
The Way to Millenial Learning
Eduward Situmorang
1
, Swara Kasih Kartini
1
, Nurul Shadrina Bintang
1
,Ummi Chairani
1
and Opy
Triansyah
1
1
Postgraduate Student Education of Economy, Universitas Negeri Medan, Medan -Indonesia
Keywords: Technology, Learning, Blended Learning
Abstract: This era is known as the 4.0 industrial revolution era where all sectors are in digital. This millennial age
must also be shown in millennial learning to improve the quality of learning. In terms of, the use of
technology in the world of education, namely the learning system has changed the conventional pattern
learning system or traditional pattern into a modern pattern of Information and Communication Technology
(ICT) media. The approach that can be done in millennial learning is the one that can integrate technology
and education, namely the Blended Learning Model (BLM). This model combines regular teaching classes
and online teaching. The strength of this model is that it can increase interaction between students whenever
and wherever.
1 INTRODUCTION
The education, trade, and government sectors are
changing due to the development of information and
communication technology. At this time the
globalization era cannot be denied that along with
the development of digital application-based
technology, the system of social interaction in
society began to erode. Technology is increasingly
fast, making it easier for people to do their activities.
Today's technological and information developments
offer many conveniences. Communities are given
supporting facilities in their daily activities. Making
it easier for people to move. With easy access to
communication, it supports the education world. The
application of communication and information
technology in the world of education is mandatory.
The reason is, now every school and other academic
institutions have used technology to support their
activities.
Globalization has penetrated the present
generation. Globalization also causes a shift in the
education world that was initially in the face-to-face
system began to lead to online systems. With the
inclusion of globalization in the world of education,
the interaction between humans has shifted and
without denying that it will be lost.
In the era of globalization-based on digital
applications in the education world, it will help the
course of the learning process and can also improve
performance results. The increasing number of
technology users in the education world will lead to
changes in the learning model. Because it is more
effective and efficient, without requiring a lot of
time and energy. So that gradually people will prefer
an online learning system than conventional (face-
to-face) learning.
The development of various learning media is in
line with the rapid technological advancements. The
technological dynamics are now achieving
tremendous acceleration. New technologies
including conventional learning have replaced the
technology that has been studied a few years ago.
The learning model provided in technology for the
world of education is considered quite useful.
Distance learning between teachers and students
who are not in one place or long distance
relationships. Moreover, technology also provides
many other learning options that can be enjoyed by
the public very quickly. Now we are also feeling the
ease of learning just by accessing digital applications
such as e-journal, e-library and so on.
One learning model that has been applied by
several communities is the E-learning model. E-
learning is a form of learning model that is
facilitated and supported by the use of information
and communication technology. The term E-learning
is more precisely intended as an effort to make a
362
Situmorang, E., Putri, S., Bintang, N., Chairani, U. and Triansyah, O.
The Way to Millenial Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0009496803620366
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 362-366
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

transformation of the learning process in schools or
colleges into digital forms bridged by internet
technology. (Munir, 2009: 169).
In Indonesia, the conventional education system
is still widely practiced in the academic community.
Especially in the area that is still classified as a rural
area. Because overseas country such as France has
also used online education services, this is evidence
of a shift in the direction of education. Especially
now, today that demands significant changes in the
world of education. Where education is used as a
benchmark in a society. So education is what has
broad knowledge to transfer knowledge.
The millennial generation born in the early 1980s
to 2000 or can be said as Gen Y. They called the
millennial generation because of the generation that
lived at the turn of the millennium. Along with the
penetration of digital technology into all walks of
life. Digital technology that has become a basic need
for this generation. In the millennial generation, that
is the generation that has been literate in digital
technology, where every information is easily
accessed via the internet.
However, many people view that there has been
a shift in the eastern social values. Because it is
more open-minded, it is easy to adopt more modern
western social values. It is true. This thing is can be
seen clearly in our lives. Many teenagers start to
look like westerners, so their social life is
increasingly eroded.
Long-distance communication relationships are
only connected by the media and the internet.
Making close communication or direct
communication is increasingly rare. So, the social
value that takes place in the communication fades.
Teenagers are vulnerable to talking to each other
directly they choose to use internet media as a way
of communication. If this is done more aggressively,
gradually the real world regarding interaction will
fade.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Definition of Blended Learning
Millennial learning can be done not only by face to
face activity but can be carried out in combination
between face to face and online learning which is
often referred to as Blended Learning. Kaye Throne
(2003: 16) in his book entitled "Blended Learning:
How to Integrate Online and Traditional Learning"
states that:
“Blended learning is the most logical and natural
evolution of our learning agenda. It suggests an
elegant solution to the challenges of tailoring
learning and development to the needs of
individuals. It represents an opportunity to integrate
the innovative and technological advances offered
by online learning with the interaction and
participation offered in the best of traditional
learning. It can be supported and enhanced by using
the wisdom and one-to-one contact of personal
coaches.”
Blended Learning is a logical and natural
learning change. It proposes a good change solution
to adjust and develop learning according to
individual needs. This is demonstrated by the
opportunity to integrate innovation and technology
provided through online learning with the interaction
and participation that occurs in traditional learning.
It can be supported by using wisdom and training
slowly.
Blended Learning is a mixture of:
1. Multimedia technology
2. Learning video CD ROM
3. Virtual class
4. Email and telephone
5. Animated text and online video
Driscoll (2002) suggests that there are four
concepts about Blended Learning, namely:
a. Blended learning is learning that combines
various web-based technologies, to achieve
educational goals.
b. Blended learning is a combination of various
learning approaches (such as behaviorism,
constructivism, cognitivism) to produce an
optimal learning achievement with or without
learning technology.
c. Blended learning is also a combination of many
learning technology formats, such as videotape,
CD-ROM, web-based training, film) with face-
to-face learning.
d. Blended learning combines learning technology
with actual work task commands to create a
good influence on learning and work.
From these definitions, it can be concluded that
millennial learning that is applied through Blended
Learning is learning that combines face-to-face
learning and online learning with the aim to further
improve the quality of learning to achieve
instructional goals.
Digital Development Model in the Education
Sector
The ICT integration model that can be described as
shown below has two dimensions: technology and
pedagogy.
1. Technology refers to all information and
communication technology (ICT), the
technology dimension is a continuum that
represents the number of increasingly/diverse
use of ICT
The Way to Millenial Learning
363
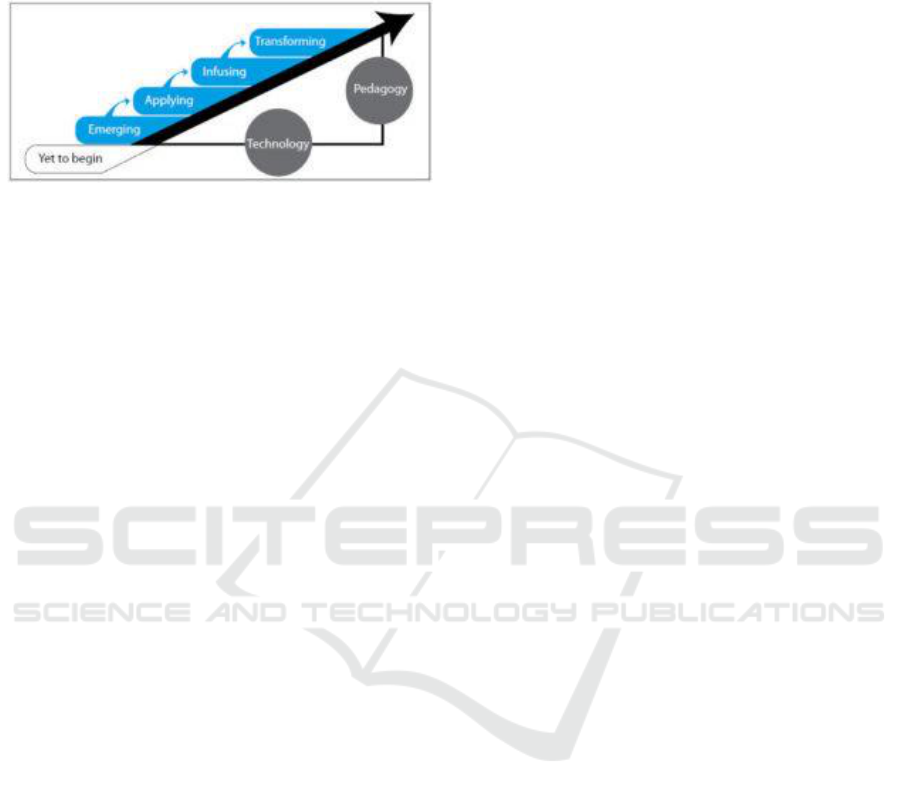
2. Pedagogy is the art and science of teaching. The
pedagogical dimension is also a continuum and
represents changes in teaching practice resulting
from the application of ICT.
Figure 1: Dimensions of Technology Interaction
In these two dimensions, there are four stages of
the integration model of ICT development in the
education and school systems. These four stages are
continuum stages, which UNESCO termed as
Emerging, Applying, Infusing and Transforming.
1. The Emerging Stage is characterized by the use
of ICT in the school at the initial stage. In the
Emerging stage, classroom practice is still very
teacher-centered.
2. The Applying stage is characterized by an
understanding of the contribution and efforts to
implement ICT in the context of school
management and learning. Schools have also
tried to adapt the curriculum so that they can
use ICT more in various subjects with specific
software.
3. The Infusing Stage requires an effort to
integrate and incorporate ICT into the
curriculum. In this approach, schools have
implemented computer-based technology in
laboratories, classes, and administration
departments. The curriculum begins to combine
learning subjects that reflect real-world
applications.
4. The Transforming Stage is characterized by the
school's efforts to plan and renew its
organization more creatively. To conclude,
when the transformation stage is achieved, the
entire ethos of the institution changes: teachers
and other support staff consider ICT as a natural
part of their institution's daily life, which has
become a center of learning for the community.
Therefore, it can be said that increasingly crowded
human mobility and the birth of new technologies, is
the background of the birth of a blended learning
model as a new innovation in answering the
challenges of times.
3 DISCUSSION
In designing Blended Learning, the accuracy of
choosing a combination of delivery media both in
traditional and online learning settings is important
because the focus is optimal learning. Also, Khan
stated that blended learning includes a combination
of various activities including face to face in class,
live e-learning, and independent learning. All of
them are a combination of traditional education
(guided by the teacher/lecturer), synchronous online
learning, asynchronous self-learning and structured
learning based on the experience of the learner and
mentor (Khan, 2005, p. 202). Howard explained that
blended learning is a term introduced by distance
learning communities as an effort to utilize
synchronous learning activities, such as face-to-face
interaction with instructors and collaborative work
with peers as an asynchronous learning activity
complement that is carried out individually by
learning participants (Howard, et al., 2006, p. 1). In
essence, blended learning can be said to be a
combination of synchronous learning that occurs at
the same time and asynchronous learning that
happens at different times and places.
Synchronous type of face to face or synchronous
face physically coincides at the same time in the
same place. Examples are face-to-face learning in
class, laboratory research, field trips, class
presentations and group discussions, and all other
traditional learning methods. The second type is
synchronous online), or also called synchronous
virtual collaboration such as audio/video
conferencing, chatting, live online learning, instant
messaging and others (Staley, 2007).
While asynchronous learning is a learning
activity that allows different learners to experience
the same teaching material at different times and
places. Staley classifies asynchronous learning
activities into two categories, namely asynchronous
collaborative (such as online discussion forums.
Mailinglist, e-mail, etc.) and independent
asynchronous (such as simulations, online tests,
searching material, material in the form of pdf, doc,
HTML, video, animation, etc.) (Staley, 2007).
The concept of 4 quadrant learning settings
according to Noord cited by Staley (Staley, 2007)
and the classification of learning strategies
according to Smaldino et al. and the standard of the
learning process in the context of the e-learning
environment that the author of Horton's (2006)
adaptation. Four Learning Settings Quadrants The
four-quadrant learning settings are as illustrated in
the following diagram (Staley, 2007):
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
364
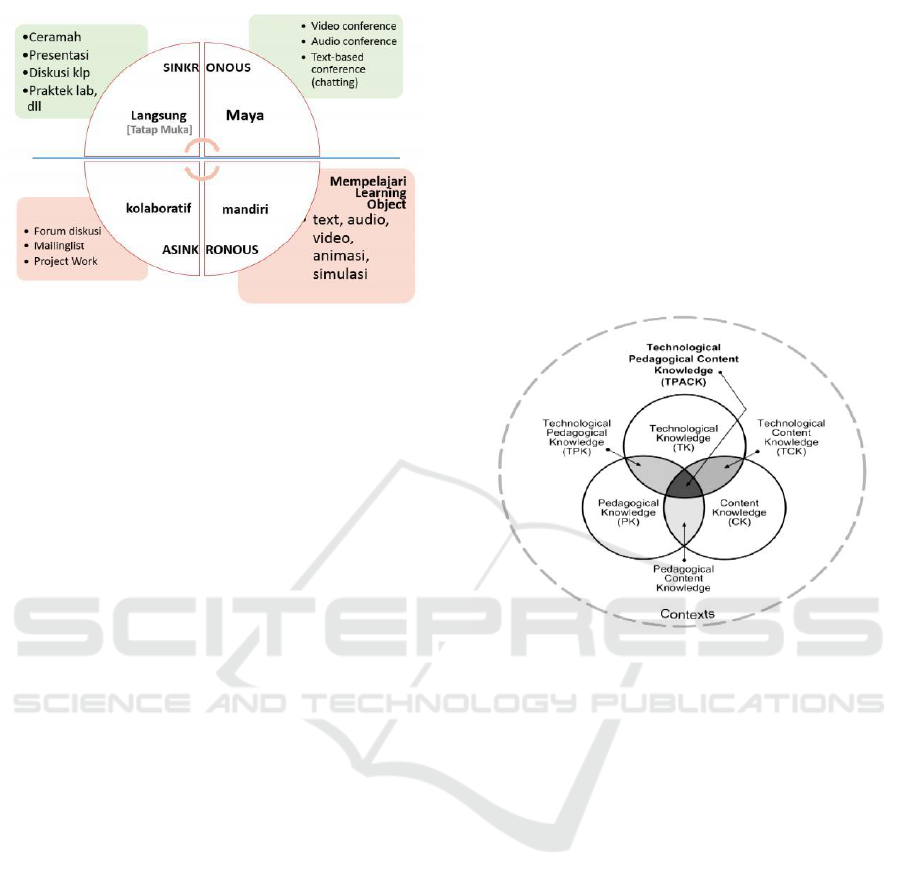
Figure 2: Kuadran Seting Belajar
Based on the diagram, it is clear that there are
four quadrant learning settings as follows:
1. Live synchronous; a condition where learning
occurs at the same time and place. Judging from
the dimensions of place and time at the same
time. Learning settings like this happen in
traditional education, where between the
learning participants and the teacher/
lecturer/tutor are in the same place and at the
same time, learning in class. Examples of
learning methods that occur in this context are
lecture, group discussions, laboratory practices,
field trips, and others.
2. Virtual synchronous; a condition where learning
occurs at the same time (real time) in a different
place from one another. In this context, learning
occurs in the same time dimension, but the
dimensions of space/place are different from
each other. Examples of learning methods that
arise in this context are presentations,
discussions, demonstrations, tutorials and others
using technology and communication tools such
as teleconference such as video-conference,
audio-conference, or maybe chatting (text-based
conference).
3. Self-paced Asynchronous; a condition in which
learning occurs independently, anytime
anywhere by the conditions and speed of their
respective learning. In this context, learning
occurs without being bound to time and place.
Its nature is more open and flexible through
independent learning methods. For self-study to
happen, the learning participants are facilitated
with digital teaching materials known as
learning objects in various media formats both
based on text, audio, video, animation,
simulation, games or a combination of these
(hypermedia)
4. Collaborative Asynchronous; a condition where
learning occurs anytime and anywhere through
a collaboration between two or more people.
Examples of learning methods that arise in this
context are discussion methods, tutorials, and
question and answer through online discussion
forums, problem-solving techniques, and
collaborative learning through online
assignments..
Besides that, Educators need to continuously
improve their knowledge and skills to teach students
in the Technological, Pedagogical, and Content
Knowledge (TPACK) framework so that they can
learn their students effectively, this TPCAK mindset
is illustrated in Figure 3.
Figure 3: TPCAK mindset
Pedagogical, and Content Knowledge / TPACK
(Source: http://tpack.org)
TPACK's framework of thought provides a way
to identify the characteristics of the knowledge
needed by educators/instructors to integrate
technology into its learning, while also being aware
of the complexities of knowledge that
educators/teachers must have in many aspects. In the
middle part of the TPACK framework, it is a
combination of three primary forms of knowledge:
knowledge of subject matter (describing what
subject matter is taught in a particular field,
including theories, processes, and practices that are
familiar); pedagogic knowledge characterized by
strategies and methods used by educators / teachers
in the classroom to teach students), and
technological knowledge that continues to evolve
and flow.
TPACK describes a critical intersection of the
three types of knowledge that educators/teachers
must possess as a place where active learning can
take place. Technology here means how
educators/instructors develop their knowledge and
technological skills to utilize online learning
resources that are available to be included in the
learning process of the subjects or courses they
The Way to Millenial Learning
365

teach. Pedagogy chosen by educators/teachers can
vary depending on the class and (students). Content
also varies, according to the guidance of each
educator/teacher.
4 CONCLUSION
Based on this conceptual discussion, the
characteristics of Blended learning are as follows:
1. Learning that combines various ways of
delivery, teaching models, learning styles, and
various technology-based media.
2. As a combination of direct teaching (face-to-
face), independent learning, and independent
learning online
3. Learning that is supported by a compelling
combination of ways of delivery, methods of
teaching and learning styles.
4. Teachers and parents of learning participants
have the same important role, teachers as
facilitators, and parents as supporters.
Blended learning is a relatively new concept in
education where instruction is delivered through a
mixture of online and traditional education that is
led by instructors or instructors in practice.
The author suggests that instructors, teachers, or
lecturers can utilize technology in carrying out
teaching and learning activities without losing face
to face activities. This can facilitate the
implementation of learning and will undoubtedly
improve the quality of Indonesian education. The
use of technology in learning can be done by
utilizing a web-based learning system that is already
available such as quipper school, edmodo, office 365
and so on. With his hopes, the quality of Indonesian
education can increase from before.
REFERENCES
Chaeruman, Anis. (2013). Merancang Blended Learning
yang membelajarakan. Seminar Nasional
Penggunaan Sumber dn Teknologi yang tepat.
Universitas Negeri Sebelas Maret.
Discoll, M. (2002). Blended Learning: Let’s Get Beyond
the Hype.
Horton, W., (2006). e-Learning by Design. San Fransisco,
CA: Pfeiffer: John Wiley & Sons, Inc..
Howard , L., Remenyi, Z. & Pap, G., (2006). Adaptive
Blended Learning Environment. Nashville, 9th
International Conference on Engineering Education,
Institute for Software Integrated Systems.
Khan, B., (2005). Managing e-Learning Strategies:
Design, Delivery, Implementation and Evaluation.
USA: Idea Group Inc. .
Munir. (2009). Pembelajaran jarak jauh ber-basis
teknologi informasi dan komu-nikasi. Bandung:
Alfabeta
Staley, L., (2007). Where Mind Meet. [Online] Available
at: http://wiki.carr.org/db/share/
onlinesupervisorwiki/Project/Archive/Examples/Ho
w/to/Blend/12475/Blended/Learning/G
uidefrom/WJ.pdf.
Thorne, K. (2003). Blended learning: How to integrate
online and traditional learning , London: Kogan
Page.
UNESCO Office in Bangkok: ICT in Education.
http://www.unescobkk.org/education/ict/
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
366
