
The Determinants of Inflation in North Sumatra Error Correction
Model
Duma Lasmaria Siagian
1
, Muhammad Yusuf
1
and Fitrawaty
1
1
Post Graduate School, State University Of Medan
Medan, North Sumatera, Indonesia
Keyword: Inflation, Government Spending, Money Supply, Exchange Rate, Economic Growth, Error Correction Model
(ECM)
Abstract: The stability of inflation is a requirement for economic growth and benefit the improvement of community
welfare. This research aims to analyze the effect of government spending, the money supply, exchange rates
and economic growth against inflation in North Sumatra. The analysis uses equations by the method of Error
Correction Model (ECM). This study analyzed the relationship between the dependent and independent
variables in both the short term and long term. Estimation results show that in the long term and the short
term, the variable amount of the money supply and economic growth was a negative and significant effect
against inflation in North Sumatra. While the variables do not affect government spending significantly to
inflation in North Sumatra. ECM model is considered valid because the value of the Error Correction Term
(ECT) is significant and in the long term and the short term only the variable exchange rate that has a
significant influence against inflation in North Sumatra. These results show that the exchange rate played an
important role in controlling the level of inflation in North Sumatra.
1 INTRODUCTION
A variety of macroeconomic indicators, inflation is
one of the important indicators for the economy of a
country. Inflation gives considerable influence
towards the achievement of some goals of
macroeconomic policy, such as economic growth,
employment, income distribution and the balance of
payments (Aulia Pohan, 2008).
North Sumatra also have experienced high
inflation that is at the moment the Government of
the old order and the last in 1998. Inflation occurs
when the old order caused by uncontrolled money
printing. In 1997-1998 have made the economy of
the North Sumatra is at an unstable state. Its impact
is the increase in the inflation amounted to 83.56
percent higher than the national figure of 77.63
percent. The condition of the rising inflation due to
rising prices of imported commodities and rising
foreign debt due to the weakening of the exchange
rate of the rupiah against the U.S. dollar and other
foreign currencies.
For it required an effort in keeping inflation at a
low and stable level. Based on Act No. 23 of the
year 1999, Bank Indonesia focuses its policy on
achieving the stability of rupiah value by placing
inflation as a cornerstone in monetary policy. Since
July 2005 the Bank Indonesia has implemented
monetary policy framework and consistent with the
Inflation Targeting Framework (ITF), which
includes four fundamental elements, namely the use
of the interest rate target as operational Bank
Indonesia (BI), the process of the formulation of
monetary policy, the communication strategy of the
anticipatory more transparent and strengthening
coordination with government policy. These steps
are intended to enhance the effectiveness of
monetary policy and governance in achieving the
target of the end of price stability to support
sustained economic growth and social welfare
(Endri, 2008).
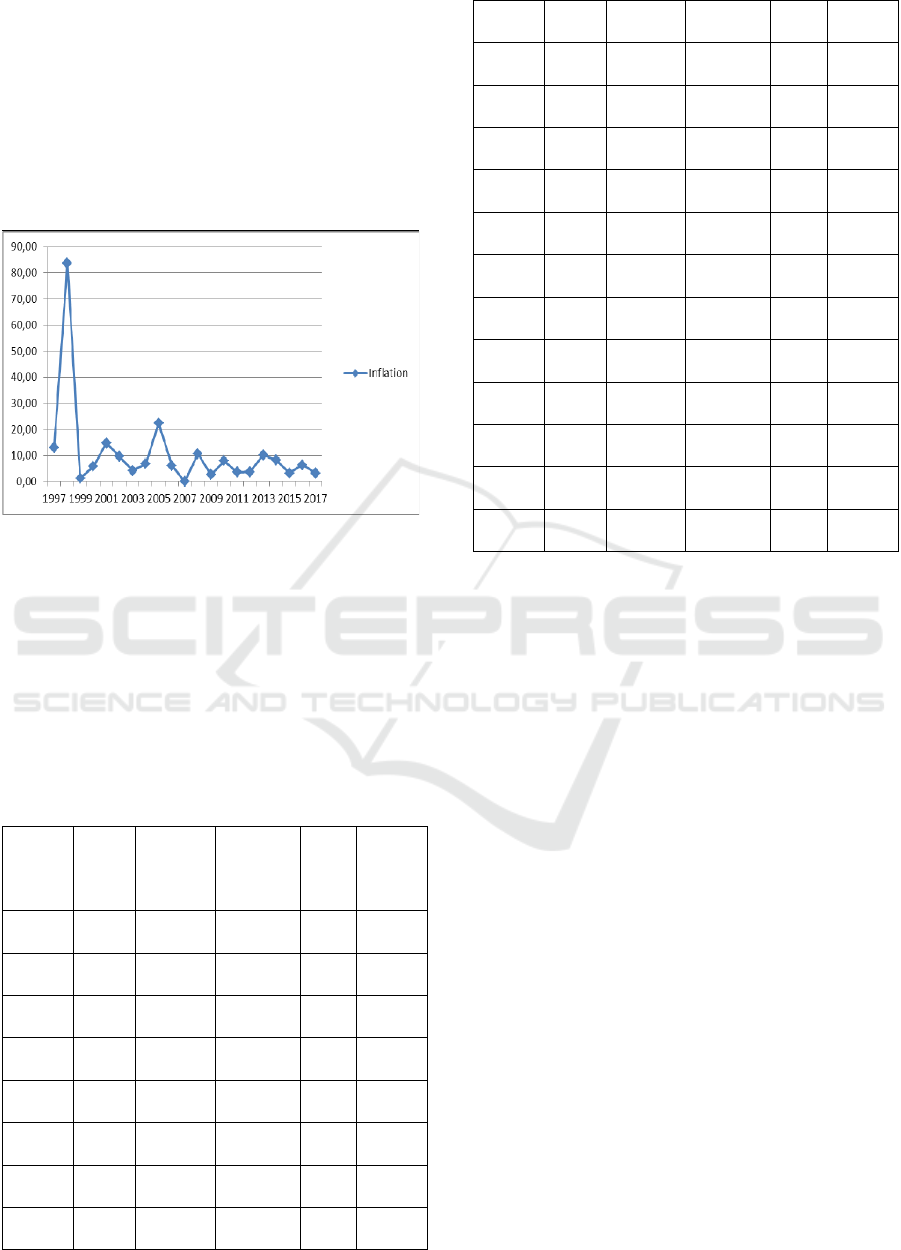
Based on the data of inflation in North Sumatra
during the 1997-2017 inflation rate trend shows up
and down from year to year. The highest inflation in
1998 reached 83.56 percent and the lowest the year
1999 reached 1.37 percent. Inflation in 2000
increased by 5.73 percent compared to the previous
period. This increase is due to rising freight rates on
1 September 2000, the increase in fuel oil as of
October 2000. With the increase in fuel oil in 2002,
2005, 2008, and the year 2013 be a contributor to
inflation are quite high in that year (Bank Indonesia,
2014).
Inflation in 2015 also belongs to a low of 3.14
percent. As one of the factors suppressing inflation
rate years 2015, this is the weakening of purchasing
422
Siagian, D., Yusuf, M. and Fitrawaty, .
The Determinants of Inflation in North Sumatra Error Correction Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0009499804220429
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 422-429
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
power due to the decline in jobs, as the
unemployment rate in February 2015 rise 428,794
people when compared with February 2014,
bringing the total reached 7.45 million people.
Inflation in 2016 exceeded the targets set by Bank
Indonesia at the beginning of the year that is 6.34
percent and also speeding the Government's inflation
target of 5.3 percent. While the year 2017 the
inflation rate decreased by 3.20 percent.
Figure 1: The Trend of inflation in North Sumatra
Years 1997-2017
Based on the classical view that the main factors
affecting inflation is the money supply and credit.
View of keynes then add some variables such as
interest rates, government spending and investment
(Ackley,1983:543).
Table 1: The Development of the inflation (INF),
government spending (GS), the money supply (MS),
exchange rate (EXC) and economic growth (GDP)
in North Sumatra.
Years
INF
(%)
GS
(billion
rupiah)
MS
(billion
rupiah)
EX
C
(Rp/
U$)
GDP
(%)
1997 13.10 771
355.643
4.65
0 5.70
1998 83.56 342
577.381
8.02
5
-10.90
1999 1.37 449
646.205
7.10
0
2.59
2000 5.73 416
747.027
9.59
5
4.83
2001 14.79 916
844.054
10.4
00
3.72
2002 9.59 1.021
883.903
8.94
0
4.07
2003 4.23 1.352
955.692
8.46
5
4.48
2004 6.80 1.501 1.033.87
7
9.29
0
5.74
2005 22.41 1.830 1.202.76
2
9.83
0
5.48
2006 6.11 2.184 1.382.49
3
9.02
0
6.20
2007 6.60 2.560 1.649.66
2
9.41
9
6.90
2008 10.72 2.967 1.895.83
9
10.9
50
6.39
2009 2.61 3.444 2.141.38
4
9.40
0
5.07
2010 8.00 3.666 2.471.20
6
8.99
1
6.42
2011 3.67 4.611 2.877.22
0
9.06
8
6.66
2012 3.68 7.633 3.307.50
8
9.67
0
6.45
2013 10.18 7.260 3.730.40
9
12.1
89
6.07
2014 8.17 7.808 4.173.32
7
12.4
40
5.23
2015 3.24 7.959 4.548.80
0
13.7
95
5.20
2016 6.34 9.476 5.003.30
0
13.3
07
5.18
2017 3.20 13.034 5.126.20
0
13.5
48
5.12
Source: Central Bureau of Statistics (BPS), Bank
Indonesia
Based on the data in table 1 that in 2005 the
inflation rate up from 6.80 percent to 22.41 percent,
the inflation rate is rising. Bank Indonesia attempted
to embody a high economic growth target but still
maintaining a relatively low inflation rate and stable,
but in the same year, the economic growth
experienced a decline from 5.74 percent to 5.48
percent. It is known that in the year 2009 the money
supply increased from 1,895,839 billion rupiahs into
2,141,384 billion rupiahs. Table 1 known also in the
same year the rupiah depreciates from Rp 10.950/US
dollar to Rp 9400/US dollar, which with increasing
money supply in the community and the occurrence
of the depreciation of the rupiah should have an
impact on high inflation. But inflation in 2009
experienced a drastic decline from 10.72 percent to
2.61 percent. While government spending has
increased from 2,967 billion rupiahs be 3,444 billion
rupiahs. This data does not match the theory. The
phenomenon certainly became one of appeal to
conduct research related to inflation. In addition, the
discovery of the difference results from earlier
studies where results are in accordance with the
theory and results that contradict the theory. This
fact certainly is questions about how big the
influence of government spending, the money
supply, exchange rates and economic growth in
The Determinants of Inflation in North Sumatra Error Correction Model
423

increasing the inflation rate and push in North
Sumatra.
Because inflation is a long-term phenomenon. So
it's interesting to do further research about inflation
in North Sumatra. In General, this research examines
the relationship between the independent variable
and the dependent variable in the short and long
term. The purpose of this research is to analyze the
effect of government spending (GS), the money
supply (MS), the exchange rate (EXC) and
economic growth (GDP) against inflation (INF) in
North Sumatra.
2 THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
Inflation is a process of rising prices of General
goods continuously (Nopirin, 2009:25). In the short
term, fiscal policy affects aggregate demand side,
while in the long run fiscal policy will affect the
supply side. Fiscal policy-oriented to improve the
supply side can overcome the problem of limited
production capacity and therefore its impact is a
more long term in nature. The impact of fiscal policy
on the economy through the approach of aggregate
demand is explained through the Keynesian
approach. The keynesian approach assumes the
existence of price rigidity and excess capacity so
that the output is determined by aggregate demand.
Keynes stated that the recession, the economy-based
market mechanisms will not be able to recover
without intervention from the Government. (Nanga,
2005). According to research conducted by Berto
Muharman (2013), the influence of fiscal
instruments against inflation found that State
spending and taxes the positive effect in the short
term while the negative effect in the long term.
The growth of the money supply happened
reasonably will provide a positive influence on the
economy in the short term, Indonesia is another case
with significant growth will trigger inflation which
would of course give negative influences. The
quantity theory of money is the oldest theories
concerning inflation, the theory highlights the role of
the addition of the money supply and expectations
about the price increase. It means that inflation can
only happen if there are additions to the money
supply. With the increase of the money supply
continuously, the community would feel rich so it
will raise consumption and this will raise prices. In
addition, the inflation rate is determined by society's
expectations about rising prices in the future.
Theoretically, there is a positive relationship
between the money supply and the inflation rate.
Increasing the money supply will increase inflation
rate. Research conducted by Ferdiansyah (2011)
shows the results that the money supply a positive
effect against inflation and Maggi and Saraswati
(2013) shows that the amount of money in
circulation a significant and positive effect in the
long term. However, research conducted by the
Issuance, et.al. (2014), Sipayung and Budhi (2013),
Symbolic (2010) shows the results that the money
supply is negative and not significant effect against
the inflation rate in Indonesia.
The occurrence of inflation triggered by the
weakening of the exchange rate of the rupiah against
the U.S. dollar since August 14, 1997, the rupiah's
exchange rate system is practiced in Indonesia is a
free-floating exchange rate system which means that
the exchange rate of the rupiah will be formed and
submitted fully to market mechanisms or based on
the laws of supply and demand of the market. The
weakening of the exchange rate of rupiah against
foreign currencies results in increasing the value of
exports. The price of domestic goods cheaper
overseas parties draws to increase the amount of
demand for the goods so that the price will go up
slowly and causes inflation (Sipayung, 2013).
According to the Keynesian Theory explaining
the relationship between inflation and economic
growth which in the short term (short-run) aggregate
offer curve is positive. The next long-term
relationships (long-run relationships) between
inflation and economic growth in which inflation
rises but economic growth down. These
circumstances justify empirically prove of some
related research between inflation and economic
growth that high inflation causes economic growth
down (Mankiw, 2003).
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This study uses secondary data in the form of time
series during the years 1997-2017. The calculation
of the inflation rate in this study uses the concept of
inflation CPI gained from the Central Bureau of
Statistics (BPS). Government spending (GS) in units
of billions of rupiah, the money supply used is
money in the broad sense in units of billions of
rupiah were sourced from publications of Bank
Indonesia. As for the data exchange rate of rupiah
against the U.S. dollar using the Middle rate set by
Bank Indonesia in units of thousands of rupiah.
Economic growth data and in units of a percent is
obtained from the Central Bureau of Statistics
(BPS).
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
424
The estimation model used in this study is the
analysis of the dynamic model with the regression
that is by using the model of error correction (Error
Correction Model/ECM) Domowitz and Elbadawi.
In the context of Economics, the dynamic model
specification is very important because it deals with
the establishment of the model of an economic
system that is associated with the change of time of
both short term and long term. This study uses
statistics programs help E-Views version 7.
4 ANALYSIS
4.1 Stationeritas Test
The first thing to do is to examine whether the data
is stationary or not. This Stasioneritas test needs to
be done because a regression analysis should not be
did when the data used is not stationary and
normally if it still done the resulting equations then
are a spurious regression.
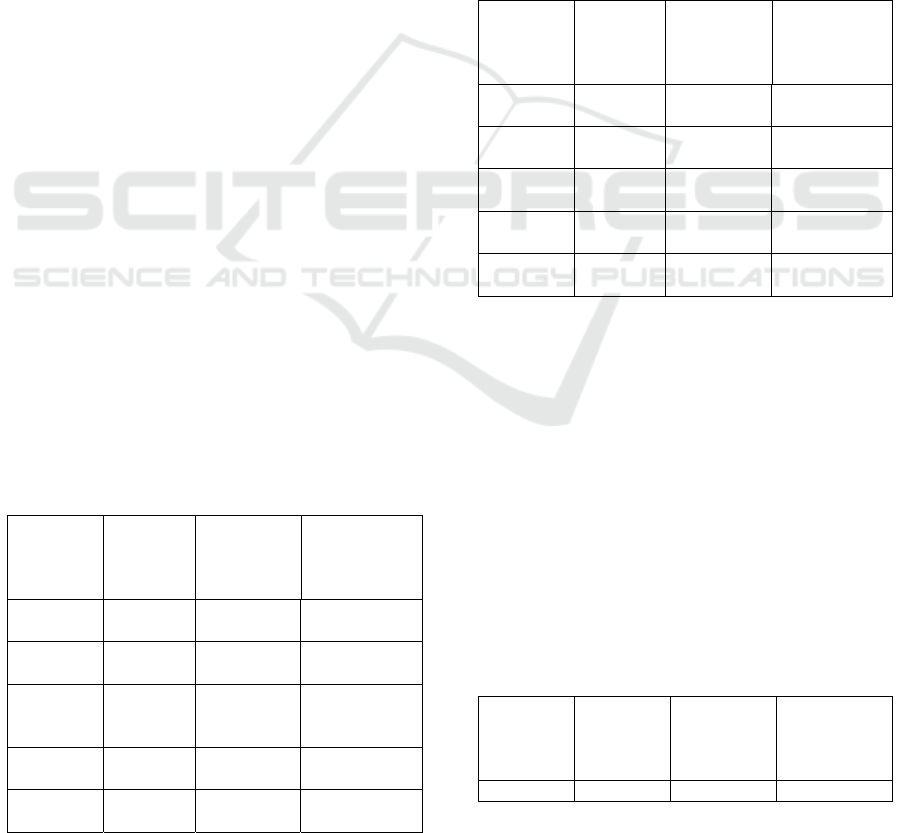
4.1.1 Unit Root Test
The unit root test is normal testing was introduced
by David Dickey and Wayne Fuller. The root test is
done to find out whether the data used stationary or
not. Data testing performed using test Augmented
Dickey-Fuller (ADF) was the count of an ADF when
the variable is greater than the critical value of
MacKinnon, means the variable is stationary, and
vice versa. Based on table II that Government
spending variables (GS) and exchange rate (EXC) is
not significant at the α = 5%. Because not stationary
at the zero degrees, then it needs to be done again
using stationeritas test the degree of integration of
the single.
Table 2: Unit Root Test Results
Variables
Value
ADF
Critical
Value
McKinnon
(α = 5%)
Descrip
tion
INF -
4.961814
-3.020686 Stationary
GS
0.034233
-3.020686
Non
Stationary
MS
-
1.429649
-3.065585
Non
Stationary
EXC -
3.570159
-3.020686 Stationary
GDP -
3.917664
-3.020686 Stationary
4.1.2 Integration Test
A test of the degree of integration is a test done to
measure at the level of difference to how data all the
variables are stationary. The taking of decision is
when the count of an ADF variable is greater than
the critical value of MacKinnon, means the variable
is stationary, and vice versa. Based on table III that
variable inflation (INF), government spending (GS),
the money supply (MS), the exchange rate (EXC)
and economic growth (GDP) has been stationary at
the same degree, that is one degree, shown from the
ADF value calculate more than the value of the
critical (Mackinnon critical values) at α = 5%. Thus,
the Granger test requires a stationary data at the
same degree can be used.
Table 3: Integration Test Results
Variables
Value
ADF
Critical
Value
McKinnon
(α = 5%)
Descrip
tion
INF -
8.791213
0.0008 Stationary
GS -
7.992085
0.9514 Stationary
MS -
8.984249
0.5417 Stationary
EXC -
7.395489
0.0165 Stationary
GDP -
12.84830
0.0079 Stationary
4.1.3 Cointegration Test
In this research to test the residual method based
cointegration test. Residual-based test method using
statistical tests Augmented Dickey-Fuller (ADF) by
observing the regression residual cointegration
stationary or not. Then this residual value will be
tested using the test Augmented Dickey-Fuller
(ADF) to find out if the residual value of the
stationary or not. The results of this research show
that the estimated value of the ADF test > Critical
Value α = 5% (-5.310626 >-3.020686). So it could
be inferred that the empirical model used in this
study to qualify for the cointegration test.
Table 4: Cointegration Test Results
Variables
Value
ADF
Critical
Value
McKinnon
(α = 5%)
Description
ECT -5.310626 0.0004 Stasionary
The Determinants of Inflation in North Sumatra Error Correction Model
425
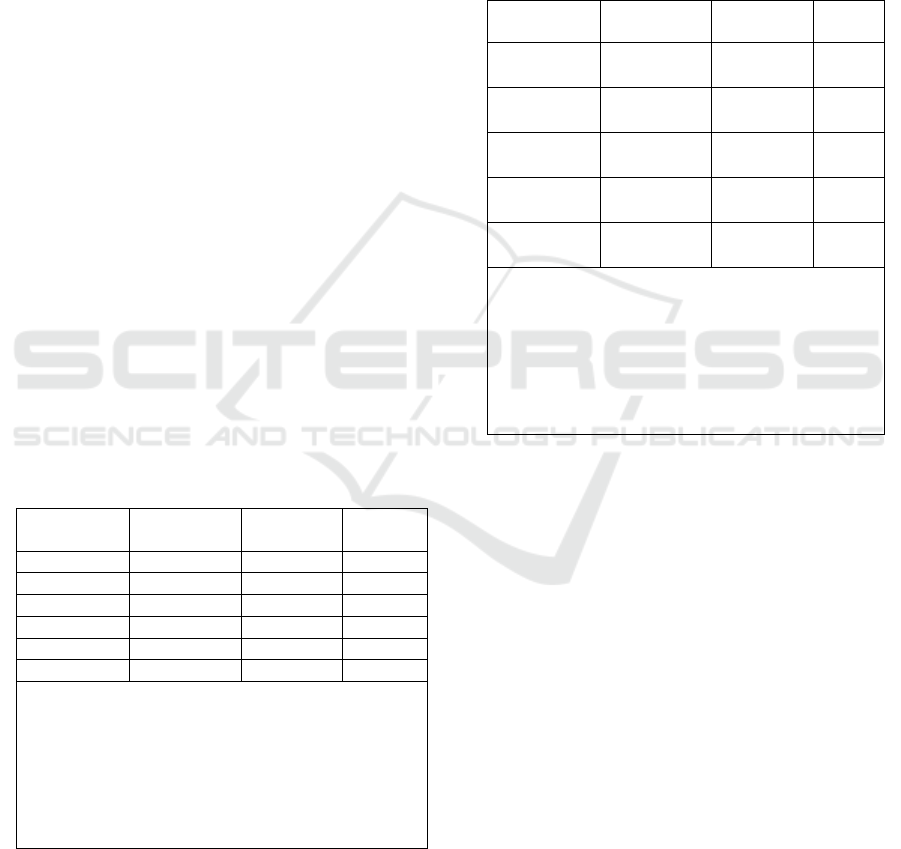
4.2 Estimation Error Correction Model
(ECM)
Estimation model of inflation using the model of
Error Correction Model (ECM) Domowitz and
Elbadawi aims to seek short-term balance or correct
an imbalance towards short-term long-term balance.
To know that a used Error Correction Model (ECM)
is valid or not can be seen from the value of the
Error Correction Term (ECT) are significant or not.
Equation Error Correction Model (ECM) for short-
term period are as follows:
The results of estimation Error Correction Model
(ECM) that short-term variable changes the money
supply (MS) and economic growth (GDP) had a
negative influence against inflation in North
Sumatra. While the Government spending variables
(GS) and exchange rate (EXC) have a positive
influence against inflation in North Sumatra. The
magnitude of the balance and changes the previous
inflation against the period now is 128 percent.
These adjustments are obtained from coefficients the
Error Correction Term (ECT) of 1.287258 while the
t-statistics is 6.002274 with probability 0.0000 so
significant at 5% and means that the model can be
used.
Table 5: The Results of The Estimation of the Error
Correction Model (ECM) Short-Term
Independen
t Variables
Coefficient t-Statistic Prob
D(LnGS) 0.683037 1.417959 0.1781
D(LnMS) -5.089649 -2.752699 0.0156
D(LnEXC) 3.658554 4.032125 0.0012
D(LnGDP) -0.493542 -4.528430 0.0005
ECT 1.287258 6.002274 0.0000
C 0.335769 1.166629 0.2628
R-squared
Adjusted R-
squared
F-statistic
Prob(F-statistic)
Durbin-Watson
stat
0.904034
0.869760
26.37686
0.000001
2.179223
Equation Error Correction Model (ECM) for
long-term periods are as follows:
The results of estimation Error Correction Model
(ECM) that long-term variable changes the money
supply (MS) and economic growth (GDP) prior
periods have a negative influence against inflation in
North Sumatra. While the Government spending
variables (GS) and exchange rate (EXC) previous
period have a positive influence against inflation in
North Sumatra.
Table 6: The Results of The Estimation of Error
Correction Model (ECM) Long-Term.
Independen
t Variables
Coefficient t-Statistic Prob
LnGS(-1)
1.445744 2.986111
0.009
2
LnMS(-1)
-2.505213 -3.236568
0.005
5
LnEXC(-1)
2.429970 2.498143
0.024
6
LnGDP(-1)
-0.663565 -4.533170
0.000
4
C
5.575499 1.033033
0.318
0
R-squared
Adjusted R-
squared
F-statistic
Prob(F-statistic)
Durbin-Watson
stat
0.671479
0.583874
7.664799
0.001429
2.572411
4.3 Test Determination (R
2
)
4.3.1 F-Test (Simultaneous Test)
F test or simultaneous test is performed to see the
effect of free variables simultaneously or together to
the dependent variable. From the results of the
estimation model for inflation in the short term is
obtained a value of F count of 26.37686 with the
level of probability of 0.000001. Then the variable
is Government spending (GS), the money supply
(MS), exchange rates (EXC) and economic growth
(GDP) in the short term significant effect
simultaneously against inflation (INF) in North
Sumatra.
From the results of the estimation model for
inflation in the long-term is obtained a value of F
count of 7.664799 with the level of probability of
0.001429. Then the variable is Government
spending (GS), the money supply (MS), exchange
rates (EXC) and economic growth (GDP) in the long
ECTGDP
MSGSD
287258.1493542.0EXC658554.3
089649.5683037,0335769.0LINF
GDP
MSGSn
663565.00EXC429970.2
505213.2445744.1575499.5INFL
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
426

term significant effect simultaneously against
inflation (INF) in North Sumatra.
4.3.2 T-Test (Partial Test)
a. The Government Spending
Based on the results of the study showed that the
change in government spending in the short term
does not influence the change of inflation in North
Sumatra with a coefficient of 0.683037. This means
if a change of government spending rose by 1 billion
rupiahs, then inflation will change up by 0.683037
percent.
While in the long-term government spending has
a positive influence and significantly to inflation in
North Sumatra. If change is Government spending
rose by 1 billion rupiahs, then change the inflation
went up by 1.445744 percent.
b. The Money Supply
Based on the results of the study showed that the
percentage of change in the money supply in the
short term to change the percentage of inflation in
North Sumatra with a coefficient of-5.089649. If
changes in the money supply rose by 1 billion
rupiahs, then change the percentage of inflation will
come down of 5.089649 percent.
While in the long-term the money supply has a
negative and significant effect against inflation in
Indonesia with a coefficient of -2.505213. This
means if the money supply rose by 1 billion rupiahs,
then inflation will be down by 2.505213 percent.
c. The Exchange Rate
Based on the results of the study showed that
changes in exchange rates in the short term to
change the percentage of inflation in North Sumatra
with the coefficient of 3.658554. If changes in the
money supply rose by Rp 1/US dollar, then change
the percentage of inflation going up by 3.658554
percent.
While in the long run Exchange rates had a
positive and significant influence against inflation in
North Sumatra. If the exchange rate rose by Rp 1/US
dollar, then change the percentage of inflation going
up by 2.429970 percent.
d. The Economic Growth
Based on the results of the study showed that the
change of the economic growth in the short term to
change the percentage of inflation in North Sumatra
with a coefficient of-0.493542. If the change of
economic growth rose by 1 percent, then change the
percentage of inflation will be down by 0.493542
percent.
While in the long run economic growth has a
negative influence and significantly to inflation in
North Sumatra. If the change of economic growth
rose by 1 percent, then the change in inflation down
by-0.663565 percent
4.3.3 Goodness of Fit Test
Test coefficient determination (R
2
) is used to see
how big the variation of free variables may explain
the variables bound. Adjusted R-squared value of
0.904034 can be explained that Government
spending variable precision (GS), the money supply
(MS), the exchange rate (EXC) and economic
growth (GDP) explains the variations change
inflation rate amounted to 90.40 percent. While the
rest of 9.60 percent described other factors outside
the model.
5 RESULTS
5.1 Influence Government Spending against
Inflation in North Sumatra
Based on the results of the study showed that the
change in government spending in the short term
does not influence the change of inflation in North
Sumatra with a coefficient of 0.683037. This means
if a change of government spending rose by 1 billion
rupiahs, then inflation will change up by 0.683037
percent. Due to North Sumatra Government
spending comes from shopping the employees,
operational expenditure and capital expenditure
because of increased demand for goods and services
could not be anticipated by the side deals. Inflation
occurred in North Sumatra due to the increasing
demand for a hand. These results can be explained
by the theory of Keynes that in the short term fiscal
policy affects aggregate demand side. Rising prices
of goods due to the increase in aggregate demand
due to rising production costs (Nanga, 2005). And
not in line with the research conducted by Berto
Muharman (2013) that influence the fiscal
instrument against inflation in Indonesia found the
country's tax and spending the positive effect in the
short term.
The Determinants of Inflation in North Sumatra Error Correction Model
427

While in the long-term government spending has
a positive influence and significantly to inflation in
North Sumatra. If change is Government spending
rose by 1 billion rupiahs, then change the inflation
went up by 1.445744 percent. This is in accordance
with the theories of keynes. In the long run fiscal
policy will affect the supply side. Fiscal policy-
oriented to improve the supply side can overcome
the problem of limited production capacity. Keynes
stated that the recession, the economy-based market
mechanisms will not be able to recover without
intervention from the Government (Nanga, 2005).
This is in line with research conducted by Marius
Masri (2010) using OLS that employee shopping
model, positive and influential operating
expenditures significantly to inflation in East Nusa
Tenggara Province.
5.2 Influence the Money Supply against
Inflation in North Sumatra
Based on the results of the study showed that the
percentage of change in the money supply in the
short term to change the percentage of inflation in
North Sumatra with a coefficient of -5.089649. If
changes in the money supply rose by 1 billion
rupiahs, then change the percentage of inflation will
come down of 5.089649 percent. Because
government policy to change the money supply has
not been effective in controlling the rate of inflation
and the money supply has not been sufficiently
lowered inflation rates in North Sumatra. These
results can be explained by the theory of Keynes that
the increase in the money supply can raise prices,
but the increase in the money supply is not always
proportional to the increase in the price of goods. In
the short ride down the amount of money circulating
in the economy does not quickly addressed by the
community, for example by changing consumption
patterns. And in line with the research conducted by
Annisa Tri Utami and Soebiyo Daryono (2013)
using OLS model is that the money supply a
negative and significant effect against inflation in
Indonesia.
While in the long-term the money supply has a
negative and significant effect against inflation in
Indonesia with a coefficient of -2.505213. This
means if the money supply rose by 1 billion rupiah,
then inflation will be down by 2.505213 percent.
Due to the money supply consists of cash in
circulation, money giral and quasi money. Although
the value is high but not enough to affect the
inflation increase in North Sumatra. This result does
not match the quantity theory that fluctuations that
occur at the price caused by the ups and downs of
the volume of money supply in the economy
(Mankiw, 2003). So it was concluded that the money
supply has a positive influence against inflation.
And in line with the research conducted by Nugroho
and Basuki (2012) stated that the money supply a
negative and significant effect against inflation in
Indonesia.
5.3 Influence Exchange Rate against Inflation
in North Sumatra
Based on the results of the study showed that
changes in exchange rates in the short term to
change the percentage of inflation in North Sumatra
with the coefficient of 3.658554. If changes in the
money supply rose by Rp 1/US dollar, then change
the percentage of inflation going up by 3.658554
percent. This is in accordance with the Purchasing
Power Parity approach in case of inflation then to
maintain the balance of the Law of One Price, the
exchange rate must depreciate. The theory of
Purchasing Power Parity also said that the country
that its currency is experiencing high inflation rates
should reduce the value of its currency against other
currencies with lower inflation rates (Mishkin,2009).
This is in accordance with the research done
Oktavia, Lakshmi, et al that the exchange rate of a
positive and significant effect against inflation in
Indonesia.
While in the long-term Exchange rates had a
positive and significant influence against inflation in
North Sumatra. If the exchange rate rose by Rp 1/US
dollar, then change the percentage of inflation going
up by 2.429970 percent. Due to the depreciating
rupiah exchange rate against the United States dollar
then inflation increased. But despite the more price
increases or inflation will not reduce the purchasing
power of money. Because of the exchange rate of
the dollar has intrinsic value that is steeper than in
foreign currency exchange rates. This is in
accordance with the research conducted by Priyono
and Setiasih (2009), the relationship of inflation with
Exchange rate is positive.
5.4 Influence Economic Growth against
Inflation in North Sumatra
Based on the results of the study showed that the
change of the economic growth in the short term to
change the percentage of inflation in North Sumatra
with a coefficient of-0.493542. If the change of
economic growth rose by 1 percent, then change the
percentage of inflation will be down by 0.493542
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
428

percent. This is not in accordance with the theories
of keynes explained the relationship between
inflation as economic growth in the short-run
aggregate supply curve is positive. Inflation in North
Sumatra on research is due to the increase in the
price of Fuel. The rising prices of fuel oil which was
followed by rising prices of goods and services will
make the price is not affordable by the people who
earn it anyway. The high price levels that cause
declining purchasing power it will make producers
suffered losses so will lower economic growth in
Northern Sumatra. This is in accordance with the
research done Izzah (2015) stated that the negative
effect of inflation towards economic growth of Riau.
While in the long run economic growth has a
negative influence and significantly to inflation in
North Sumatra. If the change of economic growth
rose by 1 percent, then the change in inflation down
by-0.663565 percent. This is in accordance with the
theories of keynes in the long-term relationship
between inflation and economic growth in which
inflation rises but economic growth down
(Mankiw,2003).
6 CONCLUSIONS
Only the variable exchange rate (EXC) that have
significant influence towards inflation in North
Sumatra in both short term and long term. The
variable amount of the money supply (MS) and
economic growth (GDP) has a negative influence
and significantly to inflation in North Sumatra.
While the Government spending variables (GS) in
the short term is not significant effect against
inflation in North Sumatra.
Because of the exchange rate (EXC) is the main
determining factor affecting inflation in North
Sumatra in both short term and long term so that
Bank Indonesia is expected to maintain the stability
of the exchange rate of the rupiah. The system of
exchange rates used for Bank Indonesia's current
exchange rate system is the right of free use for
keeping the stability of the instrument's value by
open market operations in the money markets either
rupiah or foreign currency.
REFERENCES
Ackley, Gardner. (1983). “Teori Ekonomi Makro”.
Diterjemahkan Oleh Paul Sitohang-Fakultas Ekonomi
Universitas Lampung Teluk Betung. Diperiksa dan
disempurnakan oleh Joedono-Fakultas Ekonomi
Universitas Indonesia. Penerbit Universitas Indonesia.
Jakarta.
Annisa Tri Utami, Daryono Soebagiyo. (2013). “Penentu
Inflasi Di Indonesia, Jumlah Uang Beredar, Nilai
Tukar, Ataukah Cadangan Devisa”. Jurnal Ekonomi
& Studi Pembangunan Vol. 14, No.2, Hal 144-152.
Jakarta. Oktober 2013.
Berto Muharman. (2013). “Analisis Dinamis Pengaruh
Instrumen Fiskal Terhadap PDB dan Inflasi Di
Indonesia”. Jurnal Ilmiah. Fakultas Ekoomi dan
Bisnis Universitas Brawijaya. Malang.
Endri. (2008). “Analisis Faktor-faktor yang
Mempengaruhi Inflasi di Indonesia”. Jurnal Ekonomi
Pembangunan, vol.13(1), pp.1-13, April 2008.
Ferdiansyah, Fadli. (2014). “Analisis Pengaruh Jumlah
Uang Beredar (M1), Suku Bunga SBI, Nilai Tukar,
Suku Bunga Deposito terhadap Tingkat Inflasi”.
Media Ekonomi, vol.19(3), pp. 43-68, Desember
2011.
Izzah, Nurul. (2015). “Analisis Pengaruh Indeks
Pembangunan Manusia (IPM) dan Inflasi Terhadap
Pertumbuhan Ekonomi di Propinsi Riau Tahun 1994-
2013”. Jurnal Penelitian Ekonomi dan Bisnis. Vol. 1
(2), Hal 156-172.
Maggi, Rio, Birgitta Dian Saraswati. (2013). “Faktor-
faktor yang Mempengaruhi Inflasi di Indonesia:
Model Demand Pull Inflation”. Jurnal Ekonomi
Kuantitatif Terapan, vol.6(2), pp. 71-77, Agustus
2013.
Marius Masri. (2010). “Analsis Pengaruh Kebijakan
Fiskal Regional Terhadap Inflasi di Propinsi Nusa
Tenggara Timur (Periode 2001-2008)”. Tesis.
Universitas Diponegoro. Semarang.
Mankiw, N. Gregory. (2003).“Teori Makro Ekonomi”.
Edisi Kelima. Jakarta: Erlangga.
Mishkin, F. S. (2009).“Ekonomi Uang, Perbankan, dan
Pasar Keuangan Edisi 8 Buku 2”. Jakarta: Salemba
Empat.
Nanga, Muara. (2005). “Makro Ekonomi Teori, Masalah
dan Kebijakan Edisi Ke 2”. Jakarta: Raja Grafindo
Persada.
Nugroho, P.W dan Basuki M.U. (2012). “Analisis Faktor-
Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi Inflasi di Indonesia
Periode 2000.1-2011.4”. Disertasi Fakultas
Ekonomika dan Bisnis.
Priyono, Setiasih. (2009). “Analisis Faktor - Faktor Yang
Mempengaruhi Inflasi Di Purwokerto”. Skripsi.
Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta. Surakarta.
Pohan, Aulia. (2008). “Potret Kebijakan Moneter
Indonesia”. Jakarta: Raja Grafindo Persada.
Sipayung, Putri Tirta Enistin, Made Kembar Sri Budhi.
(2013). “Pengaruh PDB, NIlai Tukar dan Jumlah
Uang Beredar terhadap Inflasi di Indonesia Periode
1993-2012”. Jurnal Ekonomi Pembangunan
Universitas Udayana, vol. 2 (7), pp. 335-343, Juli
2013.
The Determinants of Inflation in North Sumatra Error Correction Model
429
