
The Influence of Logical Intelligence of Mathematics and Soft Skills
on Students’ Learning Outcomes of Introductory Economics Course
Thamrin
1
, Abdul Hasan Saragih
1
and Abdul Muin Sibuea
1
1
Faculty of Economics, Universitas Negeri Medan, Medan -Indonesia
Keywords: Logical Intelligence, Mathematics, soft skills, learning Outcomes
Abstract: The problem of education is relatively complex because many variables influence it. One of these factors is
the characteristics (logical intelligence mathematics) and student Soft Skills. The phenomena that occur in
the field, especially in the learning process of the lecturer/teacher, that they do not pay attention to the
problems of logical intelligence of mathematics and student soft skills, so that the learning outcomes are not
optimal. This study aims to determine the effect of logical intelligence of mathematics and soft skills on
learning outcomes in students of introductory economics. This research method is the descriptive ex-post
facto method. The population in this study were all students of the economic education department in
Economics Faculty Unimed who were attending the introductory economics as many as 90 people. The data
collected was analyzed using linear regression statistics with SPSS for windows. The results of this study
indicate that logical intelligence of mathematics and soft skills have a positive and significant effect on
student outcomes in the introductory economics course.
1 INTRODUCTION
Introduction of economics is one of the primary
subjects in economics that should be taken by the
students in the economic education graduate
program. The introduction of economics course is
the essential subject of study with the aim of
learning that students are competent in identifying
and analyzing the behavior of individual economic
actors, explaining the process of equilibrium prices,
applying them in daily life both as consumers and
producers and analyzing markets.
This introductory economics course is essential
for students because these alumni from the study
program of economic education will later become
professional teachers in economics at the high
school/vocational level and teach the knowledge
related to introducing this economy to their students.
Based on this, the introductory economics course
must be truly mastered by students. But the reality
shows that student learning outcomes are not
satisfactory. Data on the acquisition of student
economic learning outcomes shows that only 5.70%
of students get the maximum score (A), 11.42% get
a B score, while those who get a C score there are
48.57% and those who do not pass with an E value
of 34, 28% (Source of data for the Final Value of
2014 economic education study program).
From the educational technology point of view,
according to the framework of learning theory, the
problem of the low quality of learning is the problem
of originating from the characteristics of students in
the form of intelligence in the form of mathematical
logics (Reigeluth, 2003; Miarso, 2004).
Furthermore, Sobur (2013) explained that children
whose intelligence level is classified as less or lower
than the level of the general ability of their age
children would experience difficulties in following
lessons that are normal for other children. For other
children, just reading and understanding what is
learned is enough, he must read many times to
understand.
Another factor that can affect learning outcomes
is that soft skills are part of a person's skills that are
more about the subtlety or sensitivity of one's
feelings towards the environment around them. Soft
skills are a person's skills in dealing with others.
Universitas Negeri Medan (Unimed) has
determined that there are eleven elements of soft
skills integrated with lectures, among others:
honesty, respect, responsibility, fairness, caring,
Thamrin, ., Saragih, A. and Sibuea, A.
The Influence of Logical Intelligence of Mathematics and Soft Skills on Students’ Learning Outcomes of Introductory Economics Course.
DOI: 10.5220/0009491900390042
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 39-42
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
39

citizenship, tolerance, toughness, dignity,
intelligence, religion. Logical intelligence of
mathematics and soft skills are thought to influence
the learning outcomes of introducing economic
students in economic education graduate programs.
2 THEORICAL FRAMEWORK
Becker and Watts (1996) and Fry, Ketteridge and
Marshall (2008) explain that learning economics is
increasingly based on analytical models that require
a high level of mathematical understanding, where
the past is more discursive and text-based. Like
other disciplines that need good mathematical skills.
The introductory economics course requires
mathematics logical intelligence in students because
introductory economics courses are not only related
to the concept of mathematically calculating but the
ability to analyze phenomena occurring in the
economy which of course requires logic to an alyze
the phenomenon and then try to solve problems
according to phenomenon. The intelligence of
mathematical logic is needed as a basis for studying
introductory economics courses.
According to Lwin et al., (2008), mathematics
logical intelligence is the ability to handle numbers,
calculations, patterns, logical and scientific thinking.
Further explained that the relationship between
mathematics and logic is that both strictly adhere to
the fundamental law. The lack of mathematical logic
results in a large number of individual and cultural
problems.
Furthermore, Armstrong (2013) explains that
mathematics logical intelligence is the ability to use
numbers. This intelligence includes sensitivity to
logical patterns and relationships, statements and
arguments (if-then, causation), functions, and other
related abstractions.
The types of processes used in logical-
mathematical intelligence services include
categorization, classification, inference,
generalization, calculation, and hypothesis testing.
Based on the explanation above, it can be seen that
mathematics logical intelligence gives a person the
capacity to use numbers effectively, sensitive to
logical patterns, statement relations, and causal
conditions. In this study students who have
mathematics logical intelligence will be able to use
numbers effectively, be sensitive to logical patterns,
statement relationships, and causal conditions that
are useful for problem-solving in learning
Introduction to economics.
Another factor that is no less important
influences the learning outcomes of introducing
economics is the Soft skills of the students
concerned. Ngang, Hashim and Yunus (2015)
explained that soft skills combine aspects of general
skills which include non-academic skills such as
communicative, critical thinking and problem
solving, teamwork, learning, and information
throughout life, entrepreneurship, professional ethics
and morals, and leadership. Cimatti (2016) further
explained that Softskills predict success in life.
Cimatti (2016) identifies causal correlations between
Soft skills and personal and professional
achievements of a person.
The results of the Mujiani's study (2016) explain
that there is an influence of high and low logical
intelligence of mathematics on learning outcomes.
From the whole opinion above, it becomes a strong
theoretical foundation to build the hypothesis of this
research that there is the influence of mathematics
logical intelligence and soft skills on the
introductory learning outcomes of the economy.
In this study, the elements of soft skills refer to
the book on the development of Unimed academic
culture where there are eleven soft skill elements
which integrated into the learning process.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This research using ex-post facto research method.
The study was conducted on students who had
participated in introductory economic lectures. The
population in this study were all economic education
students who had just joined the introductory
economics lectures as many as 90 students. The
sampling technique used is total sampling. Data was
collected through a questionnaire about soft skills
and tests to measure students' intelligence of
mathematical logics.
The data were analyzed using multiple linear
regression statistics with the help of SPSS version
20 application.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Based on the data that has been analyzed, the results
of research on mathematics logical intelligence, soft
skills and learning outcomes introducing economic
students as shown in Table 1.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
40
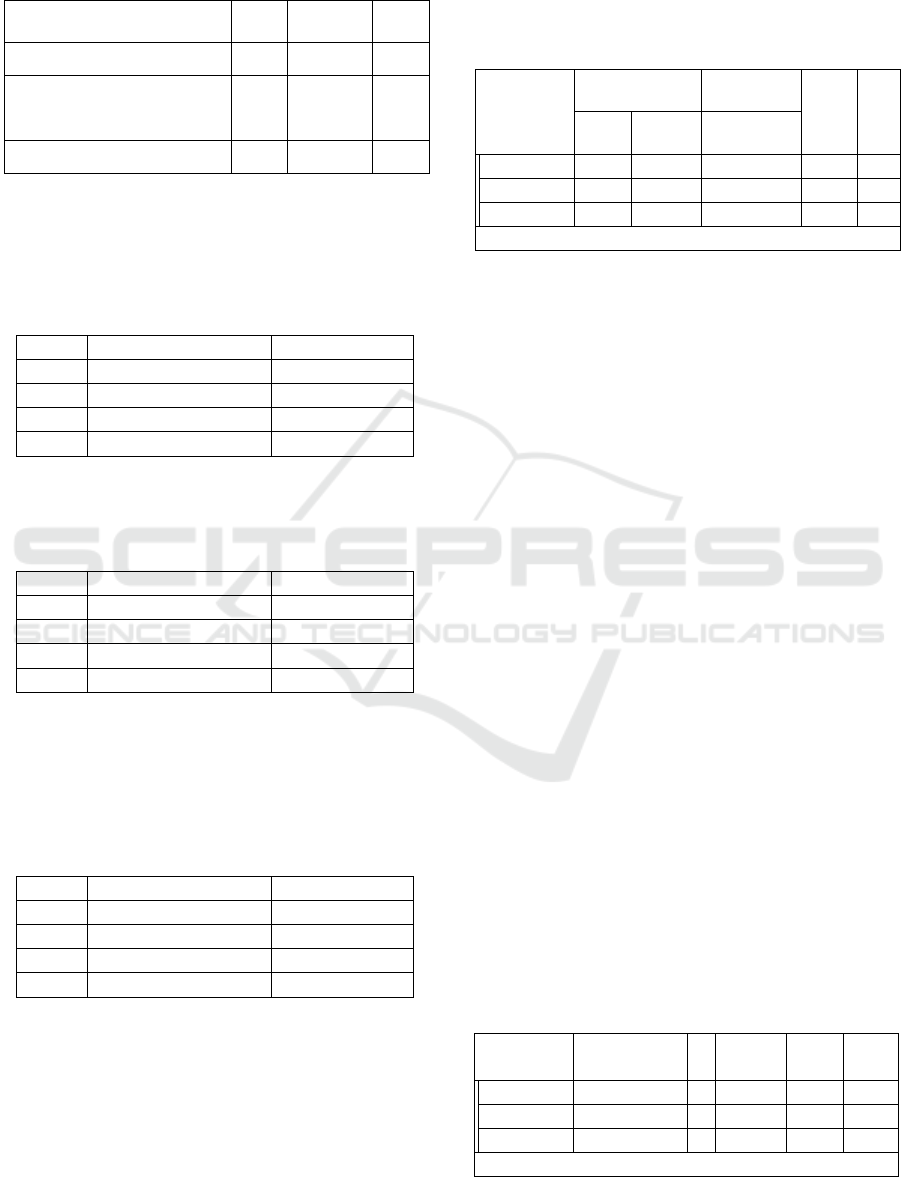
Table 1: Logical Intelligence of Mathematics, Soft
Skills and Learning Outcomes Introduction to
Economics
Mean
Std.
Deviation
N
Learning outcome
73.92
9.51
90
Mathematics Logical
Intelegence
72.93
11.26
90
Softskills
3.39
.26128
90
Refers to Table.1, it can be seen that logical
intelligence of mathematics and soft skills are in the
good category (average score of 73.92). The soft
skills category is as shown in Table.2.
Table 2: Category of Mathematics Logical
Intelegence
No
Interval
Category
1
80 -92
Very Good
2
68-80
Good
3
56-68
Sufficient
4
44-56
Poor
Furthermore, the categories of soft skills for
economic education students can observed in Table
3.
Table 3: Category of Soft Skills
No
Interval
Category
1
3,56 - 3,76
Very Good
2
3,36 - 3,55
Good
3
3,16 - 3,35
Sufficient
4
2,96 - 3,15
Poor
Based on the soft skills category in Table.3, the Soft
skills of students in economic education graduate
programs are in a good grade (average score of
3.39). Furthermore, the primary learning outcomes
of student economics categorized following to Table
4 below.
Table 4: Category of Learning Result
No
Interval
Category
1
86 - 94,09
Very Good
2
77,91 - 85,99
Good
3
69,82-77,90
Sufficient
4
61,73-69,81
Poor
According to the data in Table 4, it can be seen
that the learning outcomes of students' in the
introduction of economics subject are in a sufficient
category (average score of 73.92).
Data collected was analyzed by linear regression
statistics. Before examining the data, normality and
linearity have been tested, and the data has met the
requirements for normality and linearity test.
Furthermore, the results of data processing to see the
effect of mathematics logical intelligence and soft
skills on learning outcomes can be seen in Table 5 as
follow.
Table 5: The Result of Regression Analysis
Model
Unstandardized
Coefficients
Standardized
Coefficients
t
Sig.
B
Std.
Error
Beta
(Constant)
13.38
13.261
1.009
.316
KLM
.309
.080
.366
3.865
.000
Softskills
11.18
3.447
.307
3.244
.002
a. Dependent Variable: learning outcome.
The result shows there is a positive and
significant influence of mathematics logical
intelligence on student learning outcomes in the
introduction of economics subject (sig 0.00 5 0.05).
Likewise, the soft skills have a positive and
significant effect on economic learning outcomes
with (sig 0.002 ≤ 0.05) which means that student's
soft skills positively and significantly influence the
learning outcomes of the students. Therefore,
mathematics logical intelligence and soft skills
affect the learning outcomes as can be seen in the
results of data processing in Table 6.
Based on the table, it can be found that the linear
regression equation is:
Y = 13.38 + 0.31 X1 + 11.18 X2.
Which means that the constant 13.38 shows that
if mathematics logical intelligence and soft skills are
0, then the learning outcomes of the student are
13.38. The regression coefficient of mathematics
logical intelligence (X1) of 0.31 explains that if
students' mathematics logical intelligence increases
one unit, then the learning outcomes increase by
0.31 units assuming other independent variables
remain. The soft skills regression coefficient 11.18
shows that if a student's soft skills increase by one
unit, then the learning outcomes of the student will
increase by 11.18 units assuming other independent
variables remain. The result of the effect of
mathematics logical intelegence and softs kills on
learning outcomes can observed in table 6 below.
Tabel 6: Table of ANOVA
Model
Sum of
Squares
df
Mean
Square
F
Sig.
Regression
1788.355
2
894.17
12.39
.000
b
Residual
6277.180
87
72.15
Total
8065.535
89
a. Dependent Variable: learning outcomes
The Influence of Logical Intelligence of Mathematics and Soft Skills on Students’ Learning Outcomes of Introductory Economics Course
41

b. Predictors: (Constant), Softs kills, Mathematics
Logical Intelegence
Based on Table 6, it can be seen that together
mathematics logical intelligence and soft skills
variables have a positive and significant effect on
learning outcomes (sig 0.000<0,05).
The results of this study prove that mathematics
logical intelligence and soft skills have a positive
and significant impact on the learning outcomes of
the introduction of economics subject. The
introductory learning outcomes of the economy are
the culmination of learning activities carried out by
students and lecturers.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In recent years, a large number of studies have
established the importance of soft skills in fostering
student academic achievement and long-term
success. Some educators consider soft skills as a
critical instrument for the application of lessons
learned in core academic subjects. Educators often
frame soft skills development as a complementary
instruction in the core academic and school fields
praising the "balanced approach" to produce
graduates with "rigorous content knowledge and the
ability to apply that knowledge successfully. Other
researchers and educators highlight the direct impact
of soft skill development on achievement in core
academic subjects. Students who participate in
cooperative learning, for example, not only improve
teamwork skills but also learn faster and more
efficiently, are more likely to stay in their education,
and feel more positive about learning than students
taught in traditional classroom settings. The findings
of this study are in line with Pereira's (2013) and
Souza's et al. (2018) research, which explains that
students in all programs should emphasize the
importance of soft skills in their education
experience.
REFERENCES
Armstrong, M. A. (2013) Basic topology. Springer
Science & Business Media.
Becker, W. E. and Watts, M. (1996) ‘Chalk and Talk: A
National Survey on Teaching Undergraduate
Economics’, American Economic Review, 86(2), pp.
448–453.
Cimatti, B. (2016) ‘Definition , Development ,
Assessment of Soft Skills and Their Role for the
Quality of’, International Journal on Language,
Literature and Culture in Education, 10(1), pp. 97–
130. doi: 10.18421/IJQR10.01-05.
Fry, H., Ketteridge, S. and Marshall, S. (2008) A
handbook for teaching and learning in higher
education: Enhancing academic practice. Routledge.
Lwin, M. et al. (2008) Cara Mengembangkan Berbagai
Komponen Kecerdasan. Yogyakarta: Indeks.
Miarso, Y. (2004) Menyemai benih teknologi pendidikan.
Jakarta: Kencana.
Mujiani, D. S. (2016) ‘Pengaruh Media Pembelajaran dan
Kecerdasan Logis Matematis Terhadap Hasil Belajar
Matematika Siswa’, Jurnal Pendidikan Dasar, 7(2),
pp. 199–209.
Ngang, T. K., Hashim, N. H. and Yunus, H. M. (2015)
‘Novice Teacher Perceptions of the Soft Skills
Needed in Today’s Workplace’, Procedia - Social
and Behavioral Sciences. Elsevier B.V., 177(July
2014), pp. 284–288. doi:
10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.02.338.
Pereira, O. P. (2013) ‘Soft skills: From university to the
work environment. Analysis of a survey of graduates
in Portugal’, Regional and Sectoral Economic
Studies, 13(1), pp. 105–118.
Reigeluth, C. M. (2003) Instructional design theories and
models: An overview of their current status.
Routledge.
Sobur, A. (2013) Psikologi Umum dalam Lintasan
Sejarah. Bandung: Pustaka Setia.
Souza, M. R. d. A. et al. (2018) ‘A systematic mapping
study on game-related methods for software
engineering education’, Information and Software
Technology. Elsevier B.V., 95, pp. 201–218. doi:
10.1016/j.infsof.2017.09.014.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
42
