
Development of Taxation Teaching Materials with Problem Solving
Approach to Improve Student Learning Outcomes in Unimed
Economic Faculty
OK Sofyan Hidayat
1
and Muhammad Ridha Habibi Z.
1
1
Faculty of Economics, Universitas Negeri Medan, Medan -Indonesia
Keywords: IQF, Teaching Materials, Problem Solving Approach, Learning Outcome.
Abstract: In this case the government through KEMENRISTEKDIKTI establishes a college curriculum based on IQF.
The IQF is a statement of the quality of Indonesian human resources whose classification of qualifications is
based on the level of ability stated in the formulation of learning outcomes. To support the above, this is
where the role of the lecturer is to facilitate the improvement of student competencies through the
development of teaching materials, learning models, assignments whose completion process is specifically
designed by students so that students have hardskill and soft skills. Specifically, the objectives of this
research are 1) To find out whether the taxation teaching materials in the tax subject in KDBK are
developed in accordance with the latest tax regulations. 2) To implement and foster lecturers in improving
the quality of taxation learning through the use of taxation teaching materials with a tax problem solving
approach in KDBK at the Faculty of Economics, Medan State University. 3) Become a training facility for
lecturers to publish their research results in scientific journals, both locally and nationally accredited and
textbooks (ISBN). This study was designed with a research and development approach with the following
stages of activities: 1) Pre Development 2) Development of instructional materials and learning strategies 3)
Review and product testing 4) Test the effectiveness and application of learning strategies and teaching
materials. The subjects of this study were students of business education programs who took taxation
courses. Data analysis in this research and development uses quantitative descriptive analysis. All collected
data were analyzed by descriptive statistical techniques which were quantitatively separated by categories to
sharpen the assessment in drawing conclusions. Data analysis in this research and development is explained
in three, namely a) data analysis from practitioners and experts / experts, b) data analysis when product
trials, and c) analysis of experimental test data using Gain scores. N-gain testing is done to determine the
improvement of learning outcomes between before and after learning. The results of the study show that
taxation teaching materials as development products are "feasible and quite feasible / attractive / motivated"
improving student learning outcomes shown by the results of scores of 91.67%, 85.71%, and 87.5%. The
use of teaching material products shows an increase in student learning outcomes, which is indicated by the
difference in the mean pre-test score and post-test small group is 2.5 and the large group is 2.76. This means
that the use of instructional materials as a result of development can increase student scores by 25% and
27.6%.
1 INTRODUCTION
At present there have been important changes in the
dynamics of the relationship between higher
education and the world of work, especially related
to the gap between higher education outcomes and
competency demands in the world of work
(Mutmainah, 2006). One of the causes of the rapid
development of science and technology has resulted
in fundamental changes in qualifications,
competencies and requirements to enter the
workforce which has resulted in increasingly intense
competition among graduates so that the increasing
number of educated unemployed due to not
qualifying. In this case the government through
KEMENRISTEKDIKTI establishes a college
250
Hidayat, O. and Habibi Z., M.
Development of Taxation Teaching Materials with Problem Solving Approach to Improve Student Learning Outcomes in Unimed Economic Faculty.
DOI: 10.5220/0009495502500257
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 250-257
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

curriculum based on IQF. The IQF is a statement of
the quality of Indonesian human resources whose
classification of qualifications is based on the level
of ability stated in the formulation of learning
outcomes.
Universities as producers of educated human
resources need to measure their graduates, whether
the graduates produced have 'ability' equivalent to
'ability' (learning outcomes) which has been
formulated in the IQF qualification level. As a
national agreement, the graduates of an
undergraduate program, for example, must at least
have the "ability" which is equivalent to "learning
achievement" which is formulated at the level of 6
KKNI, equivalent Masters level 8, and so on.
Description of learning outcomes in the IQF,
contains four elements, namely elements of attitude
and values, elements of work ability, elements of
scientific mastery, and elements of authority and
responsibility. In this case, UNIMED, especially the
faculty of economics, has applied the IQF-based
curriculum to produce graduates who are highly
qualified and have high competitiveness at the
national and even international levels to answer the
needs of users, who need professionals.
To support the above, this is where the role of
the lecturer is to facilitate the improvement of
student competencies through the development of
teaching materials, learning models, assignments
whose completion process is specifically designed
by students so that students have hardskill and soft
skills. This identifies that the lecturer must be able to
improve the competence of students so that they are
able to compete in the world of work. Development
of taxation teaching materials with a problem-
solving approach is expected to improve student
competencies so that graduates meet the required
qualifications given the increasing need for labor in
the field of taxation.
The taxation course is one of the compulsory
subjects presented at the UNIMED Faculty of
Economics. This course combines theory in the form
of tax regulations that always change along with the
growth and social and economic changes and the
practice of calculating the tax itself. In the previous
learning process, this taxation was traditional where
the lecturer explained the material and gave an
example after the student presented his resume and
the results were very poorly understood by students
because the learning process was done in one
direction and students tended to be passive (just
listen). Therefore, the tax learning strategy will be
changed using Student Center Learning (SCL) with
a problem-solving approach and using taxation
teaching materials that will be changed with a
problem solving approach as well.
This is done considering the student learning
outcomes in the even semester of 2016/2017 shows
the average midterm test score of 68.5 (less) and the
average semester final examination score of 77.5
(enough). Learning evaluation results show that one-
way learning models are less favored by students
because only a few active students participate in the
learning process. In Unimed's environment, in
particular the Faculty of Economics has
implemented the Student Center Learning (SCL)
which demands student creativity but the learning
process is not yet interesting. This is a challenge for
taxation lecturers to create more interesting and not
boring learning so that the ability of students to
master taxation will increase. For this reason
researchers want to develop taxation teaching
materials must use a problem-solving approach by
adjusting the latest tax regulations and raising the
latest issues regarding taxation and adjusting it to
teaching materials.
Problem Formulation
Based on the research background, the problem of
this research can be formulated as follows: 1. Are
the teaching materials for taxation subjects
developed in accordance with the latest tax
regulations 2. How can Student Center Learning
(SCL) learning strategies with problem solving
approaches improve tax learning outcomes at the
Unimed Faculty of Economics 3. How the
implementation of Student Center Learning (SCL)
learning strategies with problem solving approaches
can improve tax learning outcomes at the Unimed
Faculty of Economics 4. Needs analysis is carried
out at the Accounting Department of the Faculty of
Economics, Medan State University in the taxation
courses contained in semester 2.
Research and Development Objectives
This Research and Development aims: 1. To find out
whether taxation teaching materials on the subjects
in the taxation KDBK are developed in accordance
with the latest tax regulations 2. To implement and
foster lecturers in improving the quality of taxation
learning through the use of taxation teaching
materials with a tax problem solving approach in
KDBK at the Faculty of Economics, Medan State
University 3. Become a training facility for lecturers
to publish their research results in scientific journals,
both locally and nationally accredited and textbooks
(ISBN).
Development of Taxation Teaching Materials with Problem Solving Approach to Improve Student Learning Outcomes in Unimed Economic
Faculty
251

2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Student Center Learning Learning Strategies
with a Solving Approach Problem
The learning process is the process of interacting
students with educators and learning resources in a
learning environment (Siti Mutmainah, 2011).
Handoko (2005) states that as educators are required
to be able to choose the most accommodating and
conducive learning method so that students can
understand something delivered. Many learning
goals can be developed ranging from gaining
knowledge, developing concepts, understanding
technical analysis, acquiring skills to use / practice
concepts, developing communication skills to
develop certain attitudes, developing thinking
patterns to developing judgment and wisdom.
Technological developments and the
advancement of the business world demand
universities to produce graduates who have high
competencies, so now there must be a change in
learning strategies centered on Student Center
Learning (SCL) students with a problem-solving
approach. Raising a question / case designed by the
lecturer that is able to bring out the students'
curiosity is then presented by randomly selecting
groups of students who will advance so that all
students have first understood and solved the
problem / case and then held a question and answer
so that the main role of the lecturer is as consultants
and facilitators, not as authorities and the only
source of knowledge. Siti Mutmainah (2011) states
that a case is called a good case if it has the
following characteristics: 1) decision-oriented
(raises a managerial situation in which a decision
must be made), 2) there is active student
participation (the case must be able to arouse
students' curiosity), 3 ) development of discussions
(the emergence of diverse views and analyzes), 4)
substantive cases (consisting of main sections that
discuss issues and other information), 5) questions
(understanding of what should be asked).
Problem solving learning strategy is a technique
in helping students learn to be able to understand
and master learning material by using problem
solving strategies. Problem solving is more likely
towards concepts or strategies. Problem solving
learning strategies can be implemented through a
learning approach, which is a way that is done by the
teacher / lecturer so that the material displayed can
adapt to the students. In addition, it can also be done
using learning methods, namely by presenting
material that is still broad (general). Problem solving
learning through the learning approach in the
subject, the lecturer conveys the subject matter by
directing students to the understanding of the
following subject matter in solving the problems.
Lecture material is seen as a problem that must be
understood, understood and resolved. Strategy
Problem solving learning as a teaching and learning
process, students are taught about problem solving
strategies by providing various examples of
problems related to lecture material concepts that
can and must be solved through problem solving
strategies.
Problem solving learning through the learning
approach in the subject, the lecturer conveys the
subject matter by directing students to the
understanding of the following subject matter in
solving the problems. Lecture material is seen as a
problem that must be understood, understood and
resolved. Strategy Problem solving learning as a
teaching and learning process, students are taught
about problem solving strategies by providing
various examples of problems related to lecture
material concepts that can and must be solved
through problem solving strategies.
According to Krulik and Rudnick (Carson, 2007:
21-22), there are five stages that can be done in
solving problems, namely as follows: 1. Read (read).
Activities carried out by students / students at this
stage are recording key words, asking other students
/ students what is being asked about the problem, or
re-expressing the problem into a language that is
easier to understand. 2. Explore (explore). This
process involves finding patterns to determine the
concept or principle of the problem. At this stage the
student / student identifies the problem given,
presents the problem in an easy-to-understand way.
The question used at this stage is, "what is the
problem like?" At this stage it is usually done
drawing or making tables. 3. Choose a strategy
(select a strategy). At this stage, students / students
draw conclusions or make hypotheses about how to
solve problems encountered based on what has been
obtained in the first two stages. 4. Solve the problem
(solve the problem). At this stage all mathematical
skills such as counting are done to find an answer. 5.
Review and discuss (review and extend). At this
stage, students check the answer again and see the
variation from how to solve the problem.
Definition of Teaching Materials
One of the initial activities in improving learning is
designing teaching materials that refer to a
development model to facilitate learning. Learning
design can be used as a starting point for efforts to
improve the quality of learning. This means that the
improvement of the quality of learning must begin
from improving the quality of learning design, and
designing learning with a system approach (Degeng,
1989 in M. Harijanto 2007).
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
252
Teaching materials are media and learning
resources that have a strategic position because
teaching materials prepare guidelines for students
both for the sake of independent learning and in
scheduled face-to-face activities, also equipped with
methods and evaluation, and guidelines for students.
Teaching materials are different from textbooks
(Anik Tri Suwarni et al, 2007).
Table 1: Teaching Materials
Text Book Teaching Materials
In general :
1. Assuming
interest from
readers
2. Written mainly
for use general
lecturer / reader
3. Designed to be
marketed widely
4. Don't always
explain the
purpose
instructional
5. Arranged
linearly
6. Structure based
on the logic of
science (content)
7. Not necessarily
giving practice
8. Don't anticipate
learning
difficulties
college student
9. Not necessarily
giving a
summary
10. Narrative writing
style
11. The material is
very solid
12. Do not have a
mechanism for
collect user
feedback
13. Do not give
suggestions on
ways study the
material in it
In general :
1. Generating interest from
readers
2. Written and designed for
student use
3. Explain instructional goals
4. Compiled based on
"flexible learning" patterns
5. The structure is based on
the final competency will
be achieved
6. Focusing on providing
opportunities for college
student
7. Accommodate student
learning difficulties
8. Always give a summary
9. Writing style (language)
communicative and semi-
formal
10. Packed for use in the
process instructional
11. Has a mechanism to collect
feedback from students
12. Includes learning
instructions
The instructional material developed must be
able to increase the motivation and effectiveness of
its users. Widodo in Lestari (2013: 2) revealed that
there are five characteristics of teaching materials,
namely 1) self instructional means that they can be
useful and used by students individually. Having
independent teaching materials can increase one's
awareness to want to try to complete their tasks
independently without seeing the work of others, 2)
self contained are various questions raised in each
chapter with the aim of sharpening the knowledge
and mastery of the knowledge that has been learned
from the teaching material 3) stand alone that does
not need help from other teaching materials. Good
teaching materials cover all subject matter so that
they do not need other teaching materials to
complete them, 4) adaptive if the teaching materials
can adapt the development of science and
technology, flexible use in various places, as well as
the contents of learning materials and software can
be used up to a certain time 5) user friendly that
makes it easier for users when they want to wear it.
The use of language is simple, easy to understand
and uses general terms.
The development of teaching materials must also
adjust to the curriculum because teaching materials
are part of curriculum development. Therefore the
procedure for developing instructional materials
must be related to the curriculum that applies as the
main reference, meaning that the instructional
material developed must be in accordance with the
IQF curriculum which refers to the learning
achievement standards and graduate competence
standards.
Development of Teaching Materials for Taxation
Subjects
Until 1960-1970 researchers had developed a
general model of problem solving to explain the
process of solving. Polya developed a problem
solving procedure on the basis of the nature of
problem solving ability as a process. There are four
stages of problem solving, namely; (1)
understanding the problem, (2) planning a solution,
(3) implementing the plan, (4) checking back
(www.kajianpustaka.com). Gick's model, 1986
(Foshay & Kirkley, 2003: 4) the following is the
latest model often used for problem solving.
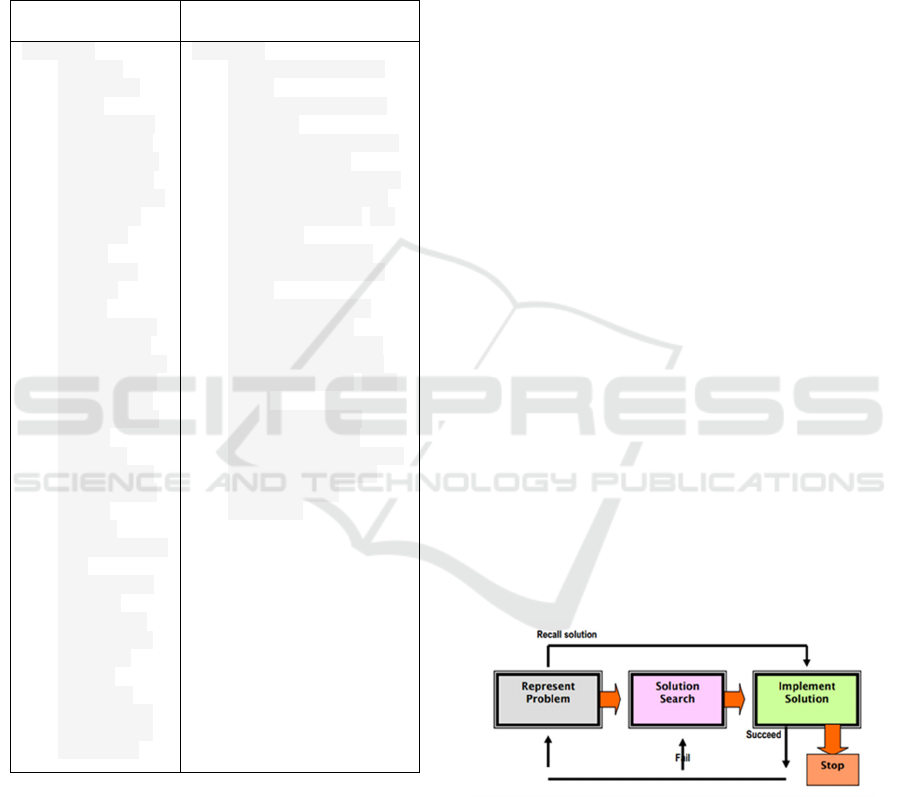
Figure 1: Gick's Model
In Gick's (1986) model there are three basic
sequences of cognitive process activities in problem
solving: (1) showing a problem (represent problem),
namely recalling the appropriate context of
knowledge, identifying goals and starting conditions
that are suitable for the problem; then (2) find a
solution (solution search), which is to clarify the
purpose and develop an action plan to achieve the
goal; and (3) the implementation of a solution
Development of Taxation Teaching Materials with Problem Solving Approach to Improve Student Learning Outcomes in Unimed Economic
Faculty
253
(implement solution), namely implementing the
planned actions and evaluating the results. For
students who are aware that the problem at hand is a
problem similar to a problem that has already been
solved, the procedure can be cut short from the first
step to the third step called recalling the previous
solution and repeating the same solution (recall
solution)
This research is Research and Development (R &
D). Development carried out in the form of Taxation
Teaching Materials. Development of Taxation
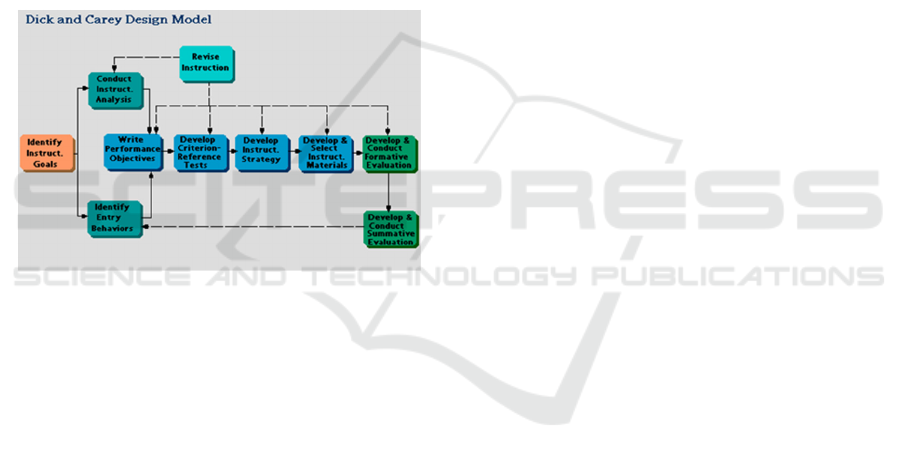
Learning Materials follows the Dick and Carey
Model. Sukmadinata (2012) explained "If the ten
steps of the Dick & Carey development model and
follow the stages of learning media development
well, it will be able to produce an educational
product that can be accounted for." The ten steps of
developing the Dick & Carey teaching materials
model are described as follows.
Figure 2: Dick and Carey Design Model
These steps are not standard things that must be
followed, the steps taken can be adjusted to the
needs of researchers. To produce interactive
teaching material products, planning is needed, good
learning design.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This research was conducted at the Faculty of
Economics, Medan State University, odd semester
2018/2019 school year. Implementation time from
May to October 2018. Research subjects were
divided into 6 study programs namely Economic
Education Study Program, Accounting Education,
Commerce Education, Office Administration
Education, Management Department, and
Accounting Department totaling ± 540 students. The
subject of this product trial was the semester v
business education student 2018/2019 school year
who were taking taxation courses. The total number
of subjects was 21 students with details of 6 students
for small group trials and 21 students for large group
trials.
In the development stage of learning media,
targeting in this case are lecturers, instructional
media experts, learning design experts, subject
matter experts. and students who assess learning
media that have been developed based on criteria, as
follows: (i) evaluators are based on the expertise
they have, (2) evaluators who carry out the
evaluation are determined based on the ability of the
practitioner / lecturer with the classification of
experts in the field of study.
This study uses a development research approach
(Research development Research). Educational
development research according to Borg & Gall
(2003), which is a process used to develop and
validate educational products, including procedures
and processes, such as learning strategies or ways of
managing learning. The development of learning
strategies and teaching materials in this study uses a
development model adopted from Dick, Carey and
Suparman, (2012). The stages of development
implementation consist of: 1) Pre Development 2)
Development of teaching materials and learning
strategies 3) Review and product testing 4) Test the
effectiveness and application of learning strategies
and teaching materials.
Data analysis activities in this study were chosen
into three, namely a) data analysis from practitioners
and experts / experts, b) data analysis when product
trials, and c) analysis of experimental test data. Data
analysis for a, b and c in this study uses quantitative
descriptive analysis. All collected data were
analyzed by descriptive statistical techniques which
were quantitatively separated by categories to
sharpen the assessment in drawing conclusions. This
analysis is intended to describe the characteristics of
the data in each variable. This method is expected to
make it easier to understand the data for the next
analysis process. The results of data analysis are
used as a basis for revising the developed media
products. Qualitative data in the form of statements
that are not feasible, less feasible, quite feasible and
feasible to be converted into quantitative data with a
value scale of 1 to 4.
The collected data is processed by summing,
compared to the expected number and percentage
obtained (Arikunto, 1996: 244), or can be written in
a formula as follows:
Percentage of eligibility (%) = (Observed
score)/(Expected score) x 100 %
The collected data were analyzed with
quantitative descriptive analysis techniques which
were revealed in the distribution of scores and
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
254
percentages on the categories of the predetermined
rating scale. After presenting it in percentage form,
the next step is to describe and draw conclusions
about each indicator. The suitability of aspects in the
development of teaching materials and learning
media can use the following table:
Table 2: Percentage scale tables
Percentage of
achievement
Interpretation
90 - 100 % Decent / attractive /
motivate
d
75 - 89 % Quite decent / attractive /
motivate
d
60 - 74 %
Less feasible / attractive /
motivate
d
0 - 59 % Not feasible / attractive /
motivate
d
In table 2 above, the percentage of achievement,
value scale and interpretation are mentioned. To find
out the feasibility of using table 2 above as a
reference for assessing data resulting from the
validation of media experts and material experts.
While the small group test of 6 students and a large
group trial of 21 students used objective tests to
obtain pre-test and post-test data. The results of the
percentage of feasibility according to material
experts, design and media and limited field trials are
then used as revision materials for the entire
teaching material before being applied to the target
population of all economic faculty students.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSIONS
The development of learning strategies and teaching
materials in this study uses a development model
adopted from Dick, Carey and Suparman, (2012).
The stages of development implementation consist
of: a) Pre-development b) Development of teaching
materials and learning strategies c) Review and
product trials d) Test the effectiveness and
application of learning strategies and teaching
materials.
a. Pre-development phase
The pre-development stage is carried out by holding
FGDs with taxation lecturers to identify learning
needs including: a) analyzing learning strategies
carried out in the learning process and analyzing
students' initial behaviors and characteristics in
following taxation courses that tend to be boring so
that they have difficulty in understanding learning
material, indicated by relatively low student learning
outcomes (pre-test) b) reviewing the course syllabus
by mapping the competency standards and basic
competencies of taxation courses based on the IQF
curriculum. c) do an explanation of the subject
matter or concepts and procedures that students will
learn.
b. Development phase of teaching materials and
learning strategies
At this stage, the collection, preparation and making
of teaching materials are carried out by holding an
FGD with tax lecturers and design experts. At this
stage, an overall review of taxation teaching
materials is carried out. All materials are adjusted to
the latest tax regulations that are generally
applicable in Indonesia. Making teaching materials
must pay attention to colors, images, language and
design (appearance) to stimulate students' thoughts,
attention and reading interest.
c. Stage of product review and trial
At this stage FGDs were carried out in each
evaluation stage, namely stage 1 evaluation
consisting of expert material, design and media
review, stage 1 analysis and revision, stage 2
evaluation consisting of small group trials, analysis,
revision 2, revision 3, Phase 3 evaluation consisted
of large group trials, student assessments and
revision 3
d. Test phase of effectiveness and application
The testing phase of product effectiveness (problem
solving based teaching materials) developed was
carried out to assess feasibility based on the
assessment of material experts, design experts and
media experts. The effectiveness test based on
expert material, design, and media aims to get
advice and material input, design, and media of
taxation teaching materials to be developed. These
suggestions and inputs are then analyzed and used to
develop teaching materials with problem solving in
accordance with the material of taxation teaching
materials so as to improve student learning
outcomes.
1. Data Description Test the Effectiveness of
Material Experts (field of study)
Expert material validation data is presented in the
following table:
Table 3: Assessment of Material Experts
N
o
Aspect
Assessm
en
t
Observat
ion Score
Score
Expect
e
d
Feasi
bility
Development of Taxation Teaching Materials with Problem Solving Approach to Improve Student Learning Outcomes in Unimed Economic
Faculty
255
1 Contents
Material
36 40 90%
2 Learning
Strategie
s
8 8 100%
Total 44 48 91,67
%
Based on table 3 above, the average total
assessment of learning material experts about
learning material with this problem solving obtained
91.67% results. In accordance with the percentage
scale in table 2, these results fall into the category of
feasible/attractive/ motivated touse.
The things suggested by the material expert are
1) the need for other sources for learning (in the
form of the latest tax regulations); 2) examples of
more efforts are made to facilitate student
understanding; 3) need to add tax cases / cases to
sharpen students' understanding (evaluation).
2. Description of Data Test the Effectiveness of
Design Expert
Design expert validation data is presented in the
following table:
Table 4: Assessment of Design Experts
N
o
Aspect
Assessm
en
t
Observat
ion Score
Score
Expecte
d
Feasi
bility
1 Textbook
Desi
g
n
48 56 85,71
%
Based on table 4 above, the average total
assessment of learning design experts about the
design of textbooks by solving this problem resulted
in 85.71%. In accordance with the percentage scale
in table 2, the results fall into the category of quite
feasible/attractive/ motivated to use.
The things suggested by the design expert are 1)
need to pay attention to the accuracy of the use of
colors, especially on the cover of textbooks; 2)
Consistent in the use of terms; 3) need to adjust the
type and form of exercises / questions to encourage
students to think critically (evaluation).
3. Description of Data Test the Effectiveness of
Media Expert
Media expert validation data is presented in the
following table:
Table 5: Assessment of Media Experts
N
o
Aspect
Assessmen
t
Observ
ation
Score
Score
Expected
Feasi
bility
1 Textbook
Media
35 40 87,5
%
Based on Table 5. above, the average total
assessment of the learning design experts on the
design of textbooks with the solution of this problem
was obtained at 87.5%. In accordance with the
percentage scale in table 2, these results fall into the
category of quite feasible / attractive / motivated to
use.
The things suggested by media experts are 1)
need to pay attention to the cover design, especially
the use of colors to increase student interest; 2) the
need for additional images to facilitate student
understanding; 3) need to pay attention to the
addition of color usage in the contents of teaching
materials.
3. Small group test results
Before conducting a small group test, the first
textbook is revised according to the advice or input
from the experts, then a small group is tested after
the revision is carried out based on the score
obtained. Aspects of small group trial evaluation for
students are carried out by pre-test and post-test.
This small group test is conducted to get input or
suggestions from potential users (students) based on
the results of the pre-test and post-test scores. The
small group test respondents were taken randomly
from 6 of the business education students of the
UNIMED economics faculty who took semester v
taxation courses in the 2018/2019 school year with
the categories of 2 high, medium and low ability
students respectively. The percentage of assessment
data for small group tests by students is presented in
the table below:
Table 6: Pre-test scores and post-test results for
small group testing
Respondent
No
Score
Pre-
tes
t
Score
Post-
Tes
t
Difference
1 6 8 2
2 7 9 2
3 4 7 3
4 6 8 2
5 5 8 3
6 7 10 3
Average 5,83 8,33 2,5
Source: Data processed, 2018
Table 6. above, shows that the mean / mean pre-
test score is 5.83, and the mean / mean post-test
score is 8.33, or an increase of 2.5. This means that
the use of instructional material products resulting
from development can increase student scores by
25%.
The assessment aspect of large group trials for
students is carried out by pre-test and post-test. This
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
256

large group test was conducted to get input or
suggestions from prospective users (students) based
on the results of the pre-test and post-test scores.
The respondents of this large group test were taken
randomly as many as 21 of the business education
students of UNIMED economics faculty who took
semester v taxation courses 2018/2019 school year
with the categories of each of the 7 high, medium
and low ability students.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of research and development of
teaching material products as stated earlier, it was
concluded:
1. Product specifications for teaching materials
that can be used by tutors and tutee (students)
The Faculty of Economics UNIMED as a
guidebook or guide in learning and completing
learning materials, tutorial tasks, and evaluation
of learning outcomes, is teaching material that:
(a) is deemed feasible / clear / interesting /
motivated, both in terms of design and content;
(b) serves as a learning medium in the
independent learning process of students of the
Faculty of Economics, UNIMED; and (c) able
to motivate independent learning and encourage
students to think critically.
2. From the assessment results according to the
material expert, it is "feasible / interesting /
motivated" with a score of 91.67%. The
assessment results according to the design
expert are "quite feasible / interesting /
motivated" with a score of 85.71%; while the
assessment results from media experts are "quite
decent / attractive / motivated" with a score of
87.5%
3. The use of teaching material products shows an
increase in student learning outcomes, which is
indicated by the difference in mean pre-test
scores and post-test small groups is 2.5 and the
large group is 2.76. This means that the use of
instructional materials as a result of
development can increase student scores by
25% and 27.6%.
Recommendations
Based on the results of this research and
development, it is recommended
1. Students can be used as an alternative source of
independent learning
2. The development of this product is proposed to
use more matching colors to make it more
attractive, both in terms of cover and contents.
3. The development of this product is suggested to
add examples of questions and exercises to
facilitate and sharpen students' understanding.
4. The research and development products in the
form of these teaching materials need to be
carried out in an operational field trial on the
larger subjects of UNIMED Faculty of
Economics students, before being used by all
UNIMED Faculty of Economics students to
improve the quality of the products produced.
REFERENCES
Borg, Walter R., & Gall, M.D. (1983). Educational
research: An introduction (4ed). New York &
London: Longman.
Foshay & Kirkley. (2003). Problem Solving.www.indiana-
edu/m
Dick, W., Carey, L., & Carey, J. O. (2005). The
Systematic Design of Instruction (6th ed.), New
York: Addison-Wesley Educational Publishers, Inc.
Handoko. (2005). Metode Kasus dalam Pengajaran
Manaemen). Makalah disampaikan pada Lokakarya
Peningkatan Kemampuan Penyusunan dan
Penerapan Kasus Untuk Pengajaran. Semarang 23
Nopember 2005
Siti Mutmainah. (2011) Pengaruh Penerapan Metode
Pembelajaran Kooperatif BerbasisKasus Yang
Berpusat Pada Mahasiswa Terhadap Efektivitas
Pembelajaran Akuntansi Keperilakuan. Undip-
journal online
Sukmadinata, Nana. S. (2012). Metode Penelitian
Pendidikan. Bandung: PT Remaja Rosdakarya
Suparman, Atwi,M (2012) Desain Instruksional Moderen,
Jakarta: Erlangga
Development of Taxation Teaching Materials with Problem Solving Approach to Improve Student Learning Outcomes in Unimed Economic
Faculty
257
