
Analysis of Cost Calculation System at X Hospital based on
Traditional Costing and Time Driven Activity based Costing: Study
at Unit Cost Hemodialysis Services
Novia Rizki
1
and Dwi Hartanti
1
1
Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta -Indonesia
Keywords: TDABC, Traditional Costing, hospital, hemodialysis services
Abstract: The purpose of this research was to show an analysis of unit cost calculation based on traditional costing
and time driven activity based costing methods and also to analyze costs and benefits of time driven activity
based costing method’s implementation at X Hospital. This Hospital was chosen as a sample because it does
not have a good cost system yet so far. X Hospital uses tariff which is determined by the regional
government. This study was conducted using qualitative and study case approach. It focused on the unit cost
of hemodialysis services at X Hospital. The result of the study showed that unit cost calculation using time
driven activity based costing is higher than by using traditional costing. Both methods used a different
driver, in which traditional costing method used the number of patients driver and time driven activity based
costing method used time as driver. Time driven activity based costing system reflected more the activities
that are consumed by hemodialysis services, and more importantly, human resources of X Hospital are
ready to implement this method.
1 INTRODUCTION
A hospital’s revenue from a certain service is a total
of the unit cost of services and the expected surplus.
Unit cost of a hospital consists of direct cost and
indirect cost. A direct cost will be charged to each
service, meanwhile, the indirect cost will be
allocated later. There are some methods that can be
used to allocate the indirect cost such as traditional
method and activity-based costing method.
Traditional method and activity-based costing
method are differed in their allocation aspect of
indirect costs, in which activity-based costing uses
activities as the base of its allocation. According to
Popesko and Nová (2014) an organization that runs
their operational activities with high complexity and
high proportion of indirect costs such as hospital
will be suitable to use activity-based costing method.
This method will give a more detail costs
information regarding the hospital’s activities.
Having known of this, yet health organizations such
as a hospital rarely uses activity-based costing
method; hospitals in Indonesia are not exception.
Therefore, this study was motivated in analyzing the
implementation of activity-based costing method in
a hospital or a health unit in Indonesia. The chosen
sample for this study is X hospital which is located
in West Nusa Tenggara.
The activity-based costing method is also not yet
implemented at X hospital. This hospital had
experienced a deficit on their operational activities
in the last couple of years, even though the recorded
increase in their income is quite high. The number of
patients at X hospital in 2017 is 160.757 patients.
The highest number of patients that are received by
the hospital is outpatients with the number of
125.403 patients, while services with the lowest
number of visits received is intensive care unit with
the number of 1.281 patients. X hospital offers
various types of services in which every service uses
different resources, therefore, it is advised that X
hospital uses activity-based costing method that
emphasizes the allocation of indirect costs on
activities.
Additionally, X hospital does not have a clear
system of costs accountancy because they are using
a tariff format that is decided by the regional
Rizki, N. and Hartanti, D.
Analysis of Cost Calculation System at X Hospital based on Traditional Costing and Time Driven Activity based Costing: Study at Unit Cost Hemodialysis Services.
DOI: 10.5220/0009504010791084
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 1079-1084
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
1079

government. There are a lot of changes that have
been experienced by X Hospital from 2015 to 2017,
but unit cost and tariff calculation were last done in
2015. Based on the information gathered through
interview, it showed that X hospital did not
categorized the costs based on the general principles
stated on the cost accounting, such as direct
material, direct labor, and overhead. The fact that
they are still using the traditional method in deciding
the unit cost and in counting the proposed tariff to
regional government has led the researcher to doubt
the accuracy of the computation system that they
use. Therefore, the time driven activity-based
costing method is proposed as the method for
computation.
Time driven activity-based costing method is
simpler and easier to be applied compared to
activity-based costing method. This method is
considered easier and reasonably cheaper. Time
driven activity-based costing method uses time
driver to allocate resources to products. In addition,
this study will also analyze the proposal to
implement time driven activity-based costing
method to calculate unit cost of hemodialysis
services that is a part of one day care service of X
hospital. There is no recorded health service unit in
Indonesia that implements unit cost calculation
using time driven activity-based costing method.
Research that discusses the proposal to apply this
method is also scarce and limited. The formulated
questions for this study are as follow:
1. What is the existing system in determining tariff
of services at X hospital and how is calculation
of the total costs of hemodialysis services at X
hospital based on traditional costing?
2. How is calculation of the total costs of
hemodialysis services at X hospital based on
time driven activity-based costing?
3. How is the calculation comparison of the total
costs of hemodialysis services at X hospital
based on traditional costing and time driven
activity based costing?
4. How is the readiness of human resources as well
as advantages and costs if time driven activity-
based costing is implemented as method to
calculate the unit cost of services at X hospital?
2 THEORICAL FRAMEWORK
Traditional Cost Accounting
There are five unit-level drivers which are generally
used in traditional costing method i.e. unit produced,
direct labor hours, direct labor dollar, machine
hours, and direct material dollar. In this system,
there are two methods in deciding cost driver for
overhead cost, i.e. plantwide rates, which is deciding
overhead cost rate using one driver. Another one is
departmental rates, which is deciding overhead cost
rate based on each production department. However,
both methods do not function well and in truth they
can cause a serious distortion in product costs,
especially, for a company with significant overhead
costs and for a company with high variety of
products which consumes varied resources (Hansen
and Mowen, 2015).
Activity based Costing System
Activity based costing is a system of costs
determination by allocating indirect costs toward a
cost object based on activity driver, not the volume
driver. This is because it is believed that the cause
for the rise in costs is the activity, not the quantity of
the product. Baker (1998) stated that an activity can
have some cost drivers which relate to that activity.
In a world of health services, an activity almost
always possesses many cost drivers. The right
implementation of cost driver will have a positive
influence toward the success of an organization.
However, activity-based costing method is
considered quite difficult because it requires detailed
interview and survey. It also needs substantial costs
in its implementation (Kaplan and Anderson, 2007).
Time Driven Activity based Costing
Time driven activity-based costing method assumed
that time is the prime mover of costs since most of
resources such as personnels and equipments have
the capacities that can be easily measured with the
number of available times to do the job (Kaplan and
Anderson, 2007). Time driven activity-based costing
method is the most agreeable with companies
dealing in service industry. This is because service
industry focuses more on providing services which
will be more accurately calculated with the time
spent to do the service activity (Szychta, 2010).
Time driven activity-based costing method in its
calculation needs predictions from two components
i.e. unit costs for the available capacity and the time
that is needed to do the transaction or activity
(Kaplan dan Anderson, 2007).
Formula for calculating costs based on time
driven activity based costing method:
capacity cost rate
cost of capacity supplied
practical capacity of resources sepplied
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1080
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This study used qualitative and case study
approaches. The data collection techniques used in
this study were interview and field study. Primary
data that was used in this study was the finance
reports period 2016 and 2017, installation data
recapitulation of patients’ medical records period
2017, and data from the field study and interview
which were conducted since May 2018 until October
2018.
This study was a single case study that was
conducted on a single unit analysis; a hemodialysis
unit at X hospital. The period that was used to
calculate the unit cost at X hospital was one year; a
year of 2017.
Based on the results of the interview and the
primary data that had been gathered, researcher did
an analysis about the system of tariff determination
which was currently used by the hospital. After that,
the researcher designed a traditional costing system
to calculate the unit cost of hemodialysis services
and compared them with the existing costs
calculating system. Next is designing time driven
activity-based costing system to the same unit cost
service and compared the calculation results of
traditional costing method dan time driven activity
based costing method. The researcher did the
calculation of unit cost using time driven activity
based costing method by referring to Kaplan and
Anderson (2007).
4 ANALYSIS
4.1 The Current Tariff Determination System
at X Hospital in Relation to Their Unit
Cost Calculation of Hemodialysis Service
using Traditional Method
X hospital has established a specific tariff team to
formulate the unit cost calculation and the selling
price or the real tariff which are applied to general
patients. The real tariff has included the 20% surplus
and the real unit cost. There are some changes in the
X hospital from 2015 to 2017 which supposedly
influence the changes in the unit cost formulation
and the tariff of services. Some of them are the rise
in the number of patients’ visit, followed by the
trend of the rise in number of the average patients’
visits which is 3.5% per year, the development of
heart services and integrated blood vessels/cathlab
center which was inaugurated on November 9
th
2016, the enhancement of the supporting service
facilities, the number of new services at the
Radiology unit, the inauguration of independent
policlinic facility, education-training unit (skill lab),
research unit (Litbangkes Institution), and
accommodation (guest house).
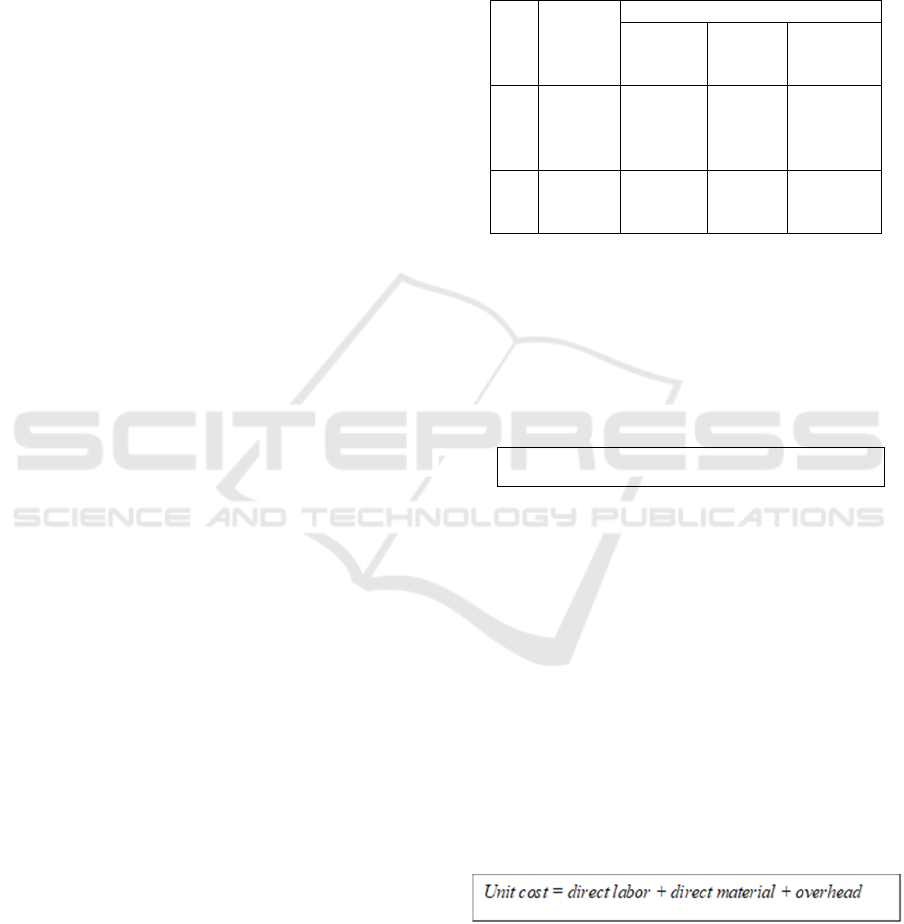
Table 1: Hemodialysis Services Tariff at X Hospital
2017
No. Types
of
Services
Class an
d
VIP (IDR)
Service
Facilitie
s
Service Tariff
1 HD
single-
use
Service
960,000 408,00
0
1,368,00
0
2 HD
Reuse
Service
840,000 240,000 1,080,000
Source: X Hospital (2017)
Referring to the result of the interview, service
facilities consist of direct material for one treatment
or one service, overhead cost, and mark-up.
Meanwhile, service consists of direct labor cost and
indirect labor cost.
Unit cost of hemodialysis services based on the
calculation of X Hospital is as follow:
Based on the above formula, then unit cost for
each hemodialysis service which was taken as
sample in this study was:
a. Unit cost of HD single-use service = IDR
1,140,000
b. Unit cost of HD re-use service = IDR 900,000
The following is the calculation of hemodialysis
services unit costs based on traditional costing
method which was designed by the researcher. The
calculation would be done based on one-year data to
eliminate the possibility of numbers’ fluctuation
each month. This calculation was based on the
analysis result of finance reports year of 2017,
interview, and observation that has been conducted.
Below is the explanation of each costs which
was used to calculate hemodialysis services unit cost
period of 2017:
1. Direct labor
The total direct labor cost of hemodialysis unit in
one year which is the year of 2017 was IDR
Unit cos
t
= Real tariff
–
mark up 20%
Analysis of Cost Calculation System at X Hospital based on Traditional Costing and Time Driven Activity based Costing: Study at Unit
Cost Hemodialysis Services
1081
661,412,000. If this figure were to be divided by the
number of hemodialysis services in one year which
is 12.123, then the direct labor costs for one-time
hemodialysis service, either for single use or re-use
is IDR 54,558.
2. Direct Material
Direct material consists of consumables material,
other equipment, medicines, safety equipment,
machinery equipment and HD set. The difference
between the single use and re use hemodialysis
services is only in the HD set that is used,
meanwhile, other components from the two types of
services consume the same resources.
a. The total number of consumables goods,
medicines, and hemodialysis unit equipment
for the year of 2017 is IDR 2,092,938,966. If
this number were to be divided with the
number of hemodialysis services in a year
which is 12.123, then the cost of consumables
goods for one-time hemodialysis service is
IDR 172, 642 for both single use or re-use
hemodialysis services.
b. HD Set package for each types of
hemodialysis services:
1) Single Use package is IDR 517,550. -
2) Reuse package is IDR 373,830.-
3. Overhead Cost
Overhead costs and indirect costs are the costs
that do not directly influence the service activities
and are consumed by variety of production
activities. The total overhead cost of X Hospital in
the year of 2017 is IDR 92,847,527,177.
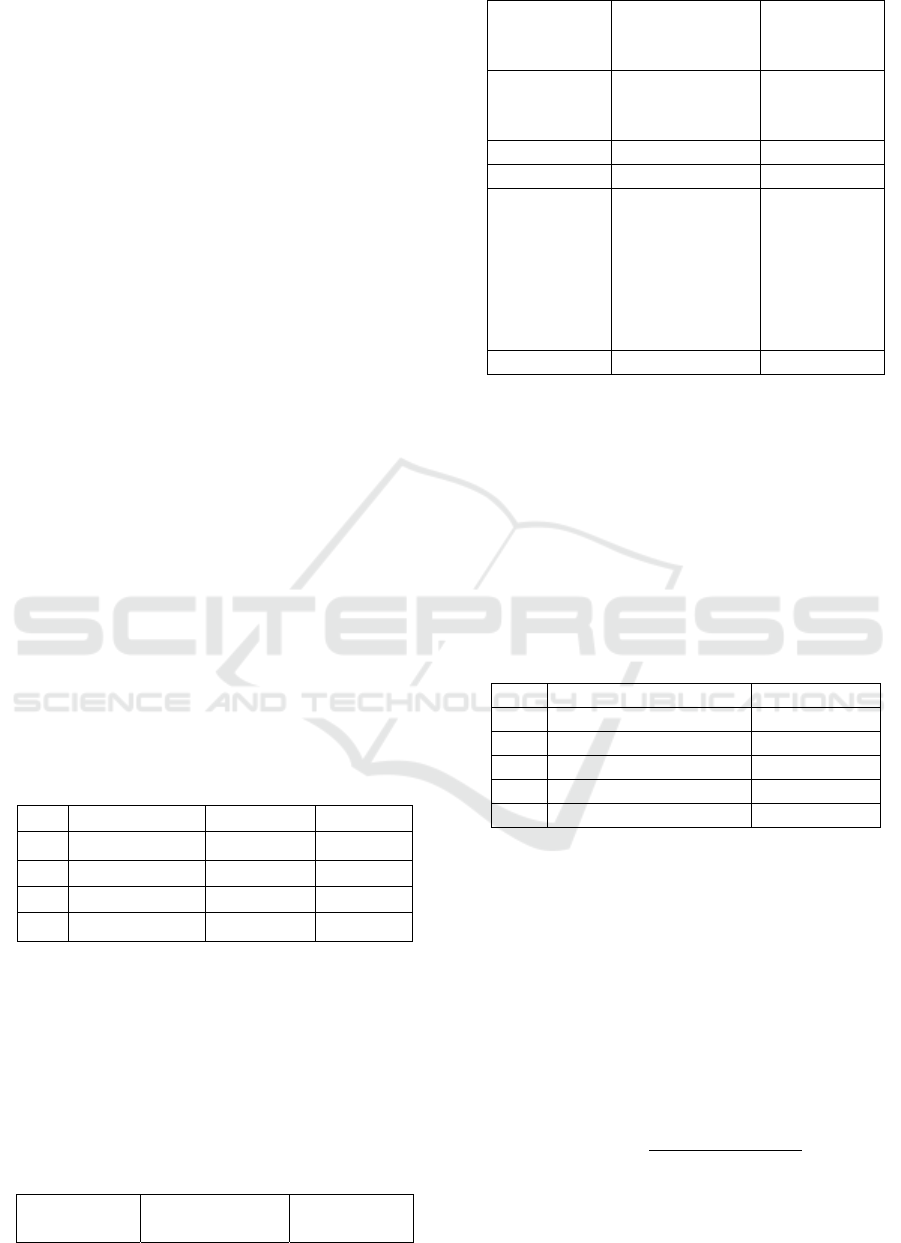
Table 2 : Unit Cost of Hemodialysis using
Traditional Costing
No Types of costs Single Use Re-Use
1. Direct Labor 54.558 54.558
2. Direct Material 690.192 546.472
3. Overhead 577.564 577.564
4. Total 1.322.314 1.178.594
Table 2 above showed the total unit cost for each
hemodialysis services using traditional costing
calculation method by applying components of the
hospital’s costs for the year of 2017. The difference
in both services is only found in the direct material
components, specifically for the HD set that is used.
Table 3 : Comparison of Hemodialysis services Unit
Cost (Traditional Costing) with the Hospitals’ Tariff
Calculation
Metho
d
Single Use
(IDR)
Re-use
(IDR)
Hospital
Unit cost
calculation
1.140.000 900.000
Unit cost
traditional
costin
g
1.322.314 1.178.594
Gap (182.314) (278.594)
Tarif RS 1.368.000 1.080.000
Traditional
costing
tariff (unit
cost
traditional
costing +
mark up)
1.586.776 1.414.313
Gap (218.000) (334.313)
Source: X Hospital (2017), has been reprocessed
4.2 Design of Hemodialysis Services Unit Cost
using Time Driven Activity based Costing
Method
Time driven activity based costing method would be
used as the method for the allocation of indirect
costs or overhead costs. The first phase is the
activities’ grouping in hemodialysis unit’s service,
and then counting the capacity cost rate.
Table 4 : Grouping Activities of Hemodialysis
Services
N
o Outlines of Activities Time
1 Administration 30 minutes
2Pre Dial
y
sis 55 minutes
3 HD Process 302 minutes
4 Post HD 30 minutes
Total 417 minutes
Source: Respondent Interview (2018), has been
reprocessed
Capacity cost rate or cost per unit of time can be
counted by dividing the costs of the available
capacities with practical capacities. The available
capacity cost is a total cost of overhead, meanwhile
the practical capacity in this study refers to indirect
labor hours in a year.
The practical capacity of one indirect staff in a
year is 108.060 minutes. The number of the indirect
staffs is 532 people, then the total practical capacity
is 54.487.920 minutes.
cost per unit time
Rp 92.847.527.177
54.487.920 minutes
cost per unit time Rp 1.704/minute
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1082
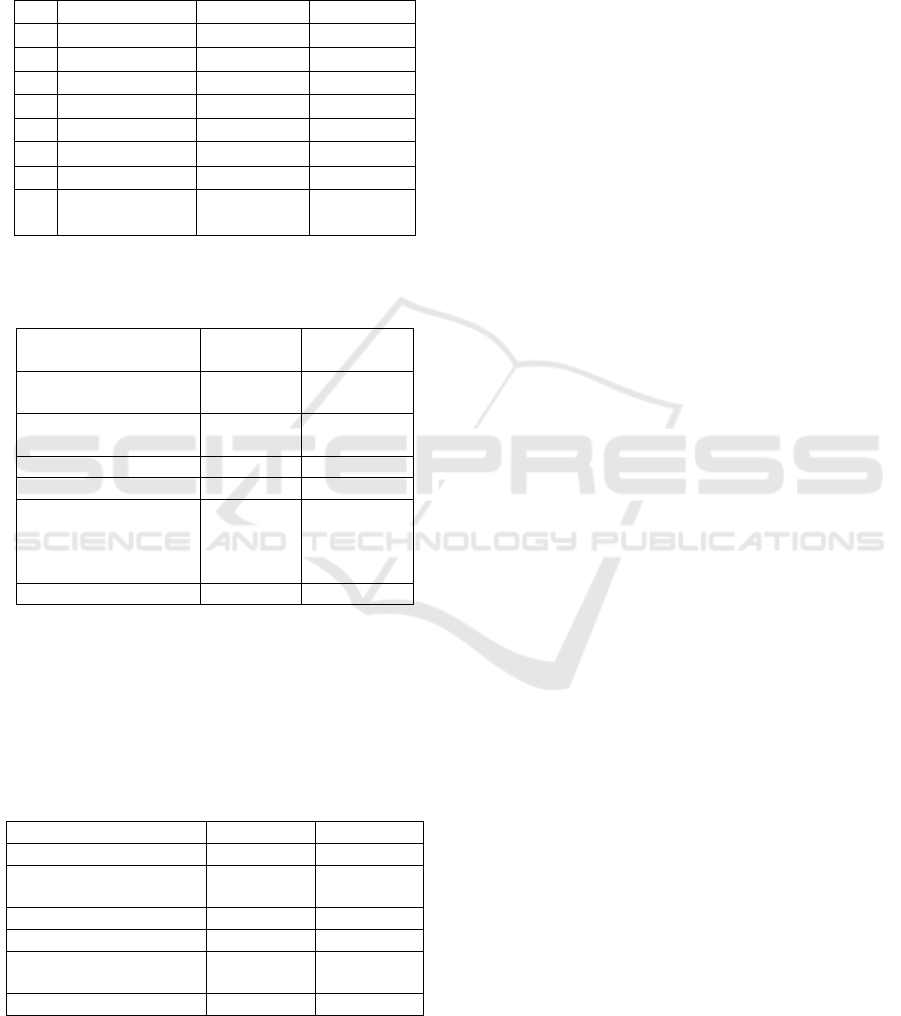
Based on the group of activities, the
hemodialysis service is divided into 4; they are
administrative group, pre-dialysis, HD process, and
post HD.
Table 6 : Unit Cost of Hemodialysis Services Based
on Time Driven Activity Based Costing
No Cost Single Use Re Use
1. Direct labor 54.558 54.558
2. Direct material 690.192 546.472
3. Administration 327.504,92 327.504,92
4. Pre HD 54.481,58 54.481,58
5. HD Process 298.905,58 298.905,58
6. Post HD 29.675,92 29.675,92
Total Unit Cost 1.455.318 1.311.598
Tariff (mark-up
20%)
1.746.381 1.573.917
Table 7 : Comparison of Hemodialysis Services Unit
Cost (Time Driven Activity Based Costing) with the
Hospital’s Tariff
Calculation Method Single Use
(IDR)
Re-use
(IDR)
Hospital calculation
of Unit cost
1.140.000 900.000
Unit cost time driven
activit
y
based costin
g
1.455.318 1.311.598
Ga
p
(
315.318
)
(
411.598
)
Hospital Tariff 1.368.000 1.080.000
Tariff of time driven
activity based coting
(unit cost traditional
costin
g
+ mark u
p)
1.746.381 1.573.917
Gap (378.381) (493.917)
Source: X Hospital (2017), has been reprocessed
4.3 Comparison of Unit Cost and Tariff based
on Traditional Costing dan Time Driven
Activity based Costing
Table 8 : Comparison of Unit Cost and Tariff Based
on Traditional Costing dan Time Driven Activity
Based Costing
Metho
d
Sin
g
le use Re-use
Traditional Costing 1.322.314 1.178.594
Time Driven Activity
Based Costin
g
1.455.318 1.311.598
Gap (133.004) (133.004)
Traditional Costing 1.586.774 1.414.313
Time Driven Activity
Based Costin
g
1.746.381 1.573.917
Gap (159.603) (159.604)
4.4 The Readiness of Human Resources,
Advantages, and Costs of Implementing
Time Driven Activity based Costing as a
Calculation Method of Service Unit Cost in
a Hospital
X hospital has possessed SPO for treatment at every
service that is provided in every unit, accompanied
with normal time or standard realization time of
every activity at that service. This indicates that X
hospital is ready to use time driven activity based
costing method when we looked at its human
resources aspect since they have gotten used to the
existing SPO. The SPO that they have had included
the understanding of action (treatment), objectives,
policies and procedures that are detailed in steps,
and the relevant units i.e. unit or installation as well
as labors who work in the activity.
The benefit of time driven activity based costing
method to X hospital is it gives information about
the costs of hemodialysis services more accurately
and gives information about the activities of every
service product. Meanwhile, in term of cost, if this
method is implemented, the tariff cannot be changed
directly. There are some things that need to be
considered such as getting approval from relevant
stakeholders, considering the purchasing capability
of the community around the area, and the
dependency toward the external stakeholders in
relation to the regional government regulations.
Even though it is quite complicated, at the end,
the calculation of unit cost for every service has to
be done in order to increase the finance management
of X hospital. Holding status as BLUD, X hospital is
expected to manage its own finance.
5 RESULTS
There was a difference calculation result of unit cost
between X hospital calculation and the traditional
costing calculation that was conducted in this study.
This difference might happen because X hospital did
not have cost system and did not do any cost
analysis. Also importantly, the unit cost calculation
formula that the hospital has been using was
obsolete and was not suitable anymore with the
current condition of the hospital.
In terms of comparison of unit cost and
hemodialysis services tariff using time driven
activity based costing method with unit cost, it
showed that there was undercosting case based on
the result of hospital’s calculation i.e. at the single
use and re use hemodialysis service. This needs to
Analysis of Cost Calculation System at X Hospital based on Traditional Costing and Time Driven Activity based Costing: Study at Unit
Cost Hemodialysis Services
1083

be X hospital’s concerns since the interview has
shown that the number of patients subjected to the
re-use hemodialysis was higher than single use
hemodialysis patients in 2017.
There was a significant difference in the result
of calculation using traditional costing and time
driven activity based costing for both types of
hemodialysis services. The result of unit cost
calculation using both methods had a significant
difference in which the result of the unit cost
calculation using traditional costing was IDR
133.004 lower than the result of unit cost calculation
using time driven activity based costing method. The
difference laid on the overhead cost calculation only,
meanwhile the charges calculation for direct
material and direct labor used the same calculation.
This difference was caused by the use of different
allocation methods for both methods i.e. traditional
costing used number of patient driver and time
driven activity based costing method allocated the
overhead cost based on the time for every group of
activities in hemodialysis services which consumed
the overhead cost component.
6 CONCLUSIONS
From the tariff calculation by adding mark-up 20%,
traditional costing and time driven activity based
costing methods had resulted in a higher tariff
compared to the current hospital’s tariff for both
types of hemodialysis services i.e. single use and re-
use. X hospital is highly advised to apply a better
unit cost calculation. The unit cost calculation will
be useful in making an informed decision regarding
the tariff that will be charged to the consumers. The
unit cost calculation is proven to be executed better
using time driven activity based costing method. It is
believed that by using the method, the resources’
allocation will be more accurate. Moreover, the
implementation of time driven activity based costing
is considered easier than activity based costing
method, which will also cost significant time and
money.
From the human resources point of view that are
available at X hospital, they can be considered ready
to implement the time driven activity based costing
method. This is supported by the existing SPO
system, in which every unit has informed counts of
the standard time to perform the given services.
Therefore, when the time driven activity based
costing method is introduced to them, it will not
change their regular activity drastically. The
implementation of time driven activity based costing
as a method for calculating the unit cost of services
also gives benefit to X hospital i.e. giving
information about hemodialysis services cost more
accurately and giving information about activities of
every service products. However, we need to keep in
mind that the changes in the tariff of services, when
time driven activity based costing method has been
implemented, cannot be done abruptly without
considering relevant factors and stakeholders.
REFERENCES
Baker, J. Judith. (1998). Activity Based Costing and
Activity Based Management for Health Care.
Gaithersburg, Maryland: Aspen Publisher, Inc.
Hansen, Don R., and Mowen, Maryanne M. (2015)
Cornerstones of Cost Management Third Edition.
South-Western: Cengange Learning.
Kaplan, Robert S and Anderson, S. R. (2007). Time
Driven Activity Based Costing. Boston,
Massachusetts: Harvard Business School Press.
Popesko, B., & Nová, P. (2014). Implementation of the
Process-Oriented Costing System in a Hospital
Department, 5(1).
https://doi.org/10.7763/IJTEF.2014.V5.345
Szychta, A. (2010). Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing
in Service Industries Time-Driven Activity-Based
Costing in Service Industries, (March).
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1084
