
Analysis of Tourism Development Strategy in North Tapanuli District
as City of Tourism
Toman Sony Tambunan
Doctoral Student in Management Science, University of North Sumatera
Keywords: Strategy, Tourism Development of North Tapanuli Regency, City of Tourism
Abstract: North Tapanuli Regency is an area that has the potential to be developed as a Tourism City through the use
of various potential natural beauty and local wisdom, so as to increase regional income, improve the
economy of the community, grow the business sector, and introduce local cultural values. This paper aims
to analyze the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats in the development of tourism in North
Tapanuli Regency as City of Tourism. Data collected through observation, interviews and literature studies.
Data analysis used qualitative descriptive analysis. The results of the data will be used to determine the
strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of tourism objects in North Tapanuli Regency as City of
Tourism. The conclusion of this paper states that for the tourism development strategy of North Tapanuli
Regency as City of Tourism, including: First, by building various infrastructure facilities that support
tourism. Second, actively carrying out various events. Third, carry out promotions continuously. Fourth,
develop various tourism products. Fifth, involves the participation of the community and all interested
parties (stakeholders) in managing tourism objects. Sixth, improve the competence of human resources for
tourism actors.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Backgorund
The tourism sector is considered important as an
increase in Regional Original Revenue for regions
that have good natural wealth potential, as well as in
general for the State. Tourism also contributes
positively to regional economic growth, increases in
people's income, increases opportunities in business,
increases the value of ownership of assets (such as:
the value of land), and is able to create employment
opportunities for local communities. Through
tourism as well, it will make the community more
concerned about the surrounding natural
environment, provide good motivation for the
community to maintain and preserve its cultural
values, provide opportunities for the community to
introduce their arts and culture, and improve social
welfare for the local community.
North Tapanuli Regency is a district located in
the administrative area of North Sumatra Province.
North Tapanuli Regency has the potential and
resources that can be developed as an area of natural
tourism, cultural tourism and spiritual tourism. The
potential of superior natural wealth owned by North
Tapanuli Regency has become an attraction for
tourists from local, domestic and overseas who want
to visit. Regency has natural wealth that can be
managed well as a natural tourist attraction.
1.2 Problem Formulation
a. What potential does North Tapanuli Regency
have as a natural tourist attraction, cultural
tourism and spiritual tourism?
b. How is the tourism development strategy of
North Tapanuli Regency as "City of Tourism”?
1.3 Purpose and Objectives
The purpose of this paper is to contribute ideas to all
parties regarding the tourism development strategy
of North Tapanuli Regency as "City of Tourism ".
The purpose of this paper is to find out the potential
of North Tapanuli Regency as a natural tourist
202
Tambunan, T.
Analysis of Tourism Development Strategy in North Tapanuli District as City of Tourism.
DOI: 10.5220/0009493802020207
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 202-207
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

attraction, cultural tourism and spiritual tourism, as
well as establishing a strategy for tourism
development in North Tapanuli Regency.
2 THEORICAL DESCRIPTION
Hubeis and Najib (2008), write in his book that the
concepts of Strength, Weaknesses, Opportunities,
and Threats (SWOT) have a basic assumption that
the organization must align its internal activities
with external reality in order to achieve the stated
goals. Opportunities will not be meaningful when a
company is not able to utilize its resources to take
advantage of these opportunities. Furthermore, it
was written that the components of the SWOT
preparation were defined as follows:
a. Strength is the organizational resources or
capacity that can be used effectively to achieve
goals.
b. Weaknessesare limitations, tolerance, or
organizational defects that can hinder the
achievement of goals.
c. Opportunitiesare supportive situations in an
organization that are depicted from similar
tendencies or changes or views needed to
increase product / service demand and enable
the organization to increase its position through
supply activities.
d. Threatsare situations that do not support
obstacles, constraints or various other external
elements in the organizational environment that
have the potential to damage the strategies that
have been prepared so that they cause problems,
damage or errors.
The Power-Opportunity Strategy (SO-Strength
Opprotunities), uses the company's internal strength
to take advantage of external opportunities. Hunger
and Wheelen (2003), mention that SO Strategy by
thinking of certain ways that a company can use its
strengths to take advantage of the opportunities that
exist.
The Weaknesses Opportunities Strategy, aims to
increase internal weaknesses by taking advantage of
external opportunities. Hunger and Wheelen (2003),
stated that the WO strategy is to take advantage of
the opportunities that exist by overcoming various
company weaknesses.
Strength-Threat Strategy (ST-Strength Threats),
uses company strength to avoid or reduce external
threats. Hunger and Wheelen (2003) stated that the
ST strategy is a defensive strategy to minimize
weaknesses and avoid threats.
Weakness-Threat Strategy (WT-Weaknesses
Threats) is a defensive tactic carried out to reduce
internal weaknesses and avoid external threats.
Hubeis and Najib (2008), stated that the WT strategy
was a strategy to reduce weaknesses to minimize
existing threats.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
3.1 Research Sites
This research was carried out in North Tapanuli
Regency, North Sumatra Province.
3.2 The Scope of Research
The limitation of this writing problem only discusses
internal factors (strengths and weaknesses) as well
as external (opportunities and threats) of the tourism
potential of North Tapanuli Regency obtained
through the Preliminary Survey, Problem
Identification, Literature Study, Identification of
writing variables and Data Analysis. Limitation on
the problem under study is the potential in North
Tapanuli Regency which is related to the
development of regional tourism is the potential of
natural tourism, cultural tourism and spiritual
tourism. The potential possessed by North Tapanuli
Regency, including the natural beauty of the hills,
the relics of ancient tombs which are the spreaders
of Christianity (missionaries).
3.3 Method of Collecting Data
Data collection used in this study is by in-depth
interviews, direct observation (observation). As well
as Literature Study through the collection of
material, data and information from various
literatures such as books, journals, and articles
related to the issues discussed. And the discussion is
carried out in a descriptive analysis to explain
various things related to the title of the writing.
3.4 Data Analysis Method
Data analysis was carried out qualitatively.
Qualitative paradigm is a research paradigm that
emphasizes the understanding of problems in social
life based on holistic, complex and detailed reality
conditions. (Indriantoro and Supomo, 2002).
Qualitative research methods are research methods
based on the philosophy of postpositivism, used to
examine the condition of natural objects, where
researchers are key instruments, data collection
techniques are carried out jointly, data analysis is
inductive / qualitative and the results emphasize the
meaning rather than generalization. (Sugiyono,
2010).
Analysis of Tourism Development Strategy in North Tapanuli District as City of Tourism
203
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSIONS
4.1 General Condition of North Tapanuli
District
Geographical conditions North Tapanuli Regency is
located in the highland development region of North
Sumatra at an altitude between 300-1500 meters
above sea level, so as to provide beautiful scenery
and produce cool air. North Tapanuli Regency is
directly adjacent to five regencies, namely, in the
north bordering Kabupaten Toba Samosir; in the east
bordering LabuhanBatu Regency; in the south
bordering South Tapanuli Regency; and on the West
bordering the HumbangHasundutan and Central
Tapanuli Regencies. The geographical and
astronomical location of North Tapanuli Regency is
very beneficial because it is in the crossing of
several regencies in North Sumatra Province. North
Tapanuli Regency consists of 15 Districts, namely
Tarutung, Sipoholon, Siborong-borong, Muara,
Pagaran, Parmonangan, Sipahutar, Pangaribuan,
Garoga, SiatasBarita, Pahae Jae, PahaeJulu,
Simangumban, PurbaTua, and Adiankoting.
4.2 SWOT Analysis of North Tapanuli
Regency Tourism Development
Based on descriptive data obtained by the method of
observation, interview and documentation search
results, the authors determine the object performance
score by means of judgment (judgment value.)
The rating scale for positive factors, namely
Strength and Opportunities is:
1 = Very Weak
2 = Weak
3 = Strong
4 = Very Strong
The rating scale for negative factors, namely
Weaknesses and Threats are:
1 = Very Strong
2 = Strong
3 = Weak
4 = Very Weak
Weights are determined based on how important
these factors are, which are according to the results
of a review of tourism theories. The total total
maximum weight value is 1 (one). To facilitate the
provision of values and weighting, the Internal Table
Factor Analysis Strategy (IFAS) and the External
Factor Analysis Strategy (EFAS) are:
The results of a study of the Internal Factor
Analysis Strategy (IFAS) on Lake Toba attractions
can be seen in Table 1, below:
Tabel 1: Internal Factor Analysis Strategy (IFAS)
No.
Strength (S) :
Score
Weight
Total
1.
Panorama of natural
beauty on
attractions.
0,2
4
0,8
2.
Beautiful
atmosphere in
providing comfort.
0,2
4
0,8
3.
Cool air condition.
0,2
4
0,8
4.
Close to
international
airports.
0,15
4
0,6
5.
Availability of
transportation to get
to tourist
attractions.
0,15
4
0,6
6.
Cultural uniqueness
that can be added
value in supporting
tourism programs.
0,2
4
0,8
Total Strength
4,4
No.
Weakness (W) :
Score
Weight
Total
1.
Lack of cultural arts
events on a regular
basis.
0,4
2
0,8
2.
Limited funding for
tourism
development.
0,3
2
0,6
3.
There are still a lot
of people doing fish
breeding in the lake
area.
0,3
2
0,6
4.
There are still many
people who dispose
of household /
livestock waste into
the lake area.
0,4
2
0,8
5.
Lack of good
infrastructure in the
tourist area.
0,3
3
0,9
Total of Weakness
3,7
Total (difference:
S-W)
0,7
The strength mentioned above is a supporting
factor in the development of tourism in North
Tapanuli Regency as City Tour. The Weakness
mentioned above, can be resolved with the policy of
determining an efficient and effective management
strategy by the Government by involving
community participation.
The results of the study of the External Factor
Analysis Strategy (EFAS) on the development of
tourism in North Tapanuli Regency as City of
Tourism can be seen in Table 2, below:
Tabel 2: External Factor Analysis Strategy (EFAS)
No.
Opportunities (O) :
Score
Weight
Total
1.
The Central Government
plans to develop Lake
0,15
4
0,6
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
204
Toba Tourism Area as a
National Tourism
Strategic Area.
2.
The Government's goal is
to make Lake Toba an
international tourist
destination.
0,1
3
0,3
3.
Tourism has been
established in North
Tapanuli Regency as a
strategic tourism
destination.
0,1
4
0,4
4.
The tourism sector of
North Tapanuli Regency
can create jobs; and grow
small and medium
businesses.
0,2
4
0,8
5.
The need for tourism for
each individual is quite
high.
0,15
4
0,6
6.
The tourism marketing
concept of North Tapanuli
Regency has been
supported by a complete
promotional media and
technology.
0,15
4
0,6
Total of Opportunities
3,3
No.
Threats (T) :
Score
Weight
Total
1.
Environmental damage
due to community
exploitation.
0,5
2
1
2.
Lack of public awareness
in maintaining the
cleanliness of water in the
Lake Toba area, which in
this case is around the
object of Muara Beach.
0,5
2
1
3.
Community income still
depends on the
availability of natural
resources around the Lake
Toba area, so that the
potential to utilize natural
resources to meet the
needs of the community.
0,4
2
0,8
Total of Threats
2,8
Total (different: O-T)
0,5
So, the internal factor evaluation value is 0.7; while
the evaluation of external factors is 0,5.
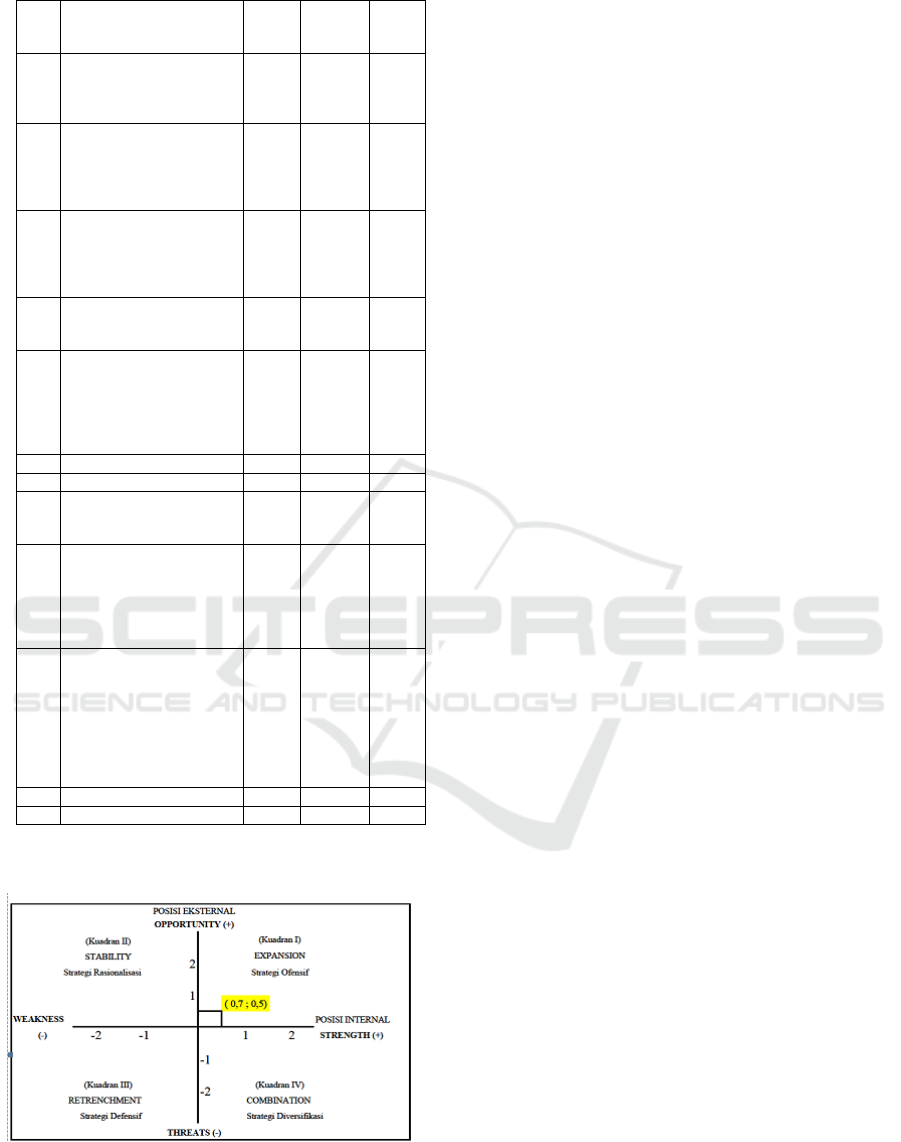
Figure 1: SWOT Matrix
Based on the figure 1 above, it can be explained that
based on the weight and rating of each element in
the SWOT Matrix, it is known that the position of
Lake Toba tourist objects is in Quadrant I, namely
the Offensive Strategy Quadrant (Expansion) which
is located at the coordinate point (0.7; 0.5). This
position explains that the tourism object of North
Tapanuli Regency as a Tourist City in the 'Strong
Internal and External Conditions', where with this
condition the tourism object of North Tapanuli
Regency has a good opportunity to be developed
into an area of Nature Tourism, Cultural Tourism
and Spiritual Tourism, which supported by various
elements of strength and opportunity, and strives to
minimize weaknesses and threats.
4.3. Tourism Development Strategy for
North Tapanuly Regency Through
SWOT Analysis
Based on the results of a SWOT analysis of tourism
in North Tapanuli Regency as the Tourism City
mentioned above, the authors try to describe some
strategies that need to be established for tourism
development in North Tapanuli Regency as a City of
Tourism through SWOT Analysis, namely:
1. SO (Strength and Opportunities) Strategy,
which is a strategy that optimizes Strength to
utilize Opportunities. The form of the SO
strategy is:
a. Growing Regional Tourism Core Competencies,
namely the excellence or uniqueness of
resources including natural resources and the
ability of an area in the tourism sector to build
competitiveness in order to develop the regional
economy towards independence. The target of
the development of the tourism sector in North
Tapanuli Regency as City of Tourism, among
others are: First, Utilizing resources, including
the natural resources owned by the region
optimally. Second, Increasing regional
competitiveness based on the superiority of the
regions they have. Third, Increase added value
along the flagship commodity tourism chain.
Fourth, Building the uniqueness of the region.
b. Build and improve facilities and infrastructure
to support comfort and safety. The availability
of good tourism accessibility is the most
important element in shaping the quality of
tourism products as a whole.
c. Building Facilities and Accommodation
Tourism that is comfortable, quality, provides
good service, and sanitation is good. The
facilities and accommodations referred to above
are hotels, villas, retail centers and hospitals that
have the best facilities. Strived to design the
tourism concept of North Tapanuli Regency as
an integrated tourism and economic area.
Analysis of Tourism Development Strategy in North Tapanuli District as City of Tourism
205

d. Adding international-standard "SILANGIT"
airport flight routes owned by North Tapanuli
Regency. The increasing number of direct flight
routes from Silangit airport is expected to
increase the number of domestic and
international tourists. At present, SILANGIT
International Airport, has opened various
domestic and international flights. To facilitate
and shorten the distance traveled by tourists, it
is necessary to add an airport that is closer to
tourism objects in North Tapanuli Regency.
Table 4: Silangit International Airport Flight
Routes
No.
Flight Route
Aircraft
Type
Start
Operating
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
Silangit –
Medan
Silangit –
Batam
Silangit –
Jakarta
Silangit –
Jakarta
Silangit –
Medan
Silangit –
BandaraSoeta
Silangit – Halim
PerdanaKesuma
Silangit –
Singapore
Silangit -
Malaysia
Commercial
Aircraft Susi
Air
Wings Air
Sriwijayatype
757-500
Garuda type
CRJ-1000
Garuda type
ATR 72-500
Batik Airbus
Citilink
Garuda CRJ
Garuda
In 2006
In 2016
In 2015
In 2016
In 2016
Desember
2017
September
2017
In 2017
Januari
2018
e. Increase annual routine events / events such as
cultural parties, folk parties, music festivals and
various national and international sports
activities. This activity aims to maintain and
promote the natural, cultural and customs
potential of North Tapanuli Regency.
f. Maintain the values of local wisdom that apply
in people's lives, so that it can be a selling point
in supporting various cultural parties and party
events.
g. Inviting people in North Tapanuli Regency to
routinely carry out cultural performances.
2. WO (Weakness and Opportunities) Strategy,
which is a strategy that minimizes Weakness by
utilizing opportunities (Opportunities). The
form of the WO strategy is:
a. Build good facilities and infrastructure to attract
tourists.
b. Utilizing and managing more professional and
well-organized tourism objects. So that it can
guarantee the quality of tourism products and
services.
c. Conduct continuous tourism promotion or
marketing of tourism objects in North Tapanuli
Regency, both domestically and abroad.
Promotions are carried out both in the form of
promotions in print and electronic media. The
purpose of this promotion is: First, introducing
various potentials owned by North Tapanuli
Regency. Second, looking for potential new
consumer opportunities abroad. Third, maintain
the loyalty of consumers (tourists) who have
come to tour tourism objects in North Tapanuli
Regency.
d. Organize, maintain, and preserve the
environment around tourist attractions so that
the environment of the tourist area is maintained
its cleanliness, coolness and beauty.
e. Improving coordination with investors. That is,
the Government must be able to establish
cooperation with the investors (investors) both
from domestic and abroad to want to invest
(invest) in supporting the development and
development of tourism in North Tapanuli
Regency in a sustainable manner.
f. Improve coordination and cooperation with
tourism institutions. The government needs to
hold meetings in the form of "Community
Tourism Business Forum" to the existing actors
or tourism institutions as well as tourism
management institutions from domestic and
abroad.
g. Empowering, counseling and training elements
of the community, in order to foster and
increase awareness and important role of the
community in the tourism sector.
3. ST (Strength and Threats) Strategy, namely a
strategy that uses Strength to overcome Threats.
The form of the ST strategy is:
a. Creating Geological Based Educative Tourism
(Geotourism). That is, the Government and the
local community must be able to make tourism
in North Tapanuli Regency a geological based
tourism area. The North Tapanuli area is
endeavored to become a research laboratory to
research or recognize various types of plants,
animal, rocks, moisture content, chemical
elements, and so on.
b. Creating Smart Environment-based Education,
which is an environmental education program
that refers to the concept of green economy.
c. Carrying out education based on local wisdom,
namely education that utilizes regional
superiority or value in terms of economic,
cultural, language, information and
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
206

communication technology, ecology, and
others.
d. Conduct reforestation activities or re-plant trees
for natural, water and forest areas that have
experienced environmental damage.
e. Create programs and facilities that can
guarantee safety, security and comfort for
tourists visiting.
f. Manage tourism objects that are better and more
professional, so as to create an impression and a
good travel experience from tourists.
4. WT (Weakness and Threats)Strategy, which is a
strategy that minimizes Weakness and avoids
Threats. The form of the WT strategy is:
a. Improving the quality of human resources, both
for the community, stakeholders, stakeholders,
and the Regional Government, so as to create
skilled and competent personnel to support the
improvement of the tourism sector.
b. Manage tourist destinations that are more
professional and quality, so as to increase the
number of tourist visitors in a sustainable
manner.
c. Increasing the special attraction for tourism
objects (differentiation), so as to give a different
impression or service than before.
d. Supervise, maintain and fix various supporting
facilities that already exist in tourist objects.
e. Maintaining the survival of natural resources
available in the tourist area.
f. Improve legal instruments for regulating the life
of a tourism industry that is conducive, safe,
comfortable and fair.
5 CONCLUSION
Based on the results of the discussion of this study, it
was concluded that for tourism development
strategies in North Tapanuli Regency as "City of
Tourism", both as Nature Tourism, Cultural Tourism
and Spiritual Tourism, including: First, by building
various infrastructure facilities that support tourism,
such as road access, transportation, and adequate
accommodation accommodation facilities. Secondly,
actively carrying out performances. Third, carry out
promotion of tourism objects on an ongoing basis to
foreign countries. Fourth, develop various tourism
products. Fifth, involves the participation of the
community and all parties interested in managing
tourism objects. Sixth, improve the competence of
human resources for tourism actors.
6 RECOMENDATIONS
North Tapanuli Regency has abundant natural
resource potential that can be utilized and managed
to support the tourism sector. The participation of all
parties (both the community, the Government,
Academics and tourism industry players) is needed
in realizing North Tapanuli Regency as a City of
Tourism, both as Nature Tourism, Cultural Tourism
and Spiritual Tourism. The role of the Government
is very large in managing and developing all tourism
objects to be better, professional and quality.
Besides that, there is also a change in mentality
(mindset) from all stakeholders supporting tourism
development.
REFERENCES
Hubeis, Musa dan Mukhamad Najib. (2008). Manajemen
Stratejik dalam Pengembangan Daya Saing
Organisasi. Jakarta. Penerbit:Elex Media
Komputindo.
Hunger, J. David dan Thomas L. Wheelen. (2003).
Management Strategis (terjemahan). Yogyakarta:
Penerbit Andi.
Indriantoro, Nurdan Bambang Supomo. (2002).
Metodologi Penelitian Bisnis untuk Akuntansi dan
Manajemen. Penerbit BPFE, Yogyakarta.
Sugiyono. (2010). Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif,
Kualitatif, R&D. Penerbit Alfabeta, Bandung.
Analysis of Tourism Development Strategy in North Tapanuli District as City of Tourism
207
