
Determinants of Customer's Decision in Selecting Banking Services in
the Province of Jambi
Ilham Wahyudi
1
and Eka Julianti Efris Saputri
1
1
Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Jambi, Jambi-Indonesia
Keywords: Islamic Bank, Conventional Bank, Profit Sharing, Interest, Reputation, Information Asymmetry
Abstract: This study was intended to examine the effect of profit sharing principle and interest, bank reputation, and
information asymmetry against customer decision in choosing banking services between islamic bank and
conventional bank in Jambi Province. In this study, data was obtained from primary data using a
questionnaire. The respondent obtained from customer of islamic bank and conventional bank in Jambi
Province. The sample selection used nonprobability sampling with acidental sampling technique and
analized by using discriminant analysis. The results showed that in choosing banking services, the customer
of islamic and conventional banks in Jambi Province did not take attention about the principle of profit
sharing and interest, bank reputation and information asymmetry.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the assessment of the Global Islamic Financial
Report (GIFR) in 2016 Indonesia got ranks sixth of
the country that has the potential and is conducive in
the development of the islamic finance industry after
Malaysia, Iran, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates,
and Kuwait, Indonesia is projected to rank first in
next few years. This optimism is in line with the
pace of institutional expansion and the accelerated
growth in the assets of islamic banks which are very
high, coupled with the volume of sukuk issuance
that continues to increase (IslamicFinancialPolicy,
2016).
Finance Minister Bambang Brodjonegoro in the
National Sharia Economy seminar at the Ministry of
Finance Complex, Jakarta, Tuesday, April 14, 2015,
stated that the reason Islamic banks have a stronger
endurance than conventional banks faced with the
global crisis is because islamic banks tend to play
safe which means every transaction in islamic
finance must be based on underlying asset. That is
different from conventional banks that tend to be
speculative. Many conventional banks play at the
level of high speculative. Whereas Islamic banks are
not in the area, they tend to be more conservative
and prioritize caution. However, it does not mean
riskless Islamic banking. If the management does
not go well, then there is a possibility that it can be
problematic (Anonim, 2015).
Islamic banks are banks that in their operations
do not use the interest system, but use the basic
principles in accordance with Islamic sharia. In
determining the rewards, both rewards given and
received, Islamic banks do not use interest systems
like conventional banks, but use the concept of
reward in accordance with the agreed contract which
is often called a profit sharing system (Ismail,
2014). Whereas according to (Undang-
UundangNo21, 2008), conventional banks are banks
that carry out their business activities conventionally
and based on their types consist of conventional
commercial banks and rural credit banks, while
conventional commercial banks are conventional
banks which provide services in payment traffic and
people's credit banks are conventional banks which
in their activities do not provide services in payment
traffic.
This research intended to examine the effect of
profit sharing and interest principle, bank reputation,
and information asymmetry against customer
decision in choosing banking services between
islamic bank and conventional bank in Jambi
Province.
Wahyudi, I. and Saputri, E.
Determinants of Customer’s Decision in Selecting Banking Services in the Province of Jambi.
DOI: 10.5220/0009501513491356
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 1349-1356
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
1349

2 THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
According to (Maisur, et al., 2015) the principle of
profit sharing is the profit obtained by sharia-
compliant banks that are shared with customers. The
level of division must be based on the percentage
ratio and not the specified amount.
Interest is additional money deposited in
financial institutions or money lent. The amount of
interest to be paid is set in advance regardless of
whether the financial institution of the deposit
recipient or the borrower is successful in his
business or not. The amount of interest that must be
paid is listed as a percentage number or per hundred
in a year which means that if money is not paid or
deposits are not taken in a few years the debt can
occur or the savings will multiply (Muhammad,
2011)
The issue of interest responsiveness to savings
and its effect on economic growth in developing
countries (LDCs) concluded that the high interest of
the people in saving was influenced by the high and
low interest rates. The higher interest rate results in
an increase in the amount of savings. If the interest
rate is high, then the community will reduce current
consumption to increase savings (Arrieta, 1988).
Financing projects are at the core of people's
lives and development bases. Funding patterns,
instruments and frameworks facilitate financing and
lead to development. Several types of financing
instruments are common in developed countries that
lubricate the wheels of development. Islam forbids
flowers and justifies profit sharing. Both provide
benefits but have fundamental differences as a result
of investment and money saving (Maisur, et al.,
2015).
In conducting transactions in Islamic banks,
customers only consider the profit sharing factor.
When it is found that the profit sharing rate of
Islamic banks is higher than the interest rate of
conventional banks, such as when the research is
conducted, they will join Islamic banks. The rest, if
the situation is reversed, it is feared they will choose
to join a conventional bank. From here a simple
prediction can be made if the interest rate is high
while the profit sharing rate is unable to keep pace
with the rate of interest, it is not impossible if the
customer will transfer funds to a conventional bank
which offers higher economic benefits (Misanam &
Liana, 2007).
The policy carried out by the company to achieve
reputation is by holding a personal selling, because it
is considered that this program can be closer to
themselves between companies and consumers
(Azis, 2001). Several things related to this are that
personal selling must take place through face to face
with customers and must be aggressive in order to
provide communication between customers and
companies that will provide a form of service (Azis,
2001).
The company's reputation is built on a network
of stakeholder partnerships through which
companies continue to improve organizational
learning and develop new business solutions. In
particular, the activation of decision processes that
involve stakeholders, partnership building, and
supportive behavioral stimulation, allows companies
to recover from severe losses of investor confidence
(Romenti, 2010).
Even though the company's reputation is
everywhere, it is still relatively replaceable. Some,
surely because reputation is rarely noticed until they
are threatened. Economists see reputation as a
transitory signal. Game theory describes reputation
as a character that distinguishes between types of
companies and can explain their strategic behavior.
Signaling Theory calls our attention to the
information content of reputation. Both recognize
that reputation is actually the perception of the
company that is owned by external observers. For
Game Theory experts, reputation is functional: they
generate perceptions among employees, customers,
investors, competitors, and the general public about
what a company is, what it does, what it means. This
perception stabilizes the interaction between the
company and its people (Fombrun & Riel, 1997).
Past behavior, attitudes and product attributes
together have a significant effect on interest in
saving (Sagan, et al., 2012). Examined the effect of
service facilities, products and promotions on
customer decisions in saving where the factors of
service facilities, products and promotions have an
influence on customer decisions in saving (Yupitri
& Sari, 2012).
Disclosure of information to bank stakeholders,
should not be limited to financial information alone,
but also non-financial information that allows
customers to know the level of suitability of bank
operations with the principles that exist in the bank.
This is because with the existence of complete
reporting of information it will support the
relationship of corporate governance that is
beneficial for both parties (Yulianto, 2010).
The desire of customers to obtain financial
information as complete as possible is difficult to
fulfill by management because it is influenced by
several factors such as the cost of presenting
information, management's desire to avoid risks to
see its weaknesses, and time used to present
information (Yaya & Ahim Abdurahim, 2003).
Besides this according to (Yaya, et al., 2007)
management needs to consider cost and benefits in
presenting disclosure in financial reports or annual
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1350

reports. management and cost can also be used by
management in providing financial information, so
that management will be more selective in delivering
financial information.
Customers need non-financial information
regarding the application of the principles and
quality of services provided by the bank. Non-
financial information will be used to assess the
quality of the application of the principles and
quality of actual bank services because this is the
main reason customers save in the bank (Yaya, et
al., 2007).
3 RESEARCH METHOD
The population in this study were customers of
conventional banks and Islamic banks in Jambi
Province. The method of data collection in this study
is to distribute questionnaires and conduct
interviews with respondents. The selection of
samples to be tested in this study using
nonprobability sampling technique. Nonprobability
sampling techniques include, systematic sampling,
quota sampling, incidental sampling, purposive
sampling, saturated sampling, and snowball
sampling. Of the six Nonprobability Sampling
techniques, this study uses accidental sampling
techniques (Sugiyono, 2012), which is the sample in
this study are customers of islamic banks in Jambi
Province and customers of conventional banks in
Jambi Province.
Exogenous variables in this study are the
principle of profit sharing and bank interest, bank
reputation, and bank information asymmetry. The
endogenous variable in this study is the customer's
decision.
The analysis used in this study is discriminant
analysis. Before discriminant analysis, the data must
first be tested whether the data is normal and the
absence of multicollinearity between independent
variables and each independent variable follows the
normal distribution function and homogeneity of
variance between groups of data (Yamin & Heri,
2014). This research was tested in the following
discriminant model:
Z = + w
1
X
1
+ w
2
X
2
+ w
3
X
3
Where:
Z = Value of the discriminant function
= Constanta value
w1 = The coefficient of the principle of profit
sharing and interest
X
1
= The principle of profit sharing and
interest
w2 = Bank Reputation Coefficient
X
2
= Bank's reputation
w3 = Information Asymmetry Coefficient
X
3
= Information Asymmetry
So the discriminant function can be written as:
Z = w1 The Principle Of Profit Sharing And
Interest + w2 Bank’s Reputation + w3
Information Asymmetry
The steps taken in discriminant analysis are
identifying discriminant variables, discriminant
functions, and classifications.
4 ANALYSIS
Before discriminant analysis, make sure the data is
normally distributed, and the absence of
multicollinearity between independent variables and
each independent variable follows the normal
distribution function and homogeneity of the
variance between groups of data (Yamin & Heri,
2014).
4.1 Multicollinearity Test Results
Seeing the results of the calculation of tolerance
values in table 1, there is no independent variable
that has a tolerance value of less than 0.10 which
means there is no correlation between independent
variables whose value is more than 95%. The results
of the calculation of the Variance Inflation Factor
(VIF) also show the same thing, namely there is not
one independent variable that has a VIF value of
more than 10. So it can be concluded that there is no
multicollinearity between independent variables.
Tabel 1: Multikolinierity Test Result
Model
Collinearity
Statistics
Toleranc
e VIF
(Constant)
Prinsip Bagi Hasil da
n
Bun
g
a
,301 3,324
Reputasi Ban
k
,428 2,334
Asimetri Informasi ,224 4,465
Determinants of Customer’s Decision in Selecting Banking Services in the Province of Jambi
1351
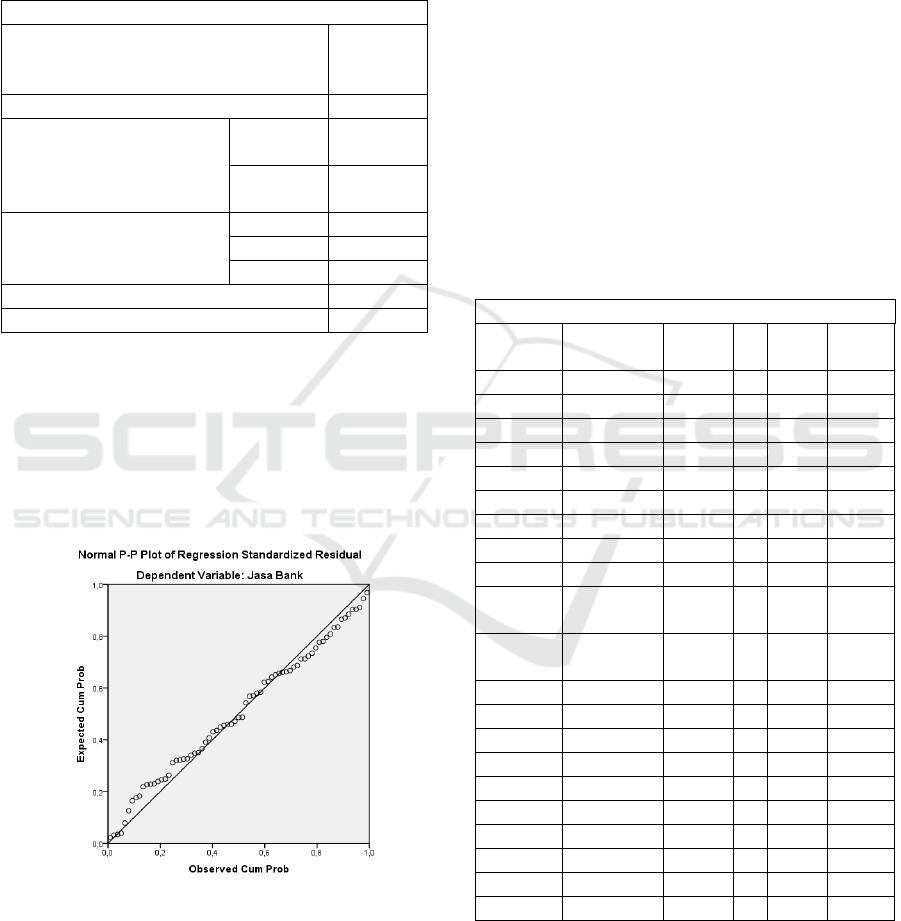
4.2 Normality Test Result
The data normality test was carried out by
Kolmogorov-Smirnov nonparametric statistical test
and normal distributed data can also be seen on
Normal P Plot Regression Standardized Residual
Graph.
Table 2 : Kolmogrov-Smirnov test Result
One-Sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test
Unstan
dardized
Residual
N
71
Normal Parameters
a,b
Mean ,000000
0
Std.
Deviation
,332989
86
Most Extreme Differences Absolute ,053
Positive ,039
N
e
g
ative -,053
Test Statistic ,053
As
y
mp. Si
g
. (2-tailed) ,200
c,d
From the results of the Kolmogrov-Smirnov Test
in table 2, the results of the Kolmogrov-Smirnov
value are 0.053 with Asymp. Sig. (2-tailed) 0.200.
This result shows normality data because of the
asymp value. Sig. (2-tailed)> 0.05, which means that
a disturbing or residual variable has a normal
distribution.
Figure 1: Normal P-P Plot of Regression Standardize
Residual
By looking at normal P-Plot of regression
standadized residual graphs in picture 1, the points
spread around the diagonal line, and the spread does
not move away from the diagonal line which means
the normal P-chart The standadized residual plot
shows a normally distributed model.
4.3 Identifying Discriminant Variables
Identifying discriminant variables can be seen F test
statistics, for F test can be used p-value in the
significant column where:
1. Sig. > 0,05, means there are no differences
between groups.
2. Sig. < 0,05, means there are differences between
groups.
From the explanation of table 3, it can be seen
that only four variables are (X2.6), (X2.7), (X2.8),
and (X2.9) which can be used to identify differences
between categories. So the variables that are feasible
and can be used for discriminant analysis are
variables (X2.6), (X2.7), (X2.8), and (X2.9).
Table 3: Discriminant Variable Identification
Results
Tests of Equality of Group Means
Wilks'
Lambda F
d
f1 df2 Sig.
X1.1 ,995 ,334 1 69 ,565
X1.2 ,993 ,513 1 69 ,476
X1.3 ,995 ,326 1 69 ,570
X1.4 ,994 ,388 1 69 ,535
X2.1 ,959 2,986 1 69 ,088
X2.2 ,984 1,092 1 69 ,300
X2.3 ,992 ,533 1 69 ,468
X2.4 ,999 ,103 1 69 ,749
X2.5 ,986 ,992 1 69 ,323
X2.6
,862
11,04
8
1 69 ,001
X2.7
,724
26,26
6
1 69 ,000
X2.8 ,943 4,174 1 69 ,045
X2.9 ,881 9,308 1 69 ,003
X3.1 ,990 ,689 1 69 ,409
X3.2 ,970 2,119 1 69 ,150
X3.3 1,000 ,000 1 69 ,989
X3.4 1,000 ,017 1 69 ,896
X3.5 ,997 ,230 1 69 ,633
X3.6 ,995 ,323 1 69 ,571
X3.7 ,986 ,972 1 69 ,328
X3.8 1,000 ,011 1 69 ,917
4.4 Discriminant Function
The discriminant function equation can be seen in
the canonical discriminant function coefficients table
in table 4. Then the discriminant function equation
in this study is:
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1352
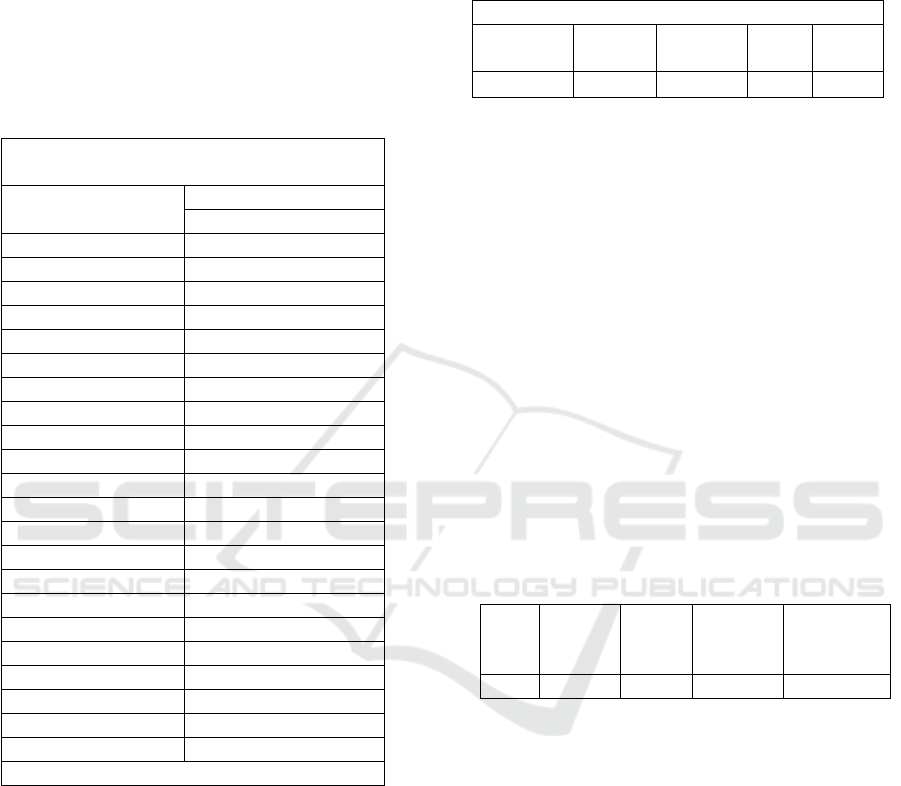
Z = 0,447 + 0,153*X1.1 + -0,467*X1.2 + -
0,048*X1.3 + 0,192*X1.4 + 0,704*X2.1 +
0,009*X2.2 + -0,032*X2.3 + -0,517*X2.4 +
-0,063*X2.5 + 0,007*X2.6 + 0,454*X2.7 + -
0,472*X2.8 + 0,776*X2.9 + -0,009*X3.1 + -
0,051*X3.2 + -0,125*X3.3 + 0,203*X3.4 + -
0,463*X3.5 + -0,069*X3.6 + 0,171*X3.7 + -
0,331*X3.8
Table 4 : Discriminant Function Result
Canonical Discriminant Function
Coefficients
Function
1
X1.1 ,153
X1.2 -,467
X1.3 -,048
X1.4 ,192
X2.1 ,704
X2.2 ,009
X2.3 -,032
X2.4 -,517
X2.5 -,063
X2.6 ,007
X2.7 ,454
X2.8 -,472
X2.9 ,776
X3.1 -,009
X3.2 -,051
X3.3 -,125
X3.4 ,203
X3.5 -,463
X3.6 -,069
X3.7 ,171
X3.8 -,331
(Constant) ,447
Unstandardized coefficients
From the equation, it can be seen that the most
dominant variable X2.9 is to predict differences in
groups of types of sharia bank customers and
conventional bank customers, because it has the
highest coefficient value of 0,776 while variable
X2.4 is a weak factor to predict customer decisions
in choosing banking services between Islamic banks
and conventional banks, this difference is seen from
the coefficient value of – 0,517.
To test the statistical significance of the
discriminant function, multivariate test of
significance is used, so to test the differences
between the two groups of banks, namely Islamic
banks and conventional banks for all variables,
multivariate tests are used together. The wilk’s
lamda test can be approximated by the chi-square
statistic (Ghazali, 2011).
Table 5 : Wilks Lamda Test Result
Wilks' Lambda
Test of
Function(s)
Wilks'
Lambda
Chi-
square df Sig.
1
,437 48,378 21 ,001
Based on table 5, the value of wilks lamda is
0.437 with a significant value of 0.001 <0.05, then
there is a significant difference between sharia bank
customer decisions and conventional bank customer
decisions which means accepting the hypothesis H0
is 48,378 compared to the value The chi-square table
that can be seen with the chi-square table (n-1 with
significance 0.05) is equal to 90.53> from the
calculated chi-square value of 48.378 with a
significant number of 0.001 so that there is a
significant (real) difference between decisions of
sharia bank customers and conventional bank
customer decisions which means accepting the
hypothesis H
0.
To test how big and meaningful the differences
between the two groups of companies can be seen
from the square canonical correlation (CR2) value
shown in table 6.
Table 6 : Eigenvalues Test Result
Eigenvalues
Func-
tion
Eigen-
value
% of
Varian-
ce
Cumula-
tive %
Canonical
Correlation
1
1,286
a
100,0 100,0 ,750
The result of table 6 shows the canonical
correlation number is 0.750 which if squared (0.750)
2 is 0.563. This means that 56.3% of the variance of
the customer's decision variables in selecting
banking services can be explained by the principle
of profit sharing and banks, bank reputation, and
bank information asymmetry.
4.5 Classification
One of the discriminant functions is to classify
future observations into one of two groups of
companies. In this study the two groups of
companies in question are the decisions of customers
in choosing banking services between conventional
Islamic banks and banks which can be seen in table
7.
Determinants of Customer’s Decision in Selecting Banking Services in the Province of Jambi
1353

Table 9 : Classification Results
Classification Results
a
Jasa
Bank
Predicted
Group
Membership
To
tal
1 2
Origin
al
Count Bank
S
y
ariaah
30 5 35
Bank
Konvensio
nal
5 31 36
% 1 85,7 14,3 100,0
2 13,9 86,1 100,0
a. 85,9% of original grouped cases correctly
classified.
Table 7 shows that there were 10 respondents
who were misclassified, namely 5 respondents who
initially decided to choose the services of a
conventional bank were then predicted to choose
Islamic banking services, and 5 respondents who
actually chose Islamic banking services were
predicted to choose the services of conventional
banks. Overall, the discriminant model formed has a
fairly high validation level is 85.9%. The survey
results above show the results of the accuracy of the
discriminant model which is quite high.
5 RESULTS
5.1 Effect of Profit Sharing Principles and
Interest on Customer Decisions
The result of the study shows that the principle of
profit sharing and interest does not affect the
customer's decision in choosing banking services
between islamic banks and conventional banks. The
tendency of customers to choose banking services
viewed in terms of profit causes customers to prefer
saving to conventional banks compared to Islamic
banks because the interest gains obtained at
conventional banks are higher even though basically
the customer knows that the principle of interest is
usury for non-Muslim customers, while profits on
Islamic banks are volatile. This was made clear by
(Arrieta, 1988) who concluded that the high interest
of people in saving was influenced by the high and
low interest rates.
The tendency of customers to choose banking
services in terms of benefits supported by (Misanam
& Liana, 2007) states that in conducting transactions
in Islamic banks, customers only consider profit
sharing factors. When it is found that the shari'ah
bank profit sharing rate is higher than the
conventional bank interest rate, then they will join a
sharia bank.
The results of the study show the customer's
perceptions of the principle and profit sharing
system and interest that the customer does not
understand well the concept of profit sharing and
interest, both in the product and the operational
mechanism, especially for the principle of Islamic
banks. In this case the socialization of the
community for Islamic bank principles in particular
and conventional banks is very necessary because
there are still many people who do not yet know the
principles of interest and profit sharing so that
customers consider basically the same.
The results of interviews with one of the
customers when interviewed claimed that if making
a loan with an Islamic bank would be more
disadvantage compared to a conventional bank, this
is because the installments paid every month on
Islamic banks are larger than conventional banks.
Conversely, there are also customers who argue that
making loans to Islamic banks can actually pay
lower interest compared to conventional banks.
Differences of opinion expressed by customers can
be caused by policies in determining profit sharing
and interest in different banks and in principle the
profit sharing system in Islamic banks and interest in
conventional banks is different.
After the research was found other factors that
influence customers in making decisions to choose
banking services, namely factors that are influenced
by aqeedah and according to Islamic law, customer
thinking about usury which is forbidden in the
Qur'an and Hadith makes customers more Islamic
banks than banks conventional. In this regard also
the factor of the length of time the customer relates
to the bank contributes to the loyalty of the tendency
of customers to choose bank services that are used
today even though the customer understands that
bank interest is contrary to Islamic sharia. Like
customers in conventional banks who are reluctant
to move to Islamic banks because they have long
been customers of conventional banks, this can be
seen from the sample that the length of time being a
customer in a conventional bank is dominated by 5-
10 years and more than 20 years for 58%. the length
of being a bank customer in sharia is dominated for
0-5 years and 5-10 years by 89%.
5.2 Reputation Effect of Banks on Customer
Decisions
The result of the study shows that the bank's
reputation does not have a significant influence on
the customer's decision in choosing banking services
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1354

for both islamic banks and conventional banks.
However, four indicators of the bank's reputation
variables are (1) the availability of strategic
locations for branch offices that are easily reached,
not far from home, and have access to public
transportation facilities to the bank office, (2) easy
location for ATM availability, (3) excellence bank
products, and (4) bank achievements that have
already been achieved and perceptions of both the
people who have used products at the bank have an
influence on the customer's decisions in choosing
banking services.
The results showed that the level of employee
honesty, speed and responsiveness of employees in
dealing with complaints of problems needs to be
improved, so that customers will be more trusting
and more loyal to use banking services. In addition,
the level of comfort of the atmosphere of the room at
the bank office given to the bank at this time (such
as the waiting room, transaction space) must be
further increased so that customers feel comfortable
despite waiting with a long queue number.
Safe bank area conditions such as the location of
the bank, parking lot, CCTV monitoring, etc. need to
be considered so that customers can feel safe to
transact with the bank, no need to worry about
unwanted things. The large availability of strategic
location of branch offices and the ease of finding
locations for the availability of ATMs can attract
customers to use bank services where customers
more easily reach bank offices and find ATMs if
they want to make transactions.
After conducting a survey and conducting
interviews with several customers, one of the
reasons customers choose bank services currently
used is due to the needs and information obtained.
The customer claims to use the bank that he is
currently using because of the need factor in which
the employee's salary is now transferred and taken
through the bank in collaboration with the office
both government and private offices. Likewise,
students who will get a scholarship where the
scholarship money will be transferred through a
bank account according to the requirements when
applying for a scholarship that inevitably requires
students to open a new account according to a
predetermined bank. In addition there are banks that
offer Hajj savings and some customers use Islamic
banks for the benefit of Hajj, this is also because
generally Hajj travel services work together with
Islamic banks.
The number of easy to find branch offices also
affects customers in choosing banking services. In
the regency area, the number of sharia bank branch
offices can be calculated compared to the number of
conventional bank offices. Recognition of customers
from one of the districts that were respondents
claimed why they prefer the services of conventional
banks, because conventional bank offices have long
been established compared to Islamic banks that
have only been established for the past 3 months.
With a bank office that has only one office location
far from the customer's home, customers are also
increasingly lazy to use Islamic banking services.
Conventional bank customers also say why to
choose the services of conventional banks. This is
because they have long been customers of
conventional banks for 5-10 years or even more than
20 years, at that time not getting information for
Islamic banks. The lack of socialization of Islamic
banks compared to conventional banks that often
socialize offering products through offices in Jambi
Province and Universities in Jambi City makes
customers prefer conventional banking services.
5.3 Effect of Information Asymmetry on
Customer Decisions
The result of the study shows that information
asymmetry does not have a significant effect on the
customer's decision in choosing banking services for
both Islamic banks and conventional banks.
The results showed that there were still many
banks that did not provide complete financial
information to customers, such as information on the
calculation of the distribution of interest and interest
for the customer and the bank, and information on
how to calculate Loan to Deposits Ratio (LDR), Non
Performing Loans (NPL), and the Bank's Capital
Adequacy Ratio (CAR) to customers. Even though
the customer already knows the benefits for the
customer, the calculation of the determination of
profit sharing and interest for the bank and the
customer remains important, because the customer
needs information to know the calculation of the
profit sharing and interest system, because the
customer is the biggest uncertainty.
The survey results of one of the bank's former
employees said why the banks did not provide
information on the calculation of LDR, NPL, and
CAR. They themselves as bank employees did not
know the calculation even the value of LDR, NPL,
and CAR, with reasons that knew financial matters.
is part of their accounting and supervisor. Although
there are several bank customers both in Islamic
banks and conventional banks do not understand the
Loan to Deposits Ratio (LDR), Non Performing
Loans (NPL), and Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR),
but this information is still important because many
Determinants of Customer’s Decision in Selecting Banking Services in the Province of Jambi
1355

customers want financial information as complete as
possible to find out how the real condition of the
bank, and should be a bank employee must also
understand this not only accounting and supervisors.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The principle of profit sharing and interest does not
have an influence on the decisions of customers in
choosing banking services, which means the
principle of interest and profit sharing does not
cause customers to choose banking services for both
conventional and Islamic banks.
Reputation has no effect on customers decisions
in choosing banking services, which means that
employee performance, facilities, environment and
products do not cause customers to choose banking
services.
Information Asymmetry has no influence on
customer decisions in choosing banking services,
which means that moral hazard and adverse
selection do not cause customers to choose banking
services.
REFERENCES
Anonim. (2015). Detik Finance. Retrieved April Tuesday,
2017, from https://finance.detik.com/moneter/
2886801/menkeu-bambang-bank-syariah-lebih-tahan-
menghadapi-krisis
Arrieta. (1988). Interest Rates, Savings, and Growth in
LDCs: An Assessment of Recent Empirical Research.
World Development, 16, 589-605.
Azis, S. (2001). Analisis Faktor-Faktor yang
Mempengaruhi Reputasi (Studi Pada Bank Mandiri
Purwokerto). Semarang: Universitas Diponegoro.
Fombrun, C., & Riel, C. V. (1997). The Reputation
Landscape. Corporate Reputation Review, 1, 5-13.
Ghazali, I. (2011). Aplikasi Analisis Multivariate dengan
Program IBM SPSS 19 (5 ed.). Semarang: BP
Universitas DIPONEGORO.
Islamic FinancialPolicy. (2016). Islamic Financial
Country Index. London: Global Islamic Financial
Repot.
Ismail. (2014). Perbankan Syariah. Jakarta: Kencana
Prenada Media Group.
Maisur, M.Arfan, & M.Shabri. (2015). Pengaruh Prinsip
Bagi Hasil, Tingkat Pendapatan, Religiusitas dan
Kualitas Pelayanan terhadap Keputusan Menabung
Nasabah Pada Bank Syariah di Banda Aceh. Jurnal
Magister Akuntansi Pascasarjana Universitas Syiah
Kuala, 4, 1-8.
Misanam, M., & Liana, L. (2007). Bunga Bank, Bagi
Hasil dan Relijiusitas: Suatu Investigasi Loyalitas
Nasabah Terhadap Perbankan Syari'ah. SINERGI, 9,
69-86.
Muhammad. (2011). Manajemen Bank Syariah.
Yogyakarta: UPP STIM YKPN.
Romenti, S. (2010). Reputation and Stakeholder
Engagement: an Italian Case Study. Emerald Insight,
14, 306-318.
Sagan, A. D., Tabrani, M., & Darsono, N. (2012). Analisis
Perilaku Nasabah PT.Bank Aceh (Survei Pada Kantor
Pusat Operasional Banda Aceh). Jurnal Ilmu
Manajemen Pascasarjana Universias Syiah Kuala, 1,
19-36.
Sugiyono. (2012). Metode Penelitian Bisnis. Bandung:
ALFABETA.
Undang-UundangNo21. (2008). Perbankan Syariah.
Jakarta: Republik Indonesia.
Yamin, & Heri. (2014). SPSS Complete: Teknik Analisis
Statistik Terlengkap dengan Sofware SPSS. Jakarta:
Salemba Infotek.
Yaya, R., Abdurahim, A., & Nugraha, D. A. (2007).
Kesenjangan Harapan Antara Nasabah dan
Manajemen terhadap Penyampaian Informasi
Keuangan dan Non Keuangan Bank Syariah. Jurnal
Akuntansi dan Investasi, 8, 1-16.
Yulianto, A. (2010). Analisis Asimetri Informasi
Keuangan dan Non Keuangan (Studi Bank Syariah di
Semarang). Jurnal Dinamika Akuntansi, 2, 110-117.
Yupitri, E., & Sari, R. L. (2012). Analisis Faktor-Faktor
yang Mempengaruhi Non Muslim Menjadi Nasabah
Bank Syariah Mandiri Medan. Jurnal Ekonomi dan
Keuangan, 1, 46-60.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1356
