
Implementation Proposal of Activity based Costing on the Loans
Department: A Case Study in PT. BPR Cincin Permata Andalas
Dissa Elvaretta
1
and Christina Juliana
1
1
Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta -Indonesia
Keywords: ABC, Traditional Costing, Loans Department, Bank
Abstract:
This study aims to determine the comparison between the result of the implementation proposal of
Activity Based Costing (ABC) system on the Loans Department at PT. BPR Cincin Permata
Andalas and the proposed implementation of the ABC system with traditional cost allocation
system that has been used so far. The research method used is single case study with a single unit
analysis by collecting data through observation, documentation, and interviews. The result of the
proposed implementation of ABC system can be utilized by PT. BPR Cincin Permata Andalas as
recommendation to arrange the next strategy. Results from this research shows the different
calculation of overhead costs with traditional cost method and ABC. ABC system describes cost
information reliable for calculating the cost of each customer better.
1 INTRODUCTION
The soaring competition leads companies engaged in
manufacturing, trading and service industries to be
extra careful in managing strategies that can enhance
their competitive advantage in order to continue to
sustain the competition. The level of competition is
due to the ease in getting information and rapid
technological developments, so that the opportunity
to conduct business activities becomes more open.
Competitive advantages cannot be maintained with
just the current market share position or resources
(Marvianti, 2013). However, companies must be able
to make innovations that will later impact the
company's profitability and increase competitive
advantage.
The rapid change in the business environment is
not only influenced by economic conditions but also
influenced by customers. The increasing number of
competitors makes it easier for customers to freely
determine which products and services to choose and
thus encouraged companies to set strategies in order
to established good relationships with customers.
The financial services industry plays an important
role in the development and economic growth of a
country, particularly in the banking industry. PT.
BPR Cincin Permata Andalas is one of the banks that
actively contributes to economic growth in Indonesia,
specifically in West Sumatra. PT. BPR Cincin
Permata Andalas contributes by channeling funds in
the form of loans to local and small business. The
provision of credit is based on the prudence principle
because it contains some substantial potential risk
which can affect the bank’s performance. Therefore
PT. BPR Cincin Permata Andalas must be able to
process, analyze, and assess every credit application
to determine that the application is safe, effective and
healthy. Hence, PT BPR Cincin Permata needs a cost
information from each credit analysis process to get a
decent and profitable customer. Raaij (2005)
explained that this cost information will be useful in
managerial decision making and be as reference for
companies in choosing their strategies to increase
their profitability. Using Activity Based Costing
system is considered capable of tracing the costs
arising from each activity influenced by the customer
and assigns costs accurately to each customer. The
results of the ABC system are expected to be able to
provide information to differentiate high-cost
customers and low cost customers so that further
strategic decisions can be measured.
This research was conducted in the credit
department in PT. BPR Cincin Permata Andalas by
considering the fact that the most important income is
credit interest income. Furthermore, this research is
986
Elvaretta, D. and Juliana, C.
Implementation Proposal of Activity based Costing on the Loans Department: A Case Study in PT. BPR Cincin Permata Andalas.
DOI: 10.5220/0009499609860990
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 986-990
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reser ved

expected to be able to provide more accurate cost
information on the calculation of credit application
fees with ABC compared with traditional cost system.
2 THEORICAL FRAMEWORK
Hansen and Mowen (2015) define costs as cash or
cash equivalents sacrificed to obtain goods or services
that are expected to provide benefits now and in the
future for the company. Horngren, et al., (2013)
argues that costs are sacrifices or resources used for
specific purposes. Different cost for different
purposes, which means that each cost classification
has different objective in the decision making
(Horngren, et al., 2012). Horngren, et al., (2012)
classified costs into two; direct costs, which is the
cost that directly related to cost objects and its
economic value can be easily calculated and indirect
costs, which is the cost that associated with product
costs but its economic value can not be traced easily.
If the procedure for assigning the costs is wrong,
this will lead to a wrong decision taken by
management. Tracing coss into cost objects is divided
into two methods (Hansen and Mowen, 2015), the
direct tracing and driver tracing method. Direct
tracing can be perform by identifying costs that
specifically related directly to the cost object and thus
charged directly into the cost object. Driver tracing is
a method of allocating or charging costs by paying
attention to the causal relationship between the cost
and the cost object. Indirect costs are costs that cannot
be traced directly so that it requires a method called
cost allocation. Allocation is usually based on
assumptions or policies set by management.
Horngren, et al., (2012) explains that there are four
reasons of why the costs allocation is very important.
It is to predict the impact of business decisions, used
as a tool to shape the motivation desired by functional
managers, to calculate income and assess the cost of
assets, and to calculate costs or justifications in
spending. Generally there are three cost allocation
systems, which are the direct costing, traditional
costing, and Activity Based Costing (ABC) systems
Traditional costing system focus on production.
costs. This system is also known as volume based
costing because the overhead is charged based on
volume of the cost drivers (Cooper and Kaplan,
1999). In its development, traditional costing is
deemed unable to produce reliable information so
Cooper and Kaplan (1999) developed an allocation
method based on activities called Activity Based
Costing (ABC). Blocher and David Stout (2012)
explain that ABC system is a cost allocation system
that allocated costs to its cost objects based on the
activities carried out for these cost objects, Stout and
Propri (2011) mentioned that if ABC implementation
is done correctly, it will be able to provide accurate
information about costs to management regarding
product costs so that the information can be used as a
basis for decision making for strategies such as the
process of repairing, pricing, and managing customer
relationships.
Blocher, Stout, and Cokins, 2012 stated that to
gain full closure on the flow of the ABC system , one
must understand about activity, resource, driver cost,
resource cost driver, and activity cost driver. ABC
described a causal relationship between resource,
activity and cost object. In conclusion, the assignment
of costs according to ABC is done through two stages,
namely assigning overhead costs to activities and
assigning activities to the cost object using two cost
drivers; the resource cost driver and activity cost
driver (Blocher, Stout, and Cokins, 2010; Cooper and
Kaplan, 1999).
In practice, it is difficult to apply the ABC system
to companies and allocate the overhead costs
compared to traditional method. ABC requires
companies to identify significant activities in their
business process. However, the allocation of costs
with ABC is considered sufficient enough to provide
more accurate information on the overhead cost of the
company.
The benefits of the ABC system are 1) ABC is
useful to determine the cost of the product more
accurately. 2) ABC system is very useful for company
management to conduct profitability analysis more
accurately, both in profitability analysis of products,
customers, processes and departments. 3) ABC can be
used as an inventory valuation measure. 4)
Appropriate and effective implementation of the
ABC system can help companies to manage their
activities better, to eliminate activities that do not
provide value and improve the quality of the
company's internal processes consistently.
The weakness of the ABC system is 1) The
application of the ABC system requires the support of
human resources and adequate information
technology and a long time to socialize to all parts of
the company. 2) Identification of causal relationships
between company operating activities and production
costs requires careful and adequate steps. Mistakes
that occur in determining the trigger of activity will
bring distorted cost information to management and
could cause serious damage. Cooper and Kaplan,
(1999) in his research explained how ABC can be
used to improve performance in insurance companies.
The application of ABC can be used in various
service industries such as banks, medical service
industries and government departments.
Implementation Proposal of Activity based Costing on the Loans Department: A Case Study in PT. BPR Cincin Permata Andalas
987

3 RESEARCH METHOD
This research is categorized as qualitative research.
Moleong (2015) explained qualitative research aimed
to understand the phenomenon of a research object so
that efforts can be determined to improve and analyze
the phenomenon. The method of data collection in
this study was conducted in 3 methods. First is the
observation by visiting the object of research directly;
Second is the documentation in the form of annual
reports, along with other data related to research; and
the third is conducting interviews with the director,
head of credit and 2 account officers. This research is
a single case study with a single unit of analysis and
it focused only on one research object. A single case
study brings a role to the research used in current
management and can provide knowledge valid
because this study focuses on one object. The object
of this research is PT. BPR Cincin Permata Andalas
where its specialty lies on providing loans to its
customer.
4 ANALYSIS
4.1 Allocation Policy Cost at PT. BPR Cincin
Permata Andalas
Based on interviews conducted with PT. BPR Cincin
Permata Andalas, the calculation of overhead costs
for processing a loan is done in a simple way, namely
by dividing the overhead costs by the amount of the
ceiling loan that has been given
Table 1: Cost Allocation at PT. BPR Cincin Permata Andalas on December 31, 2017 (in Rupiah)
4.2 Development of Activity based Costing at
PT. BPR Cincin Permata Andalas
To develop a loan calculation using the ABC system,
the steps are as follows:
1. Determine all activities of the lending process
There are 14 activities includes: marketing;
customer data collection and file administration,
customer interviews, BI Checking, Making loan
portfolio, surveys, reviews of loan portfolio,
loan approvals, scheduling agreements,
agreements and loan realization,
documentation, supervision and loan
monitoring, making supervision reports, and
handling non-performing loans.
2. Determine resource costs
After determining the activities related to
lending, the next step is identifying the amount
of resource costs to process a loan application.
To determine the amount of resource cost, this
research has been traced the resources through
observation, documents, and interviews. There
are 5 overhead costs that have been traced, i.e.
payroll expense, education and training
expense, rent expense, maintenance expense,
and fuel expenses
3. Assign resource costs to activities
4. Identify activity drivers and assign activity costs
on cost objects
This is the last step in the development of ABC
in order to search the activity costs to object
costs so as it is grouped into one cost pool. The
cost pool results at PT. BPR Cincin Permata
Andalas are batch level, unit level, and facility
level
There are 11 cost pools that are used to trace costs
into the cost object. The calculation of the total
activity costs found in each cost pool, then these costs
are allocated to each customer segment. The
following is summary table of the cost pool at PT.
BPR Cincin Permata Andalas.
Table 2: Cost pool of the loan process PT. BPR
CincinPermataAndalas (in Rupiah)
No Rated aspect Category
1 Number of visits to customers 93.680.163
2 Number of customers served 62.757.395
3 Number of customer NPWP 12.657.004
4 Number of loan portfolio made 25.256.057
5 Number of reviews conducted 87.099.074
6 The amount of analysis carried out 73.036.989
7 Loan agreement 186.509.619
8 Number of documents recorded 74.362.979
Customer
Se
g
mentation
Working capital
Loan
Investment
Loan
Consumption
Loan
Total
N
umber of plafon
d
38.779.000.000 12.146.000.000 5.280.834.000 56.205.834.000
Overhead Cos
t
618.869.272 193.836.514 84.276.178 896.981.964
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
988
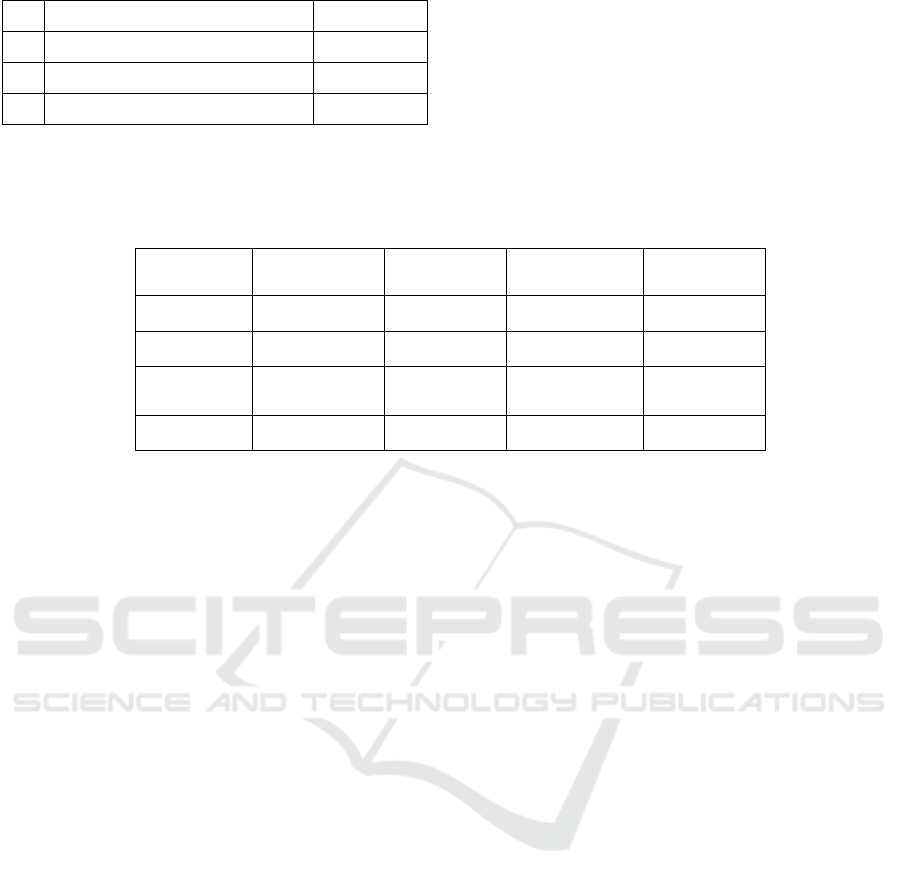
9 Number of monitoring conducted 170.551.102
10 Number of reports made 23.188.652
11 Number of actions taken 87.882.930
Total 896.981.965
Source: PT BPR Cincin Permata Andalas which has
been processed
4.3 Comparison ABC with Traditional Costing
From the table, the allocation for each customer
segment is determined, so the results can be compared
to the calculations made by management.
Table 3: Comparison of Overhead Cost Allocation of the Process of Giving Loan in PT. BPR Cincin Permata Andalas (in
Rupiah)
Cost
allocation
Working
capital Loan
Investment
Loan
Consumption
Loan
Total
Traditional 618.869.272 193.836.514 84.276.178 896.981.964
ABC 636.538.463 171.453.668 88.989.833 896.981.964
Difference (17.669.191) 22.382.847 (4.713.655)
Information Undercosted Overcosted Undercosted
By comparing the overhead costs made on
management calculations and calculations according
to the ABC system, can be seen that the allocation of
costs used by PT. BPR Cincin Permata Andalas all
this time is not quite right. This affects the profit of
each segment of loan customers at PT. BPR Cincin
Permata Andalas. They can also find out that the
allocation of costs using the ABC system provides
information on which customers are high cost to serve
and which customers who are in the low cost to serve.
The working capital loan customers experienced
a considerable undercosted amounting to Rp.
17,669,191 from management calculations. Working
capital loan customers are customers who are in high
cost to serve, because it requires a greater activity cost
to process a loan application.
The investment is overcosted quite large, which is
Rp. 22,382,847 from management calculations,
which is why it is necessary to maximize the loan for
investment loan customers.
Consumption loan customers have undercosted
not too large because this customer segment is the
smallest customer segment of PT. BPR Cincin
Permata Andalas. However, consumption loan should
also be maximized because they have the potential to
provide greater profits.
Based on the activity of the lending process of PT.
BPR Cincin Permata Andalas which was developed
through the ABC system, it can be concluded that the
activities carried out mainly in the field are activities
that generate considerable costs, namely marketing,
reviewing or surveying, monitoring loan customers,
and handling non-performing loans or bad loan. BPR
Cincin Permata Andalas can encourage AOs to work
more efficiently in conducting loan assessments in the
field without ignoring the principle of prudence.
PT. BPR Cincin Permata Andalas held an
additional number of AOs, it was expected to
accelerate the loan assessment process. The
application of ABC can identify which non value
added activities and value added. To get around
undercosted and overcosted, this research suggests
reviewing the duties, functions, and authority of each
employee's work.
The ABC system implementation provides an
overview for PT. BPR Cincin Permata Andalas that
there are costs that should be charged more to
customers.
One of the strategy is to charge these costs to
customers with provision fees and administrative
costs and service fees on the loan process, while
collateral valuation by considering high cost of goods
sold to reduce the loan risk that will occur. Therefore,
the ABC system is recommended for its application
to the loan department of PT. BPR Cincin Permata
Andalas to produce more reliable cost information.
5 RESULTS
The calculation of overhead costs carried out by PT.
BPR Cincin Permata Andalas does not reflect actual
cost information. The development of ABC system
shows that working capital loans and consumption
loans are undercosted while investment loan is
overcosted. ABC system provides an overview to PT.
BPR Cincin Permata Andalas for customers who are
Implementation Proposal of Activity based Costing on the Loans Department: A Case Study in PT. BPR Cincin Permata Andalas
989

high cost to serve and low cost to serve in processing
loan
The cost of marketing activities can be reduced by
reducing marketing activities in the field by utilizing
technology such as social media.
The cost for BI Checking can be reduced by
utilizing the latest technology managed by Bank
Indonesia, namely SLIK, which requires a shorter
check time.
The results of ABC development at PT. BPR
Cincin Permata Andalas can find out the costs that
should be charged more to customers by increasing
fees and administration fees.
6 CONCLUSIONS
PT. BPR Cincin Permata Andalas has problems with
the cost allocation system, where the cost allocation
system that has been implementedto date has not been
able to provide accurate financial information in
decision making. Costs should be measured precisely
to avoid wrong decisions that can affect the level of
profit on the bank latter.
PT. BPR Cincin Permata Andalas has not
calculated in detail the use of fees for the process of
granting a loan. This research was conducted to
provide a solution to the obstacles faced by PT. BPR
Cincin Permata Andalas by developing the ABC
system to allocate costs to operational expenses
related to the loan process as of it is expected to be
able to produce accurate cost information.
The results of the ABC system development in
calculating overhead costs for loan processing,
provide information on the rate of fees consumed by
each service activity provided to customers..
Compared to the cost calculation carried out by PT.
BPR Cincin Permata Andalas, that the ABC system is
considered capable to provide information on
charging fees to customers so that customers that are
more profitable and unprofitable can be identified.
The results of the development of ABC can be
used to measure the performance of employees at PT.
BPR Cincin Permata Andalas so the effectiveness and
efficiency in serving loan can be maximized.
REFERENCES
Blocher, Edward, and Paul Juras David Stout. (2012). Cost
Management: A Strategic Emphasis. 6th Edition. New
York: McGraw-Hill Education.
Blocher, Edward J., Stout, David E., & Cokins, Gary.
(2010). Cost management: A strategic emphasis (5
th
ed). Singapore: McGraw-Hill Education
Cooper, R., dan Robert S. Kaplan. (1999). Edisi 2. The
Design of Cost Management Systems. New Jersey:
Prentince-Hall, Inc.
Hansen, Don R., and Mowen, Maryanne M. (2015)
Cornerstones of Cost Management Third Edition.
South-Western: Cengange Learning
Horngren, C. T., Datar., S. M., & Rajan., a. M. (2012). Cost
Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis. Essex: Education
Limited.
Horngren, Charles T, Srikant M Datar, and Madhav V
Rajan. (2015). Cost Accounting : A Managerial
Emphasis. Boston: Pearson Hall.
Marvianti, S. (2013). Analisis Penerapan Activity Based
Costing terhadap Customer Profitability pada PT. X.
Moleong, L. J (2015). Metodologi Penelitian Kualitatif.
Cetakan 24. Jakarta. PT. Remaja Perkasa
Stout, David E., dan Joseph M. Propri. (2011)
“Implementing Time-driven Activity-based Costing at
a Medium-sized Electronics Company”, Management
Accounting Quarterly, Spring, Vol. 12 No. 3.
Raaij, E. M. (2005). “The Strategic Value of Customer
Profitability Analysis”. Marketing Intelligence
Planning, Vol. 23 Iss 4 , 372-381
Undang-Undang No. 10 Tahun 1998 tentang Perbankan
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
990
