USD 0,0000
USD 1,0000
USD 2,0000
USD 3,0000
The Influence of Profitability, Asset Tangibility, Growth, and Non
Debt Tax Shield on Capital Structure in Manufacture Companies
Listed in Indonesian Stock Exchange
Christina V. Situmorang
1
and Arthur Simanjuntak
1
1
Universitas Methodist Indonesia, Medan -Indonesia
Keywords: Profitability, Asset Tangibility, Growth, Non Debt Tax Shield, Capital Structure
Abstract: The objective of the research was to examine the influence of Profitability, Asset Tangibility, Growth, and
Non Debt Tax Shield on Capital Structure in manufacture companies listed in BEI (Indonesia Stock Market)
in the period of 2012-2016. The research used causal research method. The population was 136 manufacture
companies listed in BEI in the period of 2012-2016, and 85 of them were used as the samples, taken by
using purposive sampling technique. The data were analyzed by using path analysis. The result of the
research showed that the variables of Profitability, Asset Tangibility, Growth, and Non Debt Tax Shield
simultaneously had influence on Capital Structure. Partially, Profitability and Growth positive significant
influence on Capital Structure. Asset Tangibility and Non Debt Tax Shield positive unsignificant influence
on Capital Structure.
1 INTRODUCTION
Investors in equity investments want profit, in the
form of dividend yield and capital gains, but
investing in equities also involves risks. Therefore,
to attract investors to invest their capital in equities
by offering a higher profit level compared to the
profit level of other investments that are less risky.
In this case, investors need a variety of information
that can be used as a signal to assess the prospect of
the company concerned, such as seeing the value of
the business, namely by analyzing financial
statements.
The main goal of companies that have become
public is to increase the prosperity of the owners or
shareholders by increasing the value of the company
(Salvatore 2005). Business value is the perception of
investors to see a company that is often associated
with the share price of the company. In reality, not
all companies want the stock price of the company
to be high, because the company is afraid that the
shares will not sell or attract investors to buy them
by conducting a share split.
The impact of the financial crisis in Europe and
America in 2008 spread throughout the world. The
crisis of a country that other countries treft, is the
contagion effect that can occur for all events in
different areas of economic and financial crisis. The
financial crisis, such as fluctuations in stock prices
that occur on a capital market, has an impact on
falling stock returns and ultimately affects abnormal
returns as a benchmark for performance.
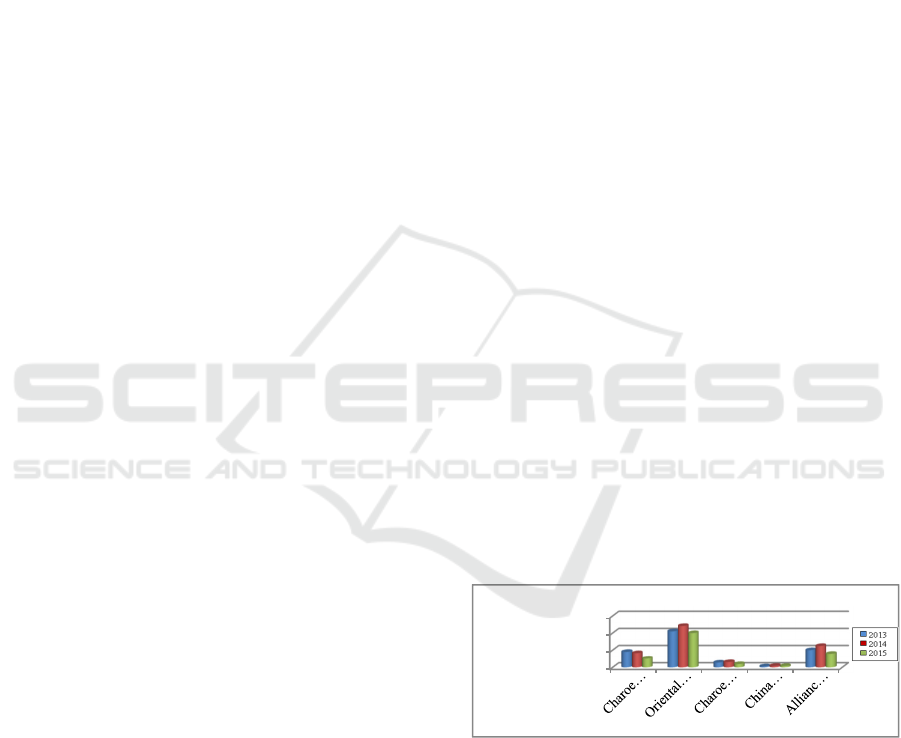
Figure 1: Diagram of the stock price of production
companies in different countries in the Southeast
Asia region 2013-2015
The image above shows that the share price data
of production companies in the Southeast Asia
region for the period 2013-2015. The share price
grew between 2013 and 2014, with the exception of
the company Charoen Pokphand Foods Public
Company Limited (Thailand), which fell and in
2015 the share price fell compared to the share price
1282
Situmorang, C. and Simanjuntak, A.
The Influence of Profitability, Asset Tangibility, Growth, and Non Debt Tax Shield on Capital Structure in Manufacture Companies Listed in Indonesian Stock Exchange.
DOI: 10.5220/0009508312821288
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 1282-1288
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

in 2014 for the five companies in Southeast Asia.
The statement indicates that there were problems
with production companies in different countries in
the Southeast Asia region, as seen from the share
price of the company that declined.
The global crisis is expected to have a greater
impact in the real sector in the longer term,
especially trade related to the slowdown of the
global economy, especially in developed countries.
The global crisis has no major impact on direct trade
between Indonesia and Europe and with the United
States. But the path of indirect trade in Indonesia
with Europe and the United States will be influenced
by China. China, the largest importer of Indonesian
goods, is expected to reduce imports as a result of
the declining demand from Chinese countries for
Chinese goods.
The crisis of a country that affects other
countries is a contagion effect that can occur for all
events in different areas, both economic and
financial crises. The financial crisis, such as
fluctuations in stock prices that occur on a capital
market, has an impact on fluctuations in falling share
returns and ultimately affects the pattern of
abnormal returns as a measure of performance.
(Franco Modigliani and Merton H. Miller 1958)
who published matters relating to the capital
structure and became one of the subjects that drew
the attention of academics on a global scale. For
more than half a century, various studies have been
conducted by academics to explain the relationship
of the capital structure with profitability, tangibility
of assets, growth and non-debt payments. In this
case, the company must be able to determine its
capital structure, namely how much is to be
borrowed from third parties by considering the
benefits and costs of using debts. There are several
developments in the theory of capital structure
(Franco Modigliani and Merton H. Miller 1958),
namely Trade-Off Theory, Pecking Order Theory
and Signaling Theory.
Some of the earlier researchers who supported
the theory of the pecking order were (Ilyas Muhajir
dan Triyono 2010), who concluded that profitability
had a positive effect on the capital structure. Groups
that do not support the pecking order theory are the
results of research (Huang & Song 2006) which
show that profitability has a negative effect on the
capital structure.
The results of empirical studies showing the
opposite results with regard to the effect of asset
tactility on the capital structure. The group of
researchers offering support is the research carried
out by (Jemmi Halim Liem 2013) that concludes that
asset tangibility (real assets) has a positive effect on
the capital structure (debt). The group of researchers
who did not support this advice was conducted by
(Booth et al. 2001), in which it was concluded that
asset tactility had a negative effect on the capital
structure.
Research carried out by (Margaretha &
Ramadhan 2010) which showed that growth has a
positive effect on the capital structure. The research
group that does not support this is the research of
(Rajan & Zingales 1995) that concludes that the
growth rate negatively affects the capital structure.
The group of researchers who support the
research of (Moh & Rimbey 1998), who came to the
conclusion that NDTS has a positive effect on the
capital structure. While the research conducted by
(Zou & Zezhong 2006) concluded that NDTS had no
influence on the capital structure.
This research focuses on manufacturing
companies listed on the Indonesian stock exchange,
because as we know, since the economic crisis in
2008, the center of global economic power from
Western countries, namely Europe and North
America, slowly shifted to Asia. In Asia, Indonesia
is one of the fastest growing economic zones.
Based on the above description, the authors are
interested in analyzing the "Effect of profitability,
tangibility, growth and non-debt tax shield on the
capital structure in manufacturing companies listed
on the Indonesian stock exchange for the period
2012-2016".
The formulation of the problem in this study is
whether profitability, tangibility of assets, growth
and non-debt tax shield partially and simultaneously
affect the capital structure of manufacturing
companies quoted on the Indonesian stock
exchange?
The aim of this research is to partially and
simultaneously identify and analyze the effect of
profitability, asset tactility, growth and non-debt tax
shield on the capital structure of production
companies that are listed on the Indonesia Stock
Exchange.
Although the contribution of research to researchers
and academics is expected to increase the
understanding and knowledge of researchers in the
field of economics, particularly in terms of
profitability, tangibility of assets, growth and non-
debt tax shield, the impact on the capital structure.
Production companies are expected to be used as
important information and input to improve business
performance in terms of improving the capital
structure.
This research is a development of research
carried out by (Yuliani et al. 2014) entitled
"Determining factors for the capital structure and its
impact on value in emerging markets (studies of the
real estate and real estate sector)". This difference
with previous research lies in the variable, where
earlier research uses independent variables, namely
The Influence of Profitability, Asset Tangibility, Growth, and Non Debt Tax Shield on Capital Structure in Manufacture Companies Listed in
Indonesian Stock Exchange
1283

the sales level, the asset structure, growth potential,
profitability, non-tax tax shield, company scale,
internal company circumstances, while this study
uses profitability, Tangibility Asset, Growth, and
Non-Debt Tax Shield. and the dependent variable of
the previous survey is the capital structure and
business value, while this study only uses variables
of the capital structure. In contrast to the previous
research period, this study period was 2012-2016,
while the previous research period was 2007-2011.
2 DEVELOPMENT OF
HYPOTHESES CAPITAL
STRUCTURE
According to (Wild et al. 2005) the capital structure
is the composition of financing between equity (own
financing) and debt in a company. Capital structure
is a permanent expense that reflects the balance
between long-term debt with equity. Capital
structure is reflected in long-term liabilities and the
element of own capital, where both elements are
permanent funds or long-term funds. In this study
the capital structure is approached by debt / equity
ratio (DER).
DER is a group of Levarage (debt) ratios. This
ratio reflects the composition or capital structure of
the total loan (debt) to the total capital that the
company holds to meet its long-term obligations.
Some theories about debt financing are:
Capital Structure Theory
Modigliani & Miller theory is a modern theory of
the capital structure that publishes its article "The
costs of capital, corporate finance and theory of
investment". MM proves that the value of a
company is not affected by the capital structure .
Exchange theory
The trade-off theory suggests that the optimal debt
ratio should take into account the benefits obtained
and the costs incurred by the company through the
use of corporate debts. This theory suggests that the
optimal capital structure will be achieved if the
benefits of the value added from the use of debts in
the form of tax savings are used to cover the rise in
the financial emergency costs associated with the
use of debt (Bradley et al. 1984)
Agency approach
According to this approach, the capital structure is
designed to reduce conflicts between different
interest groups. The conflict between shareholders
and managers is actually the concept of free cash
flow.
Signal Theory
If the manager is confident that the company's
outlook can use more debt, then this will work later
as a more reliable signal. This is because companies
that increase debt can be seen as companies that
have confidence in the future of the company. We
can therefore conclude from the above explanation
that debt is a positive sign or signal of the company.
Profitability
Profitability as a yardstick in determining alternative
financing, but the way to assess the profitability of a
company that depends on profit and shared assets is
net profit after tax (net result) derived from
operating activities in total assets. The profitability
ratio as measured by Return on Assets (ROA) is a
measure of the company's ability as a whole to make
a profit with the total available assets in the
company.
Tangibility Asset
Tangibility assets are one of the most important
factors in determining decisions about the capital
structure, because the amount of fixed assets can be
used as collateral for creditors (Joni & Lina 2010).
Because companies with a greater tangibility of
assets have a better position in providing loans. The
tactile capacity can be used as collateral for loans
provided by creditors. If the company does not
comply with its obligations towards creditors, the
tangibility of the assets is confiscated by the creditor
to pay off all obligations that the company can not
pay to the creditor.
Growth
The growth rate of the company may affect the
creditor's confidence in the company and the
willingness of investors to provide financing through
long-term debt (Firnanti 2011). Growing companies
will come under pressure to fund their investment
opportunities that exceed the retained earnings in the
company, so that it is in line with the pecking order
theory, so in this case the company will use debts
rather than equity or this case retained earnings.
Non-debt Tax Shield
Non-debt tax shield is a tax deduction for investment
write-offs and tax relief. (DeAngelo, H., and Masulis
1980) stated that the optimal capital structure model
with respect to the existence of both personal tax and
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1284
corporate tax and non-debt tax shield (tax savings of
non-debt accounts). This non-debt tax shield
(NDTS) arises because the company makes
depreciation costs as an impact on the use of assets,
particularly fixed assets. The benefits that the
company obtains from the use of loan capital as
financing for the company's investment activities
will have an impact on the taxes and interest costs to
be paid. Also with companies that cause higher
depreciation costs, they will receive tax benefits as a
result of the depreciation costs paid.
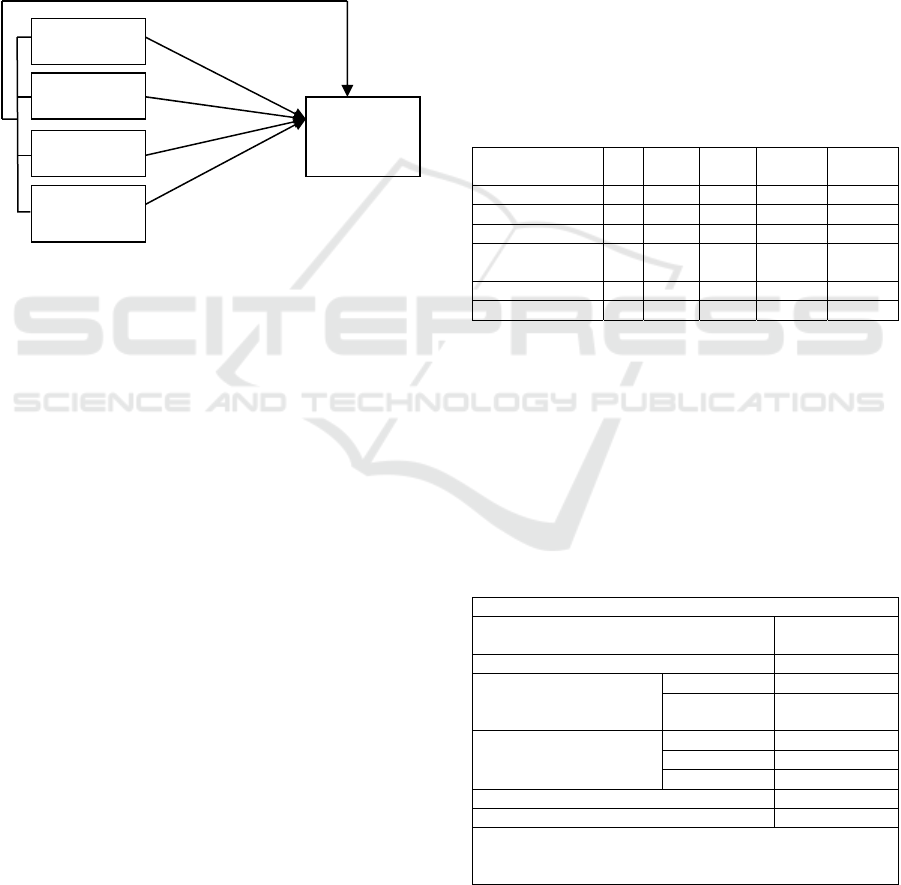
Conceptual framework.
Figure 2: Concept Drawing
The research hypothesis is:
1. Profitability, tangibility of assets, growth and
non-debt tax shield partly affect the capital
structure of manufacturing companies listed on
the Indonesian stock exchange
2. Profitability, tangibility of assets, growth and
non-debt tax shield have a simultaneous effect
on the capital structure of manufacturing
companies quoted on the Indonesia Stock
Exchange
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This type of research is a conclusive (causal)
investigation. The population in this study consisted
of production companies listed on the Indonesia
Stock Exchange (IDX) from 2012 - 2016, a total of
140 companies. The sampling technique used was
targeted sampling and a sample of 85 companies
was obtained for the period 2012-2016 with a total
observation of 425 analysis units.
Research model
The data analysis method used is multiple linear
regression by first performing descriptive statistical
tests and classical assumption tests. The equations in
the hypothesis:
Y = b1 X1 + b2 X2 + b3X3 + b4 X4 + є
at which:
Y : Capital structure
b1, b2, b3, b4 : variable coefficients independent
X1 : Profitability (ROA)
X2 : Asset Tangibility (FATA)
X3 : growth rate (TP)
X4 : Non - Debt Tax Shield (NDTS)
Ε : standard error
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Table 1: Descriptive table of research Variable
statistics
N
Min Max Mean
Std.
Deviation
Profitabilitas 425 ,0066 ,4453 ,154888 ,1009156
Aset Tangibility 425 ,0029 1,0311 ,292145 ,2343584
Growth 425 ,0475 ,3013 ,175475 ,0564156
N
on Debt Tax
Shield
425 ,0120 ,9997 ,393648 ,2555603
Capital Structure 425 ,1002 ,9996 ,428096 ,2312980
Valid N (listwise) 425
Testing Classical Assumptions.
Testing the classical assumptions used in this study
includes normality tests, multicollinearity tests,
autocorrelation tests and heteroscedacity tests.
Normality Test
In this study, the restnormality test can be performed
by the non-parametric statistical test Kolmogorov-
Smirnov (K-S).
Table 2: Normality test table
One-Sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test
Unstandardi
zed Residual
N 425
Normal Parameters
a,b
Mean 0E-7
Std.
Deviation
,18724734
Most Extreme
Differences
Absolute ,040
Positive ,040
Negative -,037
Kolmogorov-Smirnov Z ,825
Asymp. Sig. (2-tailed) ,505
a. Test distribution is Normal.
b. Calculated from data.
Profitabilitas
(ROA)
Asset
T ibilit
Growth
Non-debt tax
shiel
d
capital
structure
(
DER
)
The Influence of Profitability, Asset Tangibility, Growth, and Non Debt Tax Shield on Capital Structure in Manufacture Companies Listed in
Indonesian Stock Exchange
1285
The Kolmogorov-Smirnov Z value of 0.825 is above
α = 0.05 (Asymp., Sig = 0.505> 0.05), so the
hypothesis H0 is accepted, which means that the
remaining data are normally distributed.
Multicollinearity Test
Multicollinearity tests are done using the variance
inflation factor (VIF). Data is said to have no
multicollinearity if the tolerance value is ≥ 0.10 and
VIF ≤ 10.
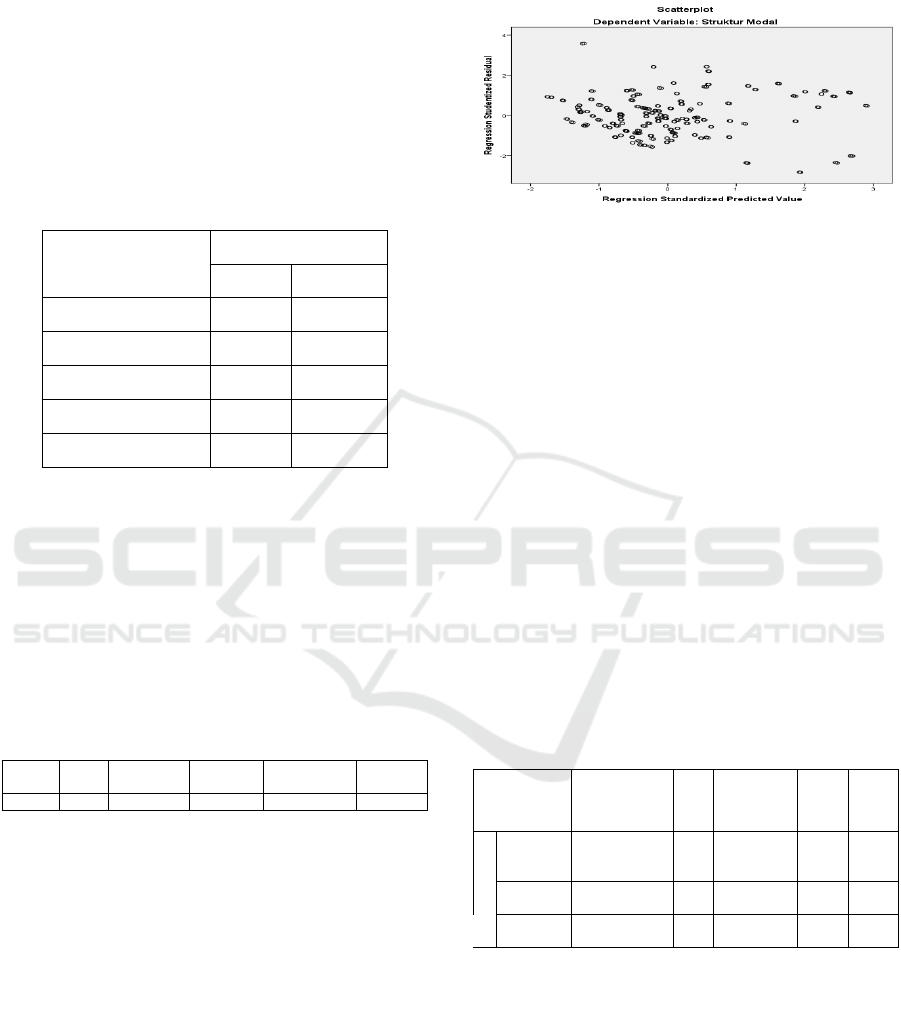
Table 3: Multicollinearity test table
Model
Collinearit
y
Statistics
Tolerance VIF
(Constant)
Profitabilitas
,804 1,244
Aset Tangibility
,996 1,004
Growth
,822 1,216
Non Debt Tax Shield
,972 1,029
a. Dependent variable: capital structure
All independent variables have VIF values ≤ 10, so
the data from this study did not experience
multicollinearity.
Autocorrelation Test.
This test is done by looking at the value of Durbin
Watson, as follows:
Table 4: Autocorrelation test table Durbin Watson
Model Summary
b
Model R R Square Adjusted
R Square
Std. Error of
the Estimate
Durbin-
Watson
1 ,587
a
,345 ,338 ,1881369 2,012
a. Predictors: (Constant), Non Debt Tax Shield, Aset
Tan
g
ibilit
y
, Growth, Profitabilitas
b
. De
p
endent Variable: Ca
p
ital Structu
r
The Durbin Watson (DW) value is 2.012. Based on
the Durbin Watson statistical table with α = 0.05, the
number of samples (n) = 85 and the number of
independent variables (k) = 4 are known to have the
value of dL = 1.82767 and the value of dU =
1.85576. So it can be concluded that: dU = 1.85576
<DW = 2.012 <4 - dU = 4 - 1.85576 = 2.14424 On
the basis of these predetermined criteria, indicates
that H0 (hypothesis 0 (zero)) is rejected means no
there are positive and negative autocorrelations.
Heteroscedasticity Test
In this study, the heterosexasticity test was observed
using a scatterplot plot between the predicted value
of the related variable (ZPRED) and the residual
value (SRESID).
Figure 3: Heteroscedasticity test image - Scatter plot
graph
The Scatterplot Heteroscedasticity test above shows
that the points above and below the number 0 (zero)
spread on the y-axis and did not form a clear pattern,
so it can be concluded that heterocedasticity does
not occur.
Hypothesis test
Testing the hypothesis in this study uses the F-test, t-
test and determination coefficient (R2)
Test F
Significant value of 0.000 small levies of 0.05, so it
can be said that the variable profitability (ROA),
Tangibility Asset, Growth and Non Debt Tax Shield
have a simultaneous effect on the dependent
variable, namely Capital Structure (DER).
Table 5: F-test table
(ANOVA
b
)
Model Sum of S
q
uares Df Mean S
q
uare F Si
g
.
1 Regression 7,817 4 1,954 55,214 ,000
b
Residual 14,866 420 ,035
Total 22,683 424
a. Dependent Variable: Capital Structure
b. Predictors: (Constant), Non Debt Tax Shield, Asset
Tangibility, Growth, Profitabilitas
T-test
The t statistical test basically shows how far
someone is independent in explaining dependent
variation.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1286
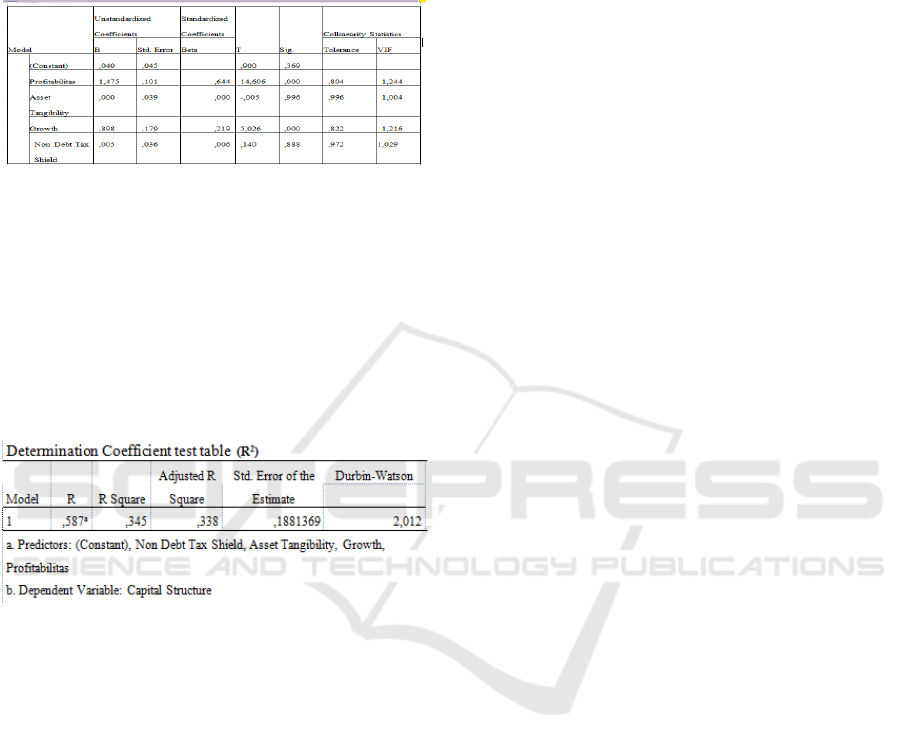
ROA and growth have a positive and significant
effect on the capital structure, while Tangibility
Assets and Non Debt Tax Shields do not have a
significant effect on the capital structure.
Table 6: T-test Table
Determination Coefficient test (R2)
The coefficient value (R) is 0.587, which shows a
strong relationship, with a (0.3% or 33.8%) fixed
coefficient of determination (Adjusted R Square).
This means that Profitability (ROA), Tangibility
Asset, Growth and Non Debt Tax Shield Capital
Structure (DER) can explain 33.8%, while the
remaining 66.2% is explained by other variables
outside this estimation model.
Table 7: Determination Coefficient Table
5 CONCLUSIONS
From the results of the research carried out,
conclusions can be drawn as follows:
1. In part, profitability (ROA) has a positive and
significant effect on the capital structure (DER).
Tangibility Asset has a positive and not
significant effect on the capital structure (DER).
Growth has a positive and significant effect on
the debt structure (DER). Non-debt tax Shield
has a positive and not significant effect on the
capital structure (DER).
2. At the same time, profitability (ROA),
Tangibility Asset, growth and non-debt tax
shield influence the capital structure (DER).
Constraint
This study has several limitations, namely :
1. Limitations on the criteria of the research
sample used are only companies with profit that
meet the criteria, but processing companies that
suffer losses do not meet the criteria. So that in
this case the profitability can not be fully
reflected in production companies that are listed
on the Indonesia Stock Exchange (IDX)
2. This study only uses independent variables
Profitability, Assibility, Growth and Non-Debt
Tax Shield, as future researchers add the
number of independent variables to be analyzed
in addition to the above variables. Investment
decisions, for example proxied by Price Earning
Ratio (PER), Growth Potential, Interest Rate
(SBBI) and others.
Suggestion
Based on the conclusions and limitations of this
study, the researcher gave some suggestions to the
following researcher, among others, as follows:
1. Can conduct research with the criteria of
companies that have profit / loss for 10 (ten)
years in a row.
2. Can add independent variables such as
investment decision (PER), growth potential,
interest rate (SBBI) and other
REFERENCES
Booth, L., Aivazian, V. & Demirguc-kunt, A., (2001).
Capital Structures in Developing Countries. The
Journal of Finance, 56(1), pp.87–130.
Bradley, M., Jarrell, G.A. & And Kim, E.H., (1984). On
the Existence of an Optimal Capital Structure: Theory
and Evidence: Discussion. The Journal of Finance,
39(3), pp.857–877. Available at: http://www.jstor.org/
stable/2327951?origin=crossref.
DeAngelo, H., and Masulis, R., (1980). Optimal Capital
Structure under Corporate and Personal Taxation*.
Journal of Fmanclal Economics, 8, pp.3–29.
Firnanti, F., (2011). Faktor faktor yang mempengaruhi
struktur modal perusahaan manufaktur di Bursa Efek
Indonesia. Jurnal Bisnis dan Akuntansi, 13(2),
pp.119–128.
Franco Modigliani and Merton H. Miller, (1958). The
American Economic Review. American Economic
Association, 48, pp.261–297. Available at:
http://pubs.aeaweb.org/doi/10.1257/aer.99.1.i.
Huang, G. & Song, F.M., (2006). (P)The determinants of
capital structure: Evidence from China. China
Economic Review, 17(1), pp.14–36.
Ilyas Muhajir dan Triyono, (2010). FAKTOR-FAKTOR
YANG MEMPENGARUHI STRUKTUR MODAL
PERUSAHAAN MANUFAKTUR PADA BURSA
EFEK INDONESIA PERIODE 2005-2009.
Universitas Muhammadiyah Semarang, 7.
Jemmi Halim Liem, W.R.M. dan B.S.S., (2013).
FAKTOR-FAKTOR YANG MEMPENGARUHI
The Influence of Profitability, Asset Tangibility, Growth, and Non Debt Tax Shield on Capital Structure in Manufacture Companies Listed in
Indonesian Stock Exchange
1287

STRUKTUR MODAL PADA INDUSTRI
CONSUMER GOODS YANG TERDAFTAR DI BEI
PERIODE 2007-2011. Jurnal Ilmiah Mahasiswa
Universitas Surabaya, 2(1), pp.1–11.
Joni & Lina, (2010). Faktor-Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi
Struktur Modal. Jurnal Bisnis Dan Akuntansi, 12(2),
pp.82–97.
Margaretha, F. & Ramadhan, R., (2010). Faktor-Faktor
Yang Mempengaruhi Struktur Modal Pada Industri
Manufaktur Di Bursa Efek Indonesia. , 12(2), pp.119–
130.
Moh, M.A. & Rimbey, J.N., (1998). The Impact of
Ownership Structure On Corporate Debt Policy : a
Time-Series Cross-Sectional Analysis. The Financial
Review, 33, pp.85–98.
Rajan, R.G. & Zingales, L., (1995). WHAT DO WE
KNOW ABOUT CAPITAL STRUCTURE ? SOME
EVIDENCE FROM INTERNATIONAL DATA.
Journal of Finance 50, 50(5), pp.1421–1460.
Salvatore, D., (2005). Managerial Economic: Ekonomi
Manajerial dalam Perekonomian Global Kelima. I. S.
Budi, ed., Salemba Empat.
Wild, J.J., Subramanyam, K.R.. & Halsey, R., (2005).
Financial Statement Analysis:, Available at:
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1300/J109v01
n04_05.
Yuliani, Umrie, R.H. & Diah, Y.M., (2014). Determinan
Struktur Modal dan Pengaruhnya Terhadap Nilai
Perusahaan pada Pasar yang Sedang Berkembang
(Studi pada Sektor Real Estate and Property). Jurnal
Manajemen Usahawan Indonesia, 39(1), pp.27–52.
Zou, H. & Zezhong, J., (2006). The financing behaviour of
listed Chinese firms. The British Accounting Review,
38, pp.239–258.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1288
