
ICT Capability Teachers at the Junior and Senior High School in
Ternate City
Said Hasan
1
, A. R. Tolangara
1
and Abubakar Abdullah
2
1
Postgraduate of Biology Education, Khairun University, Jl. Yusuf Abdurrahman, Ternate-Indonesia
2
Biology Education Study Program, Khairun University, Jl. Bandara Baabullah, Ternate-Indonesia
Keywords: ICT Literacy, Industrial Revolution, High School Teacher.
Abstract: The phenomenon of the industrial revolution has penetrated in various sectors, including in the field of
education. Teachers are required to adapt and have good IT skills in managing classroom learning. Future
teaching skills include the ability to develop innovative ways to use technology to improve the learning
environment and encourage technological literacy, deepening knowledge, and generating knowledge. This
study aims to obtain preliminary information about the perceptions and knowledge of IT Literacy for junior
/ senior high school teachers throughout the city of Ternate, as well as obtain a profile of the basic
knowledge of junior / senior high school teachers regarding IT literacy. This study uses survey research
methods with a quantitative approach. The data collection technique used is by distributing questionnaires
and conducting interviews on a sample that has been determined in 10 schools with a sample of teachers in
each school determined randomly. Data analysis was calculated based on the number of checklists filled out
by the respondents, then it was devised to determine the level of perception of each teacher. Interviews were
conducted on respondents randomly to find out information that supports questionnaire contents. The results
showed that teachers in secondary schools in Ternate had 73% ICT skills. Not all teachers have participated
in ICT training and not all teachers have good IT literacy. In the Central Middle School, almost 90% of
teachers have attended ICT training and know the term IT well, and have implemented online applications
well. Unlike the teachers in other sub-districts as sampling, approximately 80% of teachers have not
participated in ICT training. The lack of teacher participation in training has led to low IT skills that
teachers have.
1 INTRODUCTION
The framework for ICT Competencies for teachers is
part of various initiatives by the United Nations and
specialized agencies including UNESCO, to
promote education reform and sustainable economic
development. The UNESCO International
Commission on Education emphasizes that in the
21st century is a way of life-long learning and
participation in learning societies is key to meeting
the challenges posed by a rapidly changing world,
emphasizing the four pillars of learning, namely:
'Learn to live together' , 'Learn to know', 'Learn to
do', and 'Learn to be' (Fallis, 2013; Sanders, 2004).
According to Law No. 14 of 2005 concerning
Teachers and Lecturers, teachers as professional jobs
must have professional principles as stated in article
7 paragraph 1, namely: Professional teachers and
lecturers are specialized fields of work that require
professional principles as follows: (a) have talent,
interest, soul calling and idealism; (b) have
educational qualifications and educational
backgrounds in accordance with their fields of duty;
(c) have the competencies needed in accordance
with their field of duty; (d) comply with the
professional code of ethics; (e) have rights and
obligations in carrying out their duties; (f) obtain
income determined according to his performance;
(g) have the opportunity to develop their profession
in a sustainable manner; (h) obtain legal protection
in carrying out their professional duties; and (i) have
professional organizations with legal entities (Munir,
2014).
The growth of internet users from the 1900s to
2017 is increasing. The results of the 2017 survey
show a significant number, with 143.26 million
Indonesians using the internet. This figure shows
that the Indonesian people are familiar and indirectly
involved in future technological developments.
Hasan, S., Tolangara, A. and Abdullah, A.
ICT Capability Teachers at the Junior and Senior High School in Ternate City.
DOI: 10.5220/0008900302490252
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning (ICTL 2018), pages 249-252
ISBN: 978-989-758-439-8
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
249

The identification of Literacy IT skills in junior
and senior high school teachers in Ternate City is
important in facing the industry revolution 4.0 which
cannot be avoided. With a variety of applications
and technologies in learning that are varied, it can
facilitate the work of the teacher and learning in the
classroom becomes more enjoyable if the teacher is
able to master the technology well. IT literacy is an
important part in producing superior human
resources and the golden generation of the
Indonesian people, as stated in the Ministry of
Education and Culture and Ministry of Education
and Higher Education's Strategic Plan, as well as the
vision of Indonesian education 2025.
There is not much data and research that reveals
about the IT Literacy skills of teachers in primary
and secondary education (SMP and SMA) in Ternate
City. This research can be a database for policy
makers to encourage acceleration and improvement
of IT Literacy skills for teachers in order to improve
the quality of education in Ternate City. Keeping in
mind that at present, literacy is not just reading,
writing and counting, but more than that, IT Literacy
is a very important ability for every teacher.
2 METHOD
This study uses a combination of quantitative and
qualitative methods (Punch, 2009). Simple
quantitative methods are used when calculating the
number of answer choices by respondents to the
questions on the questionnaire by tabulating and
calculating the percentage. While the qualitative
method for analyzing written answers provided by
respondents, where some questions in the
questionnaire are open and also given space to
express their opinions and responses regarding
teaching with multimedia and internet computers
(Creswell, 1998).
Data collection is carried out through surveys in
all SMP / SMA in Ternate City. Samples that can
represent the population are taken using a multistage
random sampling technique. Determination of the
sample size of the population, determined by using
the formula from Slovin (Fatimah Saleh & Lim,
2010) as follows:
N= N/1+Ne
2
In order to obtain the validity and reliability of
the instruments used, first try out the instrument to
ensure that the instrument is an accurate and reliable
measuring instrument.
The data collection technique used is by
distributing questionnaires and conducting
interviews on a predetermined sample in 20 schools
with a sample of teachers in each school determined
randomly. The instrument used was a questionnaire
about the use of IT and IT knowledge related to the
industrial revolution 4.0 the questionnaire used was
in the form of a closed questionnaire.
Data analysis was calculated based on the
number of checklists filled out by the respondents,
then it was challenged to determine the level of
perception of each teacher. Interviews were
conducted at respondents randomly to find out
information that supports questionnaire contents.
The category of each indicator is transferred to
an absolute number as follows:
Table 1: Indicator Category.
No. Cate
g
or
y
Score
1 Proficien
t
3
2 Able 2
3 Underprivilage
d
1
4 Disable 0
Furthermore, each respondent scores summed
with other respondents and averages so that the
overall score of respondents' perceptions is obtained
as follows:
Average Score= Score of all Respondents/ Total
Respondents
For frequency data and school facilities support,
the same thing is also done, namely:
Table 2: Frequency of Facility Support
No. Cate
g
or
y
Score
1 Often (more than twice) 3
2 Rarel
y
(more than once) 2
3 Eve
r
(once time) 1
4
N
eve
r
0
Data processing and analysis is carried out
through several steps, namely data editing, coding,
tabulation, and data validation. Furthermore, the
analysis is carried out using descriptive statistical
techniques and associations for correlational data.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSS
The target school that became the sampling in this
activity was representative of 4 sub-districts of
Ternate City, namely Ternate Island sub-district,
South Ternate sub-district, Central Ternate sub-
district, and North Ternate sub-district. The number
of schools that were sampled were 20 secondary
schools in Ternate City. Of the 20 schools taken data
ICTL 2018 - The 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning
250
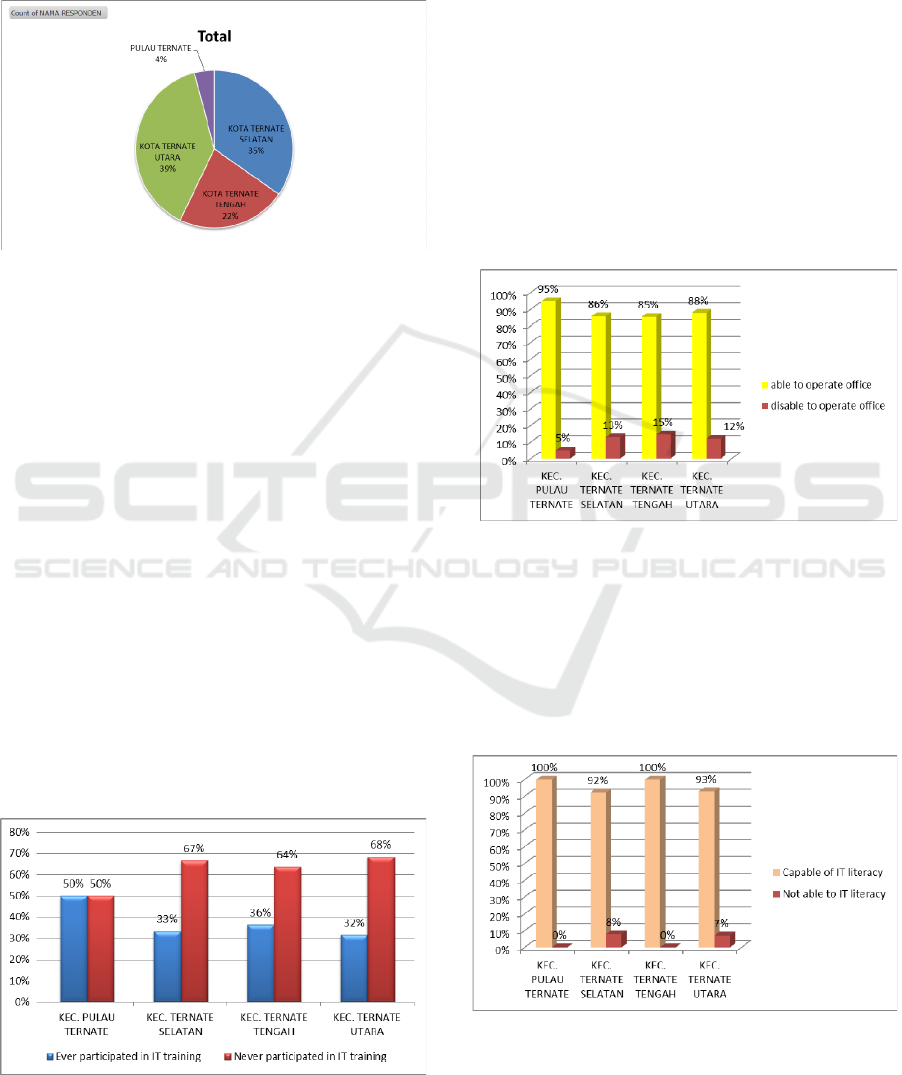
using questionnaire and interview instruments, it
was presented in the form of a teacher's ability
profile with 4 indicators, namely (1) whether or not
there had been training activities, (2) the ability to
operate Microsoft office, (3) IT support capabilities,
and (4) basic IT literacy skills.
Figure 1: Number of Sample Schools.
The data needed to measure indicators of the
ability to operate Microsoft Office for teachers is
with a number of questions to measure teacher
knowledge related to their ability in office
operations and general problems that exist in office
software.
The data needed to measure the indicators of IT
supporters' abilities are a number of questions in the
questionnaire to gather information related to the
teacher's knowledge of other IT supporting software
such as photoshop, corel draw, spss, and windows
movie maker. Some of the software is a support for
teachers in making learning media or supporting
media so that the presentation looks interesting.
IT's basic literacy ability is one of the teacher's
soft skills related to its relationship with the internet,
and its problems and ability to operate learning
online. Some indicators of elementary school
teachers' IT skills are obtained through
questionnaires with closed or open answers. The
data that has been analyzed is shown in the
following figure.
Figure 2: The condition of junior / senior high school
teachers related to whether or not they took part in IT
training.
Based on the graph, we can see that the
distribution of teachers participating in IT training is
still relatively small in 3 sub-districts within Ternate
City, namely schools in the Central Ternate sub-
district, Kec. Ternate Island, Kec. South Ternate,
and Kec. North Ternate (> 80% of teachers who
have never participated in IT training activities).
Teachers residing in schools in the Ternate sub-
district area, there were many who attended training
activities, namely> 50%. In understanding and
obtaining basic and advanced IT skills, continuous
training is needed and intensive mentoring is
needed. Not limited to fulfilling program
implementation and purely project fulfilment.
Figure 3: The Condition of Junior / Senior High School
Teachers Related to the Ability to Operate Office.
Based on the graph, we can see that the teacher's
ability to operate office more than 80% is good.
Teachers who are in several sampling schools in the
Central Ternate sub-district, South Ternate and
North, are considered to have been able to operate
offices, namely> 80%, and only a small number are
not proficient.
Figure 4: The State of Junior / Senior High School
Teachers Related to Basic IT Literacy Skills.
ICT Capability Teachers at the Junior and Senior High School in Ternate City
251

Based on the graph, we can see that the teacher's
ability to cultivate IT literacy is in the form of
searching and browsing the internet, and making
online learning very high. More than 80% of
teachers have cultivated IT literacy and carry out
online learning. This shows that the learning process
carried out by the teacher has been digital based.
More than 80% of teachers concluded that they had
good IT (internet) literacy skills.
The ability to design good learning media,
becomes an important thing that needs to be owned
by teachers (teachers), both elementary, secondary
and higher education. One supporter of the ability to
make learning media is the ability of information
and technology or information and communication
technology (ICT). The need for teaching soft skills
for IT is needed in the era of industrial revolution
4.0 today.
4 CONCLUSIONS
IT capability is one of the supporting skills in the
'Age of Now' which is really needed to achieve
satisfying learning outcomes, but not a key factor for
student learning outcomes. Coaching to teachers can
be done in various ways, including involving
teachers in training, bringing in resource persons to
carry out training in schools, activating teacher
learning forums (KKG and MGMP), collaborating
with external parties (Universities, Teacher
professional organizations, and field NGOs
education) to carry out training activities in schools,
and provide IT support facilities for teachers in
schools.
With the role of technology in learning, the use
of media plays an important role in the learning
process. Teachers are required to be able to integrate
ICT in learning by using more attractive media so
that learning can take place more interactively,
inspirational, fun, challenging, efficient and
motivate students to actively participate and provide
sufficient space for students to be creative and
independent according to their interests , talents and
psychological development of students.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Te researchers conveyed ‘Thank You’ to the Head
of the LPPM Khairun University for her support in
funding this research. We would like to thank you
and appreciation to the teachers’s in the sample
schools who helped fill out our research
questionnaire.
REFERENCES
Christiono, A. T., & Tambotoh, J. J. C. (2014). Analisis
Pemanfaatan Teknologi Informasi Menggunakan
Pendekatan Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of
Technology 2 (Studi Kasus: Flexible Learning (F-
Learn) UKSW). Konferensi Nasional Sistem Informasi
2014, 2(Utaut 2), 1–7.
Creswell, J. W. (1998). Qualitative inquiry and research
design: Choosing among five traditions. Qualitative
Health Research. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-
9299.00177
Fallis, A. . (2013). Unesco Ict Competency Framework for
Teachers. Journal of Chemical Information and
Modeling, 53(9), 1689–1699.
https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004
Fatimah Saleh, & Lim, C. S. (2010). Analisis Data
Kualitatif. Penyelidikan Dalam Pendidikan.
Munir. (2008). Kurikulum Berbasis Teknologi Informasi
dan Komunikasi. Journal of Chemical Information and
Modeling (Vol. 53).
https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004
Munir. (2014). KERANGKA KOMPETENSI TIK BAGI
GURU. (Munir, Ed.). Bandung: Alfabeta.
Punch, K. (2009). Introduction to research methods in
education. Research methods in education.
Sanders, J. (2004). Competency Framework for Teachers.
Department of Education and Training, 1–48.
Retrieved from
http://www.det.wa.edu.au/policies/detcms/policy-
planning-and-accountability/policies-
framework/guidelines/competency-framework-for-
teachers.en?oid=com.arsdigita.cms.contenttypes.guide
line-id-5245769
Syarifuddin. (2014). Literasi Teknologi Informasi dan
Komunikasi. Jurnal Penelitian Komunikasi, 17(2),
153–164.
ICTL 2018 - The 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning
252
