
Does the Risk Profile, Liquidity Ratio, Good Corporate Governance and
Intellectual Capital Able to Affect the Financial Performance of Islamic
Banks in Indonesia?
Abdurrahman
1
, Ahmad Rodoni
2
and Muhammad Yusuf
3
1
University
Of Esa Unggul
2
UIN Syarif Hidayatullah
3
University Of Sahid
Keywords: Risk Profile, Liquidty Ratio, Good Corporate Governance, Intelectual Capital
Abstract: Financial performance is one consideration for investors in investing in a bank. The decline in financial
performance can affect banks in obtaining future earnings. the prospect of a bank is highly dependent on the
ability of management in managing risk, the level of liquidity, banking governance, and managing
intangible assets. The sample in this study were all Islamic commercial banks operating in Indonesia, the
observation period of this study was 2012 to 2016. The variables used were Performance measured through
the Return On Asset approach, Risk Profile measured through the Non Performance Financing ratio,
Liquidity through Capital Adequacy Ratio ratio approach, Good Corporate Governance through the IPCG
index approach, and Intellectual capital through the Value Added Capital Employed approach, Value Added
Human Capital, and Structural Capital Value Added. This study uses Multiple Regression as an analytical
tool. The results of this study indicate that only the risk profile, level of liquidity and Intellectual capital of
Value Added Capital Employed have influence while Good Corporate Governance, Intellectual capital from
Value Added Human Capital and Structural Capital Value Added have no influence over financial
performance of Islamic Banking in Indonesia.
1 INTRODUCTION
Financial performance is one of the big
cnsiderations for investors in investing in a bank.
The decline in financial performance can affect
banks in obtaining future earnings. the prospect of a
bank is highly dependent on the management's
ability to manage risk, the level of liquidity, banking
governance, and managing intangible assets.
Financial system (financial system) is a
collection of institutions. market. provisions of
legislation. law / regulations. and ways or techniques
where securities (securities) are traded. interest rates
are determined and financial services are produced
and offered to all corners of the world (A.Rose et.al
2006). Financial experts agree that in the financial
system there are seven important main functions,
namely the savings function. wealth function.
liquidity function. credit function. payment fuction
function. risk function and policy function.
Banking systems in Indonesia are the largest part
of the financial system. Its role is very strategic and
significant in accelerating national economic
growth. The interaction between the financial system
and the real sector has actually occurred in various
business cycles. Although in general the financial
system is only a derivation of the real sector but in
reality what happens is that both of them influence
each other in forming a long-term balance. The
development of the financial sector through
improving the structure and integration of financial
markets within it is certainly expected to be able to
increase the acceleration of economic activity in the
community and accelerate the turnaround of the
national economy.
The need for banks is vital because all activities
carried out by the community are always related to
money, and money is always related to the world of
banking. In Indonesia the majority of the population
is Muslims also need banking services. Started in
1992 but only fully operational in 1998 The first
Sharia Bank was operational, namely Bank
Abdurrahman, ., Rodoni, A. and Yusuf, M.
Does the Risk Profile, Liquidity Ratio, Good Corporate Governance and Intellectual Capital Able to Affect the Financial Performance of Islamic Banks in Indonesia?.
DOI: 10.5220/0009495812231228
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 1223-1228
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
1223
Mualamat, Tbk and was followed by 12 other
Islamic banks until 2018. The development of
sharia-based banks indicated that the Islamic
economy had developed in Indonesia Falikhatun and
Assegaf, 2012).
The banking business is a business of trust,
where banks must have very much Human
Resources, which have a role as intermediaries
between those who have excess funds and those who
lack funds and institutions that function to facilitate
payment flow, as well as the Sharia banking needs to
be trusted in carrying out its activities. This can be
seen from the 2016 data which states that the market
share of Islamic banking is only 5.33% of
Indonesia's national banking.
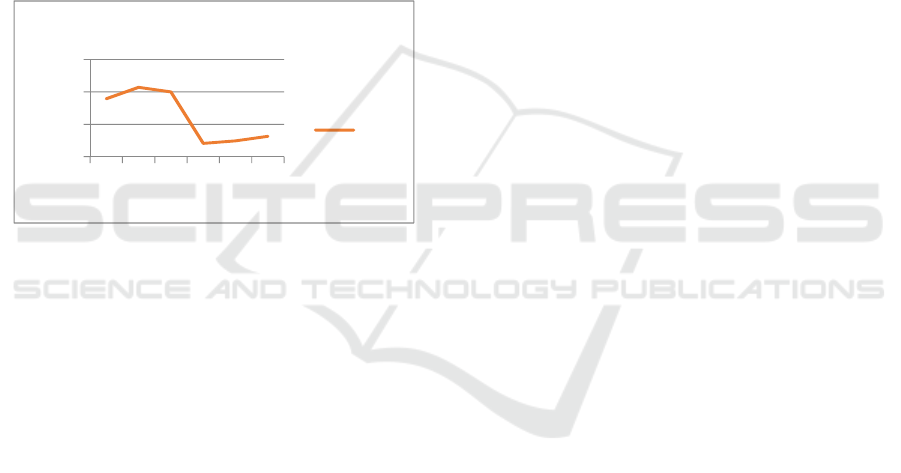
Growth and development of profitability (Return
On Asset) from 2011-2016 in Islamic banking in
Indonesia tends to fluctuate.
Figure 1: Growth and development
The future and prospects of the organization,
especially banking management, are highly
dependent on the ability of management to manage
risk, manage liquidity, and how management's
ability to increase company value. The role and
standard of Risk profile, Liquidity level, Good
Corporate Governance and Intellectual Capital are
very significant in influencing the performance of
Islamic banking so it is interesting to be investigated
further.
2 THEORICAL FRAMEWORK
The decision making role of the firm has progressed
from the neoclassical standpoint of profit
maximization to sales maximization, utility
maximization, and satisficing. From the Operation
Research point of view. The ideal picture is that
someone, presumable the firm that hires the
operations researcher, hands him, on a silver platter,
an objective function. By talking to the engineers, or
by looking into a few scientific laws, he determines
the policy alternatives available and also the model.
(Arrow, 1984).
Resource Based Theory (RBT)
Resource Based Theory is a theory that illustrates
that a company can increase its competitive
advantage by developing resources so that it can
direct the company to survive in the long term. The
key to the RBT approach is the strategy of
understanding the relationship between resources,
capabilities, competitive advantage, and profitability
in particular to be able to understand the mechanism
by maintaining competitive advantage over time.
This model requires the use of unique characteristics
of the company.
This theory was first put forward by Wernerfelt
(1984) in his work entitled "A Resource-based view
of the firm". But much of the reference research is
articles by Barney (1991) "Firm Resource and
Sustained Competitive Advantage". Firm resource
explained helps companies improve the efficiency
and effectiveness of the company's operations.
Furthermore, competitive competitiveness can be
understood by instilling an understanding that the
company consists of heterogeneous and immovable
elements. Steps to maximize competitive advantage,
companies must meet four criteria, namely valuable,
awareness, inimitability and non-substitutability.
Risk Profile
The bank's risk profile is a description of the main
risks that exist in bank activities. Banks in running a
business contain a variety of risks. The risk profile is
a summary that provides an overview for risk
management what needs attention.
The risk profile is measured by identifying the
inherent risks in various business activities, or the
risks inherent in bank activities, and evaluating the
quality of controls, and the plan to improve quality
control.
Bank Indonesia makes the risk category
consisting of credit risk, market risk, liquidity risk,
operational risk, compliance risk, strategic risk,
reputation risk and legal risk. For the eight risks, it
can be determined what risks need to be prioritized
by management's attention to be managed properly,
because they are seen as potentially harming the
bank. (Bank Indonesia Regulation Number: 13/1 /
PBI / 2011)
Liquidity Level
The term liquidity is basically a term absorbed from
English, namely the word liquid which means liquid.
This term usually indicates the level of liquidity of
funds or wealth owned by a company organization.
According to KBBI (Indonesian dictionary)
itself, the definition of liquidity is the position of
1.79
2.14
2.00
0.41
0.49
0.63
‐
1.00
2.00
3.00
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
2016
ROA of Islamic Banking 2011-2016 (%)
ROA
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1224

money or cash of a company and its ability to fulfill
obligations that are due on time; ability to fulfill
obligations to pay debts on time.
The company's liquidity level is usually
indicated in the form of certain numbers such as fast
ratio numbers, current ratio numbers, and cash ratio
figures. The whole number in these three ratios is a
comparison between the level of current assets and
the amount of liabilities held by the company.
Good Corporate Governance
Good Corporate Governance (GCG) is the principle
that directs and controls the company in order to
achieve a balance between the strength and authority
of the company in providing its accountability to the
shareholders in particular, and stakeholders in
general. Of course this is intended to regulate the
authority of Directors, managers, shareholders and
other parties related to the development of
companies in certain environments.
The Center for European Policy Studies (CEPS)
has another formula. GCG, said the center of study,
is an entire system formed from rights, processes,
and controls, both within and outside the
management of the company. For the record, rights
here are the rights of all stakeholders, not limited to
shareholders only. Rights are the various strengths
that individual stakeholders have to influence
management. The process, meaning the mechanism
of these rights. Control is a mechanism that allows
stakeholders to receive the information needed about
various company activities.
Meanwhile, ADB (Asian Development Bank)
explained that GCG contains four main values,
namely: accountability, transparency, predictability
and participation. Another understanding came from
the Finance Committee on Corporate Governance in
Malaysia. According to the agency, GCG is a
process and structure used to direct and manage the
business and business of the company towards
increasing business growth and corporate
accountability. The ultimate goal is to increase the
value of shares in the long term but still pay
attention to the various interests of other
stakeholders.
Intellectual Capital
In There are many corporate valuation methods.
Nevertheless, studies find contradictory results, and
the corporate finance community is not even close to
a universal methodology of company valuation.
Different methods have different advantages in
different situations, and some capture important
aspects of valuing a business, which are not
recognized by others. Traditional company valuation
methods pay more attention to either historical
figures (based on the balance sheet, income or cash
flow statement) or inexact forecasting [for example,
free cash flow and weighted average cost of capital
(WACC) for subsequent periods]. These methods
are mostly taking into consideration the physical
assets of the company, while in the knowledge-
based economy more emphasis is put on employees
and intellectual capital. Therefore, afore mentioned
corporate valuation methods are not suitable in
today’s world.
Intellectual capital has been recognized as
knowledge applied to practice, reflecting
organizations ability to perform and not just
calculating the value of knowledge in financial
terms. The application of knowledge in innovation
and agility to succeed in business is what
differentiates today's organizations, i.e., the
distinctive capacity of these organizations is their
'knowledge in action' (Davenport and Prusak, 1998).
For this knowledge to be reflected, organizations
should disclose an IC report showing the
transactions on knowledge, as the annexto financial
statements reflects the transactions within the
accounting system (Mouritsen, 2006).
We live in an economy where dematerialization
of production, and information and communication
echnologies, especially the internet, have a leading
role, creating a network economy with intensive use
of knowledge and innovation in the production of
goods and services. Knowledge is then the main
factor of production and competitive pressures have
made innovation the key factor for businesses
survival. The type of IC disclosure is valuable
information for investors, as it can help them
reducing the uncertainly of the bank’s future
prospect and facilitate in valuing the bank. Table 1
provides the main contributions of some of the IC
disclosure models available in the literature.
3 RESULT METHODS
This study examines the level of influence of
Independent variables (X) in this case are Non
Performance Finance (NPF), Capital Adequacy
Ratio (CAR), Good Corporate Governance (GCG)
and Intellectual Capital (Value Added Capital
Employed-VACA, Value Added Human Capital-
VAHU, and Structural Capital Value Added-STVA)
on the dependent variable (Y) in this case is Return
On Assets (ROA). The design of this study is
causality. The type of data used is quantitative data
Does the Risk Profile, Liquidity Ratio, Good Corporate Governance and Intellectual Capital Able to Affect the Financial Performance of
Islamic Banks in Indonesia?
1225
data in the form of numbers that have been
processed from the financial statements of Islamic
banks sourced from the site www.bi.go.id and
www.ojk.go.id.
The research population is Islamic banking
registered at Bank Indonesia for the period from
2012 to 2016. The samples in this study were 11
(eleven) Islamic banks in Indonesia. The operational
definitions in this study are as follows:
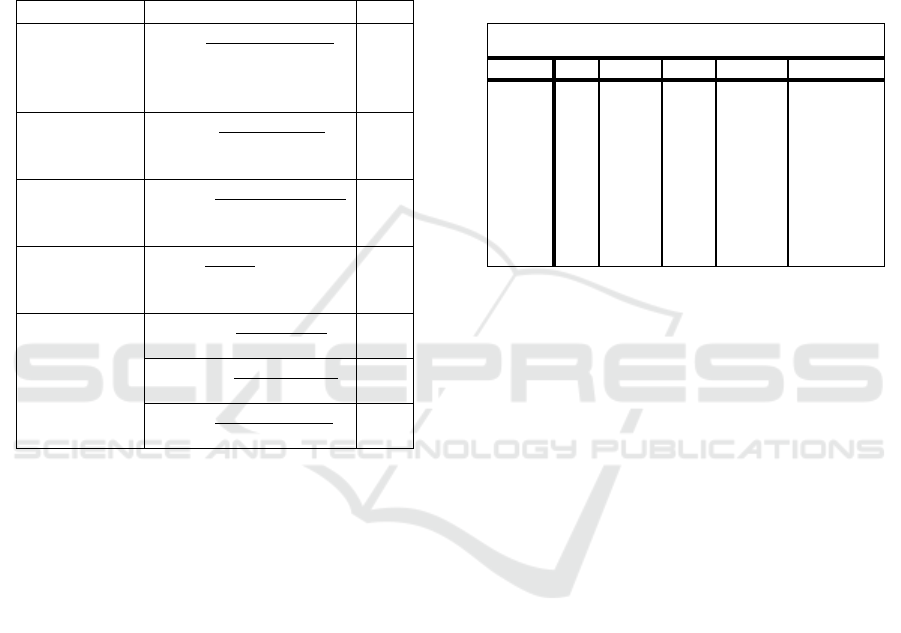
Table 1: Operating Variable
Variable Formula Scale
Return on Asset
(ROA)
ROA = Earning Before Tax x
100%
Total Credit
%
Risk Profile (
NPF)
NPF = Problem Credit x
100%
Total Credit
%
Good Corporate
Governance
(GCG)
IPCG = Item scor disclosure
x 100%
Maximum scor
%
Capital
Adequacy Ratio
(CAR)
CAR = Capital x 100%
ATMR
%
Intellectual
Capital (VAIC)
VACA = Value Added x
100% Capital Employed
%
VAHU = Value Added x
100% Human Capital
%
STVA = Structural Capital x
100% Value Added
%
The data analysis technique in this study uses
multiple linear regression techniques using statistical
software. The following is the data technique used in
this study, namely: 1). Descriptive statistics are used
to give an overview of variables and data seen from
the mean, standard deviation, maximum, minimum,
variance and so on. 2). Classical Assumption Test
which includes normality test, multicollinearity,
autocorrelation and heteroscedasticity. and 3).
Hypothesis Test consists of F Test and t Test 4)
Determinant Coefficient Test.
4 ANALYSIS
This study shows the results in the form of
descriptive statistics, the results of testing the quality
of data and the results of statistical tests for
hypotheses that are suitable or not in accordance
with the theory used by researchers in this study
Descriptive statistics
Descriptive statistics provide an overview of
research data in the form of Non-performance
Financing (NPF), Good Corporate Governance
(GCG), Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR), Intellectual
Capital (Value Added Capital Employed-VACA,
Value Added Human Capital-VAHU, and Structural
Capital Value Added-STVA) and Return On Assets
(ROA). As stated in table 1. The following
descriptive statistics:
Table 2: Deskriptive Statistics
Descriptive Statistics
N Min Max Mean S. Deviation
NPF 55 .10 13.00 4.5864 7.32093
GCG 55 11.63 77.91 48.3721 17.06835
CAR 55 7.91 89.16 23.9973 17.57944
VACA 55 -.48 .92 .2376 .22478
VAHU 55 -12.52 4.24 1.1425 2.22429
STVA 55 -5.90 3.07 .2091 1.12440
ROA 55 -5.57 4.31 .5566 1.35334
Valid N
(listwis
e)
55
Based on table 2 that this study has 55 sample data.
The variables discussed are as follows: NPF shows
an average of 4.5864%, which means that Islamic
banking has a risk that is close to the maximum
value set by Bank Indonesia which is 5% so that it
can be said that Islamic banking still has high risk,
GCG shows an average amounting to 48.37% which
means that Islamic banking is still not serious in
implementing GCG, CAR shows an average of
23.99%, which means that Islamic banking has a
good level of liquidity, while Intellectual Capital
including VACA shows an average of 0.2376 or
23.76% meaning that the ownership of a sharia
banking company has a pretty good added value,
VAHU shows 1.1425 or 114.25%, which means that
Islamic banking gets a considerable value added
from employees, and STVA shows an average of
0.2091 or 20.91% which means that structural
capital has a contribution for value added banking
sharia and ROA show an average of 0.5566 or
55.66%, which means that Islamic banking has a
performance that can be said to be good because it is
able to manage its assets well in earning profits.
F Test
The F test is used to determine the extent to which
the independent variables are able to explain
together the dependent variable.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1226
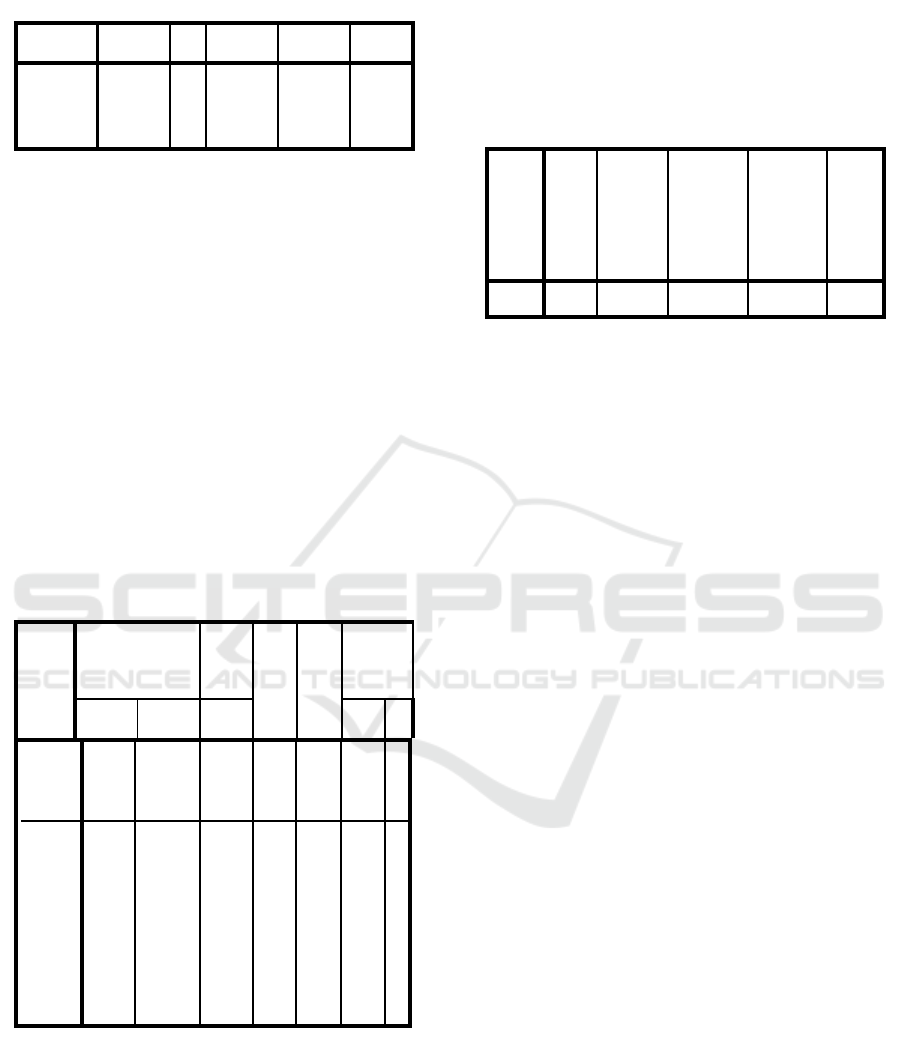
Table 3: F Test Output
ANOV
A
a
Sum of
Squares df
Mean
Square F Sig.
Regressi
on
70.808 6 11.801 20.163 .000
b
Residual 28.095 48 .585
Total 98.903 54
Based on the table above shows a significant value
of 0.000 <0.05. meaning independent variables are
able to influence together Dependent Variables. It
can be concluded that the variables are Non-
performance Financing (NPF), Good Corporate
Governance (GCG), Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR),
Intellectual Capital (Value Added Capital
Employed-VACA, Value Added Human Capital
VAHU, and Structural Capital Value Added-STVA )
able to explain together the ROA variable.
t Test
This test is used to find out whether the regression
coefficient has a partial or significant influence
between the independent variable (X) on the
dependent variable (Y)
Table 4: t Test Output
Coefficients
a
Unstandardized
Coefficients
Standar
-dized
Coeffi-
cients
t Sig.
Collinearit
y
Statistics
B
Std.
Error Beta Tol
VI
F
(Constan
t)
-.881 .420
-
2.100
.041
N
PF
-.130 .049 -.239
-
2.679
.010 .741
1.3
50
GCG
-.000 .006 -.006 -.073 .942 .887
1.1
27
CAR
.031 .007 .404 4.340 .000 .684
1.4
62
VACA
4.582 .694 .761 6.599 .000 .445
2.2
47
VAHU
.065 .060 -.107 1.090 .281 .611
1.6
37
STVA
-.074 .097 -.061 -.760 .451 .908
1.1
01
a. Dependent Variable: ROA
Based on the table above it can be concluded that
NPF is able to influence ROA, GCG is not able to
influence ROA, CAR is able to influence ROA,
VACA is able to influence ROA, VAHU is unable
to influence ROA, and STVA is unable to influence
ROA
Determinant Coefficient Test
The coefficient of determination is used to find the
contribution of the independent variable (X) to the
dependent variable (Y)
Table 5: Determinant Coefficient Test Output
Based on table 5 shows that the number of
coefficients (R) is 0.846 which indicates that the
relationship between the independent variable and
the dependent variable is strong because it has R>
0.5. The R2 value is 0.716, indicating that 71.6% of
the dependent variable variation (ROA) can be
explained by variations in the independent variables
(NPF, CAR, GCG, VACA, VAHU, and STVA) in
this study. While the remaining 28.4% is explained
by other variables outside the model.
5 RESULT
The results of this study indicate that basically a
sharia banking company is one company that is
categorized as an industry that has so many
provisions in its operational management that are not
immune from risk management, capital adequacy,
good corporate governance, and management of
intangible assets.
However, in this study it can be explained that
only risk management, capital adequacy and the
management of intangible assets of value added
capital employed have an influence on the
performance of Islamic banking.
Risk management is important in banking
performance given that Islamic banking is a
company engaged in services. Whereas the level of
liquidity is an absolute provision for a bank to
operate in Indonesia, and Intellectual Capital in
Value Added Capital Employed (VACA) is
important because in VACA it consists of physical
capital and financial assets. This means that Islamic
banking companies must be efficient in running the
company by optimally utilizing existing assets.
Model Summary
b
Mo
del R
R
Square
Adjusted
R Square
Std.
Error of
the
Estimate
Durbi
n-
Watso
n
1 .846
a
.716 .680 .76506 2.192
a. Predictors: (Constant), STVA, VACA, GCG, CAR, VAHU, NPF
5. Dependent Variable: ROA
Does the Risk Profile, Liquidity Ratio, Good Corporate Governance and Intellectual Capital Able to Affect the Financial Performance of
Islamic Banks in Indonesia?
1227

6 CONCLUSIONS
This study concludes as follows: where the research
model is feasible because the independent variables
in this study jointly influence the performance of
Islamic banking. while the results of the partial test
found that only NPF, CAR and Intellectual Capital
in VACA were able to influence the Performance of
Islamic Banking while GCG, Intellectual Capital in
VAHU and STVA were not strong enough to
influence the performance of Islamic banking. the
relationship between independent variables and the
dependent variable is quite high and the contribution
of independent variables in explaining the dependent
variable is also quite high.
REFERENCES
Arrow, Kenneth J. (1984). Collected Papers, vol. 4: The
Economics of Information. Oxford: Basil Blackwell.
A.Ross, Stephen, Randolp W. Westerfield, dan Bradford
D. Jordan. (2006). Fundamentals of Corporate
Finance. New York: McGraw-Hill Irwin.
Bank Indonesia, (2011), Surat Edaran No.13/24/DPNP
Date 25 Oktober 2011, regarding the guideline for the
rating system for commercial banks ", accessed on 11
November 2018 from www.bi.go.id.
Bank Indonesia, (2011), Surat Edaran No.13/1/PBI/2011
Date 05 Januari 2011, regarding the assessment of the
soundness level of commercial banks ", accessed on
11 November 2018 from www.bi.go.id.
Barney, J. B.(1991). ‘Firm Resources and Sustained
Competitive Advantage.’Journal of Management
17(1):99–129
Bontis, Nick & Chua Chong Keow, William &
Richardson, Stanley, (2000), Intellectual Capital and
Business Performance in Malaysian Industry. Journal
of Intellectual Capital. 1. 85-100.
Davenport, T. H., Prusak, L, (1998). Working knowledge:
How organizations manage what they know, Harvard
Business School Press, Boston.
Falikhatun and Assegaf, 2012, Bank Syariah Di
Indonesia: Ketaatan Pada Prinsip-Prinsip Syariah Dan
Kesehatan Finansial. Accounting and Management
(CBAM).Vol. 1 No. 1 December 2012, 245 –254
Gozali, Imam, 2011, Aplikasi Analisis Multivariate
dengan program SPSS. Semarang, universitas
Diponegoro
Jan Mouritsen, 2006 "Problematising intellectual capital
research: ostensive versus performative IC",
Accounting, Auditing & Accountability Journal, Vol.
19 Issue: 6, pp.820-84
Otoritas Jasa Keuangan, 2016, Statistik Perbankan
Indonesia accessed on 07 October 2018 from
www.ojk.go.id
Sahara Ayu Yanita, (2010), Analisis Pengaruh Inflasi,
Suku Bunga BI, dan Produk Domestik Bruto terhadap
Return On Asset (ROA) Bank Syariah di Indonesia.
Jurnal Ilmu Manajemen, Vol 1 No.1 Januari 2013.
Umum, Ihyaul, (2008), Pengaruh Intellectual capital
terhadap kinerja keuangan perusahaan perbankan di
Indonesia. Pontianak: Call for paper symposium
Nasional Akuntansi XI, Ikatan Akuntan Indonesia,
Wernerfelt, B. (1977), 'An information based theory of
nlicroeconomics and its consequences for corporate
strategy', Unpublished Dissertrrtion, Harvard
University, Graduate School of Business
Administration.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1228
