
The Influence of Teacher Readiness to Learning Achievement of
Vocational High School Students in South Minahasa, North Sulawesi,
Indonesia
Morris S. S. S. Tumanduk, Rifana S. S. I. Kawet, Christine T. M. Manoppo, and Tendly S. Maki
Faculty of Engineering, Universitas Negeri Manado, Kampus UNIMA Tondano 95618, Indonesia
Keywords: Teacher Readiness, Learning Achievement, Teacher Competency, Correlation Research, Vocational High
School
Abstract: This study presents the relationship between teacher readiness and learning achievement of vocational high
school students in South Minahasa regency. The method used the correlation study which aims to find out
the relationship between independent variables with non-independent variables and the extent of the
correlation based on correlation coefficients. The results are showed that there were 36.67% 26.67%, and
36.67% of respondents with the categories of below-average, medium, and high or above average learning
achievements respectively. The teacher readiness values are showed that 33.33%, 26.67%, and 33.33% of
respondents included in the categories of below-average, moderate groups, and high or above average
respectively. The testing hypothesis is evident that the teacher readiness variable (X) has a positive and
significant effect on student achievement which is the equation of Y = 34.70 + 0.41 X that is the meaning if
the readiness of teachers increases by one unit Student achievement will increase by 0.361 units. The results
are inadequate that to improve the teacher competency in the readiness of the teaching and learning process
and the data the students` learning achievements generally need to be improved.
1 INTRODUCTION
The teacher has the task to encourage, guide, and
provide learning facilities for students to achieve
learning goals. The teacher has the responsibility to
see everything that happens in the classroom to help
the development process of students. However, this
is not easily done by the teacher, this is because the
main problem faced by the teacher is the readiness
of the teacher in teaching.
The readiness of teachers in teaching has not yet
fully had sufficient readiness to carry out the
teaching and learning process. Thus, effective
teacher readiness is a requirement for effective
teaching. If the teacher's readiness in teaching is less
effective, the learning process will be less effective,
and of course this will have an impact on student
learning achievement.
Vocational schools in Kabupaten Minahasa
Selatan, student learning achievements are generally
low. The low student achievement is of course
influenced by many factors, both internal, such as
intelligence, talent, interest, motivation, maturity and
readiness. While external factors are include teacher
readiness, classroom management, curriculum,
teaching methods, and family economy. Of these
various factors, in the author's observation that the
more dominant cause of low student achievement is
teacher readiness in teaching. In this case, the
teacher is not ready to teach because he does not
master the existing material and improper teaching
methods.
Based on the description above, the writer is
interested in conducting research with the title "The
Relationship between Teacher Readiness and
Learning Achievement of Vocational Students in
South Minahasa Regency"
The purpose of this study was to determine the
relationship between teacher readinesses for student
achievement in vocational schools in the district of
South Minahasa.
As for the objectives in this study are: to get a
picture, the influence of the readiness of vocational
teachers in South Minahasa Regency.
Tumanduk, M., Kawet, R., Manoppo, C. and Maki, T.
The Influence of Teacher Readiness to Learning Achievement of Vocational High School Students in South Minahasa, North Sulawesi, Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0009013704810486
In Proceedings of the 7th Engineering International Conference on Education, Concept and Application on Green Technology (EIC 2018), pages 481-486
ISBN: 978-989-758-411-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
481

2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Teacher Readiness
2.1.1 Materials Preparation
The task of the teacher before carrying out certain
teaching needs to prepare the material to be taught,
this is because it is one of the basic competencies of
a teacher. According to Widodo S A (2017), that:
"Preparation and teaching planning of teachers is
able to provide techniques for presenting material /
learning materials that are in accordance with the
needs of students". From the above theory, it can be
concluded that the material preparation carried out is
closely related to a teaching profession as a teaching
staff in the school, so as not to misplace the meaning
or purpose of learning to be achieved. And every
planning or material preparation carried out by a
teacher depends on the objectives to be achieved, as
stated by Marshall, H. & Weinstein, R. (1984), that:
To determine teaching material depends on the
objectives to be achieved, individualist structures
children / students and educational goals.
Teaching planning and material preparation in
principle is as one of the foundations for achieving
goals, because the goal is a component that is first
formulated by the teacher in the teaching and
learning process. The role of goals is very important
because it determines the direction of the teaching
and learning process. A clear goal will also provide
clear instructions on the selection of teaching
materials, the establishment of teaching methods and
teaching aids and provide guidance on assessment.
Education and teaching are businesses that have
a purpose, more than educational activities and
bound teaching and directed to achieve goals. In
education we have general guidelines or are
common targets to be achieved. This is clearly
formulated in the form of general education goals.
2.1.2 Teacher Ability
The ability according to Sudjana, (1989) is a
qualitative intrinsic representation of teacher
behavior that is very meaningful. While. From the
above understanding, it can be said that the teacher's
ability is the ability or the power possessed by a
teacher to carry out a teaching action. In this case a
teacher must have the ability to teach, because this is
closely related to the results that will be achieved by
the teacher as a teacher and students in the
achievement of learning.
The learning process and student learning
outcomes are not only determined by the structure
pattern and curriculum content but are also
determined by the competence of teachers who teach
and guide them. It is clear that the teacher is a very
important part and is responsible for the success or
failure of the teaching and learning process.
Therefore the teacher must have the ability in
teaching quality and professional Widodo S A
(2017).
1. Dominate Materials
Before the teacher appears in front of the class
to manage the interaction of teaching and
learning, first must have mastered what material
will be given and what materials can support the
course of the teaching and learning process. By
mastering the material, the teacher can convey
the subject matter dynamically. In this case
what is meant is mastering the material, for a
teacher will contain two spheres of mastery of
matter. There are two scope of control in
question:
1) Mastering the field of study in the
curriculum.
2) Mastering enrichment / supporting material in
the field of study
Mastering the material in the field of study
in the curriculum in question in this case the
teacher must master the material or the branch
of knowledge held by him, in accordance with
what is stated in the curriculum in the school.
2. Managing Teaching and Learning Programs
A competent teacher is required to also be able
to manage teaching and learning programs that
will be implemented so that in the learning
process what is the goal will be achieved. The
steps that must be taken by a teacher in
managing the teaching and learning program
are:
1. Formulate instructional / learning objectives.
2. Get to know and can use the right
instructional process.
3. Carry out the teaching and learning process.
4. Get to know the ability of students.
5. Plan and implement a remedial program.
3. Manage Classes
To teach a class, the teacher is required to be
able to manage the class, which is to provide
conducive conditions for the teaching and
learning process. If it is not conductive, then the
teacher must try as optimally as possible to
correct it. Therefore, classroom management
activities will involve arranging an adequate
EIC 2018 - The 7th Engineering International Conference (EIC), Engineering International Conference on Education, Concept and
Application on Green Technology
482

classroom system for teaching and creating a
harmonious teaching and learning climate.
The problem of managing classes is not a
light task. Various factors are that cause the
complexity. In general, the factors that influence
classroom management are divided into two
groups, namely Aldo Enrico (2014: 5), student
internal factors and student external factors.
Internal student factors are related to emotional,
thought, and behavioural problems. Students'
personalities with their respective characteristics
lead students to be from other students
individually. This difference between
individuals is seen from biological, intellectual,
and psychological differences. While the
external factors of students are related to
problems in the atmosphere of the learning
environment, student placement, grouping of
students, number of students in the class, and so
on. The problem of the number of students in
the class will colour the dynamics of the class,
and the more number of students in the class,
for example 30 people tend to be younger and
conflict occurs. Conversely, the fewer numbers
of students in the classroom tend to be smaller
in conflict. As long as there is an effort from the
teacher, chaos in the class can certainly be
overcome. Admittedly, class, from time to time,
from day to day, today, tomorrow, or the day
after tomorrow, always shows a different
atmosphere. Yesterday the class atmosphere
was calm. Maybe today the atmosphere of class
is noisy and hot. At times, the learning goodness
of students is interrupted by the coming of
disturbances from outside the classroom in
various forms and types, for example there are
fires around the school, there are thieves in
broad daylight, and there is a motor vehicle
collision and its luggage.
2.2 Student Learning Achievement
Learning is an important process for changing
human behaviour and includes everything that is
thought and done. Learning plays an important role
in development, habits, attitudes, beliefs, goals,
personality, and even human perception. Learning
according to James, W. (1890), "Learning may be
defined as the process by which behavior originates
or is through training or experience. Learning can be
defined as the process of generating or changing
behavior through practice or experience. Learning is
a mental / psychic activity in active interaction with
the environment, which results in changes in
understanding knowledge, skills and attitudes.
Learning is a series of activities of the soul of the
body to obtain a change in behaviour as a result of
individual experience in interaction with the
environment concerning cognitive, affective, and
psychomotor.
Bjorklund, D.F. (1995), also formulates the
notion of learning, namely a business process carried
out by individuals to obtain a new behaviour change
as a whole as a result of the individual's own
experience in interaction with the environment.
From some of the opinions above it can be
concluded that learning is a process of change in
human beings that appears in behavioural changes
such as habits, knowledge, attitudes, skills, and
thinking power.
2.2.1 Learning
Learning can be in the form of students, learners,
learning citizens, and trainees. Learners have
sensory organs that are used to capture brain stimuli
that are used to transform their sensing results into
complex memory and the nerves or muscles used to
display performance that shows what has been
learned.
2.2.2 Stimulus
Events that stimulate learner sensing are called
stimulus situations. Examples of these stimuli are
sound, light, color, heat, cold, plants, buildings, and
people. In order for learners to be able to learn
optimally, they must focus on certain stimuli that are
of interest.
2.2.3 Memory
Learning memory contains various abilities in the
form of knowledge, skills, and attitudes that result
from previous learning activities.
2.2.4 Response
Response is an action that results from memory
actualization. The learner who is observing the
stimulus, then the memory inside him then responds
to the stimulus.
3 METHOD
This research is correlation research which aims to
find out whether there is a relationship between
independent variables with non-independent
variables and the extent of the correlation between
The Influence of Teacher Readiness to Learning Achievement of Vocational High School Students in South Minahasa, North Sulawesi,
Indonesia
483
independent variables with non-independent
variables based on correlation coefficients.
The variables examined in this research field
consist of 2 variables:
1. Independent variable: Teacher readiness (X)
Teacher readiness is an effort made by the
teacher, especially the subject of Building
Construction to help create optimal learning
conditions so that the goals of teaching can be
achieved, with the following indicators:
1) Preparation of material,
2) Manage teaching and learning programs,
3) Manage the class,
4) Using media / sources,
5) Mastering the educational foundation
6) Manage teaching and learning interactions
7) Assessing student learning achievement for
teaching purposes.
Completeness instruments for Teacher
Readiness are developed by compiling items that
are based on indicators from the Teacher
Readiness variable. For this variable the
statement uses a Likert scale. For positive
statements, the score is as follows:
Very often = 4
Often = 3
Almost never = 2
Never = 1
For negative statements the score is opposite
to a positive statement. The number of items in
the class management completeness instrument
is 30 items.
For negative statements the score is opposite
to a positive statement. The number of
instrument items for teacher readiness is 25
items. Instrument lattice can be seen in table 1.
Table 1: The teacher's readiness grid.
Indicator
Item Number
Total
Positive Negative
Material Preparation
Manage the Teaching
and Learning Process
Classroom Manage
Using Media /
Resources
Mastering the
Educational Platform
Manage Teaching and
Learning Interactions
Assessing Student
Learning
Achievement
1, 2
6, 8, 23
9, 10, 16
25
20, 22
11, 12,
24
4, 13, 18
3
7
19
17
21
15
5, 14
3
4
4
2
3
4
5
Total 17 8 25
2. Non-independent variables:
Learning achievement (Y).
Data from the instrument of learning
achievement was taken through report card
grades of Basic Competency in class XI
Vocational School in South Minahasa Regency.
The sampling technique in this study is by the
technique of "Side Judgment Purposive". In this
case a sample based on consideration is most
appropriate to the purpose of the study. Thus the
sample taken is all students of class XI
Vocational High School in South Minahasa
Regency who take the Basic Competency subject
in 2017.
To obtain the data needed in this study,
questionnaire and documentation instruments
were used, namely Teacher Readiness variables
using questionnaires, and learning achievement
using documentation (Report Card Score).
For the purposes of analyzing data, simple
linear regression analysis and product moment
correlation techniques are used, with the formula
in Sujana (1986: 236), as follows:
This correlation analysis is intended to
determine the relationship between two
variables, in this case the relationship between
teacher readiness and student learning
achievement. Furthermore, variance analysis is
conducted with the intention to find out whether
the results obtained are correct so that they can
be used to estimate or predict student learning
achievement if the teacher readiness results are
known, it will show that the regression model is
good enough and can be used to estimate or
predict learning achievement (Y) if the teacher's
readiness (X) is known.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The variable readiness of the teacher shows the
highest score of 78 and the lowest of 65. After
calculating the average price is 71, 73.
Standard deviation = 1 + 3.3 Log n
= 1 + 3.3 Log 30 = 5.88
= 5 or 6, taken 5.
Length of Class Interval = (79-65) / 5 = 2.80
rounded 3.
The copyright form is located on the authors’
reserved area.
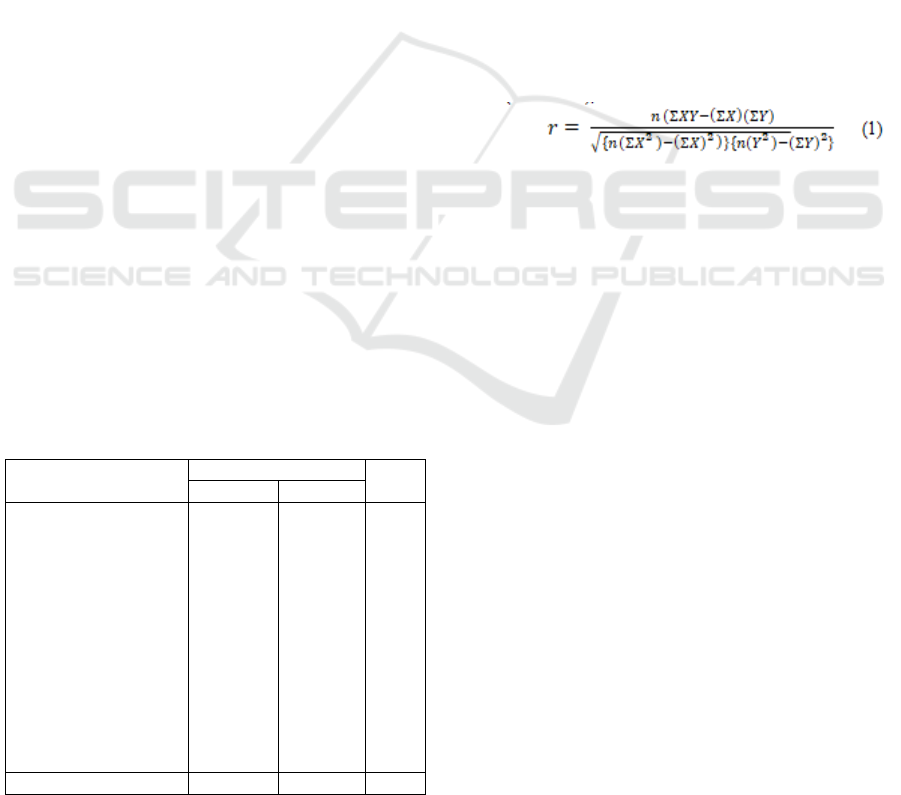
Based on Table 2, it can be seen that around
33.33% of teachers' readiness is above average, and
EIC 2018 - The 7th Engineering International Conference (EIC), Engineering International Conference on Education, Concept and
Application on Green Technology
484
66.67% is below the average. If the data is grouped
into 3 categories, the high score is 33.33% (score 74-
79); medium 36, 67% (score 71-73); and low
30.00% (score 65-70).
Data of student learning achievement for basic
competency subjects showed the highest score of 81
and the lowest of 60 after being calculated using a fx
3800P calculator, the average score was 70.33.
Table 2: Distribution of Teacher Readiness Frequency.
No.
Class
Interval
Absolute
Frequency
Relative
Frequency (%)
1 65 – 67 4 13.33
2 68 – 70 5 16.67
3 71 – 73 11 36.67
4 74 – 76 9 30.00
5 77 - 79 1 3.33
Total 30 100.00
Figure 1: Teacher Readiness Data Histrogram.
Table 3: Distribution frequency of student learning
achievement.
No.
Class
Interval
Absolute
Frequency
Relative
Frequency
(%)
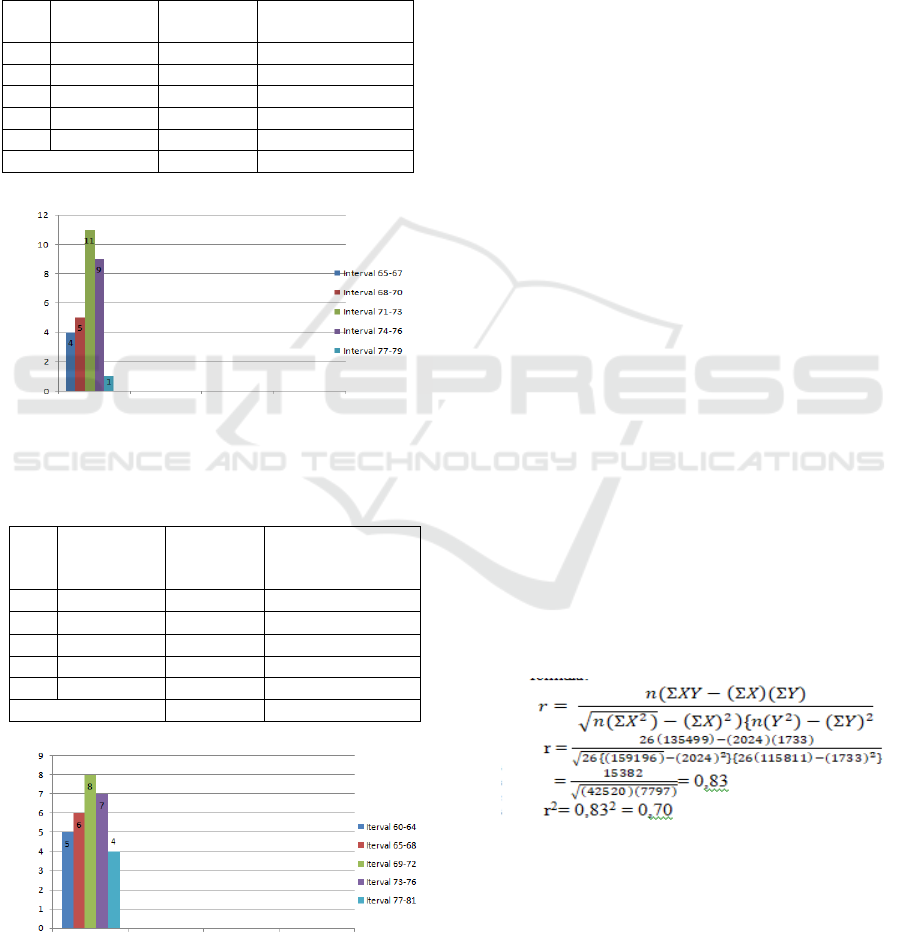
1 60 – 64 5 16.67
2 65 – 68 6 20.00
3 69 – 72 8 26.67
4 73 – 76 7 23.33
5 77 - 81 4 13.33
Total 30 100.00
Figure 2: Student Learning Achievement Data
Histrogram.
Standard deviation = 1 + 3.3 Log n
= 1 + 3.3 Log 30 = 5.88
= 5 or 6, taken 5.
Length of Interval = (81-60) / 5 = 4.20 rounded 4
The results of the frequency distribution of student
learning achievement can be seen in Table 4.2.
Based on table 4.2, it can be seen that there are
36.67% above the average, and 63.33% below the
average. If the scores are grouped into 3 categories
then students who have high achievement are
36.67% (score 73-81); medium 26.67% (score 69-
72); low 36.67% (score 60-64).
From the calculation of regression coefficient
analysis in appendix 7, the results can be stated as
follows:
ỷ = 34.70 + 0.41 X
The results above illustrate that if the teacher's
readiness increases by one unit, then the average
student achievement will increase by 0.361 units.
Analysis of variance is carried out with the
intention to find out whether the results obtained
above are appropriate so that they can be used to
estimate or predict student learning achievement if
teacher readiness is known, with results (see
Appendix 7, p. 45).
These results show that the regression model is
good enough, because based on the model deviation
test shows that the deviation is not real at the 5%
level in this case F (Calculate) = 0.73 <F (Table) =
2.43. Thus, the regression equation above can be
used to estimate or predict learning achievement (Y)
if teacher readiness (X) is known. As for the test of
the regression model, it shows that the model is real
or significant at the 5% test level, in this case F
(Calculate) = 101.45> F (Table) = 4.20.
This correlation analysis is intended to determine
the relationship between two variables, in this case
the relationship between teacher readiness and
student learning achievement, with the following
formula:
The results above show that r2 = 0.70, this means
that the regression model has been able to explain
the diversity of student learning achievement around
70% or in other words that the teacher's readiness
contributes to student learning achievement by 70%.
The results of the description of the data of the
value of student learning achievement shows that out
The Influence of Teacher Readiness to Learning Achievement of Vocational High School Students in South Minahasa, North Sulawesi,
Indonesia
485

of 30 respondents there were 11 or 36.67% of
respondents included in the category of under-
average learning achievement. 8 or 26.67% of
respondents included in the category of moderate
group, and 11 or 36.67% of respondents entered the
high achievement category or above the average.
From the results of the description of the data the
students' learning achievements generally need to be
improved.
The results of the description of the data the
teacher readiness value shows that out of 30
respondents there were 9 or 33.33% of respondents
included in the category of teacher readiness below
the average, 11 or 26.67% respondents who entered
the category of moderate groups, and 10 or 33, 33%
of respondents entered the high or above average
category. From the results of the description of the
data, it shows that the readiness of the teacher is
inadequate and needs to improve teacher
competency in the readiness of the teaching and
learning process.
Based on the results of hypothesis testing, it is
evident that teacher readiness variables (X) have a
positive and significant effect on student
achievement, this can be explained as follows:
Based on the results of simple linear regression
analysis of teacher readiness variables and
Vocational Student Achievement in District South
Minahasa obtained the regression line equation ỷ =
34.70 + 0.41 X, which illustrates that if the teacher's
readiness increases by one unit the student's learning
achievement will increase by 0.361 units. Similarly,
the results obtained are that the regression model is
good enough, because based on the model deviation
test shows that the deviation is unreal at the 5% level
in this case F (Calculate) = 0.73 <F (Table) = 2.43.
Thus, the regression equation above can be used to
estimate or predict learning achievement (Y) if
teacher readiness (X) is known. Similarly, to test the
regression model, it shows that the model is real or
significant at the 5% test level, where F (Calculate)
= 101.45> F (Table) = 4.20., With a coefficient of
determination of r2 = 0, 70, this means that the
regression model has been able to explain the
diversity of student learning achievement around
70% or in other words that teacher readiness
influences Learning Achievement of Vocational
Students in South Minahasa District by 70%.
5 CONCLUSION
Based on the theoretical description and results and
discussion, the conclusions of this study can be
formulated as follows: that there is a significant and
positive relationship between teacher readiness and
learning achievement of vocational students in South
Minahasa Regency. Need to increase teacher
competency in the readiness of the teaching and
learning process to improve the learning
achievement of vocational students in the South
Minahasa regency.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors wish expressed to Prof. Dr. Julyeta P.A.
Runtuwene, M.S, DEA as Chancellor of Manado
State University who has funded this research and to
Prof. Dr. H. Sumual, M.Sc, as Dean of the UNIMA
Faculty of Engineering which has provided
motivation and recommendations so that this
research can be carried out.
REFERENCES
Aldo, E., Ritchie, A., & Weriyen, O., 2014. “The Factors
that Influenced Consumptive Behavior: A Survey of
University Students in Jakarta”, International Journal
of Scientific and Research Publications, Vol. 4, No. 1,
pp. 1-6.
Bjorklund, D.F., 1995. Children’s Thinking &
Developmental Function and Individual Differences,
Pacific Grove, Brooks/Cole Publishing Company. 2nd
edition.
James, W., 1890. The principles of psychology, Holt.
(Reprinted 1950, Dover Publications). New York.
Sudjana, N., 1986, Statistical Method, Tarsito. Bandung.
Sudjana, N., 1989, PBM Basics. New Light. Bandung.
Widodo S A, Prahmana R C I, Purnami A S, & Turmudi,
2017. “Teaching materials of algebraic equation”, IOP
Conf. Series: Journal of Physics: Conf. Series 943,
pp.1-8.
Marshall, H. & Weinstein, R., 1984. “Classroom factors
affecting students' self-evaluations: an interactional
model”, Review of Educational Research, 54, pp.301-
325.
EIC 2018 - The 7th Engineering International Conference (EIC), Engineering International Conference on Education, Concept and
Application on Green Technology
486
