
The Development of Mind-Mapping-Based Textbook for Assessment
and Evaluation Subject
Charles Fransiscus Ambarita
1
, Rotua Sahat P. Simanullang
1
and Choms Gary G. T. Sibarani
1
1
Faculty of Economics, Universitas Negeri Medan, Medan -Indonesia
Keywords: Mind Mapping, Textbook, Development, Assessment and Evaluation
Abstract: This study aims to develop Textbook in assessment and evaluation courses by implementing mind mapping
as a stimulus for constructing student knowledge. Mind mapping is seen as being able to provide a big
picture of a conceptual framework with various linkages with other pieces of knowledge so that it can
describe the full construction of knowledge systematically. It is important considering that evaluation and
evaluation are systemic parts of teaching and learning activities that will be conducted by prospective
teachers in the classroom. The result shows that the Textbook which developed had a good value of validity,
practicality, and effectiveness. It can be observed from the expert appraisal and student responses. Further
improvements that are concerned in this study are linguistic reviews. The results of this study can be a
reference for lecturers to use mind-mapping in constructing a conceptual framework of Textbook.
Furthermore, the results of this study will be further tested at the disseminate stage to ensure general
acceptance of teacher education students.
1 INTRODUCTION
The State University of Medan is one of the Teacher
Education Institutions which produces qualified
teachers over the years. Furthermore, the Faculty of
Economics as an integral part of Unimed contributed
to the success of Unimed's mission to answer
challenges, opportunities, community demands, and
prepare competitive teachers. To solve these
challenges, the development of learning needs to be
a concern especially in developing learning to
improve the mastery of Learning Outcomes.
Based on pre-study observations, the student has
a constraint to mastery the framework of assessment
and evaluation courses because of the lack of
literature or references of assessment and evaluation
which available at the library. Students are only
guided by the dictates or module that have been used
by lecturers without any other learning resources. To
address this problem, efforts are needed to optimize
the development of learning media, especially the
development of textbooks as the instructional
material. One of the optimization efforts that can be
done is by developing mind map-based textbook.
This method is considered adequate to help the
student in mastering Learning Outcomes in
assessment and evaluation courses. Mind maps are
designed to enable students to map all knowledge
comprehensively. Mind maps are one of the easiest
ways to put information into the brain and take
information out of the brain.
Mind maps can help students learn to compile
and store as much information as they want and how
to classify it naturally, that is, by giving easy and
direct access to something desired. With various
advantages, mind maps are predicted to facilitate
students in mastering the Learning Outcomes
Evaluation material. Based on the above reality, it is
essential to develop a mind map based textbook
among students in the Faculty of Economics
Unimed. Textbooks are developed using language
that is simple and easily understood by students, and
equipped with colorful images that can attract
students' attention. This textbook is different from
other books that are developed with a mind map and
are expected to provide solutions for students who
have difficulty mastering assessment and evaluation.
Therefore this study aims to 1) Describe the process
of developing mind map-based textbooks for
assessment and evaluation courses; 2) Assessing the
validity and practicality of the textbooks.
Ambarita, C., Simanullang, R. and Sibarani, C.
The Development of Mind-Mapping-Based Textbook for Assessment and Evaluation Subject.
DOI: 10.5220/0009498001750180
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 175-180
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
175

This study will contribute in 1) producing a mind
map-based assessment and evaluation textbook
which can facilitate students to mastering the
assessment and evaluation material; 2) adding a
reference for other lecturers to improve the quality
of learning; 3) produce comparison material to solve
specific problems in instructional activity.
2 THEORICAL FRAMEWORK
Teaching materials placed a critical position in
achieving learning goals. It is in line with the
opinion of Prastowo (2015) which states "teaching
materials are all materials (both information, tools,
and texts) that are arranged systematically and
displays the complete figure of the competencies
that students will master and use in the learning
process with the aim planning and reviewing
learning implementation.
Textbooks consist of knowledge, skills, and
attitudes that students must learn which are
systematically arranged so that accumulatively can
achieve predetermined learning outcomes. The
teaching standard functions for lecturers are to direct
student activities in the learning process as well as
the substance must be explained to students, while
for students, teaching material serves as a guide in
the learning process and is a learning achievement
that must be achieved.
Prastowo (2015), argues that according to its
form, teaching materials can be divided into four
types, namely (1) printed documents, namely some
teaching materials prepared in the paper, which can
function for learning or information delivery.
Example: handouts, books, modules, worksheets,
brochures, leaflets, wall charts, photos/drawings,
methods, and models; (2) hearing teaching materials
or audio programs are all systems that use a direct
radio system that can be played or heard by a person
or group of people. Examples of cassettes, radios,
LPs and audio compact disks; (3) hearing teaching
material is anything that allows audio light to be
combined with moving images sequentially.
Examples of videos and films; and (4) interactive
teaching materials namely a combination of two or
more media (audio, text, graphics, images,
animation, and video) which the user manipulated or
treated to control command and or natural behavior
of the presentation. For examples on the interactive
compact disks.
Textbooks are the development of instructional
designs that emphasize the principles adopted from
the theory and findings of research on learning. The
orientation of teaching materials is to optimize
learning activities to achieve learning outcomes.
Therefore, teaching materials must be able to present
learning material that is meaningful for students as
subjects who are learning.
According to BSNP (2007), the feasibility of
textbooks can be observed by four dimensions,
namely: (1) the usefulness of the content means that
a good textbook should contain material that
supports learning achievement and has indicators
namely the breadth of material, depth of material,
completeness of material, and accuracy of content;
(2) presentation feasibility means that the
presentation of textbooks can be assessed from
several sub-components and/or indicators such as
presentation techniques, supporting presentation,
consistency of performance, and presentation of
learning materials; (3) language feasibility means
that textbooks are written with rules and terminology
that are correct, clear, and in accordance with the
development conditions of the readers. The indicator
is the use of proper and correct Indonesian language
rules, following the improved spelling rules,
terminology in accordance with the concepts that are
the subject, the explanation for difficult or
uncommon terminology, the language used is
simple, straightforward and easy to understand by
students, and the language is adjusted with the stages
of student development and communicative and
developing students' thinking skills; and (4) the
feasibility of graphics implies that textbooks can be
seen from the aspect of book size, book skin design,
and book content design.
In the preparation of textbooks, there are
principles that must be considered, namely (1) the
principle of relevance is the learning material should
be relevant which means that there is a relationship
between learning outcomes as an embodiment of the
curriculum. At learning outcomes implied concepts
that must be taught and the characteristics of the
idea; (2) the principle of consistency, namely the
conformity between learning outcomes that students
must master with textbooks, (3) the principle of
sufficiency, namely the material taught should be
sufficient enough to help students to master the
learning outcomes explained.
Evaluation and Assessment Courses
Assessment and evaluation are courses in semester
5th and should be given to all students at Unimed
including at the Faculty of Economics. The primary
consideration of the distribution of courses in the
Indonesian Qualification Framework (IQF) includes
courses on assessment and evaluation in semester
5th so that students as prospective teachers are
equipped with knowledge on how to provide an
assessment and evaluation at the end of learning
with a thorough understanding.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
176

The course of assessment and evaluation is an
educational subject in a graduate education program
with a weight of 3 credits. The discussion of
assessment and evaluation courses covers the basic
concepts of testing, measuring, evaluating, and
evaluating. The next chapter discusses the principles
and strategies for assessing learning outcomes, then
presents the assessment parameters, techniques for
preparing and evaluating learning outcomes,
processing techniques, and final grades, and at the
end of the discussion about proper test requirements.
Mind Mapping
Mindmap was first discovered by Tony Buzan in the
1970s. This technique is known as Radiant
Thinking. A mindmap has a central idea or central
image; there are 5 to 10 other ideas that come out of
the central idea. According to Buzan (2009), the
mindmap is a powerful graphic technique that
provides a universal key to unlocking the full
potential of the human brain so that it can use all the
capabilities in both hemispheres of the brain such as
words, images, numbers, logic, rhythm, color in a
unique way.
Using mind maps means using concepts
contained in the brain, formed in such a way with
interesting and colorful ideas. The results of the
concepts created in the form of mind maps will help
students to assemble thoughts into an interesting
discourse. So, this mindmap helps to conceptualize
existing knowledge. Dryden (2013) argues as a
substitute for making a linear note making mind
maps based on several principles, namely (a) the
central theme printed in the middle; (b) there are
main branches in each sub-theme; (c) single words
are used for each concept; and (d) if possible each
idea has an image. The principle of making a mind
map is a way that can be done to help create their
concepts on a topic.
DePorter and Hernacki (2012: 157), the steps to
make a mind map are as follows. (1) make a circle in
which there is the main idea in the middle of hard;
(2) from the ring add a branch for each key point; (3)
write keywords for each chapter; (4) add symbols or
illustrations; (5) use capital letters; (6) essential
ideas are written in capital letters; (7) turn on the
mind map by highlighting the words were written;
(8) be creative; (9) use random forms and make
mind maps horizontally; (10) use images in each
part of the mind map.
Mind Mapping and The Development of
Teaching Material
Assessment and evaluation courses are important
courses that must be mastered by the teacher.
Knowledge and understanding of the correct
lecturers about the characteristics of the material
Assessment and evaluation will guide the lecturer to
make the right textbook for students. The right
textbook will produce meaningful and quality
learning so that the transfer of knowledge carried out
by the lecturer can run optimally and the learning
objectives can be achieved.
Learning Assessment and evaluation using
mindmap methods can be done by lecturers by
helping to create a pleasant classroom atmosphere,
giving students the freedom to actively and
creatively explore, discuss with fellow friends and
teachers so that students practice expressing
opinions, statements and questions. In that learning,
the lecturer also provides media that can support
learning in the form of books/articles, markers or
colored pencils.
The use of images and colors applied to this
method will have a positive impact that can activate
creativity and memory. The reason why picture
language is used to compose, develop and remember
is that the brain has natural abilities for visual
recognition. It is why many mind maps use images
as a presentation because they are believed to help
retain information.
Learning process in this Assessment and
evaluation course, students begin their learning with
the introduction of the concept of mind maps, their
functions, and benefits. From the introduction stage,
the students then discuss and then get the motivation
from the lecturer to complete the task, namely
making a book summary with the mind map method.
Students create mind maps in advance to make it
easier for students to focus on the subject matter.
Students get special attention in choosing images
and giving color to mind maps. Based on the mind
map created, the student continues at the stage of
making a book summary. Students will get special
attention when students feel difficulties in
completing tasks.
The number of words or length of a book
summary must also be considered so that the
original work and review are different. Making
outlines is best done after carefully reading certain
parts to be summarized. Taking the essence of
reading can save words or sentences in summary.
And this can distinguish between original works and
summary results.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This study uses the 4D (four-D models) model. 4D
models are implemented with four main stages,
namely: 1) define, 2) design, 3) develop, and 4)
disseminate (Thiagarajan, Semmel, & Semmel,
1974). In this research, it is only done until the
The Development of Mind-Mapping-Based Textbook for Assessment and Evaluation Subject
177

develop stage. In the define phase, researchers
conduct a needs analysis related to the objectives of
the course in the curriculum, conceptual analysis,
and analysis of student characteristics. Curriculum
analysis is carried out by analyzing the suitability of
learning outcomes based on the IQF. The theoretical
study aims to develop the Textbooks based on the
main concepts of topic Assessment and evaluation.
While the analysis of student characteristics to find
out the characteristics of students includes age,
motivation, knowledge, and skills tendencies.
Furthermore, at the design stage (construction)
Textbook construction refers to various criteria that
have been obtained in previous times. Textbooks
that are developed will integrate multiple mind
mapping charts. This serves to strengthen the
conceptual framework that students must
understand. Thus students will have a big picture of
the concept of assessment and evaluation they
learned.
Finally, at the develop stage, expert appraisal and
initial developmental testing are carried out. Expert
appraisal serves to test whether the developed
teaching material meets the content standards, while
the initial development testing serves to verify the
acceptance of the instructional material that has been
formed in a limited sample so that feedback is
known regarding the effectiveness of Textbooks
from its target trainees (Thiagarajan, Semmel, &
Semmel, 1974).
4 RESULT
This research has successfully developed a prototype
1 of Textbooks for assessment and evaluation
courses. Textbooks are developed using mind
mapping as a form of novelty rather than books in
general. Integrating mind mapping in Textbooks can
stimulate students to get the full concept of
assessment and evaluation material.
In the define phase, there is 1) adjusting learning
objectives based on research findings and the
Indonesian national qualification framework so that
standardized learning outcomes are achieved in
accordance with the development of global
knowledge and national education goals; 2)
Development of a conceptual framework related to
Textbooks in accordance with scientific literature
and the results of the latest research so as to obtain
generally accepted material standards; 3) Analysis of
student characteristics so that the delivery style of
the material in the Textbooks is developed so that
students can easily digest it into a comprehensive
understanding.
The define phase has produced the initial
framework for the development of Textbooks. The
structure is then used as the basis for the design
process. The design process through a series of
Textbooks development processes to become a draft.
The components that become concentrated in the
design stage are the suitability of the format and
systematic delivery of the material with the stages of
achieving the learning objectives, the suitability of
the content with learning achievement, the
readability of the language used, the suitability of
the delivery model and strategy of the material with
the characteristics and needs of students, the truth
and completeness of the material content, suitability
of mind mapping that is presented with learning
objectives, and suitability of questions or bills with
learning objectives. Assessment of these indicators
is then carried out in the next stage, namely,
develop. The developing phase is the actual
development stage because there is a scientific
process in it. The output of the scientific method is
the improvement and refinement of the draft (results
from the design stage) to prototype one which is
ready to be disseminated. The scientific process is
the expert appraisal and initial development testing
(Thiagarajan, Semmel, & Semmel, 1974).
To guarantee the validity of the draft Textbooks
that have been designed, validation is assessed by
expert opinion. The expert appraisal is carried out by
evaluation and assessment experts and curriculum
experts at Medan State University. The expert
appraisal process produces several recommendations
for improvement. Quantitatively the results of the
expert appraisal are described in table 1 below.
Furthermore, after an increase based on the expert
appraisal, initial development testing is also carried
out. Initial development testing is done by reviewing
student responses as target users of the textbook.
Initial development testing was carried out on a
limited sample of 36 people who joined in one class.
Initial development testing is used as a basis for
improvement to achieve acceptable Textbooks in the
population. This process is not to guarantee
acceptance but to get an overview of student
expectations so that further approval can be tested at
the dissemination stage. Student responses in limited
samples are used as references for further
improvements to the expectations of Textbooks that
are suitable for student characteristics. So that, the
output from this development stage is the prototype I
which must then be re-tested for its acceptance in the
dissemination stage to get prototype 2. The results of
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
178
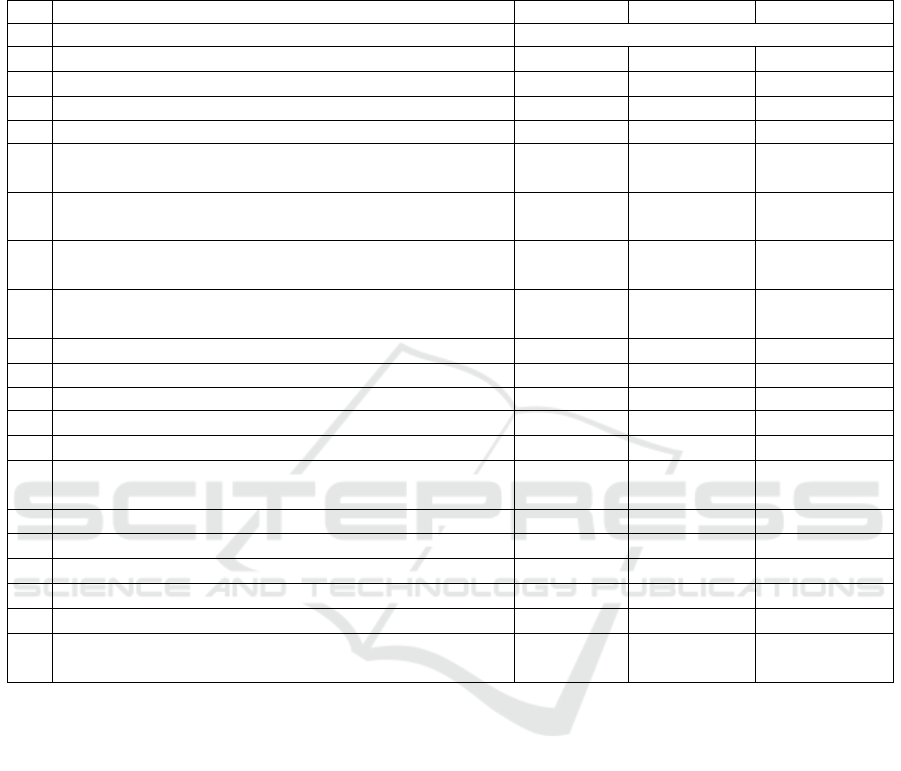
the initial development testing are also summarized
in Table 1 below.
Table 1: Expert Appraisal and Initial Development Testing
No
Aspect
Expert 1
Expert 2
Students
1
Format
Score
a. Clarity in the distribution of material
4
4
4.35
b. Layout setting
4
3
4.15
c. Suitable type and font size
4
4
4.35
2
Language
a. The materials are delivered with straightforward and
simple sentences
4
3
4.43
b. The materials are delivered with communicative and
interactive sentences
3
3
4.15
c. Spelling is delivered with acceptable structure and
grammar in Bahasa Indonesia
4
4
4.15
d. Spelling is using the sentences which following
Indonesian Language Rules
4
4
4.15
e. using effective sentences
4
3
4.63
f. using efficient sentences
3
3
4.35
3
Content
a. The truth of the material
5
5
4.86
b. Material and competence adequacy
4
4
4.86
c. Suitability with learning objectives and learning
outcomes
4
5
5
d. Suitability with problem-based learning
3
4
4.46
e. Suitability of mind mapping
4
4
4.86
f. Feasibility and completeness of resources
4
4
4.66
g. Suitability of content regarding allocation of time
3
4
4.86
h. Suitability of material to stakeholders' needs
3
3
4.86
i. Compatibility of assignment and evaluation tests with
the learning objective and learning outcomes
4
5
4.93
The results of expert appraisal and initial
development testing indicate that some minor
improvements to the Textbook have been made.
Generally, improvements that need to be made on
the aspect of legibility and selection of sentences
that are effective and efficient. The development
will then be consulted with linguistic experts to
produce sentences that have good readability so that
they are easily understood by students and following
the Indonesian language rules. Furthermore,
improvements are concentrated on the suitability of
the material weight with the available time
allocation. Submission of teaching material is ideally
by the credit weight possible for the course, namely
assessment and evaluation. Therefore the extraction
of the material is adjusted again referring to the key
elements to achieve the learning objectives. Finally,
improvements are concentrated on the suitability of
the content with the needs of stakeholders. This
aspect does have its difficulties because of the broad
scope of assessment and evaluation material and the
specificity of stakeholder needs. So that, the
extraction of material previously carried out must
still pay attention to the specificities of stakeholder
needs. So improvements are focused on clarifying
the practical implications of the evaluation concepts
that are taught so that they are following the
functional requirements of the evaluation and
assessment of stakeholders.
Furthermore, limited testing of students on
Textbooks that have been improved based on expert
opinion has a reasonably good response. With a
mean response above 4 with a scale of 5 indicates
that Textbooks has a reasonably good level of
acceptability. Student recommendations based on
the results of the draft still refer to readability/easy
to read level and the use of sentences in Textbooks.
So that the improvement by involving linguistic
experts is a step that will be done next before
dissemination.
The Development of Mind-Mapping-Based Textbook for Assessment and Evaluation Subject
179

5 CONCLUSION
According to the results of the research and
discussion above, this study produces several
conclusions as follows:
1. This study has successfully developed
Textbooks in the form of mind mapping based
assessment and evaluation courses.
2. Mind mapping-based textbooks developed in
this study have been through the process of
expert appraisal and initial development testing.
3. The concentration of further improvements is
focused on linguistic aspects
4. The next step that must be done from the results
of this research is dissemination includes 1)
summative test; 2) final packaging; and 3)
diffusion (see: (Thiagarajan, Semmel, &
Semmel, 1974).
Based on the above conclusions, this study
produces the following recommendations.
1. This study has practical suggestions for
educators on instructional design updates on
assessment and evaluation lessons that are
oriented to the use of mind mapping. The use of
mind mapping in the delivery of learning
material can provide a complete picture to
students regarding the conceptual framework to
be taught. The big picture conveyed in mind
mapping will stimulate students to fully
understand the concept of assessment and
evaluation to avoid missing links between
theory and practice.
2. For stakeholders, can review the Textbook that
has been developed, re-validated, and further
developed so that it can be generally accepted
and used in a standard manner both at the study
and faculty level.
3. For further research can empirically test the
implementation of the Textbook that has been
developed, empirical testing is critical to get
evidence of the performance of the Textbook. In
the research phase of developing Thiagarajan,
Semmel, & Semmel (1974) Textbook, this stage
is incorporated in the disseminated stage. This
stage will ensure the feasibility of the Textbook
developed by 1) summative test; 2) final
packaging, and 3) diffusion.
The limitation of this research lies in the stages
of research that are still reaching the stage of
developing. The limitations of achievement are due
to limited costs and time. The next stage will be
carried out by the researcher as further research. So
that, the further research will be a series of
continuous research in a research roadmap.
REFERENCES
Badan Standar Nasional Pendidikan. (2007). Standar
Penilaian Bahan Ajar. Jakarta: Badan Standar
Nasional Pendidikan.
Buzan, Tony. (2009). Buku Pintar Mind Map. Jakarta:
Gramedia Putaka Utama.
De Porter, Bobbi dan Hernacki. (2002). Quantum
Learning: Membiasakan Belajar Nyaman Dan
Menyenangkan. Bandung: Kayfa
Dryden, G. (2013). Revolusi Cara Belajar. Bandung:
Kayfa.
Lubis, Mina Syanti. (2015). Pengembangan Modul
Pembelajaran Bahasa Indonesia Berbantuan Peta
Pikiran Pada Materi Menulis Makalah Siswa Kelas
XI SMA/MA. Jurnal Bahasa, Sastra dan
Pembelajaran, 2(1): 16-27.
Manalu, Pienti Mala Ningsih. (2018). Pengembangan
Bahan Ajar Menulis Teks Eksplanasi Berbasis Peta
Pikiran Pada Siswa Kelas XI SMA Negeri 5 Medan.
Medan: Program Pasca Sarjana Unimed
Prastowo, Andi. (2015). Panduan Kreatif Membuat Bahan
Ajar Inovatif. Jogjakarta: Diva Press.
Sugiyono. (2013). Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif,
Kualitatif, dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Thiagarajan, S.; Semmel, Dhoroty S.; & Semmel, Melvin
I. (1974). Instructional development for training
teachers of exceptional children: A sourcebook.
Center for Innovation in Teaching the Handicapped,
Indiana University, Bloomington, Indiana
Trianto. (2012). Mendesain Model Pembelajaran Inovatis-
Progresif. Jakarta: Kencana.
…….... (2014). Pengantar Pendidikan Bagi
Pengembangan Profesi Pendidikan dan Tenaga
Kependidikan. Jakarta: Kencana Prenada Media
Grup.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
180
