
The Effect of Soft Skills Competency, Teamwork, and Innovative
Work Behavior on the Quality of Human Resources in the Digital Era
Eni Lestariningsih
1
, Madhakomala
1
, Asmawi
1
and Hamidah
1
1
Ilmu Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia, Universitas Negeri Jakarta
Keywords: Soft Skill Competency, Teamwork, Innovative Work Behaviour, Quality of Human Resources, Digital Era
Abstract: This paper describes a conceptual framework for investigating the effect of soft skills competency,
teamwork, and innovative work behavior on the quality of Human Resources. Quality of human resources is
needed to support the achievement of the organization's strategic goals and to support the improvement of
organizational services to the community. The characteristics of human resources quality needed in this
Digital Age today include innovative, creative, ethical, and never stops learning. This paper show research
model for quantitative analysis by presenting the theoretical framework for each variables in the research.
This study could be influential for organization’s effectiveness by considering quality of human resources at
work, in which need to continuous improvement from good to great. Good is enemy of great. Moreover, the
findings of this study could enrich to the limited empirical research evidence about the dimension of quality
of human resources which contribute to the effectiveness and competitiveness of the organization,
especially in the Digital Era. This study had objective to examine the significance of characteristics factors
influencing the quality of human resources which include soft skill competency, innovative work behaviour,
and team work. Significant contributions to the theoretical and practical implications can be drawn from this
research. The theoretical contribution to the body of knowledge includes the understanding of how human
resources quality relate to soft skill competency, innovative work behaviour, and team work, in which this
may enrich repertoire of knowledge that related to dimensions of quality of human resources in public
organization in Indonesia in the Digital Era. In management practices, policy maker of the organization can
determine policies based on the model of quality of human resources that significantly influences the
achievement of Vision, Mission and Strategic’s goals organization.
1 INTRODUCTION
The empirical research evidence related to the
dimension of quality of human resources which
contribute to the effectiveness and competitiveness
of the organization in the Digital Era is still limited.
The purpose of this paper is to present a conceptual
framework for investigating the effect of soft skills
competency, teamwork, and innovative work
behavior on the quality of Human Resources. The
urgency of understanding the factors which have
effect to the quality of human resources among
others is the importance of quality Human Resources
(HR) who are needed to achieve competitive
advantage, support the achievement of the
organization's strategic goals, and to support the
improvement of organizational services to the
community, especially in the current digital era
which are dynamic, connected and collaborative.
One of the characteristics of high-performance
organizations in the 21st Century is an organization
that is sustainable and highly competitive driven by
"superior employee performance" / quality human
resources (Soni, 2011). The characteristics of quality
human resources needed in the Digital Era today
include innovative, creative, ethical, and never stops
learning (Gilabert, 2017). Whereas according to
Raymond A. Noe, John R. Hollenbeck, Barry
Gerhart (2015), challenges faced by organizations to
achieve competitive advantage include:
sustainability challenge, global challenge, and
technology challenge.
In this Digital Era, work systems is changing, in
which influences the competencies that must be
possessed by workers. This is a challenge which
triggers an urgent need to improve quality in all
types of organizations, including public
organizations and private organizations. For this
860
Lestariningsih, E., Madhakomala, ., Asmawi, . and Hamidah, .
The Effect of Soft Skills Competency, Teamwork, and Innovative Work Behavior on the Quality of Human Resources in the Digital Era.
DOI: 10.5220/0009509208600866
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 860-866
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

reason, employees must evolve in terms of work
ethic. The quality of HR needs to be continuously
improved, not just stopping at the level of "Good"
but needs to be continuously increased towards the
level of "Great". According to Collins (2001), good
is the enemy of great . Gilabert (2017) stated that the
Era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution or the Digital
Era is for highly qualified human resources who
have a large capacity for adaptation, flexibility and
continuous learning.
2 THEORICAL FRAMEWORK
2.1 Quality of Human Resources
According to Ruky in (Mokodompis, 2008), the
quality of Human Resources is "The level of
knowledge, ability, and willingness that can be
demonstrated by human resources". That level is
compared to the level needed from time to time by
organizations. The ability of employees as human
resources in an organization is very important
meaning and existence to increase work productivity
in the organization. Humans are one of the most
important elements that determine the success or
failure of an organization to achieve its Vision,
Mission and strategic goals. Meanwhile according to
Gilabert (2017) , the characteristics of quality human
resources needed in the Digital Era currently include
innovative, creative, ethical and never stops
learning.
The human resource largely accepted as the most
important resource of any organization may be
described by different qualities like creativity,
education level, communication skill, leadership
skill, and many others. These qualities may become
more or less important according to the specific
requirements of each position. Every organization
needs competent HR, so that it can provide excellent
and valuable services. No matter how small an
organization is, the effectiveness of Human
Resource Management is seen as influencing the
performance of the organization. This is in line with
John M. Ivancevich (2013) who stated that human
resources management is the function performed in
organizations that facilitates the most effective use
of people to achieve organizational and individual
goals.
Jeff Schwartz, Collins, Stockton, Wagner, &
Walsh (2017) mentioned that Rapid changes is not
limited to technology, but encompasses society and
demographics as well. Business and Human
Resource Leaders can no longer continue to operate
according to old paradigms. They must now
embrace new ways of thinking about their
companies, their talent, and their role in global
social issues”. Joan E. Pynes (2009) said that Human
resource management is the design of formal
systems in an organization to ensure the effective
use of employees’ knowledge, skills, abilities and
other characteristics to accomplish organizational
goals. Meanwhile Tracey & Heathfield (2018)
defines Human Resources as, the people that staff
and operate an organization, as contrasted with the
financial and material resources of an organization.
A human resource is a single person or employee
within your organization. Human resources refer to
all of the people you employee.
Public Organizations / Governments have
reformed the paradigm of "low performance - poor
service quality" by abandoning the traditional
management system; implement "New Public
Management": the application of a professional
management system in the Public sector which
among others aims to improve the quality of public
services, strengthen organizational culture, and
motivate to make changes and continuous and total
improvements. Quality service is an effort made by
the company to meet the expectations of its
customers. Quality service emphasizes customer
satisfaction. Lupiyoadi stated that there are five
dimensions of service, namely tangibles (physical
evidence), reliable (reliability), responsiveness,
assurance (guarantee) and empathy. Reliability,
namely the company's ability to provide services as
promised accurately and reliably. Performance must
be in accordance with customer expectations which
means timeliness, the same service for all customers
without errors, sympathetic attitudes, and with high
accuracy.
John M. Ivancevich (2013) defines quality as
follows “quality is defined as meeting costumers’
needs and expectation”. Robbins & Coulter (2018)
define quality as follows: quality as the ability of a
product or service to reliable do what it’s supposed
to do and to satisfy customer expectations.Goetsch
& Stanley B. Davis (2010) define quality as follows,
“quality is a dynamic state associated with products,
services, people, processes, and environments that
meets or exceeds expectations”. Edwards Deming
in Wibowo (2016) mentioned that to be successful in
implementing TQM (Total Quality Management), an
organization must concentrate on 8 key elements,
such as Customer Focus, Total Employee
Involvement, Process-centred, Integrated System,
Strategy and Systematic Approach, Continuous
The Effect of Soft Skills Competency, Teamwork, and Innovative Work Behavior on the Quality of Human Resources in the Digital Era
861

Improvement, Fact-based decision making, and
Communication.
Based on the description of the quality of human
resources above, it can be synthesized the quality of
human resources is organizational resources that
have a strategic role in the enlightenment of
organizational goals, which have high performance
characters, continuously learn to improve their
competencies, so as to provide excellent service to
meet stakeholder needs, with indicators: (1) focus on
customers (responsive), (2) never stops learning, (3)
reliable, and (4) systemic.
2.2 Softskill Competency
Employees must be skilled in managing conflict and
creating inclusions to improve team performance
and to collaborate in generating innovative ideas.
Having a college diploma does not guarantee that
someone has all the competencies needed to succeed
in the work environment. Employers look for people
who have hard skills and soft skills. According to
Wats and Wats (2008) in Meeks (2017), a person's
success in the work environment depends on 85%
soft skills, and only 15% hard skills. Soft skills are
defined as a combination of personal qualities,
interpersonal skills, and additional skills/knowledge
that help an employee better perform their job”. Soft
skills correspond to the skills in the human,
conceptual, leadership, and interpersonal categories.
Kim-Spoon, Maciejewski, Lee, Deater-Deckard,
& King-Casas (2017) defines competence as
follows, “competence is expected to improve as
young people mature and learn across multiple
domains of adaptation in basic capabilities and
coordinated execution of actions”. Competence is
basically the process of increasing a person's ability
from a low ability to a better ability in accordance
with standards and all his actions are well
coordinated.
Stevens & Campion (1994) suggested a
taxonomy of individual competencies needed for
teamwork to measure knowledge, skill, and ability
(KSA) for staffing teams within the organization.
The taxonomy for five dimensions of competencies
consist of:
1. conflict resolution (managing effectively and
resolving conflict),
2. collaborative problem solving (recognizing
opportunities and involving all teams),
3. communication (including establishing both
verbal and non-verbal communication
networks),
4. goal setting and performance management
(establishing specific, challenging, and realistic
goals, then monitoring feedback on
performance),
5. planning and task coordination (coordinating
tasks, and information to establish role
expectations) – Weber et.al., (2012)
Based on the description of soft skills
competencies above, it can be synthesized that soft
skills competencies are competencies needed by
someone who is related to other people and their
self-regulating skills at work, with indicators, 1)
communication, 2) problem solving, 3) working in
teams, 4) managing information, and 5) professional.
2.3 Teamwork
Teamwork is a form of group work with
complementary skills and is committed to achieving
previously agreed missions to achieve common
goals effectively and efficiently. It must be realized
that teamwork is a variety of personal fusion that
becomes a person to achieve a common goal. A
team really needs the willingness to join hands to get
the job done.
Edward Sallis (2002) defines team work as
follow, “team work is based on mutual trust and
established relationship, only when a team has an
identity and purpose to operate effectively”. An
effective team is a team that allows its members to
be able to produce a task that is larger than the
results of individual work because the results of their
work are the result of the contributions of team
members together.
John R. Schemerhorn (2013) mentioned that
“teamwork is the process of people working together
to accomplish these goals”. Teamwork is a work
process in groups with participatory leadership,
shared responsibilities, goal alignment, intensive
communication, focus on the future, focus on tasks,
creative talents and quick responses to achieving
organizational goals. John R.Schemerhorn, Osborn,
Uhl-Bein, & Hunt (2012) stated that “teamwork
occurs when team members accept and live up to
their collective accountability by actively working
together so that all their respective skills are best
used to achieve team goals”. Teamwork is a group
whose individual efforts produce higher
performance than the number of individual inputs.
This means that the performance achieved by a team
is better than the performance per individual in an
organization.
Harris & Hartman (2002) defines team work as
follows, “teamwork is people working together for
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
862

the common good”. Fredh Luthans (2008)
mentioned that: A working group’s performance is a
function of what its members do as individuals. A
team’s performance includes both individual results
and what we call collective work-products. A
collective work product is what two or more
members must work on together, reflects the joint,
real contribution of team members.
Stueart & Morgan (2002) mentioned that “a
work team is a group of people who interact and
coordinate their work in order to accomplish specific
work goals”. Debra L. Nelson (2006) define that
“team work is a group of people with
complementary skill who are committed to a
common mission, performance goals and approach
for which they hold themselves mutually
accountable”. Team collaboration is defined as the
actions of flexible behaviours, cognitions, and
attitudes related to changes in the internal and
external environment, which include a collaborative
process that enables ordinary people to achieve
extraordinary results. Team collaboration integrates
thoughts, feelings, and actions among team members
to achieve performance goals (Scarnati 2001, Salas
et.al.2007) in Renny Rochani Budijanto (2013).
Team collaboration is becoming increasingly
important in public and private organizations,
because collaboration and synergy among team
members results in achieving better goals. In
addition, the interdependent effects of team
collaboration at the individual, group level and
organizational level are believed to accelerate the
process, improve quality assurance, expand
innovation, encourage more efficient work
behaviour, expand work capacity, and develop social
sensitivity and personality (Scarnati 2001, Salas
et.al.2007, Marosi & Bencsik 2009) in Renny
Rochani Budijanto (2013).
Based on the description of team work above, it
can be synthesized that team work is a group of
people with different abilities, talents, experiences,
and backgrounds who gather together in the same
place in a team to achieve a goal, with indicators, 1)
have one direction goal, 2) delegation /
interdependence between team members, and 3)
have one commitment.
d. Innovative work behavior
The term innovation in organizations was first
introduced by Schumpeter in 1934. Innovation was
seen as the creation and implementation of new
combinations. The term new combination can refer
to new products, services, work processes, markets,
policies and systems. In innovation, added value can
be created, both for organizations, shareholders, and
the wider community. Therefore most definitions of
innovation include the development and
implementation of something new. Scoot and Bruce
in Bos-Nehles, Renkema, & Janssen (2017) define
innovative work behaviour as follows : innovative
work behaviour is more than creativity although
creativity is a necessary part of innovative work
behaviour, especially in the beginning, in order to
generate new and useful ideas. Innovation can be
interpreted as the introduction and application of
new ideas, processes, products or procedures in
work, work teams, or organizations that are designed
to benefit the organization, work team, or the work
of the employee itself.
Woods, Mustafa, Anderson, & Sayer (2017)
define innovative work behaviour as creativity and
innovation at work are the process, outcomes, and
products of attempts to develop and introduce new
and improved ways of doing things. Meanwhile,
Amabile in Messmann, Stoffers, Van der Heijden, &
H.Mulder (2017) describe innovative work
behaviour as follows: based on models of creativity,
innovative work behaviour is defined as the sum of
all physical and cognitive work activities which
employees carry out individually or interactively in
their work context with the intention of
accomplishing a set of interdependent requirements
that are necessary for the development of an
innovation. Due to the complex nature of innovation
processes, individuals may be repeatedly and
simultaneously involved in the accomplishment of
these requirements for innovation development.
In conceptualizations of innovative work
behaviour, the dimensions opportunity exploration,
idea generation, idea promotion, and idea realization
are distinguished. These dimensions represent both
the creative side (i.e., opportunity exploration and
idea generation) and the implementation side of an
innovation (i.e., idea promotion and idea
realization). Innovative work behaviour is not just
to generate new ideas but also involves the
implementation process of these ideas, especially on
every job. De Jong and Den Hartog in Messmann et
al., (2017) define innovative work behaviour as
follows: innovative work behaviour is as the
recognition of problems and initiation and
intentional introduction within a work role, group, or
organization of novel and useful ideas concerning
products, services, and work methods, as well as set
of behaviours needed to develop, launch and
implement these ideas. West and Farr in Agarwal,
Datta, Blake‐Beard, & Bhargava (2012) stated that,
“innovative work behaviour is intentional creation,
The Effect of Soft Skills Competency, Teamwork, and Innovative Work Behavior on the Quality of Human Resources in the Digital Era
863
introduction, and application of new ideas within a
work role, group, or organisation to benefit role
performance, a group, or an organization”.
Innovative work behaviour as creativity and
innovation at work are the process, outcomes and
product of attempts to develop and introduce new
improved ways of doing things. The creativity stage
of this process refers to idea generation and
innovation to the subsequent stage of implementing
idea toward better procedures, practices or products.
From the description above, it can be synthesized
that innovative work behaviour is everything a
person does in his job with oriented to develop new
ideas that can lead innovation, with indicators 1)
developing new ideas, 2) creativity in work, and 3)
make a breakthrough to implement the new ideas.
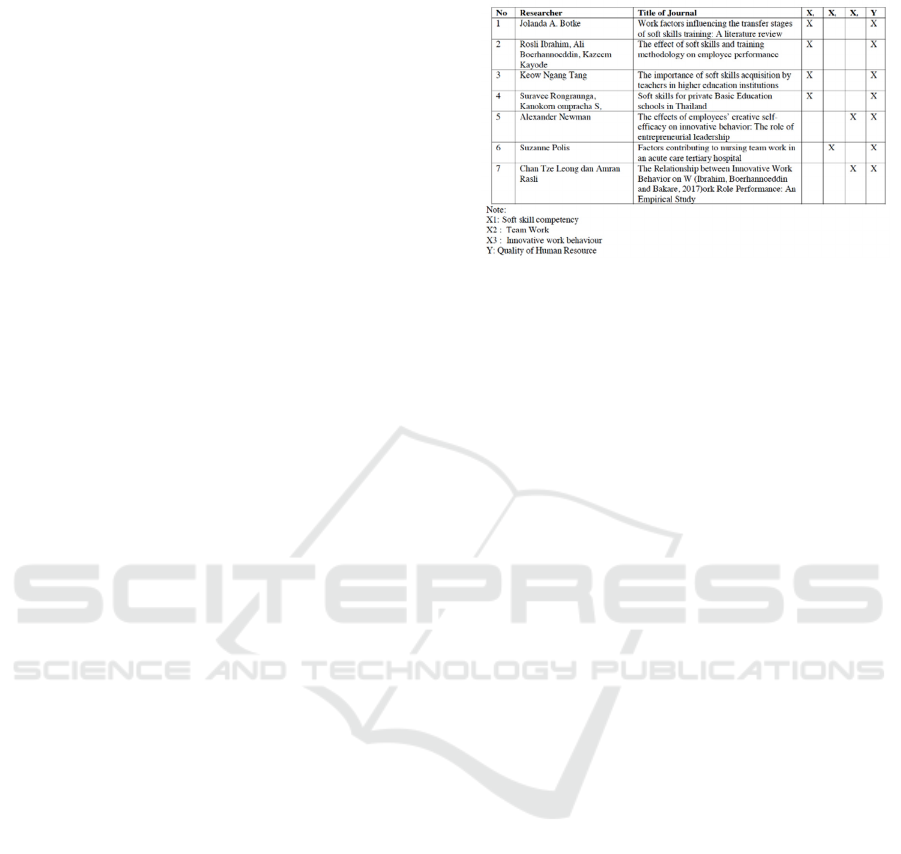
3 RESEARCH METHODS
In prior studies, many researchers investigate
relationship between quality of human resources and
motivation, performance, employee satisfaction, and
many others. However, there is still rare study which
examine the dimension factors of human resources
quality towards soft skill competencies, innovative
work behavior, and team work. Herewith some of
the results of research related to soft-skill
competencies, teamwork, innovative work behavior,
and the quality of human resources which is
presented in the Table 1 below.
4 CONCEPTUAL REVIEW
In prior studies, many researchers investigate
relationship between quality of human resources and
motivation, performance, employee satisfaction, and
many others. However, there is still rare study which
examine the dimension factors of human resources
quality towards soft skill competencies, innovative
work behavior, and team work. Herewith some of
the results of research related to soft-skill
competencies, teamwork, innovative work behavior,
and the quality of human resources which is
presented in the Table 1 below.
Table 1: Summary of Related Research.
4.1 Soft Skill Competency and Quality
of Human Resources
Mitchell in C. Wesley, Prier Jackson, & Lee (2017)
suggested that a soft skill could be viewed as the
level of commitment of a person that sets them apart
from other individuals who may have similar skills
and experience. In today’s changed work world, soft
skills are as important as cognitive skills and make
up of a combination of universally desired
interpersonal skills and personal attributes. The lack
of soft skills can certainly sink the promising career
of someone who has technical ability and
professional expertise but who has no interpersonal
qualities.
Based on the description above there is a positive
relationship between soft-skill competence and the
quality of human resources.
4.2 Team Work and Quality of Human
Resources
Rohtwell and Arnold in Ibrahim et al. (2017)
described that most employers today expect workers
to demonstrate and excel in many ‘soft’ skills such
as teamwork and group development. Employee
creates such as teamwork influence on the quality of
human resources in organizations. To achieve a
high work performance culture, an organization
must provide its employees' training and
development programs designed specifically to
install, build and change their attitudes and/or
behaviors towards several organizational functions.
Based on the description above there is a positive
relationship between teamwork and the quality of
human resources.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
864
4.3 Innovative Work Behaviour and
Quality of Human Resources
Shalley in Prieto & Pérez-Santana (2014) mentioned
that as environments become more complex and
dynamic, firms must become more innovative in
order to identify more opportunities for sustained
superior performance. Innovative work behavior
influence to quality human resource management.
Innovation initiatives tend to depend heavily on
employees’ human capital and behavior at work as
key inputs in the value creation process.
Based on the description above there is a positive
relationship between innovative work behavior and
the quality of human resources.
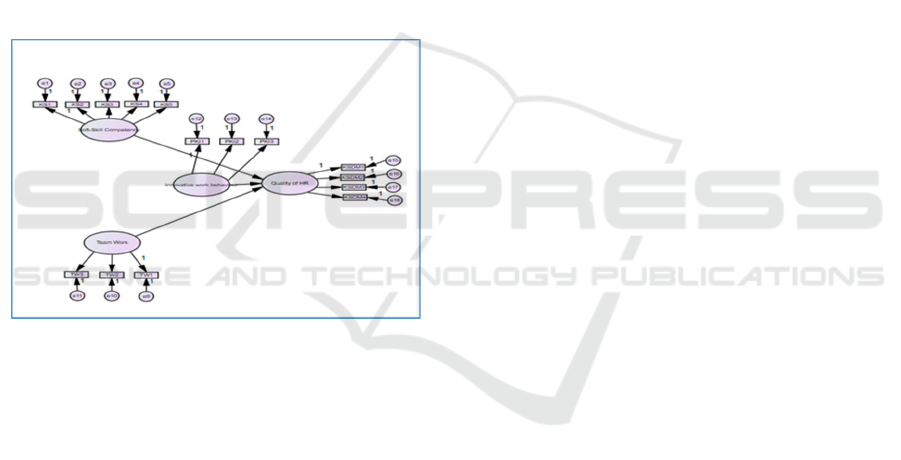
Based on all the description above, it can be drawn
the research model as follows:
Figure 1: Research Model
From the research model above, the statistical
hypothesis that can be developed, namely:
a. First Hypothesis: there is a positive direct effect
of soft skill competence (X1) on the quality of
human resources (Y)
H
0
: βy
1
0
H
1
: βy
1
0
b. Second Hypothesis: there is a positive direct
effect of teamwork (X2) on the quality of human
resources (Y)
H
0
: βy
2
0
H
1
: βy
2
0
c. Third Hypothesis: there is a positive direct effect
of innovative work behavior (X3) on the quality
of human resources (Y)
H
0
: βy
3
0
H
1
: βy
3
0
5 CONCLUSIONS
One aim of this paper is to describe a conceptual
framework for investigating the effect of soft skills
competency, teamwork, and innovative work
behavior on the quality of Human Resources. The
theoretical framework presented here confirm that:
1. there is a positive relationship between soft-skill
competence and the quality of human resources,
with the indicators are: 1) focus on customers
(responsive), 2) never stops learning, 3) reliable,
and 4) systemic.
2. there is a positive relationship between
teamwork and the quality of human resources,
with the indicators are 1) have one direction
goal, 2) delegation / interdependence between
team members, and 3) have one commitment;
3. there is a positive relationship between
innovative work behaviour and the quality of
human resources, with the indicators are 1)
developing new ideas, 2) creativity in work, and
3) make a breakthrough for the application of
new ideas.
This study could enrich to the limited empirical
research evidence about the dimension of quality of
human resources which contribute to the
effectiveness and competitiveness of the
organization, especially in the Digital Era.
REFERENCES
Agarwal, U. A. et al. (2012) ‘Linking LMX, innovative
work behaviour and turnover intentions’, Career
Development International, 17(3), pp. 208–230. doi:
10.1108/13620431211241063.
Bos-Nehles, A., Renkema, M. and Janssen, M. (2017)
‘HRM and innovative work behaviour: a systematic
literature review’, Personnel Review, 46(7), pp. 1228–
1253. doi: 10.1108/PR-09-2016-0257.
C. Wesley, S., Prier Jackson, V. and Lee, M. (2017) ‘The
perceived importance of core sof skills between
retailing and tourism management students, faculty
and businesses’, Employee Relations, 59(1), pp. 602–
614. doi: 10.1108/EL-01-2017-0019.
Collins, J. (2001) ‘Good To Great: Why Some Compnies
Make the Leap’.
Debra L. Nelson (2006) Organization Behavior
Foundations, Realities and Challenges. Thomson
South Western, Australia.
Edward Sallis (2002) Total Quality Mangement In
Education. Philadelphia-London.
Fredh Luthans (2008) Organizational Behavior. New
York: McGraw-Hill.
The Effect of Soft Skills Competency, Teamwork, and Innovative Work Behavior on the Quality of Human Resources in the Digital Era
865

Gilabert, E. R. (2017)
http://www.uoc.edu/portal/en/news/actualitat/2017/01
8-21st-century-employee.html.
Goetsch, D. L. and Stanley B. Davis (2010) Quality
Management. 6th editio. New Jersey:Prentice Hall.
Harris, O. J. and Hartman, S. J. (2002) Organizational
Behavior. New York: Haworth Press.
Ibrahim, R., Boerhannoeddin, A. and Bakare, K. K. (2017)
‘The effect of soft skills and training methodology on
employee performance’, European Journal of
Training and Development, 41(4), pp. 388–406. doi:
10.1108/EJTD-08-2016-0066.
Jeff Schwartz et al. (2017) ‘Rewriting the rules for the
digital age: 2017 Deloitte Global Human Capital
Trends’, Report, (March), pp. 1–137. doi:
10.1016/j.neuro.2014.04.002.
Joan E. Pynes (2009) Human Resources Management For
Public and non Profit Organizations. 3rd editio. San
Francisco, Wiley.
John M. Ivancevich, R. K. (2013) Human Resources
Management. 12th Editi. New York: McGraw-Hill.
John R. Schemerhorn (2013) introduction management.
12th editi. Asia:JohnWiley.
John R.Schemerhorn, J. et al. (2012) Organizational
behavior. 12th editi. Asia:JohnWiley.
Kim-Spoon, J. et al. (2017) ‘Longitudinal associations
among family environment, neural cognitive control,
and social competence among adolescents’,
Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 26, pp. 69–
76. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcn.2017.04.009.
Meeks, G. A. (2017) ‘Critical Soft Skills to Achieve
Success in the Workplace’, ProQuest Dissertations
and Theses, p. 254. doi: UMI : 3257958.
Messmann, G. et al. (2017) ‘Joint effects of job demands
and job resources on vocational teachers’ innovative
work behaviour’, Personnel Review. doi:
10.1108/09574090910954864.
Mokodompis, H. (2008) ‘Pengaruh Kualitas Sumber Daya
Manusia Aparatur Terhadap Peningkatan Kinerja Di
Badan Kepegawaian Daerah Kabupatenbolaang
Mongondow Utara’, pp. 1–14.
Prieto, I. M. and Pérez-Santana, M. P. (2014) ‘Managing
innovative work behavior: The role of human resource
practices’, Personnel Review, 43(2), pp. 184–208. doi:
10.1108/PR-11-2012-0199.
Raymond A. Noe, John R. Hollenbeck, Barry Gerhart, P.
M. W. (2015) The Ninth Edition of Human Resource
Management: Gaining a Competitive Advantage.
Renny Rochani Budijanto (2013) Thinking Styles ,
Teamwork Quality and Performance A thesis
submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
Renny Rochani Budijanto. University of Canberra.
Robbins, S. P. and Coulter, M. (2018) Management. 14th
edn. USA: Pearson.
Soni, V. (2011) ‘A general framework for understanding
21stcentury public sector organizations’, International
Journal of Public Administration, 34(1–2), pp. 76–83.
doi: 10.1080/01900692.2011.536083.
Stevens, M. J. and Campion, M. A. (1994) ‘The
knowledge, skill, and ability requirements for
teamwork’, Journal of Management, 20(2), pp. 503–
530. Available at:
http://www.krannert.purdue.edu/faculty/campionm/Kn
owledge_Skill_Ability.pdf.
Stueart, R. D. and Morgan, B. B. (2002) Library and
information Center Management. US: Greenwood.
Tracey, W. R. and Heathfield, S. M. (2018) What is a
Human Resource? Available at:
https://www.thebalancecareers.com/what-is-a-human-
resource-1918144.
Wibowo (2016) Manajemen Kinerja. 5th editio. Rajawali
Pers.
Woods, S. A. et al. (2017) ‘Innovative work behavior and
personality traits: ezamining the moderating effects of
organizational tenure’, Journal of Managerial
Psychology, p. JMP-01-2017-0016. doi: 10.1108/JMP-
01-2017-0016.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
866
