
Obstacle Factor Influencing the Application of Health, Safety, and
Environment (HSE) Management on Construction Projects in
Indonesia
Riza Susanti and Bambang Setiabudi
Department of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universitas Diponegoro, Semarang, Indonesia
Keywords: Construction, Health, Risk, Safety, Project
Abstract: Activity along the construction project is one of the most hazardous compared to other industry. In Indonesia,
many construction projects are still facing numerous accidents and or fatalities during the project. It shows by
the high rate of work accidents in the construction sector throughout 2017 where at least there are any 7 the
national strategy projects that have been in an accident. This indicates the Health, Safety, and Environment
(HSE) may have not been implemented properly in the project. The aim of this research is to identify the
obstacle factors influencing the implementation of health, safety and environment management on
construction projects in Indonesia. The questionnaire method was used to collect the data. The research
identified 10 obstacle factor in implementing of health and safety management i.e lack of attention to safety
by workers, lack of attention to safety by main contractors, problem sub-contractor, an absence of safety
provisions in contractual clause, lack of integration of safety in the construction activities, rules and
regulation, financial pressure, insufficient safety training, tight schedule and low labor education. From a total
10 factors identified, respondent agreed that lack of attention to safety by workers as the highest obstacle
factor in implementing HSE management in the construction project. The finding can be used to manage HSE
risk efficiently and effectively for another construction project.
1 INTRODUCTION
The construction industry related to numerous of the
accident which occurs worldwide (Gunduz & Ahsan
2018). According to (Bavafa et al., 2018) the
percentage of the accident on the construction project
in developing countries are relatively high, including
Indonesia. For instance in Indonesia, in 2017 it has
been reported that from a total of 47 national strategy
projects there was accident occurred in 7 national
strategy projects. Oswald et al. (2018) and Bavafa et
al. (2018) pointed out as common the accident in the
construction project is mainly caused due to the
unique characteristic including the unique working
environment of the project itself. Additionally, the
construction industry is having complicated
characteristics, and site conditions that differentiate it
from other industries (Alruqi et al., 2018).
Unfortunately, the accident in a construction project
can cause various direct and indirect cost in the
project (Bavafa et al., 2018). Moreover, Mohammadi
et al. (2018) mentioned the cost of the accident will
increase up to 15% to the project cost.
Nowadays, Safety issues are considered as the
major concerns related the cost of these occurrences
can be huge and they are borne by the victims, their
families, employers, the industry, government and
society as a whole (Manu et al., 2018). Ironically, the
previous study by Harvey et al. (2016) mentioned that
Occupational Safety and Health in construction has
been slower than in other sectors. To implementing
HSE properly in the project, it is needed for active
participation not only by the contractor but also the
owner since the planning phase until the completion
of the project (Gunduz & Ahsan 2018).
Following to Mohammadi et al. (2018)
construction industry is including as the main factor
of development for countries, then it is needed any
special attention to the construction project. Hence,
since safety management is a key element to the
success of the project, it also needs special attention
in implementing safety to the project properly since
in the planning phase. Gunduz & Ahsan (2018)
140
Susanti, R. and Setiabudi, B.
Obstacle Factor Influencing the Application of Health, Safety, and Environment (HSE) Management on Construction Projects in Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0009007501400144
In Proceedings of the 7th Engineering International Conference on Education, Concept and Application on Green Technology (EIC 2018), pages 140-144
ISBN: 978-989-758-411-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
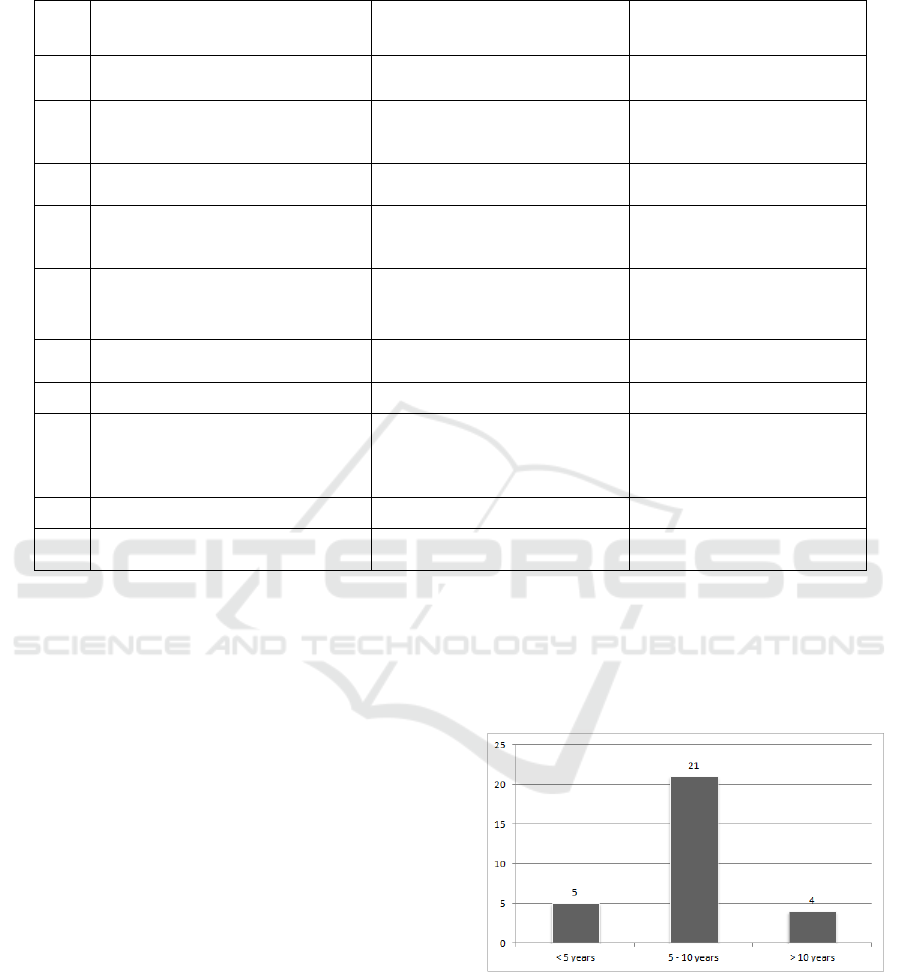
Table 1: Obstacle Factor Influencing the Application of HSE
No Main factors References Obstacle Factors in this
research
1 HSE competency and behaviour (Mohammadi et al., 2018);
(Gunduz & Ahsan 2018)
Lack of attention to safety
protection by workers
2 HSE competency and behaviour (Mohammadi et al., 2018);
(Gunduz & Ahsan 2018)
Lack of attention to safety
management by main
contractors/project managers
3 Subcontractors (Bavafa et al., 2018); (Gunduz
& Ahsan 2018)
Problem with sub-contractor
4 Contract formation (Tanabe & Turco 2016);
(Loganthan & Siddiqui 2018)
An absence of safety
provisions in contractual
clause
5 Safety program and management
systems
(Bavafa et al., 2018); (Gunduz
& Ahsan 2018); (Manu et al.,
2018)
Lack of integration of safety
in construction activities
6 Rules and regulation (Manu et al., 2018);
(Mohammadi et al., 2018)
Rules and regulation
7 Financial aspects (Mohammadi et al., 2018) Financial pressure
8 Safety training (Mohammadi et al., 2018);
(Bavafa et al., 2018); (Manu et
al., 2018); (Gunduz & Ahsan
2018)
Insufficient safety training
9 Work pressure (Mohammadi et al., 2018) Tight schedule
10 Low education level (Mohammadi et al., 2018);
(SAEED, 2017)
Low labor education
mentioned that safety management is one of the
important keys to the success of the construction
project in order to minimize costs and delays the
project. The number of problems caused by improper
application of HSE causes the question actually what
obstacle factors in implementation HSE to the
project. The aim of this research is to identify the
obstacle factors influencing the implementation of
health, safety and environment management of the
construction project in Indonesia.
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The survey was sent to numerous respondent that
participate in the construction industry. From a total
of 30 respondent, there were 5 consultants, 20
contractors, and 5 owners out of 30 respondents.
Respondents from various professional background
and expertise engaged in the construction sector were
selected. Out of 30 respondents, there were 8
managers, 10 project engineers, 5 owners and 7 others
involved in the construction.
The total years of the construction work
experiences of the respondents are categorized into 3
groups of less than 5 years (<5 years), 5 – 10 years
and more than 10 years experience. Over a half of
respondents have been practicing in the construction
industry for 5 to 10 years as seen in Figure 1 the
number of respondents based on total years of
construction experience.
Figure 1: The Number of Respondents Based on Total
Years of Construction Experience.
A questionnaire survey was used to gather
information and collect the data. The questionnaire
survey was divided into two section: 1) respondents
information and 2) assessing obstacle factor HSE.
The first section was used to gain background
Obstacle Factor Influencing the Application of Health, Safety, and Environment (HSE) Management on Construction Projects in Indonesia
141

information of the respondent. This section requires
the respondent to give information relating to
organization type, job designation and total years of
work experience in the construction industry. Section
two containing 10 obstacle factors the application of
HSE in the construction project. Furthermore,
respondents were requested to assess the obstacle
factor on 5 points Likert scale (1= very low, 2= low,
3= moderate, 4= high and 5=very high).
Several factors were used as obstacles factor in the
implementation of HSE in construction projects in
Indonesia. These factors are shown in Table 1.
Furthermore, the results of the respondent’s
questionnaires will be analyzed using mean rank
analysis. In the mean rank analysis, the observation
value on each row is ranked and the average is sorted
to find out the ranking of an observation. Mean rank
can be calculated by using Equation 1 and 2.
(1)
(2)
Where, n is the number of respondents, Ri is the
number of respondent's assessment data and Xi
represents observation value obtained from
respondents.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
This research has identified a total number of 10
obstacle factors influencing the application of HSE
management in the construction project in Indonesia.
Detail analysis was shown in Table 2.
Based on Table 2, respondents assess lack of
attention to safety protection by workers as the
highest obstacle factor influencing the application of
Health, Safety, and Environment (HSE) management
on construction projects in Indonesia. Previous
studies showed that attitude and behavior is one of the
important factor influencing application HSE in
construction project (Mohammadi et al., 2018),
furthermore, according to Mohammadi et al. (2018)
negative attitude of worker that underestimate the risk
and take short to done the job was major root of
causes of accident in construction project. Similar
with factor 1, obstacle factor lack of attention to
safety management by the main contractor/ project
managers was also one of the important factors.
Mohammadi et al. (2018) pointed out the importance
of managers to identify and control the factors
influencing the safety performance of the project.
Table 1: Obstacle Factor Influencing the Application of
Health, Safety, and Environment (HSE) Management on
Construction Projects in Indonesia.
No Factors Average
1 Lack of attention to safety protection
by workers
4,70
2 Lack of attention to safety
management by main
contractors/project managers
4,43
3 Problem with subcontractors 4,43
4 An absence of safety provisions in
contractual clause
4,40
5 lack of integration of safety in the
construction activities
4,37
6 Rules and regulation 4,30
7 Financial pressure 4,10
8 Insufficient safety training 4,07
9 Tight schedule 3,83
10 Low labor education 3,80
In this research, the problem with subcontractor
was ranked in the top three the obstacle factor
influencing the application of HSE in the construction
project in Indonesia. Similar with the previous study
according to (Gunduz & Ahsan 2018) subcontractors
safety behavior is important in implementing HSE
(rank 16 out of 40), so the problem was made by the
subcontractor can be dangerous to the project.
Furthermore Bavafa et al. (2018) mentioned that is
important to select subcontractors personnel by
considering their safety and health performance.
According to Mohammadi et al. (2018) the main
contractor must ensure subcontractors to follow
safety protocol and are integrated with safety culture
during the project.
The previous study pointed plan for safety as a
basis of an effective construction safety program
(Bavafa et al., 2018). Furthermore, according to
(Gunduz & Ahsan 2018) owner must be actively
participating in project safety since the project still in
planning phase i.e making safety guidelines to
contractors, incorporate safety requirement in the
contract and push contractors to set safety as goals in
the project. In this research, respondent asses this
factor into middle group, it means lack of integration
of safety in construction activities including safety
planning is one of the main obstacle factor
influencing the application HSE in the project.
According to Mohammadi et al. (2018), rules and
regulation are one of the major factor influencing
safety performance on the construction project, this
factor includes safety rules, rules compliance, and
EIC 2018 - The 7th Engineering International Conference (EIC), Engineering International Conference on Education, Concept and
Application on Green Technology
142

paperwork of regulation. The previous study by
(Manu et al. 2018) pointed this factor categorized into
the high category in implementing HSE in Malaysia,
but in Vietnam and Cambodia, this factor categorized
into the moderate category similar with the result of
this research.
Financial is one of the obstacle factors in
implementing HSE in the construction project.
According to Mohammadi et al. (2018) project cost
would be increased up to 15% if there is an accident
in the project. Although in this research, this factor is
not included in 3 the highest obstacle factors in
applicating HSE, but the range average still more than
4 (in Likert scale which used 4 means high). This
means financial is one of the important factors in
applicating HSE to the project. (Manu et al., 2018)
mentioned that is important to allocate price in
covering HSE requirement in every project.
Furthermore Mohammadi et al. (2018) argued that the
financial in the project can reduce by cutting of the
safety budget, unfortunately, this can lead to polemics
in Indonesia where many procurement systems are
more using the lowest price bidding system than best-
value method. High demand for implementing HSE
in the project but not balanced with a qualified
finance as the result of procurement system chosen
will result in financial pressure in the project.
Then, Contrary with previous study, respondent
asses insufficient safety training in 3 lowest obstacle
factor influencing the application HSE in the
construction project. While the previous study
pointed safety training as one of the most critical
factors for effective implementation of safety
programs in construction project (Bavafa et al.,
2018). Similar with Bavafa et al, according to
Mohammadi et al. (2018) HSE competency,
including safety experience, training, and education,
is one of the main factor influencing safety
performance in the construction project. Furthermore
Mohammadi et al. (2018) pointed out that in the end,
the age and experience of the workers as the
important factor to make safety condition in the
construction project. This also contrary with the result
that asses low labor education as the lowest obstacle
factor influencing the application of HSE in the
construction project in Indonesia. The gap between
this research with the previous study may happen
caused by the different perception of the respondent.
(Gunduz & Ahsan 2018) pointed out that the
perception of safety changes with more safety
experience. In this research, most of the respondents
are from category 5 to 10 years experience while the
respondents in the previous study are having more
than 10 years experience in the construction project.
Furthermore, there are any 2 kind obstacle factors
that having a mean average less than 4 but still almost
in the high category, a thigh schedule and low labor
education (mean average 3.83 and 3.80). According
to Mohammadi et al. (2018) the work pressure factor
includes production pressure, work overload, fatigue
and burnout, working pace, working time, overtime
work and schedule delay. Additionally, the previous
study pointed out that tight schedule can make
workers only focus to complete the work quickly
despite their knowledge of the possible outcomes
(Mohammadi et al., 2018).
The last obstacle factor is low labor education, the
previous study mentioned that different individual
with different educational and different background
experiences will approach safety in the different way
(Provan et al., 2018). Unfortunately, in project there
are a number of people with any kind of educational
background whose active participating to the project,
but almost construction workers are employed for
their skill of education are low which it can be barriers
to the application of HSE in project (Harvey et al.,
2016) added with and contract system which used
limits opportunities to invest in people. So it is needed
for any person in charge may emphasize to make sure
all individual including subcontractors to follow
safety protocol and are integrated with safety culture
during the project.
4 CONCLUSION
This study has identified a total number of 10 obstacle
factor influencing the application of HSE in the
construction project as perceived by the private
sector. i.e lack of attention to safety by workers, lack
of attention to safety by main contractors, problem
sub-contracting, an absence of safety provisions in
the contractual clause, lack of integration of safety in
the construction activities, rule and regulation,
financial pressure, insufficient safety training, tight
schedule, and low labor education. This research
showed the highest obstacle factor influencing the
application of HSE is Lack of attention to safety
protection by workers. While the lowest obstacle
factor is low labor education. The outcome of this
study would help the construction and safety
professional on assessing and quantifying the safety
obstacle factor the application of HSE also it can be
used to manage HSE risk efficiently and effectively
for the construction project in Indonesia.
Obstacle Factor Influencing the Application of Health, Safety, and Environment (HSE) Management on Construction Projects in Indonesia
143

REFERENCES
Alruqi, W. M., Hallowell, M. R. & Techera, U., 2018.
“Safety Climate Dimensions and Their Relationship to
Construction Safety Performance: A Meta-Analytic
Review”, Safety Science, Vol. 109, No. September
2018, pp. 165–73.
Bavafa, A., Mahdiyar, A. & Marsono, A. K., 2018.
“Identifying and Assessing the Critical Factors for
Effective Implementation of Safety Programs in
Construction Projects”, Safety Science, Vol. 106, No.
February 2018, pp. 47–56.
Gunduz, M. & Ahsan, B., 2018. “Construction Safety
Factors Assessment through Frequency Adjusted
Importance Index”, International Journal of Industrial
Ergonomics, Vol. 64, pp. 155–62.
Harvey, E. J., Waterson, P. & Dainty, A. R. J. 2016.
“Applying HRO and Resilience Engineering to
Construction: Barriers and Opportunities”, Safety
Science, in Press.
Loganthan, S. K. & Siddiqui, N. A. 2018. “Development &
Evaluation of Smart HSE [Health Safety &
Environment ] Assurance Program in a Construction”,
International Journal of Technical Innovation in
Modern Engineering & Science, Vol. 4, No. 7, pp. 347–
62.
Manu, P., Mahamadu, A. M., Phung, V. M., Nguyen, T. T.,
Ath, C., Heng, A. Y. T. & Kit, S. C., 2018. “Health and
Safety Management Practices of Contractors in South
East Asia: A Multi Country Study of Cambodia,
Vietnam, and Malaysia”, Safety Science, Vol. 107, pp.
188–201.
Mohammadi, A., Tavakolan, M. & Khosravi, Y., 2018.
“Factors Influencing Safety Performance on
Construction Projects: A Review”, Safety Science, Vol.
109, No. December 2017, pp. 382–97.
Oswald, D., Sherratt, F. & Smith, S., 2018. “Problems with
Safety Observation Reporting: A Construction Industry
Case Study”, Safety Science, Vol. 107, No. April, pp.
35–45.
Provan, D. J., Dekker, S. W. A. & Rae, A. J., 2018.
“Benefactor or Burden: Exploring the Professional
Identity of Safety Professionals”, Journal of Safety
Research, Vol. 66, pp. 21–32.
Saeed, Y. S. 2017. “Safety Management in Construction
Projects”, The Journal of The University of Duhok, Vol.
20, No. 1, pp. 546–60.
Tanabe, M. & Turco, C., 2016. “Technical-HSE
Management System in the Design Phase of an LNG
Plant Project”, 15Th International Symposium on Loss
Prevention and Safety Promotion (Loss 2016), Vol. 48,
pp. 541–46.
EIC 2018 - The 7th Engineering International Conference (EIC), Engineering International Conference on Education, Concept and
Application on Green Technology
144
