
The Development of Practicum Teaching Materials based on IFRS to
Improve Learning Outcomes of Accounting Students’
Erny Luxy D. Purba
1
and Yulita Triadiarti
1
1
Faculty of Economics, Universitas Negeri Medan, Medan -Indonesia
Keywords: Accounting, IFRS-Based Accounting, Teaching Material
Abstract: The research problem is that the business environment and Indonesian accounting standards are changing
rapidly. Therefore, the development of material in practical introductory accounting textbooks must reflect
new developments in accounting standards as well as practical business. Since 2012, PSAK refers to the
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) which became effective from January 1, 2009.
Indonesia's commitment is to support IFRS standards as accounting standards that are accepted globally and
continue with the process of convergence of IFRS standards, to minimize gaps between SAK and IFRS.
This is the reason for the need for international accounting standards to eliminate barriers to international
capital flows by reducing differences in financial reporting provisions, reducing financial reporting costs for
multinational companies and costs for financial analysis. The subjects of this study were first semester
students majoring in accounting who took introductory accounting practice courses. Data analysis in this
study used quantitative descriptive analysis. All collected data were analyzed by descriptive statistical
techniques which were quantitatively separated according to categories to sharpen judgments in drawing
conclusions. Qualitative data in the form of very inadequate, inadequate, moderate, feasible and very
feasible statements are converted into quantitative data with a scale of grades 1 to 5. The results are
averaged and used to assess the quality of learning media. Media criteria will be converted into values on a
scale of five using Scale Likert. The results of the study obtained that the development of teaching materials
was deemed feasible to use and able to improve student learning independently.
1 INTRODUCTION
At present the curriculum used by Universitas
Negeri Medan is based on the Indonesian National
Qualifications Framework (KKNI) which requires
the determination of learning outcomes for four
aspects namely attitudes, general skills, special
skills, and knowledge mastery in order to be able to
answer and shape graduates who answer the needs
of users, who need energy professional. One way to
realize the achievement of the effectiveness of the
implementation of learning is to form a Study
Lecturer Group (KDBK) based on the alignment of
studies in the course. One of the KDBK in the
Department of Accounting is the Financial
Accounting KDBK which is a forum for developing
professionalism and lecturer performance, especially
developing lecturer competencies in developing
teaching preparation such as developing learning
processes and materials in financial accounting
KDBK courses, each lecturer can discuss and help
each other if there is a special difficulty in the
implementation of accounting practice courses
which are part of KDBK financial accounting.
Renewal of the learning process and teaching
materials must be done to improve the quality of
learning itself and ultimately will be able to improve
the quality of graduates. The renewal of the learning
process and introductory accounting practicum
materials, especially in the business environment
and Indonesian accounting standards change rapidly.
Therefore researchers want to develop material in
practice accounting interventions to reflect new
developments in accounting standards as practical
business. This is in accordance with the Statement of
Financial Accounting Standards (PSAK) issued by
258
Purba, E. and Triadiarti, Y.
The Development of Practicum Teaching Materials based on IFRS to Improve Learning Outcomes of Accounting Students’.
DOI: 10.5220/0009495602580265
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 258-265
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

the Accounting Standards Board (DSAK IAI) under
the auspices of the Indonesian Institute of
Accountants or IAI. Since 2012, the PSAK refers to
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
which are effective since January 1, 2009.
Indonesia's commitment is to support the IFRS
standard as an accepted accounting standard globally
and continue with the IFRS standard convergence
process, to minimize the gap between financial
accounting standards (FAS) and IFRS
The question arises why adopt International
Financial Reporting Standard (IFRS)? Practically
speaking, adoption of IFRS is not an option for
Indonesia, but a necessity, with hope, foreign
investment will continue to enter or even increase
and we are not excluded from international relations
and even get maximum recognition from the
international community. Companies in the world
have been and are in the process of adopting IFRS
with very impressive developments. Most G20
member countries are also IFRS adopters. This is the
reason for the need for international accounting
standards to remove barriers to international capital
flows by reducing differences in financial reporting
provisions, reducing financial reporting costs for
multinational companies and costs for financial
analysis for analysts and improving financial
comparability in providing quality information on
international capital markets.
(http://maiyasari.wordpress.com, 2012)
The development of IFRS-based introductory
accounting practicum teaching materials is one of
the efforts taken to be able to improve the ability of
student practicum in accordance with new
developments in international accounting standards,
because accounting is one of the fields of science
that is not sufficiently studied only in terms of
theory, but accounting is easier to understand with
real bookkeeping practices.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Definition of Teaching Materials
One of the tasks of educators is to provide a pleasant
learning atmosphere. One way to make learning fun
is to use fun teaching materials too. (Prastowo Andi,
2011) Teaching materials are basically all materials
(both information, tools, and texts) that are arranged
systematically, which displays the complete figure
of the competencies that will be mastered by
students and used in the learning process with the
objectives of planning and reviewing the
implementation of learning.
Teaching materials that are well designed by
lecturers will be able to make learning more
effective and students' understanding of accounting
increases. The results of Demaja W's research in
(Pujiati, 2007) show that: Learning outcomes of
PAK learning strategies between students who use
teaching materials for Dick and Carey models with
students using traditional teaching materials differ
significantly. It was found that the learning
outcomes of PAK learning strategies for students
who use teaching materials compiled by researchers
are higher than students who use traditional teaching
materials.
Usually teaching materials are "independent",
meaning that they can be studied by students
independently because they are systematic and
complete. (Paulina, Pannen, 2001). Further
explained that:
"Teaching materials designed
and developed based on good
instructional principles will be
able to: 1) assist students in the
learning process, 2) assist
lecturers to reduce material
presentation time and increase
lecturer guidance time for
students, 3) assist universities in
completing curriculum and
achieving goals instructional
with the time available.
"(Paulina, Pannen, 2001.)
Independent learning shows that students are not
dependent on continuous supervision and lecturer
direction, but students also have their own creativity
and initiative, and are able to work alone by
referring to the guidance they obtain (Self Directed
Learning, Knowles, 1975 in (Paulina, Pannen,
2001). The main role of the lecturer in independent
learning is as a consultant and facilitator, not as an
authority and the only source of knowledge.
(Wadjadi Faried, 2004) explained that good
teaching materials are materials that: (1) can arouse
students' interest in learning, (2) have instructional
purpose clarity, (3) present material with good
structure, (4) provide opportunities for students to
practice and provide feedback to students, and (5)
create two-way communication. In addition to the
above to stimulate students' creativity and interest in
learning, instructional materials are designed as
attractive as possible including the use of color,
shape, font size and thickening of letters, lacing and
lines are also needed to clarify the contents of the
message. Like Leshin, Pollock, and Reigeluth,
(1992: 280) describes the tools used to be able to
The Development of Practicum Teaching Materials based on IFRS to Improve Learning Outcomes of Accounting Students’
259
create the focus of the attention of the following
readers :
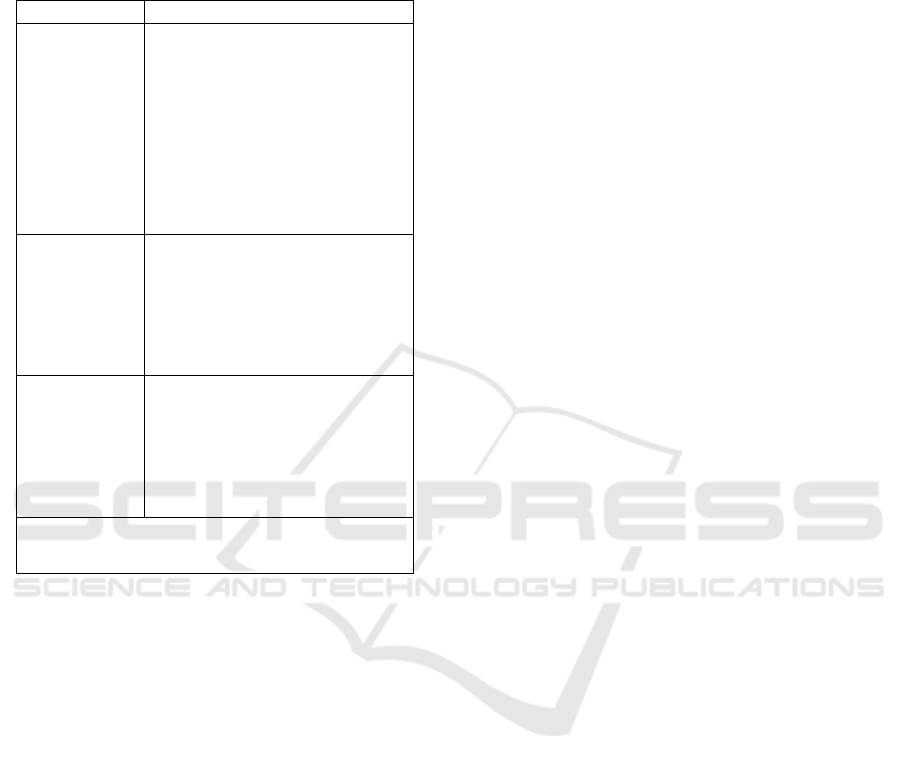
Table 1: Tools used for attention-centering
Equipmen
t
Usa
g
e Description
Color
Use color as a pointing
device to pay attention
directly to something
important.
Always be consistent in
using color when giving
emphasis on key words or
items that are important.
Font Style
Use letters that attract the
eye, italics, or bold to
emphasize keywords or
naming. Use of italics is
recommended.
Boxes and
lines
Staining to surround
important information.
Do not use the underscore
as a pointing device; this
makes words harder to
read.
Note: Avoid excessive use of equipment as a
pointing device
Adapted from Guidelines, Using Tools For
Emphasis (Leshin, Pollock, and Reigeluth, 1992:
280 in (Pujiati, 2007)
International Financial Reporting Standards
(IFRS) International Financial Reporting
Standards
The SFAS has gradually changed according to
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
and International Accounting Standards (IAS) from
2008 to 2011. The application of this revised PSAK
early in corporate accounting and education is
strongly recommended, because on January 1, 2012
all new PSAK MUST be implemented. This change
in PSAK requires changes in accounting books, both
in universities and vocational high schools (SMK)
majoring in accounting. (Linda S, 2011)
In December 2008, the Indonesian Institute of
Accountants (IAI) has launched a full PSAK to
IFRS convergence in 2012. Since 2009, the
Financial Accounting Standards Board - Indonesian
Accountants Association (DSAK-IAI) has carried
out work programs related to the convergence
process up to year 2011.
It is targeted that in 2012, all PSAK will not
have material differences with IFRS which will be
effective as of January 1, 2009. After 2012, PSAK
will be updated continuously as changes in IFRS.
Not only adopting IFRS that has been published,
DSAK-IAI is also determined to play an active role
in the development of world accounting standards.
International Financial Reporting Standards
(IFRS) is indeed a global agreement on accounting
standards supported by many countries and
international bodies in the world. The popularity of
IFRS at the global level is increasing over time. The
G-20 Agreement in Pittsburg on September 24-25,
2009, for example, stated that the authorities that
oversee international accounting rules must raise
global standards in June 2011 to reduce the rule gap
among G-20 member countries. Through global
participation, IFRS is indeed expected to become a
high-quality theory and principle-based accounting
standard. The application of the same accounting
standards throughout the world will also reduce
problems related to comparability in financial
reporting.
Rosita also added that the IFRS 2012
convergence challenge is the readiness of
practitioners of management accountants, public
accountants, academics, regulators and other
supporting professions such as actuaries and
assessors. Public Accountants are expected to be
able to immediately update their knowledge
regarding changes in IFRSs, update SPAP and adjust
audit approaches based on IFRS. Management/
Company accountants can anticipate by immediately
forming the IFRS convergence success team in
charge of updating Management Accountant
knowledge, conducting gap analysis and developing
IFRS convergence road maps and coordinating with
other projects to optimize resources. Academics/
University Accountants are expected to form IFRS
convergence success team to update Academics'
knowledge, revise curriculum and syllabus and
conduct various related studies and provide input/
comments on ED and Discussion Papers published
by DSAK and IASB. (Linda S, 2011)
Based on some of the opinions above, it can be
concluded that there is a need to develop
introductory accounting practicum materials that suit
student needs, curriculum demands, international
financial accounting standards in this case IFRS,
business environment, target characteristics and
learning problem solving demands.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
260

3 RESEARCH METHOD
This research uses research and development
approach (R & D). Development of Practical
Learning Materials Introduction to Accounting
follows the Dick and Carey model, using a system
approach, because it emphasizes the relationship
between each component. The system approach can
also increase the opportunities for integrating all the
variables that affect learning in learning design.
These steps are not the standard things that must be
followed; the steps taken can be adjusted to the
needs of the researcher. To produce interactive
teaching material products, planning, learning design
is needed
.
The steps for developing teaching materials
according to the models of (Dick, W., Carey, L. and
Carey, 2005) are as follows: (1) identifying general
objectives, (2) conducting instructional analysis, (3)
identifying initial behavior / entry behavior lines, (4)
formulating performance goals, (5) developing
reference test items, (6) developing instructional
strategies, (7) developing and selecting instructional
materials, (8) designing and implementing formative
evaluations, and (9) designing and implementing
summative evaluations, (10) revising instructional
activities
The development of material substance in
accordance with International Financial Reporting
Standards (IFRS) and International Accounting
Standards (International Accounting Standards /
IAS) will be integrated in the following steps:
1. Conduct preliminary research, which includes:
a. Identify learning needs and determine
Competency standards for introductory
An accounting practice courses.
b. Conduct an analysis of learning material that
Has been given to introductory accounting
courses (literature studies).
c. Conduct an analysis of learning that has been
done so far in introductory accounting practice
courses.
d. Identify the characteristics and initial behavior
of students in practical courses in accounting,
namely students in accounting semester 1.
e. Write basic competencies and indicators.
f. Write a benchmark reference test.
g. Develop learning strategies that consist of,
(1). Explanation of instructional goals; (2).
Explanation of the relevance of the contents of
the lecture, (3). Explanation of subject matter
Or concepts, principles, and procedures that
students will learn, (4). Formative tests and
feedback, (5). Follow up.
2. conducting the development stage, which
Includes:
a. Preparation of draft teaching materials
b. Make Prototypes teach
c. Material expert assessment
d. Revision 1
e. Small group trials
f. Revision 2
g. Design and media assessment
h. Revision 3
3. Conduct testing of product effectiveness
a. Pre Test-Post Test control design
b. Revision 4
c. Field trials (large groups)
d. Revision 5
e. Final product teaching material
Data analysis in this research used qualitative
data and quantitative descriptive analysis. All data
were collected by analysis with descriptive statistical
techniques that were quantitatively separated
according to categories to sharpen the judgment in
drawing conclusions. Qualitative data in the form of
statements that were very inadequate, less feasible,
moderate, feasible and very feasible were changed to
quantitative data with a value scale of 1 to 5.
However, in frequent measurements, the tendency of
respondents to choose more in category 3 is to avoid
the likert scale being modified by only using the
choice of 4 choices, 4 (Very good); 3 (Good); 2
(Enough); 1 (Less) (Direktorat Pembinaan Sekolah
Menegah atas Dirjen Manajemen Pendidikan Dasar
dan Menengah Atas, 2008). The data analysis
technique in this study uses percentage descriptive
analysis through exposure to data or conclusions of
data processed using percentage techniques which
are divided into four categories with the following
formula:
Percentage of eligibility (%) =
Observe score/expected score x 100 %
The collected data is processed by summing,
compared with the expected number and obtained by
the percentage (Arikunto, 1996).
The product of developing practical teaching
materials introducing accounting requires feedback
in the context of formative evaluation. The
feedbacks were obtained from subjects consisting of
1 learning design expert, 1 material expert, 1
instructional media expert, and product user, namely
first semester students majoring in Accounting
Faculty of Economics, Medan State University
consisting of 8 students to test try small groups and
24 students for big group trials.
The Development of Practicum Teaching Materials based on IFRS to Improve Learning Outcomes of Accounting Students’
261

4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Product Development Results
This research and development aims to produce
practical teaching material introducing accounting
based on IFRS. The development in this study uses a
development model adopted from Dick, Carey and
(Suparman, Atwi, 2012). The stages of
implementation of development consist of: a)
Preliminary Research b) Product development and c)
Test the effectiveness of the product
a. The stage of conducting preliminary research
At the preliminary research stage, FGD was held
with the introductory lecturer in accounting and
practicum introductory accounting to identify
learning needs including: a) determining learning
achievement standards and learning outcomes in the
field of knowledge introducing accounting practice
in accordance with the KKNI curriculum by
conducting an analysis of learning which had been
done so far in introductory accounting practice
courses; b) Identifying the characteristics and initial
behavior of students in accounting introductory
practical courses, namely students in accounting
semester 1; c) Writing basic competencies,
indicators and developing learning strategies
consisting of, 1. Explanation of general and specific
instructional objectives, 2. Explanation of the
sequence of subject matter needed in developing
teaching materials, concepts, principles, and
procedures that are in accordance with reporting
standards international finance (IFRS) that will be
studied by students. 3. Explanation of benchmark
reference tests to measure student mastery of the
overall material between accounting and improve
student knowledge to solve accounting cases /
questions in the introductory accounting practice. 4.
Explanation of learning strategies to create a more
lively learning process so as to encourage students to
think more critically by making cases or looking for
the latest cases discussed in the class.
b. Product Development Phase
At this stage the sources of teaching materials or
literature are collected, preparation and making
teaching materials by holding FGDs with lecturers
of accounting introductory subjects and accounting
introductory practicum’s and design experts. At this
stage, reviewing the entire introductory teaching
accounting material by synchronizing introductory
accounting and practicum accounting material so
that students can more easily understand the material
/ concepts in theory and master accounting practices.
The entire material is adjusted to the latest
applicable international financial reporting
standards. In general in Indonesia (IFRS). Making
teaching materials must pay attention to colors,
images, language and design (display) to stimulate
students' minds, attention and reading interest and
certainly encourage students to learn more
independently.
c. The stage of testing the effectiveness of the
Product
The stage of product effectiveness testing
(introductory accounting practice teaching material)
that will be developed first is carried out the analysis
phase of data processing that has been obtained from
observations to find out the learning materials based
on the assessment of material experts, design
experts, media experts, small group trials, and trials
large groups. Then product revisions / improvements
are made and conclusions are drawn
1. Data Description Test Material Effectiveness
(field of study)
Test the effectiveness of material experts including
aspects of content feasibility, language feasibility,
and graphic feasibility. The due diligence process is
carried out to find out whether the material
presented in the teaching material is in accordance
with the semester learning plan, the language used is
appropriate and graphics are in accordance with the
subject matter and to get advice and input on
introductory accounting teaching material to be
developed. These suggestions and inputs are then
analyzed and used to develop practical introductory
accounting teaching materials that are in accordance
with IFRS-based introductory accounting material so
that they can improve student learning outcomes and
answer the needs of stakeholders who have made /
produced financial reports in accordance with IFRS.
The effectiveness test data of the practicum
Materials experts introducing IFRS-based
accounting in the development of learning media
with case-based / problem-based approaches can be
seen in the following table:
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
262
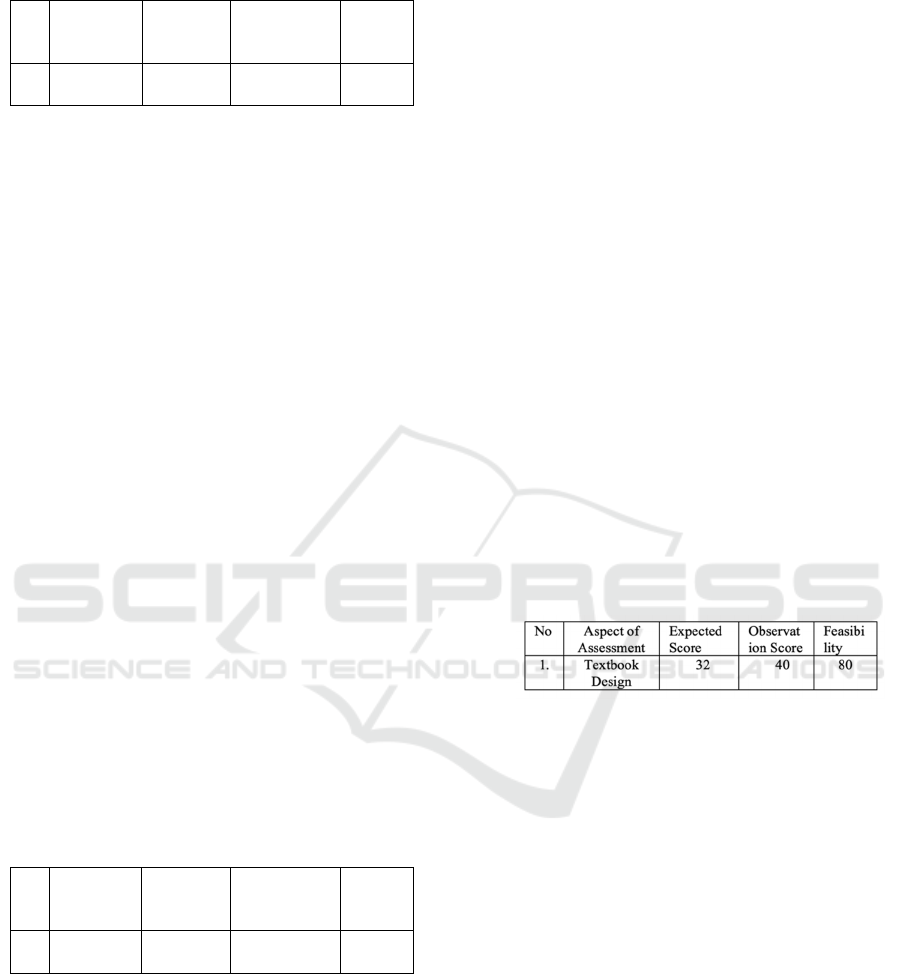
Table 2: Scores of Material Assessment
Based on table 2 above, the average total assessment
of this learning material expert obtained 83.92%
results. In accordance with the percentage scale the
results fall into the category of "proper to use".
The things suggested by material experts are
1) There needs to be other sources for learning (in
the form of an IFRS based accounting book); 2)
More transactions are made to sharpen students'
understanding of the journal; 3) More varied level of
difficulty of questions / cases to sharpen students'
ability to solve accounting cases / questions
2. Description of Data Test the Effectiveness of
Designers
Test the effectiveness of Learning media design
experts aims to get input and suggestions regarding
the design of practical teaching books for
accountants in developing practical teaching
materials introducing IFRS-based accounting to
improve understanding of concepts/material and
mastering accounting practices in making/producing
financial reports on accounting introductory
practical courses in accounting study programs non
education-faculty of Economics Universitas Negeri
Medan. The input is then analyzed and used to
revise the design of the practical introductory
accounting textbook so that it can increase students'
interest in reading interest so that it will improve
student learning outcomes.
Table 3: Design Expert Assessment Score
Based on table 3 above, the average total
Assessment of learning design experts about the
Design of the introductory practical accounting
Textbook is 80.76%. In accordance with the
Percentage scale the results fall into the the category
of "proper to use".
The things suggested by design experts are 1) the
need for image clarity and image function; 2) Need
to clarify the compatibility between tables and
material; 3) Need to pay attention to the accuracy of
color selection, and need to pay attention to the
number of tables to facilitate student work.
3. Data Description Test the Effectiveness of
Media Experts
Test the effectiveness of instructional media experts
includes aspects of non-visual communication that
can lead to reciprocal benefits so as to be able to
solve a problem because teaching materials become
the center of the development of knowledge of
understanding a material / concept for students. The
results of the effectiveness test aim to get input and
suggestions regarding taxation textbooks as a
medium that will be developed with the approach of
working on questions / cases to improve the function
of the textbook as a practicum media that can
improve conceptual understanding / material and
mastery of accounting practices in accounting
introductory practical courses in Universitas Negeri
Medan Faculty of Economics. The input is then
analyzed and used to revise accounting practice
teaching books so that it can improve the quality of
textbooks that are very feasible to use which will
result in high student learning outcomes
Table 4: Media Expert Assessment Scores
Based on table 4. above, the average total
assessment of learning design experts about the
design of textbooks with problem solving obtained
80% results. According to the percentage scale these
results fall into the category of quite feasible /
attractive / motivated to use.
The things suggested by media experts are 1)
need to pay attention to aspects of typos and pages
that are missing; 2) the concept should be equipped
with examples to facilitate student understanding.
4. Small group test results followed by
revisions and large group trials followed by
revisions
Small Group Test Result
After the effectiveness of teaching materials
products is tested by material experts, design experts
and media experts, then revised according to
suggestions or comments from the valuators. The
revised product then enters the testing phase of
students as end product users. Teaching materials
developed were tested on 9 students called small
N
o
Aspect of
Assessm
ent
Expected
Score
Observation
Score
Feasib
ility
1 Contents
Material
47 56 83,92
N
o
Aspect of
Assessm
ent
Expected
Score
Observation
Score
Feasib
ility
1. Textbook
Design
42 52 80,76
The Development of Practicum Teaching Materials based on IFRS to Improve Learning Outcomes of Accounting Students’
263

groups representing non-first semester accounting
students who took accounting introductory practical
courses with the criteria of 3 high, medium and low
ability students. The assessment aspects given in the
small group trials included aspects of the feasibility
of content, aspects of graphics, and aspects of
benefits. This small group test was conducted to get
input or suggestions from prospective users
(students) based on the use of practical teaching
materials so far. Small group test score scores by
students are presented in the table below:
Table 4.4 Student Assessment Scores
Based on table 4.4 above, the average total
assessment of learning design experts about the
design of textbooks with this problem solving
obtained 83.47% results. In accordance with the
percentage scale the results fall into the appropriate
category for use.
Large Group Test Results
This large group test was conducted to get input or
suggestions from prospective users (students) based
on the results of the assessment on the questionnaire.
The respondents of this large group test were taken
randomly as many as 24 of UNIMED's economics
faculty business education students who took
taxation courses in semester V of the 2018/2019
academic year with categories of 8 high, medium
and low ability students respectively. The percentage
of large group test assessment data by students is
presented in the table below:
Based on table 5 below, the average total
assessment of learning design experts about the
design of textbooks with this problem solving
obtained 83.71% results. In accordance with the
percentage scale the results fall into the appropriate
category for use.
Table 5: Student Assessment Scores
5 CONCLUSIONS AND
RECOMENDATION
5.1 Conclusions
Based on the results of research and product
development introductory accounting practice
teaching materials that have been stated previously,
it can be concluded as follows:
1. From the results of the assessment according to
material experts it is "feasible to use" with a
score of 83,92,%. The assessment results
according to the design expert are "worthy of
use" with a score of 80.76%; while the results
of evaluations from media experts are "feasible
to use" with a score of 80%
2. The use of teaching material products by
students shows a score of 83.47% for small
groups and large groups 83.71%. This means
that the use of instructional materials products
developed is deemed feasible to use and able to
improve student learning independently, high
questioning ability and the better understanding
of the transaction settlement cases in
accounting material.
5.2 Recommendation
Based on the results of this research and
development, it is recommended
1. For lecturers, product introductory practical
teaching materials can be used as a source of
learning for Universitas Negeri Medan Faculty
of Economics students, especially accounting
majors.
2. For students, it can be used as an alternative
source of independent learning
3. Development of this product is recommended to
pay attention to more attractive packaging
including matching colors
4. Development of this product is recommended to
add transaction and case questions to simplify
and sharpen student understanding.
5. The research and development products in the
form of teaching materials need to be conducted
in a larger field trial for student subjects in the
accounting department before being used by all
students to improve the quality of the products
produced.
REFERENCES
Arikunto. (1996). Prosedur Penelitian. Rineka Cipta :
Jakarta.
Dick, W., Carey, L. and Carey, J. O. (2005) T. systematic
N
o
Aspect of
Assessme
nt
Expected
Score
Observa
tion
Score
Feasibility
1 Content
Feasibility
720 864 83,33
2 Integrity 481 576 83,50
3 Benefits 326 384 84,89
Total 1527 1824 83,71
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
264

design of instruction. P. and B. (2005). The
systematic design of instruction. Pearson/Allyn and
Bacon.
Direktorat Pembinaan Sekolah Menegah atas Dirjen
Manajemen Pendidikan Dasar dan Menengah Atas,
T. P. (2008). Panduan Pengembangan Bahan Ajar.
Jakarta : Depdiknas.
Paulina, Pannen, P. (n.d.). penulisan-bahan-ajar.pdf.
Jakarta : PAU-PPAI, Universitas Terbuka.
Prastowo Andi. (2011). Panduan Kreatif Membuat Bahan
Ajar Inovatif : Menciptakan Metode Pembelajaran
yang Menarik dan Menyenangkan. Yogyakarta:
Diva Pres.
Pujiati. (2007). Pengembangan Bahan Ajar Praktikum
Pengantar Akuntansi Untuk Mahasiswa Jurusan
Akuntansi. Jurnal Ekonomi & Pendidikan, Volume
4 N, 36–53.
Suparman, Atwi, M. (2012). Desain Instruksional
Moderen. Erlangga : Jakarta.
Wadjadi Faried. (2004). Pengaruh Pemberian Bahan
Belajar Terhadap Hasil Belajar pada Mata Kuliah
Rangkaian Dasar Listrik (Suatu Studi di Jurusan
Teknik Elektro UNJ). Jurnal Teknodik, No. 15/VII,
105.
The Development of Practicum Teaching Materials based on IFRS to Improve Learning Outcomes of Accounting Students’
265
