercial Training, 43(2), 79–87.
Garc ́ıa, I. A. L., Moscoso, S., & Ramos, V. P. J. (2012).
Reactions to the Fairness of Promotion Methods:
Procedural justice and job satisfaction.
International Journal of Selection and Assessment,
20(4), 394–403.
Hasibuan, Malayu S.P. (2003). Human Resources. Jakarta.
Bumi Aksara, p. 104
Hunter, S. T., Cushenbery, L., & Friedrich, T. (2012).
Hiring an innovative workforce: A necessary yet
uniquely challenging endeavor. Human Resource
Management Review, 22(4), 303–322.
Jung, J., & Kim, Y. (2012). Causes of newspaper firm
employee burnout in Korea and its impact on
organizational commitment and turnover intention.
International Journal of Human Resource
Management, 23(17), 3636–3651.
Kaliski, B. S. (2007). Encyclopedia of business and
finance (2nd ed., p. 446). Detroit: Thompson Gale.
Koch, A. K., & Nafziger, J. (2012). Job assignments under
moral hazard: The Peter principle revisited.
Journal of Economics and Management Strategy,
21(4), 1029–1059.
Mahazril, A. Y., Zuraini, Y. Z., Hafizah, H. A. K.,
Aminuddin, A., Zakaria, Z., Noordin, N., et al.
(2012). Work motivation among Malaysian public
servants. Asian Social Science, 8(12), 238–242.
Park, S. M. (2010). The effects of personnel reform
systems on Georgia state employees’ attitudes: An
empirical analysis from a principal-agent
theoretical perspective. Public Management
Review, 12(3), 403–437.
Parvin, M. M., & Kabir, N. M. M. (2011). Factors
affecting employee job satisfaction of
pharmaceutical sector. Australian Journal of
Business and Management Research, 1(9), 113–
123.
Sahar F. Abu-Jaraour, “Person Demotivation in
Organizational Life”, International Journal of
Business and Social Sciences, Vol 5 No.1 January
2014.
Satyawadi, R., & Ghosh, P. (2012). Motivation and work
values in Indian public and private sector
enterprises: A comparative study. International
Journal of Human Resources Development and
Management, Volume 12 Issue 3.
Wahjono, Sentot Imam, Perilaku Organisasi (Jakarta:
Graha Ilmu, 2010), p. 78-79.
Wiley, C. (1997). What motivates employees according to
over 40 years of motivation surveys. International
Journal of Manpower, 18(3), 263–280.
Wickramasinghe, V. (2009). Predictors of job satisfaction
among IT graduates in offshore Outsourced IT
firms. Personnel Review, 38(4), 413–431.
Williams, E. S., Konrad, T. R., Linzer, M., McMurray, J.,
Pathman, D. E., Gerrity, M., et al. (2003). Refining
the measurement of physician job satisfaction:
Results from the physician work life survey.
Medical Care, 37(11), 1140–1154.
Yamamoto, H. (2013). The relationship between
employees’ perceptions of human resource
management and their retention: From the
viewpoint of attitudes toward job specialties.
International Journal of Human Resource
Management, 24(4), 747–767.
Zhang, H. Q., & Wu, E. (2004). Human resources issues
facing the hotel and travel industry in China.
International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality
Management, 16(7), 424–428.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
622
