
Improvement of Accounting Value Relevance Post Convergence IFRS
Elly Astuti
1
Universitas PGRI Madiun, Madiun -Indonesia
Keywords: Value Relevance, IFRS Convergence, Banking Company
Abstract: The purpose of this study is to evaluate the increasing relevance of accounting values after IFRS convergence
in Indonesia. The research focused on banking companies in two stages of full adaptation, namely in 2012 for
the first and 2015 stages for the second phase. The research method uses multiple linear regression and chow
test follow-up tests to evaluate structural changes in the relevance of accounting values during the adaptation
period. The results of the study using price models found that after IFRS convergence in Indonesia there was
an increase in the relevance of the value of accounting information in banking sector companies. But when
testing is done with the return model, IFRS convergence has no effect. This condition indicates that investors
in the banking sector companies pay more attention to the company's fundamental valuation for long-term
investments rather than short-term capital gains. Increasing the relevance of values after IFRS convergence
with price models, indicates that the market responds positively to IFRS adaptation policies in Indonesia so
as to strengthen the country's economic stability. Future research is expected to carry out testing using the
proxy of earnings management and timeliness to represent the relevance of accounting information values.
1 INTRODUCTION
IFRS is a set of global accounting standards that have
been required to be applied in the process of preparing
financial statements of business entities throughout
the world. IFRS convergence in various parts of the
world, has increased the value relevance of
accounting information (Agostino, Drago, & Silipo,
2011; Rodr, Aimer, Alejandro, & M, 2017; Trabelsi
& Trabelsi, 2014) However, increasing the relevance
of these values will differ between IFRS adaptation
processes carried out voluntarily with mandatory
IFRS adaptation (Kouki, 2018). A country's
economic growth rate also influences the increase in
the relevance of accounting values after IFRS
convergence. Less consistent results occur in
developing countries. IFRS convergence is able to
increase the relevance of accounting values in Latin
American countries (Rodr et al., 2017). But when
tested in Nigeria showed different results, IFRS
convergence did not have a significant impact on
increasing the relevance of accounting values
(Olowolaju, Ogunsan, & Plc, 2016).
Indonesia has carried out continuous
harmonization of standards to further improve the
quality of reporting produced. Full IFRS convergence
is a decision to further improve the quality of
information, where the information presented is
increasingly relevant and is used as the basis for the
company's economic decision making. However, the
convergence process is slightly different from other
countries. Indonesia adapted IFRS gradually and
carried out continuously. This might result in an
increase in the relevance of different accounting
values.
The banking industry is one of the most affected
sectors due to the full IFRS convergence process.
IFRS which provides a different perspective with its
fair valuation concept requires a lot of assessments
that involve complex aspects of the economy. One of
them is a financial instrument component that is very
sensitive to the entity's business environment. The
main components forming the sacrificial industrial
assets derived from financial instruments, may also
have a different effect on the value relevance of
accounting information after IFRS convergence in the
banking industry.
In stage 1 IFRS convergence in Indonesia it was
stated that IFRS did not have a significant impact on
value relevance due to institutional environmental
Astuti, E.
Improvement of Accounting Value Relevance Post Convergence IFRS.
DOI: 10.5220/0009500409951000
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 995-1000
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
995
conditions based on code law (Cahyonowati &
Ratmono, 2013). Juniarti et al., (2018) extended the
observation period with 4 years before and 4 years
after convergence, IFRS had an impact on increasing
the relevance of accounting values in Indonesia.
However, the study was limited only to
manufacturing companies. Different institutional
environmental conditions have an impact on the
relevance of values after different IFRS convergences
(Karampinis & Hevas, 2011). For this reason, the
research will focus on banking companies because
research on IFRS is usually only focused on
manufacturing companies.
2 THEORICAL FRAMEWORK
Value relevance is the ability of accounting
information in financial statements to influence the
economic decision making of investors. This is
reflected in stock price movements after the financial
statements are published (Barth et al., 1996). The
relevance of values can be fulfilled by the existence
of a good set of accounting standards, so that the
information delivered is more transparent and able to
reduce information asymmetry that can reduce
management opportunistic behavior.
IFRS is an accounting standard designed by the
IASB to be applied internationally to improve
transparency and comparability of company financial
statements. The main objective of establishing the
standard is to expand investment opportunities for
investors globally. Investors can obtain adequate
information so they can carry out investment
portfolios. On the other hand, this also benefits the
company in gaining access to funding its operational
activities.
Clarkson et al., (2011) suggested that after IFRS
convergence there was no change in the relevance of
values in European and Australian countries.
However, there are similar impacts between common
law and code law countries. This indicates that IFRS
can improve comparability. In line with this, Callao,
Jarne, & Laínez (2007) state that perhaps local
standard convergence to IFRS does not show an
increase in value relevance because the gap between
book value and market value is wider than the impact
of IFRS convergence. However, in the long run, the
benefits of IFRS will definitely be felt.
Daske, Leuz, & Verdi (2008) and Alali & Foote
(2012) document that the government environment
influences the relevance of accounting information.
When in a volatile period, the role of the government
must be greater by increasing compliance with
regulations to convince investors that the information
presented in the company's financial statements is
relevant. Thus, the institutional environment also
influences value relevance (Ball, Robin, & Shuang,
2003; Daske et al., 2008) which is one of the
qualitative characteristics of accounting information.
The Indonesian government's commitment to
converging local standards to IFRS has been seen
since 2008. IAI as an accounting standard-making
body in Indonesia has converged local standards to
IFRS gradually since 2008 with full adoption stage I
in 2012. In the banking sector, BI also issued PAPI
(Indonesian Banking Accounting Guidelines) in 2008
which was harmonized with the IFRS convergence
stage at that time. In 2015 there was a matching and
full adoption stage II. Adjustments in stage II were
carried out to reduce the gap between local
accounting standards and IFRS from 3 years to 1 year.
All companies listed on the IDX are required to use
accounting standards that have converged IFRS
H1: There is an increase in the relevance of
accounting values in banking companies after IFRS
convergence in Indonesia.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This research method uses a positive approach with a
quantitative form using multiple linear regression in
analyzing changes in the value relevance of
information. The research population is all banking
companies listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange
from 2007 to 2015. The sample collection technique
uses purposive sampling with criteria; 1) registered
on the IDX since 2007, 2) functional currency using
rupiah, 3) data related to research variables available.
Measurement of the relevance of accounting
values using price regression models (PRM) and
return regression models (RRM) (Onali, Ginesti, &
Vasilakis, 2017). Price model refers to the equation
proposed by Barth (2008) as follows:
(1)
While the return model refers to Barth and Clinch
(2009) as follows:
(2)
Where and
P is the stock price after the end of the company's
fiscal year (Barth, Landsman, and Lang, 2008;
Lang, Raedy, and Wilson, 2006). This study use the
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
996
stock prices 90
th
after the end of the fiscal year
because the relevance of information is a test of
whether the information submitted by the company
gives a difference in economic decision making
reflected in the stock price. In capital market
regulations and auditing standards that apply in
Indonesia, companies are allowed to submit
financial reports no later than 90 days after closing
the book (fiscal year). Prahesti, Utomo, & Astuti
(2016) documented that banking company audit
delay is between 7 - 90 days. Thus, the company's
financial statements are published a maximum of 90
days after the accounting period.
To test the effect of IFRS convergence on the
relevance of values, we examine whether structural
changes occur before after convergence. The test
uses the chow test. Besides that, there are also some
control variables that might influence company
adjustments with accounting standards that have
converged IFRS. Some of the control variables used
in this study are the size and level of corporate debt.
4 ANALYSIS
This research is a follow-up study from the previous
study to reexamine the impact of IFRS convergence
on value relevance (Astuti & Sulistyowati, 2017;
Cahyonowati & Ratmono, 2013; Juniarti et al., 2018).
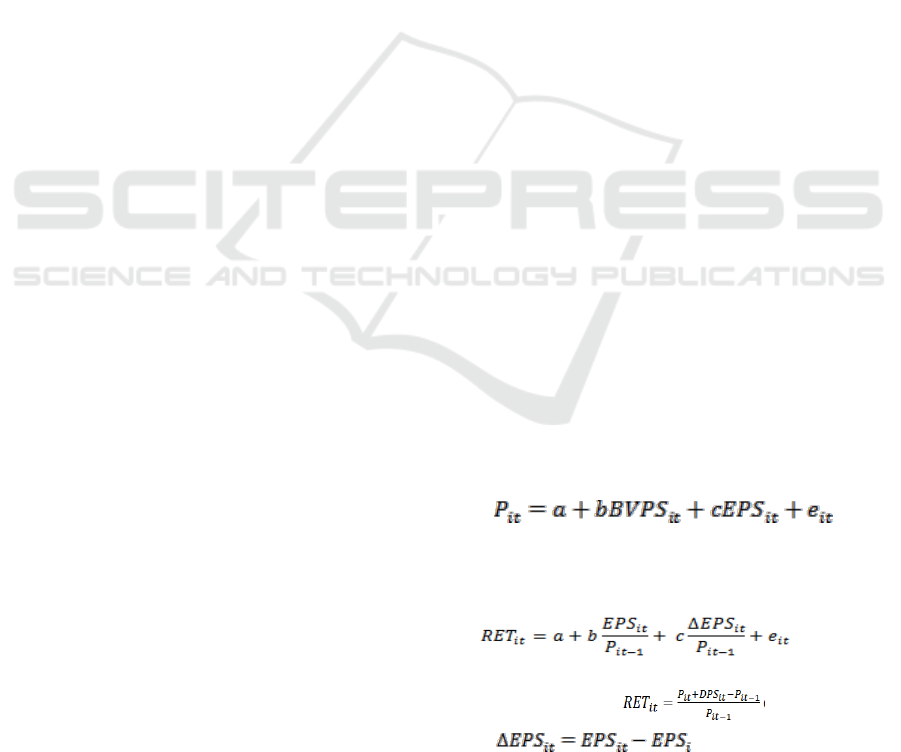
The test results in Table 1 show that there was an
increase in value relevance in the first phase of
convergence, namely in 2012, whereas in the second
period there was no increase. This can be seen from
the adjusted R square value from 2007 to 2012 which
has increased and from 2012 to 2015 has decreased.
Table 1: Results of Hypothesis testing (Price Model)
In the period before IFRS convergence investors
paid more attention to the fundamental value and
stock market value in a balanced manner. Investors
consider profitability (EPS), company market
performance (PER), company risk (LEV) and assets
that are capable to support the company's operations
(Ln_TA). However, in the period after stage I
convergence (2012-2013), the company considered
more fundamental values than market performance.
Investors do not consider stock prices in their
investment decisions (PER doesn’t effect stock
prices). This indicates that investors trust the intrinsic
value of the company rather than market performance
which is much influenced by the
external environment beyond the control of the
company.
In stage II the value of Adjusted R2 has
decreased. this indicates that there is no increase in
the relevance of values from stage I to stage II. In
stage II, investors also do not consider the company's
profitability (EPS) in making economic decisions. It
is possible to avoid mistakes, because of the existence
of earnings management practices that usually occur
in companies. overall it can be concluded that
investors use accounting information in financial
reports that reflect the intrinsic value of the company
for the decision making process.
Table 2: Results of Combined Regression (Price
Model)
Variabel
Pra IFRS + IFRS I
IFRS I + IFRS II
Coefficien
t
P Value
Coeffici
ent
P Value
Constant
-5,825
0,012
-2,991
0,261
BVEPS
0,000028
0,671
0,00042
1
0,001
EPS
0,003
0,000
0,001
0,173
PER
0,001
0,030
0,00027
4
0,825
LEV
-1,097
0,220
-1,328
0,127
Ln_TA
0,412
0,000
0,323
0,001
F value
26,046
0,000
31,857
0,000
Adjusted R
Square
0,601
0,650
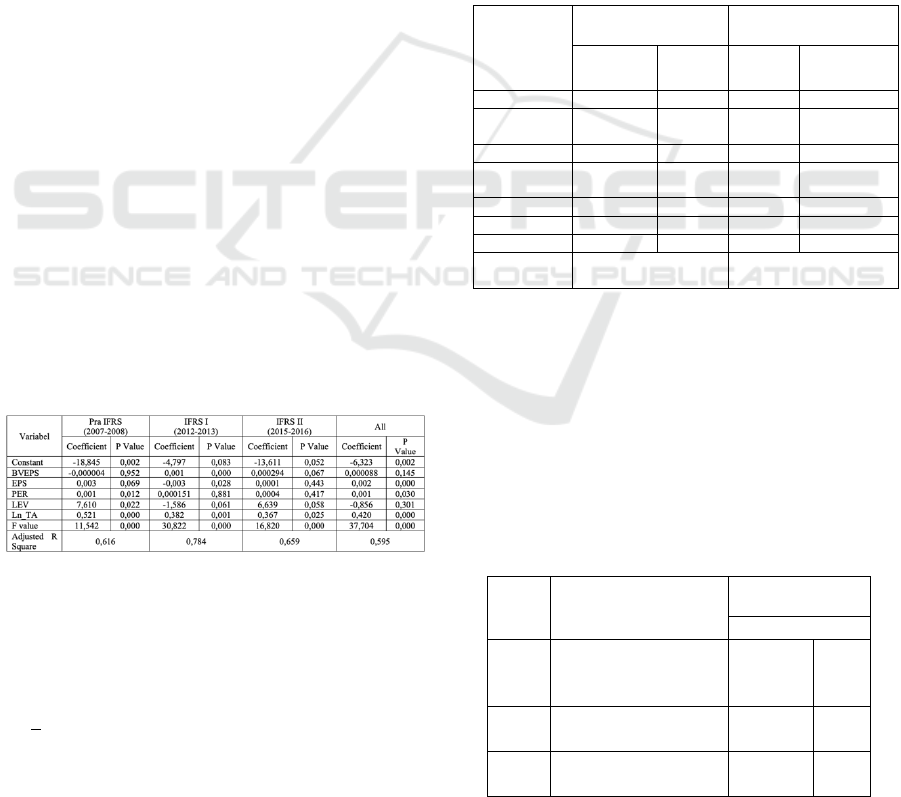
The follow-up test was carried out by combining
pre IFRS data with stage I. Combined data was
regressed and compared with the combined results of
data after stage I and II IFRS convergence. The
adjusted R2 value shows an increase (see table 2).
This shows that there is an increase in value relevance
in stage II even though it is not as big as stage I.
Further analyses using the chow test found that there
were structural changes in both stages I and II of IFRS
convergence (see Table 3 and Table 4).
Table 3: Results of Chow Test Stage I (Price Model)
Notati
on
Description
Pre IFRS + Post
IFRS I
Value
RSS
r
Sum of square residual
(2007-2008 s.d 2012-
2013)
71,567
RSS
1
Sum of square residual
(2007-2008)
32,233
RSS
2
Sum of square residual
(2012-2013)
19,250
Improvement of Accounting Value Relevance Post Convergence IFRS
997
Notati
on
Description
Pre IFRS + Post
IFRS I
Value
RSS
ur
RSS
1
+ RSS
2
51,4
83
k
Number of parameters
estimated
5
n
1
Number of observations
before IFRS
convergence
42
n
2
Number of observations
after IFRS convergence
(stage I)
42
F
value
((RSS
r
-
RSS
ur
/k)/(RSS
ur
)/(n
1
+n
2
-2k)
5,77
13
F
table
2,34
Table 4: Results of Chow Test Stage II (Price
Model)
Nota
tion
Description
Post IFRS I +
Post IFRS II
Value
RSS
r
Sum of square residual (2012-
2013 s.d 2015-2016)
68,532
RSS
1
Sum of square residual (2012-
2013)
19,250
RSS
2
Sum of square residual (2015-
2016)
31,993
RSS
u
r
RSS
1
+ RSS
2
51,2
43
k
Number of parameters
estimated
5
n
1
Number of observations after
IFRS convergence (stage I)
42
n
2
Number of observations after
IFRS convergence (stage II)
42
F
value
((RSS
r
-
RSS
ur
/k)/(RSS
ur
)/(n
1
+n
2
-2k)
4,99
32
F
table
2,34
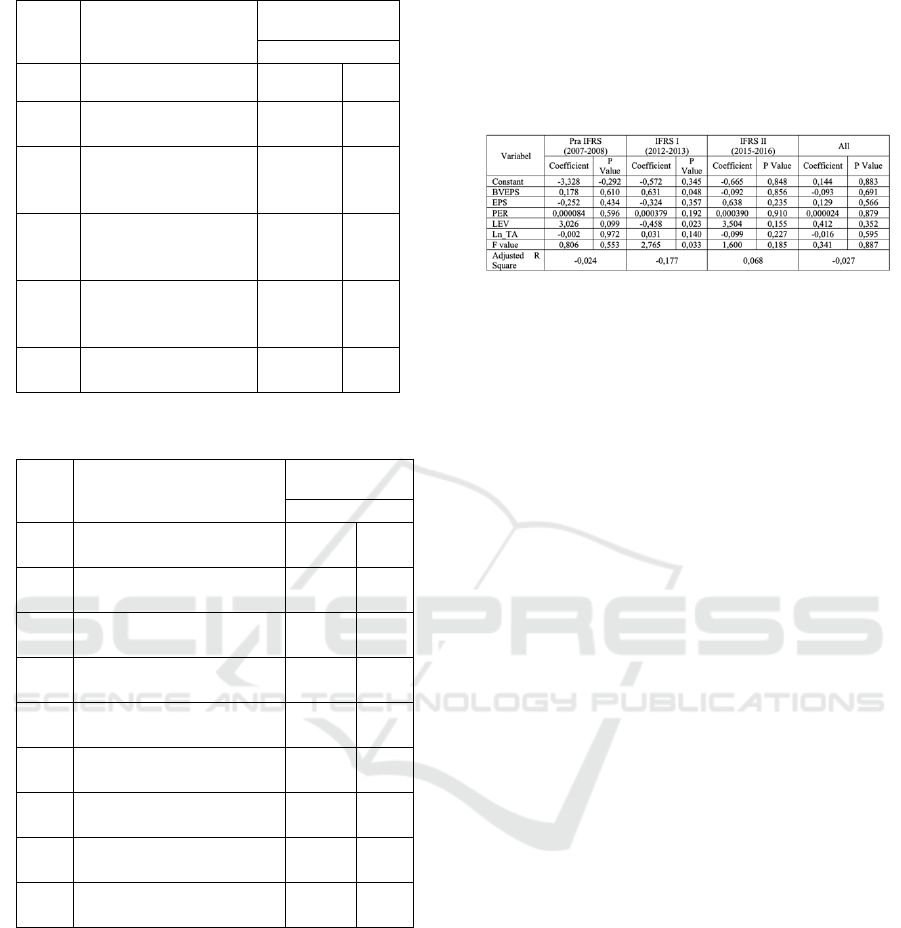
Table 3 and Table 4 show that the value of F is
greater than F table. These results support the
previous test, there were structural changes during the
period of IFRS convergence. Thus it can be
concluded that there is an increase in the relevance of
values after IFRS convergence, both in stage I and
stage II. However, the increase in stage II is not as big
as stage I.
Further analysis uses the return model. Table 5
shows that when using the return model analysis
cannot be done, because it is unable to meet the
classical assumption test. Influence between variables
is not consistent. Thus it can be concluded that the use
of return models is not relevant to test the increase in
value relevance in the banking sector in Indonesia.
Table 5: Results of Hypothesis testing (Return
Model)
5 RESULTS
The results of the study show that there is an increase
in value relevance after IFRS convergence using the
price model, but not with the return model. This
indicates that investors in the banking sector prefer
long-term investments rather than obtaining capital
gains in the short term. The results of this study
confirm the previous literature (Agostino et al., 2011;
Ebaid, 2014; Kouki, 2018; Palea & Scagnelli, 2017)
that IFRS is able to improve the quality of financial
reports with increasing the relevance of value.
These results also confirm (Daske et al., 2008;
Nurunnabi, 2015) which states that increasing the
relevance of values after IFRS convergence occurs if
there is support from the national and international
institutional environment. IFRS convergence in
Indonesia can increase value relevance because it is
strongly supported by the government. The
conversion of SAK (Indonesian Accounting
Standards) to IFRS in stage I was able to have a
positive impact because it was followed by Bank
Indonesia policy by issuing PAPI (Banking
Accounting Guidelines) at 2008 with strict
regulations and legal. Whereas in stage II the increase
in value relevance is not as big as in stage I because
there has only been a change in financial accounting
standards without being accompanied by the issuance
of relevant new regulations related to banking by
Bank Indonesia.
However, further analysis of the return model,
the results of the study failed to document the impact
of IFRS convergence on the relevance of accounting
values. Testing using the return model does not meet
the classic assumption test. Clarkson et al., (2011)
explained that, the impact of IFRS on value relevance
in the banking sector cannot fulfill classical
assumptions because two things, there are influence
the conservatism in the previous period and earnings
fluctuations before testing.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
998

6 CONCLUSIONS
IFRS has a positive impact on increasing the
relevance of accounting values in the Indonesian
banking sector. Structural changes occur in the period
before convergence, stage I convergence and stage II
convergence. These changes differ depending on how
big the role of the government is. The government
acts as a mediation to convince investors that
accounting numbers in financial statements can be
relied upon by enforcing regulations on compliance
with applicable standards (Daske et al., 2008; Ebaid,
2014).
This condition also occurs in some countries that
evaluate the impact of IFRS on increasing value
relevance (Alali & Foote, 2012; Karampinis & Hevas,
2011). When IFRS convergence is done voluntarily,
management will be more open if there is an increase
in incentives obtained. Also the convergence decision
depends on bad news or good news that happens to
the company. Thus IFRS convergence that is applied
voluntarily will not have any impact on increasing the
relevance of IFRS values (Christensen, Lee, Walker,
& Zeng, 2015). But when the standard regulatory
body mandatory IFRS convergence, it is found that
value relevance increases significantly.
The limitations of this study are not able to reveal
the impact of IFRS on value relevance by using the
return model. Future research is expected to be able
to eliminate conservatism and earnings fluctuations
so as to reveal an increase in value relevance
holistically. At the beginning of 2018, SAK 71 was
introduced for the regulation of financial instruments,
which were mandatory implemented at the beginning
of 2020. The adoption of the new standard may will
have a significant impact on the relevance of
accounting values in banking companies because
financial instruments are the main components
forming a company's balance sheet.
REFERENCES
Agostino, M., Drago, D., & Silipo, D. B. (2011). The
value relevance of IFRS in the European
banking industry. Review of Quantitative
Finance and Accounting, 36(3), 437–457.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11156-010-0184-1
Alali, F. A., & Foote, P. S. (2012). The Value
Relevance of International Financial Reporting
Standards: Empirical Evidence in an Emerging
Market. International Journal of Accounting,
47(1), 85–108.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intacc.2011.12.005
Astuti, E., & Sulistyowati, N. W. (2017). Analysis Of
Implementation Sak Converged Ifrs For
Financial Instruments (Psak 50, 55 And 60) In
Banking Company. In Proceedings of the 2nd
International Conference on Accounting,
Management, and Economics 2017 (ICAME
2017). https://doi.org/10.2991/icame-
17.2017.8
Ball, R., Robin, A., & Shuang, J. (2003). Incentives
versus standards : properties of accounting
income in four East Asian countries $. Journal
of Accounting and Economics, 36, 235–270.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacceco.2003.10.003
Barth, M. E., Beaver, W. H., Landsman, W. R., Barth,
M. E., Beaver, W. H., & Landsman, W. R.
(1996). Value-Relevance of Banks ’ Value
Disclosures under No . The Accounting Review,
71(4), 513–537.
Cahyonowati, N., & Ratmono, D. (2013). Adopsi
IFRS dan Relevansi Nilai Informasi Akuntansi.
Jurnal Akuntansi Dan Keuangan, 14(2), 105–
115. https://doi.org/10.9744/jak.14.2.105-115
Callao, S., Jarne, J. I., & Laínez, J. A. (2007).
Adoption of IFRS in Spain: Effect on the
comparability and relevance of financial
reporting. Journal of International Accounting,
Auditing and Taxation.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intaccaudtax.2007.06.
002
Christensen, H. B., Lee, E., Walker, M., & Zeng, C.
(n.d.). Incentives or Standards : What
Determines Accounting Quality Changes
around IFRS Adoption ?, (April 2015), 37–41.
https://doi.org/10.1080/09638180.2015.10091
44
Clarkson, P., Hanna, J. D., Richardson, G. D., &
Thompson, R. (2011). The impact of IFRS
adoption on the value relevance of book value
and earnings. Journal of Contemporary
Accounting and Economics, 7(1), 1–17.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcae.2011.03.001
Daske, H., Leuz, C., & Verdi, R. S. (2008).
Mandatory IFRS Reporting Around the World :
Early Evidence on the Economic Consequences
Mandatory IFRS Reporting Around the World :
Early Evidence on the. Journal of Accounting
Research, 46, 1085–1142.
Ebaid, I. E.-S. (2014). International Accounting
Standards and Accounting Quality in Code
laws Countries the Case of Egypt. Journal of
Financial Regulation and Compliance, 24(1),
Improvement of Accounting Value Relevance Post Convergence IFRS
999

41–59.
https://doi.org/http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/MRR-
09-2015-0216
Juniarti, J., Helena, F., Novitasari, K., & Tjamdinata,
W. (2018). The Value Relevance of IFRS
Adoption in Indonesia. Jurnal Akuntansi Dan
Keuangan, 20(1), 13.
https://doi.org/10.9744/jak.20.1.13-19
Karampinis, N. I., & Hevas, D. (2011). Mandating
IFRS in an Unfavorable Environment: The
Greek Experience. The International Journal of
Accounting, 46(3), 304–332. Retrieved from
https://econpapers.repec.org/article/eeeaccoun/
v_3a46_3ay_3a2011_3ai_3a3_3ap_3a304-
332.htm
Kouki, A. (2018). IFRS and value relevance: A
comparison approach before and after IFRS
conversion in the European countries. Journal
of Applied Accounting Research, 19(1), 60–80.
https://doi.org/10.1108/JAAR-05-2015-0041
Nurunnabi, M. (2015). The impact of cultural factors
on the implementation of global accounting
standards (IFRS) in a developing country.
Advances in Accounting, 31(1), 136–149.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adiac.2015.03.015
Olowolaju, P. S., Ogunsan, J. O., & Plc, Z. B. (2016).
VALUE RELEVANCE OF ACCOUNTING
INFORMATION IN THE DETERMINATION
OF SHARES PRICES OF QUOTED
NIGERIAN DEPOSIT MONEY BANKS.
International Journal of Economics,
Commerce and Management, IV(10), 128–147.
Onali, E., Ginesti, G., & Vasilakis, C. (2017). How
should we estimate value-relevance models?
Insights from European data. The British
Accounting Review.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bar.2017.05.006
Palea, V., & Scagnelli, S. D. (2017). Earnings
Reported under IFRS Improve the Prediction of
Future Cash Flows? Evidence from European
Banks. Australian Accounting Review, 27(2),
129–145. https://doi.org/10.1111/auar.12115
Prahesti, E., Utomo, S. W., & Astuti, E. (2016).
Pengaruh Profitabilitas Dan Solvabilitas
terhadap Audit Delay pada Perusahaan
Perbankan Yang Terdaftar di Bursa Efek
Indonesia (BEI). FIPA: Forum Ilmiah
Pendidikan Akuntansi, 11, 1–8.
Rodr, P., Aimer, K., Alejandro, C., & M, A. B.
(2017). Does an IFRS adoption increase value
relevance and earnings timeliness in Latin
America? Emerging Markets Review, 30 (C),
155–168.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ememar.2016.11.001
Trabelsi, N. S., & Trabelsi, M. (2014). The Value
Relevance of IFRS in the UAE Banking
Industry : Empirical Evidence from Dubai
Financial Market , 2008-2013. International
Journal of Academic Research in Accounting,
Finance and Management Sciences, 4(4), 60–
71. https://doi.org/10.6007/IJARAFMS/v4-
i4/1241
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1000
