Determination of Food Price Increase in Indonesia: RICE, FOOD,
SOY Period 2007 - 2017
Elpina Idola Malau
Post Graduated of Economic Universitas Negeri Medan
Keywords: High food price, Inflation specific, Macroeconomic
Abstract: The purpose of study to analyze the effect of broad money (m2), narrow money (m1), exchange rate,
amount of rice and soybean production, rainfall and the maximum temperature on the high food prices in
Indonesia for the period 2007-2017. The study used multiple linear regressions, to examine the study
hypothesis. The empirical analysis show that broad money (m2) narrow money (m1), amount of rice and
soybean production, rainfall and the maximum temperature significant and positively affects on the high
food prices in Indonesia and exchange rate significant and negative affected on the high food prices in
Indonesia, particularly rice and soybean. This study also found that narrow money (m1) had the most
dominant influence on high food price in Indonesia. caused look at the society of velocity of money fast,
that is trough economy and business transaction, that impact on the high food prices in Indonesia.
1 INTRODUCTION
The issue of rising food prices is one of the severe
problems that Indonesia always experiences every
year, this is very burdensome, especially for middle-
income and lower income communities, starting
with the rising prices of foodstuffs such as rice,
soybeans, corn, and other foodstuffs. already and
almost reached 100% increase.
Hariharan and Kumar (2012) state that the
increase in food prices is caused by several factors,
namely a shift in population and a shift in habits to
food consumption, an increase in fertilizer prices, an
increase in fuel prices which are key to
transportation of agricultural commodities
(distribution, production, food commodities),
demand-side pressures, natural factors such as
rainfall, hurricanes, floods, droughts, pests and
diseases, resulted in a decline in agricultural
productivity, which led to an increase in food prices.
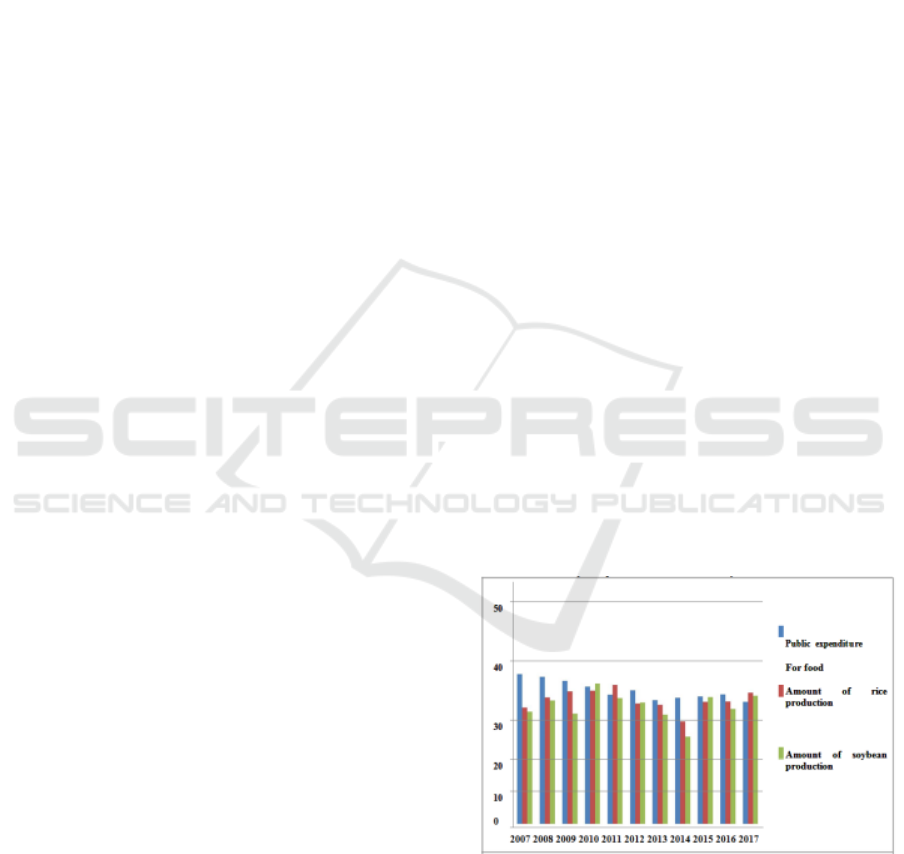
Looking at the form of consumption patterns of
the Indonesian people, average public expenditure
on food each year ranges from more than 50%,
meaning that public expenditures are very high, the
high form of expenditure (demand) that is not
balanced with the offer will cause a problem that is
scarcity which ultimately results in an increase in
food prices. One of the factors underlying the high
level of consumption patterns (public expenditure) is
the amount of money circulating, Irvin Fisher (1987)
states that with the increasing level of circulation of
money will have an impact on the increasing form of
consumption patterns of the community.
Source: The central statistics agency (in though,
2017)
Figure 1: Indicators of Indonesian Community
Expenditure on food and the amount of rice and
soybean production in the last eleven years
The annual inequality between public
expenditure and the amount of food production
which will later reflect supply, this will directly
Malau, E.
Determination of Food Price Increase in Indonesia: RICE, FOOD, SOY Period 2007 - 2017.
DOI: 10.5220/0009509108510859
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 851-859
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
851
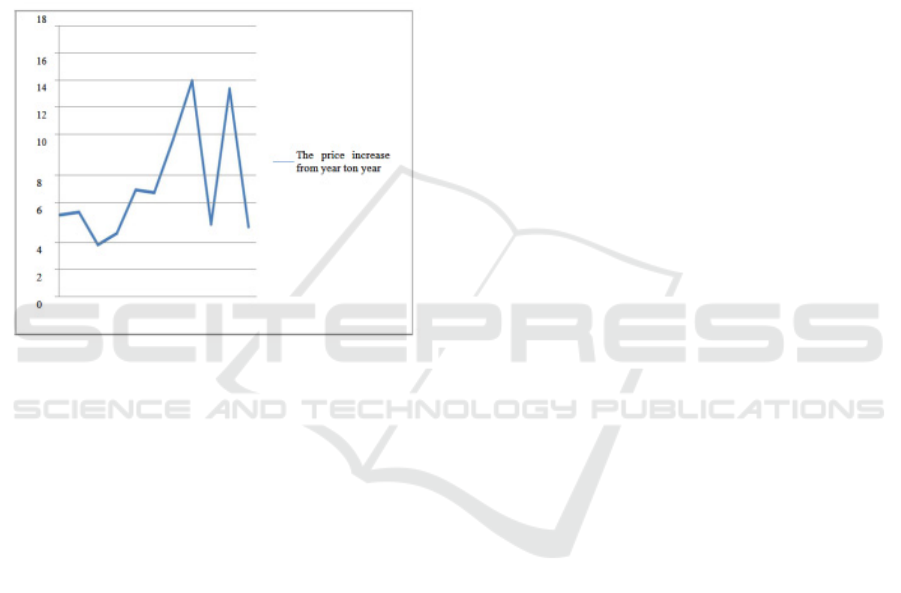
cause problems in macro and micro, these problems
include not fulfilling the demand for food needed by
the community, the increasing form of imports made
will be at risk of being negatively affected by the
international economy due to the depreciation of the
rupiah exchange rate which has made the price of
imported food to rise and has an impact on
fluctuations (changes) in local food prices, and will
not achieve equilibrium conditions for the economy,
because every year there is always an imbalance
between supply and demand this ultimately led to an
increase in food prices and a negative impact on the
country's economy.
Source: BPS (2007 – 2017), processed.
Figure 2: Graph of percentage increase in food
prices (panangan rice, soybean, corn and other
whole food ingredients)
Besides the influence of weather is also very
influential on rising food prices, Lazzaroni (2012)
states that weather changes have an impact on
economic activities in various sectors, but the
agricultural sector becomes the most influential,
because the agricultural sector has the most vital
relationship with the weather, due to growing food
growth in addition to being supported by care and
fertilizer, it must be supported by normal weather
conditions, besides the smoothness of the form of
food distribution is also determined by the weather.
In view of the increase in food prices in
Indonesia every year, an evaluation of the problems
that have been drawn based on reality and existing
data is about increasing food prices, it is important
to note and furthermore, an analysis of important
food price increases, as for factors which affects the
increase in food prices including the amount of
money in circulation (m2) and narrow (m1), the rate
of exchange (exchange rate), the amount of food
production of rice and soybeans, weather (rainfall
and maximum temperature). The variable variable is
the parts that most influence the increase in food
prices in Indonesia, this study aims to analyze the
effect of rising food prices in Indonesia especially in
rice and soybean foods.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Food Definition
Food is a commodity that is a basic human need for
food does not mean economically strategic, but also
means as a form of community needs, which is
categorized as food generally contains carbohydrates
which function as main calories, and can be used for
other needs such as processed raw materials based
on the benefits obtained to produce the needs
needed, which are included to. foodstuffs such as
grains, tubers and stems of palms, soybeans, maize
and non-carbohydrate foods such as onions, red chili
which is the biggest need which is very important
for most of the population (Hasan, 1998).
Increase in Food Prices
The increase in food prices can be interpreted as an
increase in the price of one or more food
commodities, these food commodities consist of
rice, corn, soybeans, green beans, peanuts, sweet
potatoes, cassava, chili and onions. The price
increase is called volatile good (the tendency of
changes in the value of goods), an increase in food
prices is one of them based on factors increasing
demand for food that is not balanced with food
productivity (Central statistical agency, 2013).
The factors that cause increases in food prices
according to Hariharan and Kumar (2012) are:
1. Continued increase in population and shifting
habits of food consumption.
2. The increase in prices of other inputs such as
fertilizers, seeds, etc. in recent times has caused
inflation.
3. Continuous increase in fuel prices, which is a
key input for transportation of commodity
agriculture for central processing or
consumption, so, prices Crude oil affects input
costs and causes inflation to a large extent.
4. Natural factors such as rainfall, hurricanes,
floods, droughts, pests and diseases result in
decreased production and productivity of
agricultural production in many countries
5. Increasing people's purchasing power is one of
the main factors of inflation.
6. The increase in minimum support for food prices
has caused inflation.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
852

Money supply and rising food prices
In the quantity theory of money explained because
the emergence of price increases is due to the
excessive form of demand caused by changes in the
money supply (Nopirin, 2000), according to Irving
fisher, the effect of the money supply on price
changes is formulated through MV = PT, namely M
(money) = money supply, V (Velocity) = velocity of
money circulation, P (Price) = price of goods, T
(Trade) = Number of goods traded, according to
Fisher the price of goods is influenced by the money
supply due to purchasing power owned by the
community it causes high consumption power
owned by the community so that the consumption
cycle owned by the community stimulates the flow
of goods from producers to consumers. And
according to Mankiw (2003) that the relationship
between the money supply and the price increase
cannot be done if it is only seen in the short term,
but it must be seen in the long term in order to get
good results and significant results. the relationship
between the money supply and the price increase
cannot be seen in the short term, therefore in
explaining the relationship between the increase in
prices and the money supply it will not be as tight as
if it was seen over a ten year period friedman and
Schwartz (1987).
Exchange Rate (Exchange Rate) and Increase in
Food Prices
According to Cassel (1918) the exchange rate
between the two countries should be equal to the
price level of the country's ratio, the fall in the form
of domestic purchasing power of a domestic
currency will directly be followed by a depreciation
in the country's currency against domestic money
market but if it happens otherwise the domestic
purchasing power becomes increased it will cause
deflation which is directly followed by a form of
appreciation in the currency, this theory is the theory
that is most often tested for validity because there is
a form of comparison that sees the form of power
capability buy high which causes inflation / price
increases (Cassel, 1918). According to Bob (2002)
Purchasing Power Parity Theory is a theory that
states that the exchange rate between money tends to
lead to an equilibrium condition, purchasing power
should be a society equivalent to the purchasing
power of people in other countries. The occurrence
of price increases, can be seen through the decline in
the exchange rate of the rupiah against the value of
foreign currencies because the depreciation of the
exchange rate will cause an increase in the price of
imported goods, this directly affects the fluctuations
in domestic prices.
Total Food Production (rice and soybeans) and
Increase in Food Prices
The reduced availability of food will have an impact
on the reduction in basic needs needed by the
community, this will lead to a form of food crisis,
food availability involves three aspects, namely
production, distribution, consumption, food
availability supported by actors such as producers,
processors (suryanan, 2004 ) The form of imbalance
between the amount of production (reflection of
supply) and demand will cause changes in the value
of elasticity, as well as the result of demand and
supply that will cause price fluctuations (Nicholson,
2000). The form of production, trade and
consumption of food will affect fluctuations in food
prices (changes in food prices) due to forms of
processing that require costs and forms of demand
and supply that make food prices rise and fall,
therefore maintaining stability will cause a price
balance ( Ellis, 1992).
Weather (rainfall and maximum temperature)
and increase in Food Price Increase
According to Gilbert and Morgan (2010, in Alisher
and Daniel 2012) Weather change is considered as
one source of variability in the prices of agricultural
commodities. Trovero and Von Braun (2008 in
Lazzorini 2012) mention weather changes can cause
a form of potential, such as floods, droughts which
ultimately damage food crops and hamper the form
of food distribution, which in turn has an impact on
rising prices of food commodities Trovero and Von
Braun (2008 in lazzorini 2012 According to
Banumurty, PamiDua and Lokendra (2012) the
impact of weather is very influential on
macroeconomic policies because weather is a
fundamental factor that affects the positive and
negative significance of the results of the
agricultural sector, and the impact of climate change
directly has a very negative impact on price
increases and production growth food. food price
increases can be caused by weather because the
weather influences the shape of the crop, and the
form of crop failure, besides the weather also causes
disruption of the form of distribution patterns such
as the occurrence of landslides causing obstruction
of the distribution, resulting in scarcity of food
commodities in the end it caused a tendency to
increase food prices, due to problems in the form of
distribution patterns
Previous research
Previous research was conducted by Salman and
Adnan 2013, which is about the Determinants of
High Food Prices of the Case of Pakistan wherein
this research examines the factors that cause food
price increases in Pakistan, which are seen through
Determination of Food Price Increase in Indonesia: RICE, FOOD, SOY Period 2007 - 2017
853
the consumer price index, GDP, and agricultural
sector loans. The results of this study explain that
the variables that become the object of research, one
of which is the agricultural sector credit has the most
significant influence among other variables on
changes and increases in food prices, seen through
the method of autoregresive distributed lag analysis
by comparing the total value of the past agricultural
credit sector and value the present as a result, credit
obtained from the agricultural sector has a
significant effect on changes and the occurrence of
food inflation
Previous research was carried out by Aviral
Kumar 2010, which discusses the Impact of Supply
of Money on Food Prices in India: A Causality
Analysis, in this study using Vector error correction
model (VECM) analysis method to determine the
causality between variables, variables that used in
this study is the money supply in area (M2) and the
money supply in narrow measure (M1). the results
of this study explain that the size of the money
supply in a narrow measure (M1) significantly
causes food inflation while the broad amount of
money supply does not affect food inflation because
in the analysis framework it is found that changes in
the money supply are wide (M2) it will only have a
significant impact on food inflation in just three
years.
The next study was conducted by Alisher and
Daniel 2012, in his discussion discussing Effects of
weather shocks on agricultural commodity prices in
Central Asia, in this study using the Feasible
Generalized Least Squares (FGLS) analysis of panel
regression, this study uses several variables
consisting of price local local wheat and prices of
fried potatoes, global wheat prices and global potato
prices, exchange rates, inflation rates, water
irrigation, weather changes, potato stocks. wheat
stock, the amount of wheat and potato production,
The results of this study show that weather changes
and water availability have a significant effect on the
prices of wheat and potatoes in central Asia, whereas
in potato commodities the effect is more apparent in
the amount of yield obtained from potato
production.
Ficture 3: Mindset
3 RESEARCH METHOD
In this study using several determinants in
assessing the form of increase in food prices is
the amount of money that varies widely (m2) and
narrow (m1), the exchange rate, the amount of
rice and soybean food production, rainfall, and
maximum temperature. All observations of the
data amounted to 132 observations. To analyze
the effect of factors increasing food prices,
multiple linear regression was used and using the
classic assumption test it aims to determine the
effect of independent variables on dependent.
The time period in this study was from 2007-
2017
The regression equation is described as
follows:
Y = β0 + β1 X1 + β2 X2 + β3 X3 + β4 X4+ et.
Information :
Y = Increase in food prices (food inflation)
β0 = Constants
β1, β2 = Regression Coefficient
X1 and X2 = The money supply area of M2 and
the money supply is narrow (M1)
X3 = Exchange rate
X4 and X5 = Amount of rice production and total
soybean production
X6 and X7 = Rainfall and Maximum
Temperature (Rainy and hot weather)
Det = error
Data source
The data used in this study was obtained online or
through official institutions / agencies. Data from the
determinants of rising food prices were obtained
from the Central Statistics Agency Bank.
Meteorology Climatology and Geophysics Council.
In addition, data also used from journals, books,
articles, and other relevant sources used in this
study.
4 RESULT
For estimation of multiple linear regression in this
study, the aim is to find out whether the independent
variable has a positive or negative influence and is
significant to the increase in food prices in
Indonesia, these results are shown by the form of
coefficients (positive) and probability values < 0.05
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
854
to find out the results have a significant effect or not,
and see the results of the R2 value which shows how
much influence the independent variable on the
dependent variable, these results are obtained based
on the following results:
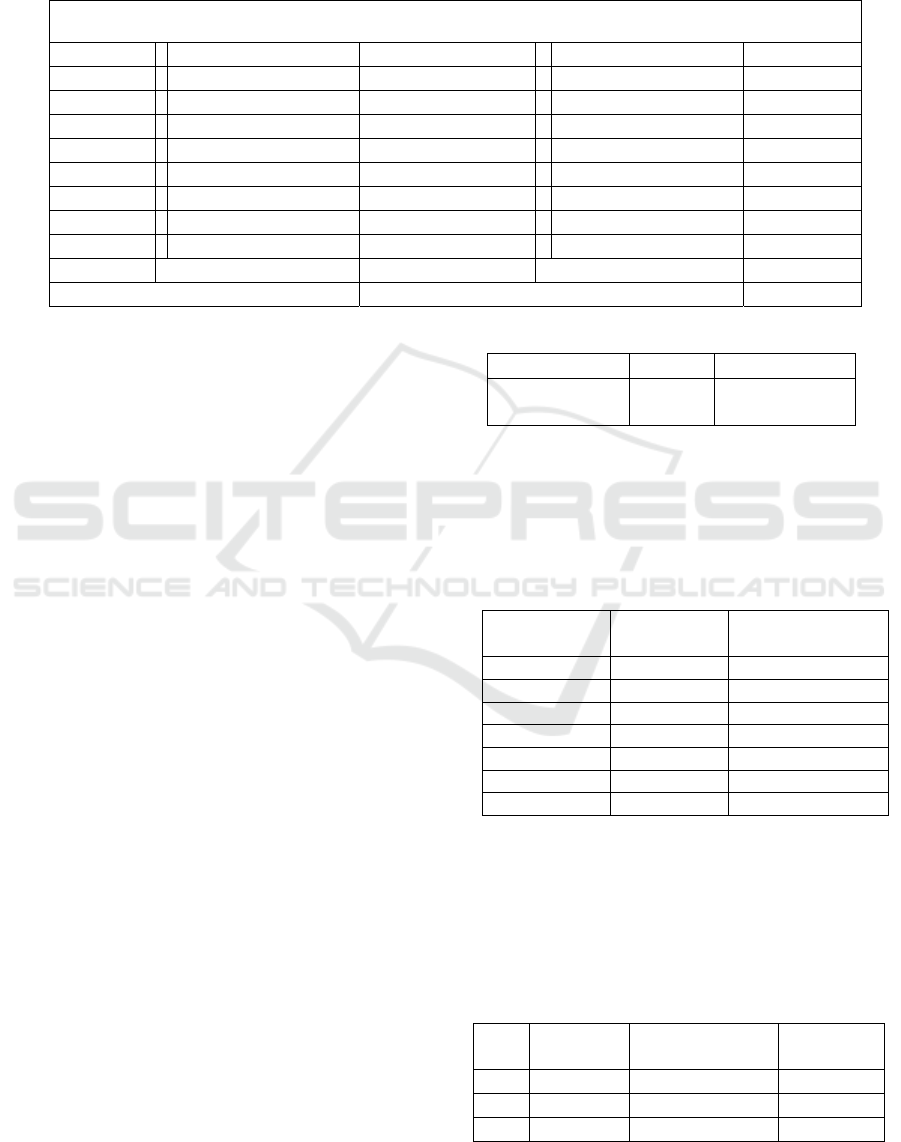
Table 1: Results of multiple linear regression
Dependent
Variable:Y
Variable Coefficient Std.Error t-Statistic Prob
C -97.21513 8.355733 -11.63454 0.0000
X1 1.380341 0.596226 2.315132 0.0222
X2 5.126113 0.546585 9.378443 0.0000
X3 -0.778071 0.250492 -3.106167 0.0023
X4 3.964014 1.141838 3.471609 0.0007
X5 4.080209 1.152318 3.540870 0.0006
X6 4.118688 1.405513 2.930380 0.0040
X7 0.050615 0.023266 2.175481 0.0315
R-square:
0.931469
F statistic: 240.7703
Observasion: 132 Prob (F statistic): 0,0000
Source:Data processed Eviews 7, 2014
The coefficient of determination (R-Squared)
shows a number of 0.931469, meaning that the
variable money supply area (m2) and narrow (m1),
exchange rate (exchange rate), amount of food
production of rice, soybean, rainfall and maximum
temperature can explain 93% variable variation in
food price increases in Indonesia, while the rest
(7%) can be explained by other variables outside the
model. The F-test of 0.00000 indicates that the
variable amount of food production of rice,
soybeans, rainfall and maximum temperature has a
significant effect on the variable increase in food
prices in Indonesia. In the t test, the value> t table is
1.979 which means that the t statistic is fulfilled and
looking at the probability value of the seven
variables has a carry value of 0.05 meaning that the
variable has a significant influence on the Y
variable, it can be concluded from 7 independent
variables tested, has a spositive and significant
influence on the increase in food prices in Indonesia.
After regression analysis on all variables, both
the dependent and independent variables, from the
estimation results that have been obtained, it is
necessary to do a classic assumption test. Tests to
find out whether the estimation model has fulfilled
the form of criteria in econometrics means that there
are not enough forms of errors based on assumptions
that must be fulfilled in the Ordinary Least Square
(OLS) method. The result of a good estimate is
regression that has met Blue criteria (best linear
Unbiased Estimator) (Gujarati, 2002).
Table 2: Normality Test
Statistic test Sig value Information
Kolmogorov-
Smirnov Z 0,431
N
ormal sprea
d
Based on the results of normality testing in the
table above, it is known that the residual regression
significance value formed is greater than the 5% real
level so that it can be said that the assumption of
normality is fulfilled.
Table 3: Assumption of Normality
Independent
Variabel Sig. Information
X1 0,298 Homoskedastisitas
X2 0,363 Homoskedastisitas
X3 0,823 Homoskedastisitas
X4 0,947 Homoskedastisitas
X5 0,458 Homoskedastisitas
X6 0,909 Homoskedastisitas
X7 0,232 Homoskedastisitas
Based on the table above, it is known that the sig
value. > 0.05, it can be concluded that there is
homoskedasticity or in other words the assumption
that heteroscedasticity does not occur has been
fulfilled statistically.
Table 4: Multicolenearrity test (Variance Inflating
Factor VIF)
Mode
Collinearity
Statistics
Tolerance VIF
1 (Constant)
X1 ,175 5,708
Determination of Food Price Increase in Indonesia: RICE, FOOD, SOY Period 2007 - 2017
855
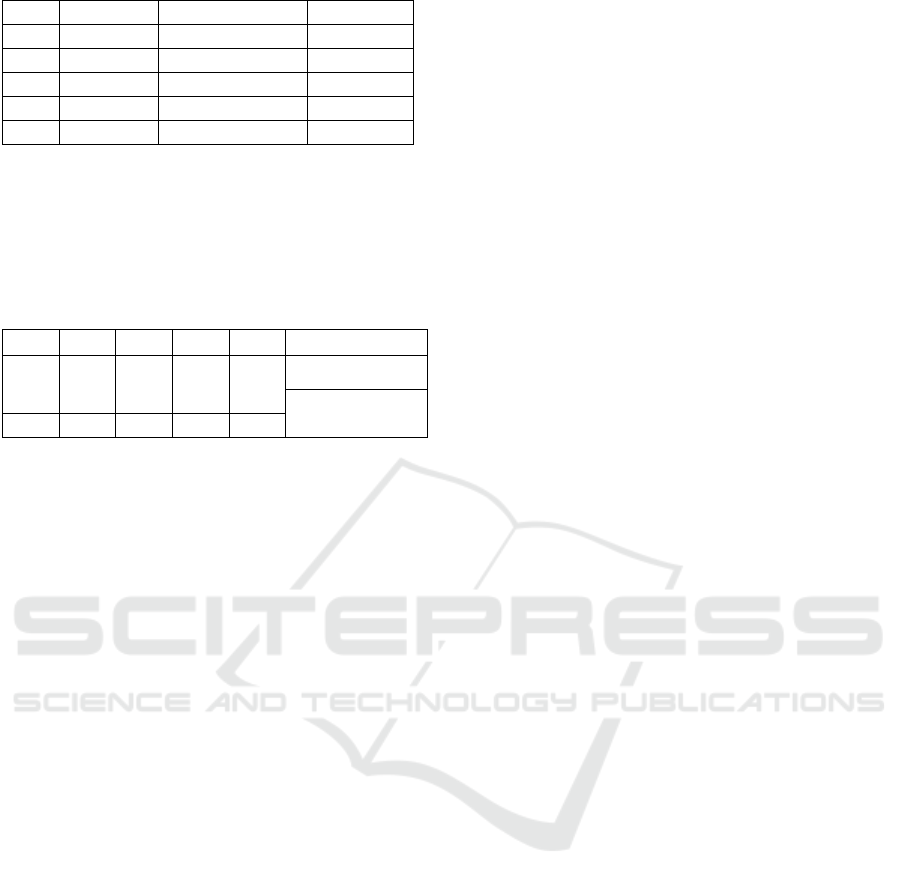
X2 ,157 6,370
X3 ,730 1,370
X4 ,562 1,779
X5 ,483 2,071
X6 ,354 2,828
X7 ,282 3,552
Based on the table above, it can be seen that the
independent variables in this study have a Variance
Inflation Factor smaller than 10, so that it can be
said that there are no symptoms of multicollinearity
between the independent variables in this study.
Dl
Du 4-du
4-dl
Dw
Interpretation
1,60
6
1,82
9
2,17
2
2,3
94
1,93
7
not occur
Autocorrelation
5 DISCUSSION
In general, the regression model used in this study
has a good outcome. Free Vaiabel is used, namely
the money supply area (m1) and narrow (m2), the
exchange rate (exchange rate), the amount of food
production of rice, soybeans, rainfall and maximum
temperature can
Explain the effect on the increase in food
prices with ahigh percentage ( 93% ), Together
these variables have a significant effect on the
increase in food prices in Indonesia. Individual
influences can be explained as follows:
Variablewide money supply (M2) has a
Significant influence on rising food prices, the
results of the coefficients obtained in this variable
are positive, this indicates, that the existence of a
positive direction means that an increase in the
money supply will affect the increase in food prices.
The value of the regression coefficient obtained is
1.380341 it shows, if there is a form of increase
experienced by the money supply of 1% or one unit
directly causing an increase in food prices by 1.38%
with the form of asusmi other variables remain and
there is no change. The results obtained based on
this regression analysis are in accordance with the
theory put forward by Irvin Fisher who explained
that the higher level of money circulation would lead
to the high purchasing power of the community. And
the results obtained are also the same as stated by
Nophirin, according to him in the theory of money
complexity that because of the rise in price, the
excess form of demand owned by the community is
a form of high demand due to the money supply.
Narrow money supply (M1)
Based on the results of the t test, the results show
that the variable money supply narrow M1 has the
most dominant, significant and positive influence on
the increase in food prices, the result of which the
coefficient obtained is positive, this indicates that
there is a positive direction affect the increase in
food prices and vice versa. The coefficient of the
narrow money supply variable is 5.126113, it shows
that there is an increase in the money supply
amounting to 1% which will cause an increase in
food prices which is equal to 5.12%, with the form
of other variables remaining fixed or no changes to
other variables (constant). The results of the analysis
obtained are in accordance with the theoretical form
proposed by Mankiw (2000) that a high price
increase will occur if the existence of a high level of
circulation in the amount of money circulating
directly will cause a boost in public consumption.
The increase in money distribution both narrowly
and broadly will cause a high form of public
consumption power, based on the manki theory, an
increase in the money supply causes a form of
positive increase in consumption which will
gradually lead to increases in food prices (Mankiw,
2000)
From the results of the t test that has been done,
it is found that the variable rate of exchange /
exchange rate has a significant influence on the
increase in food prices (food inflation) Indonesia.
The coefficient obtained in this variable is negative,
meaning that the increase experienced by the
exchange rate / exchange rate causes a decrease in
the increase in food prices, and vice versa the
occurrence of depreciation (decline) by the exchange
rate will cause an increase in food prices. The
regression coefficient obtained is - 0.7787071,
which shows that the increase in the rate of
exchange / value of 1% will cause a decrease in the
increase in food prices by -0.77% with the
assumption that there is no change in other variables
(constant variable) . The results of the analysis
obtained in accordance with the form of theory put
forward by Cassel (1918) the exchange rate between
the two countries should be equal to the price level
of the country's ratio, the fall in the form of domestic
purchasing power of a domestic currency will
directly (increase the inflation rate) followed by
deperesiasi form on the country's currency against
the domestic money market but if it happens
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
856

otherwise domestic purchasing power becomes
increased it will cause deflation which is directly
followed by a form of appreciation in the currency,
this theory is the theory that is most often tested for
validity is because there is a form of comparison that
looks at the form of high purchasing power that
causes inflation / price increases. The same thing
was stated by Bob (2002) The occurrence of price
increases, can be seen through the decline in the
rupiah exchange rate against the value of foreign
currencies because the depreciation of the exchange
rate will cause an increase in the price of imported
goods, this directly affects domestic price
fluctuations.
Amount of Rice Production
Based on the results of the t test, it was found that
the rice production variable had a significant effect
on the increase in food prices in Indonesia. The
coefficient of the rice production variable obtained is
positive, which means that a decrease in the form of
rice production will cause an increase in food prices
and conversely the positive increase in the form of
rice production will suppress the form of rising food
prices. The value obtained from the regression
coefficient of rice production is equal to 3.964014,
which shows that the increase in rice production
which is equal to 1% will cause an increase in food
price increases of 3.96% with the assumption that
there is no change in other variables (constant
variable) . The results of the analysis above show
that the results are in accordance with the theory
explained by Ellis (1992) that the forms of
production, trade and consumption of food will
affect the fluctuations in the price of goods.
Soybean Production Amount
Based on the results of the t test, the results show
that the variable amount of soybean production has a
significant effect on the increase in food prices. The
coefficient value of the rice production variable
obtained is positive, this indicates that if a decrease
in soybean production will cause an increase in food
prices and vice versa if the increase towards the
positive towards soybean production will cause a
decrease in the increase in food prices. Regression
coefficient value of soybean production obtained is
equal to 4.080209. The results show that the increase
that occurs in soybean production which is equal to
1% will cause an increase in the increase in food
prices by 4.08% assuming no changes occur by other
variables (all variables are constant) . The results of
the analysis obtained show that the results are in
accordance with the theory put forward by Ellis
(1992) that the forms of production, trade and
consumption of food will affect the fluctuations in
the price of goods and according to Suryana (2004)
explain that the form of food supply involves three
aspects, namely distribution , consumption,
availability that is supported by actors who have
interests such as producers,
Rainfall
Based on the results of the t test, it was found that
the rainfall variable had a significant effect on the
increase in food prices. The coefficient of rainfall
variables is positive, these results show that positive
increases that occur in rainfall will cause an increase
in food prices, so the decrease in rainfall will cause a
decrease in the increase in food prices. The bulk
regression coefficient huja is equal to 4.118688, the
results show that the increase that occurred at 1%
will cause an increase in the increase in food prices
by 4.11% with the assumption that other variables
are constant without change. The results of the
analysis obtained in accordance with the relevant
theory put forward by Gilbert and Morgan (2010)
according to him weather changes are considered as
one source of variability in the prices of agricultural
commodities. The same thing was stated by Trovero
and Braun (2008) that changes in weather can cause
a form of potential, such as floods, droughts which
ultimately damage food crops and hamper the form
of food distribution, which in turn has an impact on
rising prices of food commodities (Trovero and Von
Braun, 2008
Maximum Temperature (Hot Weather)
Based on the results of the t test, the results show
that the maximum temperature variable has a
significant effect on the increase in food prices. The
coefficient value of the rainfall variable is positive.
This result shows that the occurrence of a positive
increase in maximum temperature causes an increase
in food prices and conversely the decrease in
maximum temperature will cause a decrease in the
increase in food prices. The maximum temperature
regression coefficient value is 0.050615, the results
show that an increase in the number of 1% will
cause an increase in food prices by 0.05%, this
applies with the assumption that other variables are
constant and do not change.
After performing various tests both on the
questionnaire and on the variables; it turns out that
this research deserves to be continued by multiple
linear analysis. In multiple linear regression test to
four independent variable of reliability, competence,
credibility and communication have influence to
Determination of Food Price Increase in Indonesia: RICE, FOOD, SOY Period 2007 - 2017
857

employee job satisfaction. The effect of these four
variables varies greatly. Reliability has the greatest
influence; followed by communication, then
credibility and competence. The four variables gave
effect of 61.0%, meaning 39.0% influence on
satisfaction contributed by other variables not
included in this research model.Similarly, the
correlation of each independent variable with
satisfaction indicates that the most dominant and
strongest positive correlation is between the variable
of reliability and job satisfaction, followed by
communication variables with job satisfaction,
competence with job satisfaction and lastly between
credibility and jobsatisfaction.
In hypothesis test by simultaneous test method (F
Test) also called ANOVA, it turns out sig value
alpha 0.000 < alpha 5% (0.05). The value of f
arithmetic is also greater than f table. This means
that four variables together will have a positive and
significant impact on jobsatisfaction.In the Partial
Test (Test T), it is found that the variable reliability
and communication significantly affect job
satisfaction, but the credibility and competence
variables do not significantly affect job satisfaction.
The variable of reliability in the performance
appraisal system gives a significant influence in
affecting job satisfaction, which means satisfaction
and job dissatisfaction of employees influenced by
variable reliability.
Based on the background of research that the
performance appraisal system has not been able to
provide job satisfaction, so the variable reliability is
one factor in the performance appraisal system that
has not been able to provide job satisfaction. This
can be explained through several things, employees
feel reward or punishment miss promotion
promotion, increase salary levels are often not based
on performance appraisal results; so that employees
feel the performance appraisal is not done or
executed as promised. Or the company is often late
in doing performance appraisal which will then slow
down the promotion process or a raise.
Communication variables also gained a
significant influence in affecting job satisfaction,
which means communication in the performance
appraisal system is one factor that has not been able
to provide job satisfaction. This can be explained by
several things; the company has not really explained
well the performance appraisal system. The
company also rarely discusses the
employee'sappraisal system that has not been able to
provide job satisfaction. This can be explained
through several things, employees feel reward or
punishment miss promotion promotion, increase
salary levels are often not based on performance
appraisal results; so that employees feel the
performance appraisal is not done or executed as
promised. Or the company is often late in doing
performance appraisal which will then slow down
the promotion process or a raise.
Communication variables also gained a
significant influence in affecting job satisfaction,
which means communication in the performance
appraisal system is one factor that has not been able
to provide job satisfaction. This can be explained by
several things; the company has not really explained
well the performance appraisal system. The
company also rarely discusses the employee's next
performance plan after the performance appraisal.
Employees expect performance planning together
with the company. Competence variables, although
partially ineffective in affecting job satisfaction but
together with other variables have an influence on
satisfaction. Officers who carry out assessment in
the eyes of employees is quite strong and skilled and
have sufficient knowledge; but it is not a major
factor that gives a sense of satisfaction. Credibility
variables are also partially ineffective in influencing
job satisfaction, but together with other variables
have an influence on satisfaction. The courteous,
honest and respectful examiner is the capital to be an
appraiser that pleases employees; but it is not
enough if it does not get a reliable and well-
understood performance appraisal system.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the explanation of the problems,
hypotheses, discussion and analysis results in the
previous chapter, it can be concluded that the
variable money supply, the rate of exchange, the
amount of food production, the weather has a
positive and significant effect on the increase in food
prices in Indonesia.
1. The form of increasing the money supply,
besides being influenced by currency held by
the public is also influenced by credit, because
easily the form of credit or loans obtained
directly will cause many people to do a form of
credit or loan which in the end, easily obtained
and the amount of funds obtained will directly
increase people's consumption patterns, this is
the same as the theory proposed by Irvin Fisher
regarding the effect of the money supply on
price increases, therefore the most the basis of
influencing the increase in the money supply is
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
858

the community and the process of credit
facilitated by the bank so that there is a
tendency for people to make loans so as to
increase the form of business activity and the
economy of the community.
2. The occurrence of depreciation (rate of decline)
on the rate of exchange (exchange rate) can be
seen from the form of imports of some food
commodities that Indonesia does every year,
due to the form of structural inequality, namely
the productivity gap associated with weak asset
allocation and production factors, and forms of
dependence on foreign debt which has a
negative impact on the economy (the impact of
business people who often engage in foreign
exchange) and the equilibrium trap phenomenon
(trap imbalance) related to the structure between
the three production sectors that underlies the
economic crisis which ultimately impacts
depreciation of the exchange rate (exchange
rate) which ultimately causes an increase in
prices of imported goods, the amount of food
production that is not matched by demand and
the demand for imported food every year,
without increasing production facing domestic
food commodities eventually led to an increase
in prices, especially imported food, due to the
depreciation of the exchange rate (declining
exchange rate) against foreign currencies.
The problem of rising food prices caused by
weather, because the weather influences the
growth and development of food crops, for
example, such as rainfall, very high rainfall
causes the food crops to be inundated and
become damaged, which causes crop failure for
food crops so that with yields that are small and
high in demand cause an imbalance between
supply and demand so that in the end it will lead
to a tendency to increase prices, and looking at
hot weather (drought) can cause disruption to
plant growth due to hot weather affecting
drought to food crops so that it ultimately does
not the fulfillment of sufficient water for food
crops, this is the basis of the occurrence of crop
failure caused by hot weather, as well as an
explanation of rainfall, crop failure caused by
maximum temperature (cu aca heat) will cause a
reduced form of production to be obtained so
there will be an imbalance between demand and
supply which ultimately leads to an increase in
food prices.
REFERENCES
Aviral (2010), Impact of Supply of Money on Food Prices
in India: A Causality Analysis
Alisher Mirzabaev and Daniel Tsegai (2012), Effects of
weather shocks on agricultural commodity prices in
Central Asia. ZEF-Discussion Papers on
Development Policy No. 171
Badan pusat statistik (2014), data komoditas pangan,
Surabaya
Banumurty, pamidua dan lokendra 2012), driving food
price
Cassel (1918), Purchasing power parity; journal of
economic, Volume 2 No.9
Ellis (1992), Aspek penyebab perubahan harga
Gujarati, D., 1995, Regresi linier berganda, Singapore:
McGraw-Hill Book Co
Glasson (1990), Basic of theory economic
Hariharan dan kumar 2012.An Analysis Of Food Inflation
In India, Volume 2, issue
Hasan (1998). Komoditas pangan dan bentuk
permintaanya
Mankiw, N. Gregory (2000). Principles of
Macroeconomic edisi 3 (e-book)
Muh.Yunanto (2007), Uang beredar dan kebijaka moneter
Imran, Ayyoubdan Fatima, (2013). Does Inflation Matter
For Sectoral Growth In Pakistan, An Empirical
Analysis. Volume 51, No. 1 (Summer 2013), pp. 71-
92
Mankiw, N. Gregory (2003). Teori Makro ekonomi Edisi
Kelima. Terjemahan. Jakarta: Penerbit Erlangga.
Nicholson (2000), demand and supply. . Volume 47, No. 2
(Summer 2000), pp. 15-19
Suryanan (2004), ketersediaan dan ketahanan pangan.
Salman dan Adnan, (201)3.Determinants of High Food
Prices The case of Pakistan,Volume51, No. 1
(Summer 2013), pp. 93-107
Sara Lazzaroni (2012), Weather variability and food
consumption: Evidence from Uganda; The Hague,
The Netherlands
Determination of Food Price Increase in Indonesia: RICE, FOOD, SOY Period 2007 - 2017
859
