
Coastal Groundwater Quality Identification of Ternate City
Vrita Tri Aryuni, Ramdani Salam, and Rahim Achmad
Faculty of Teacher Training and Education, Universitas Khairun, Ternate, Indonesia
Keywords: Coastal, Groundwater, Quality
Abstract: The south-east of Ternate City, North Maluku, is one of the densely populated areas which have a higher
risk with domestic pollution, especially in the coastal area. The objective of the research is to determine the
quality of coastal groundwater of Ternate City. Samples were taken from dug wells and it was measured
using multi water quality parameters, for nitrate and chloride were tested in the laboratory. Data were
compared with drinking water quality standards from the Health Ministry (Permenkes). The average pH of
groundwater was 8,15 indicates it’s slightly alkaline type. The temperature of groundwater varies between
28,7 – 31,1˚C. The salinity varies between 0,0294 -0,130 ppt, indicates as freshwater. Total Dissolved
Solids varies between 0,367
g
/L – 1,650
g
/L, while turbidity varies between 0,848 – 8,100 NTU and
electrical conductivity (EC) varies from 0,572
mS
/
cm
– 2,590
mS
/
cm
. Nitrate concentration varies between
6,493 – 4,824, and 5,152
mg
/
l
in average, while chloride concentration varies between 29,689
mg
/
l
and
709,694
mg
/
l
. Chloride mean concentration in the groundwater was 146,731
mg
/
l
and the standard deviation
was 214,765. The distribution of chloride and salinity increased as closer to the coastal line. The
physicochemical characteristics (i.e., nitrate, chloride, salinity, pH, electrical conductivity (EC), turbidity,
and temperature).
1 INTRODUCTION
The decreasing of groundwater quality could happen
as the seawater moves forward to the land,
especially in deep aquifers where the seawater
mixed with groundwater because of the increasing
of seawater level, land subsidence and constant
groundwater uptake (Marintoh et.al., 2015;
Ardaneswari et.al, 2016). Over uptake of the
groundwater might cause the empty space of the
land getting bigger inside the aquifers, thus seawater
level getting higher compared to the groundwater.
Seawater contains an element of salt, such as
chloride (Cl) could leak to the groundwater and
caused groundwater pollution (Marintoh et.al., 2015)
Alluvial and shallow aquifer areas were very
vulnerable to nitrate pollution compared with deep
and depressed aquifer (Voudouris et.al., 2004;
Eldridge,2002 in Kite_powell, A and Harding,
2006). In Ternate island, coastal area was where the
most population lives. Its slope and groundwater
supply were factors that promote the site selection.
Most of the area was quite flat compared to the
middle or top slope which hilly and deep
groundwater source. More and more residents lives
and doing their activities on the coastal areas, make
the higher its demands of groundwater, while the
number of domestic waste was higher. This
condition has made domestic waste contamination
higher, and the seawater intrusion increases if the
carrying capacity of the environment exceeded with
the higher of groundwater consumption in the areas.
A large sum of chloride could cause salty taste,
corrosion in hot water pipes. As a disinfectant, chlor
could bound with organic material as halogen
hydrocarbon (Cl-HC), which cause cancer
(Soemirat, 1994). The main source of nitrate
pollution came from organic and inorganic fertilizer,
animal waste, domestic waste, septic tank system
and industry (Mikkelsen, 1992 in Voudouris et.al.,
2004). Nitrate is carcinogenic and could cause
intestine cancer (Ida, 2009 in Kurniawan, 2017;
WHO, 1996 in Voudouris et.al., 2004) A large sum
of nitrate could cause glucose index (GI) problems,
diarrhea with blood, convulsion and could lead to
death. In chronical level could cause a headache,
mentally disorder dan depression (Soemirat, 1994).
Salinity defined as total ion within water body
that describes total solids after all the carbonates
converted as oxide, bromide, and ionide replaced by
chloride and organic matter has been oxidized
Aryuni, V., Salam, R. and Achmad, R.
Coastal Groundwater Quality Identification of Ternate City.
DOI: 10.5220/0008896800250029
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning (ICTL 2018), pages 25-29
ISBN: 978-989-758-439-8
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
25
(Effendi, 2003 in Ardaneswari et.al, 2016). Water
type classified into four different type based on
salinity, which are freshwater (<1.000
mg
/
l
), brackish
(1.000-3.000
mg
/
l
), salty (3.000-35.000
mg
/
l
) and very
salty (>35.000
mg
/
l
) (Ardaneswari et.al., 2016).
Electricity conductivity (EC) defined as the
electrical conductivity ability which affects by
ionized solute material and connects ion moves in
the solution, thus could use to understanding the
leachate distribution ((Lopes et.al., 2012; Reyes-
Lopes et.al., 2008). Resistivity linearly with EC, as
the bigger its EC, the bigger its TDS (Meilasari and
Pandabesie, 2013).
2 METHOD
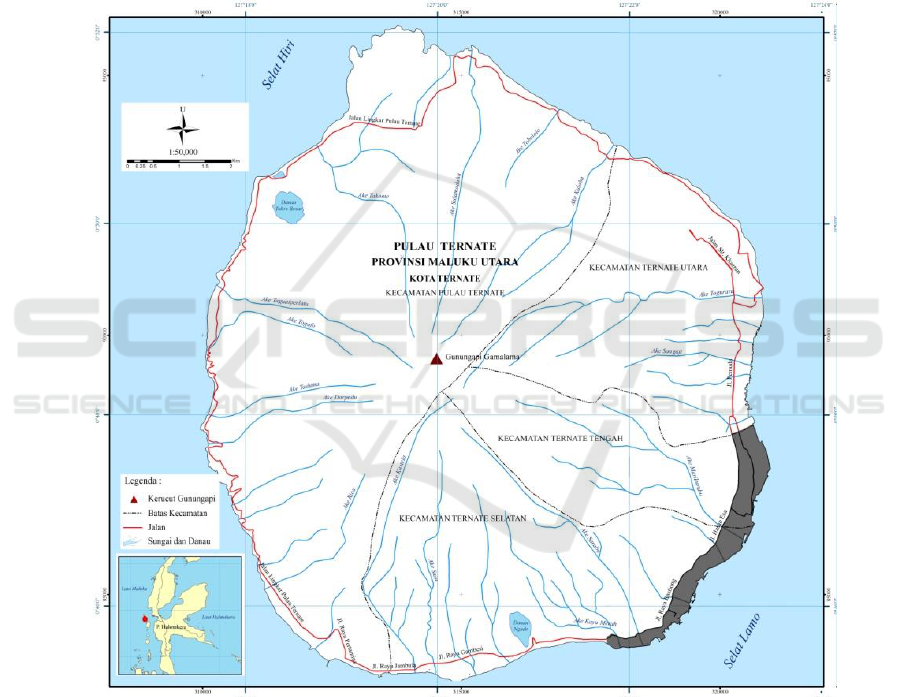
Area of studies is part of the coastal area in the
south-east of Ternate City, North Maluku (Figure 1).
This area is one of the densely populated which have
higher risked with domestic pollution. Fifty-two
wells were selected from the area to collect samples
of pH, electrical conductivity, dissolved oxygen,
turbidity, salinity, total dissolved solids, and
temperature, while nine of them were added with
nitrate and chloride parameters.
Figure 1. Location of Study Area
Primary data collections were wells location and
physic-chemical groundwater quality. Primary data
collection technique was purposively based its
distance from the coastal line, while the other
parameters were taken randomly. Samples position
determined with GPS data, on-screen digitation and
ground check. Secondary data were taken from
government agency Dukcapil. The groundwater
temperatures, pH, salinity, turbidity, TDS, DO and
EC was in-situ measured from 52 wells. Nitrate and
chloride were laboratories analyzed from 9 samples.
The water samples from the water body were
collected from resident dug wells. The parameters
pH, electrical conductivity, dissolved oxygen,
turbidity, salinity, total dissolved solids, and
ICTL 2018 - The 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning
26
temperature were measured at the sampling site using
multi water quality parameters, and other parameters
like nitrate and chloride were analyzed in the
laboratory. Data were compared to drinking water
standard from the health ministry (Permenkes) No.
492 the year 2010
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Fifty-two groundwater samples were collected from
dug wells were analyzed for its salinity, pH, total
dissolved solids (TDS), electrical conductivity (EC),
turbidity, and temperature with multiparameter
water sample were measured in situ, while nitrate
and chloride samples analyzed in the laboratory. The
average, maximum and minimum concentration are
presented in table 1.
Table 1: Analysis of Water Sample.
Parameters
average
maximum
minimum
Standard
deviation
variation
pH
8,15
10,62
5,11
1,416
2,005
Temperature (˚C)
28,756
31,070
26,840
0,784
0,615
DO (
mg
/
l
)
9,112
17,760
8,200
1,302
1,695
TDS (
g
/
l
)
0,367
1,650
0,233
10,196
0,39
Turbididty (NTU)
0,848
8,100
0,00
1,506
2,27
EC (
mS
/
cm
)
0,572
2,590
0,358
0,309
0,96
Salinity (ppt)
0,0294
0,130
0,020
0,160
0,00
Nitrate (
mg
/
l
)
5,152
6,493
1,394
1,551
2,407
Chloride (
mg
/
l
)
146,731
709,694
29,689
214,765
46,124
Based on Table 1, the average pH of
groundwater is 8,15 indicates it’s slightly alkaline
type. The standard limitation for drinking water was
6,5 – 8,5 so that it can be concluded in a good
condition. The temperature varies between 28,756 –
31,070˚C while dissolved oxygen (DO) varies
between 9,112
mg
/
l
- 17,760
mg
/
l
and 9,112
mg
/
l
in
average. Dissolved oxygen indicates oxygen
dissolved in water. Higher DO indicated the higher
its oxygen on the water and it’s better for drinking
water.
Total dissolved solids varies between 0,367
g
/
l
–
1,650
g
/
l
, while turbidity varies between 0,848 –
8,100 NTU and electrical conductivity (EC) varies
from 0,572
mS
/
cm
– 2,590
mS
/
cm
. The TDS standard is
500
mg
/
l
or 0,5
g
/
l.
which showed that the TDS of the
water has exceeded the safety limit for drinking
water. The total dissolved solid showed the amount
of solid dissolved in the water, but in this case was
not from the chloride which was still in a safe
amount.
The salinity of the water varies between 0,0294
-0,130 ppt, indicates as freshwater. Low salinity
showed there was not intrusion from the
seawater. It was supported by the chloride data,
which hasn’t exceeded the safety limit for drinking
water. Chloride varies from 29,689 – 709,694
mg
/
l
and 146,731
mg
/
l
in average and the standard
deviation was 214,765. Chloride were in safety limit
for consumption as it does not exceed tolerance limit
250
mg
/
l
(based on drinking water standard from
health ministry regulation No. 492 the year 2010),
except for East Makassar that was higher. The
higher the chloride might cause seawater intrusion
because of exploitation risk (Vouduris et.al, 2000 in
Vouduris, 2002). Chloride is one of important
parameter in water quality assessment. Chloride
could indicate a high degree of organic pollution as
the higher its concentration. The distribution of
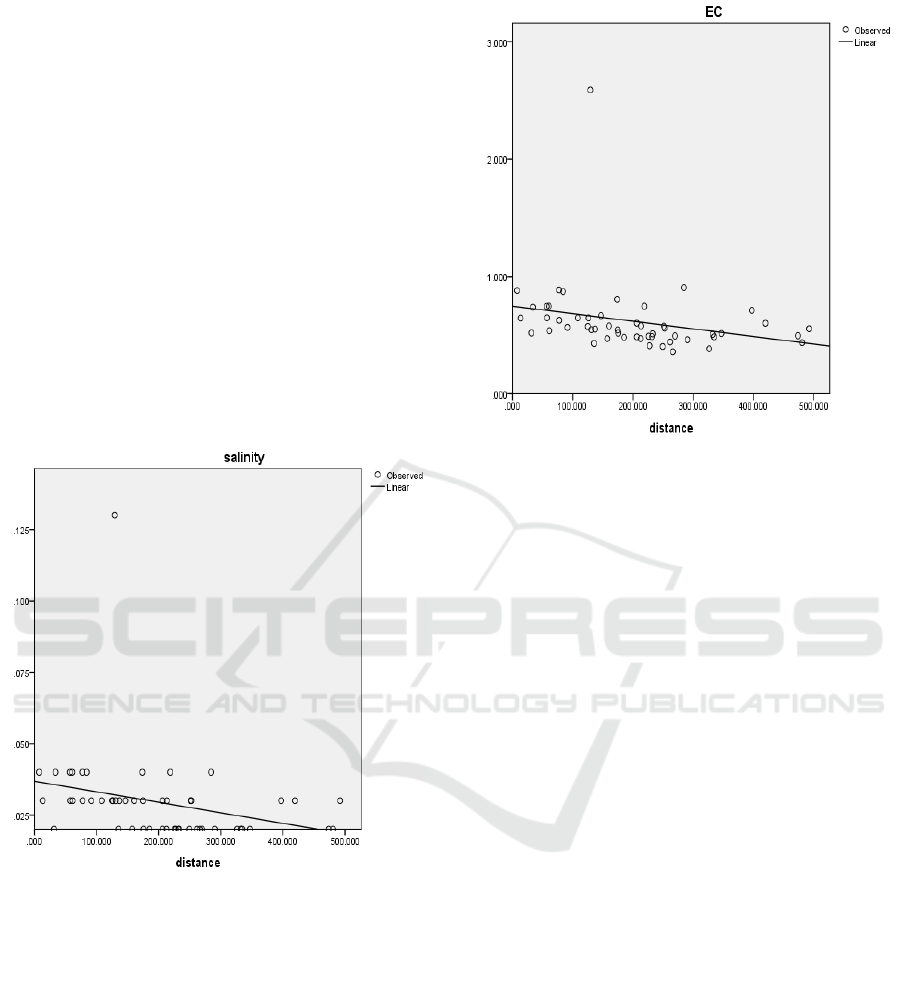
chloride increased as it got closer to the coastal line
as presented in Figure 2.
Coastal Groundwater Quality Identification of Ternate City
27
Nitrates varies 4,824 – 6,493
mg
/
l
and 5,152
mg
/
l
in average. Nitrate were in safety limit for
consumption as it does not exceed tolerance limit 50
mg
/
l
based on drinking water standard from health
ministry regulation No. 492 the year 2010. Based on
drinking water standard from health ministry
regulation No. 492 the year 2010, groundwater
quality of study area was in good condition, as it has
not exceeded the maximum standard for nitrate,
chloride, pH, EC, and turbidity.
High chloride number might cause salty taste and
corrosion in the hot water supply system (Soemirat,
1994). This condition as the salt content, as it
showed in EC and TDS data which higher than the
other samples, which is 2,59 and 1,65 while its
salinity 0,13ppt. The salinity and EC tend to increase
as it getting closer to the sea, but there wasn’t any
correlation between distance and salinity nor EC as
it showed in figure 2.a and 2.b below.
(a)
(b)
Figure 2: Distribution of salinity (a), and EC (b) to the
distance of wells to the sea.
The salinity and EC of the groundwater tend to be
lower as it gets further from the ocean, but there
wasn’t any correlation between its distance and
salinity nor EC as could be seen in Figure 2.
4 CONCLUSION
The physicochemical characteristics (i.e., nitrate,
chloride, salinity, pH, electrical conductivity (EC),
turbidity, dissolved oxygen (DO) and temperature)
in the study area were within the acceptable limits
health ministry drinking water standard No. 492 the
year 2010. As the water quality of the area was still
in good condition, it could be recommended as one
of the water source for the community than the
government public water utilities.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by research grants
PKUPT and support by the Environmental
Laboratory, Basic and Integrated Laboratory,
Khairun University to provide the device and water
quality testing.
ICTL 2018 - The 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning
28

REFERENCES
Ardaneswari, T.A., T. Yulianto, dan T.T. Putranto.2016.
Analisis Intrusi Air Laut Menggunakan Data
Resistivitas dan Geokimia Airtanah di Dataran Aluvial
Kota Semarang. Youngster Physics Journal. 5 (4),335-
350
Kite_Powell, A.C. and A.K Harding. 2006. Nitrate
Contamination on Oregon Well Water: Geologic
Variability and The Public Perception. Journal of The
American Resources Association, pp: 975-987
Morintoh, P., J.F. Rumampuk dan F. Lintong. 2015.
Analisis Perbedaan Uji Kualitas Air Sumur Di Daerah
Dataran Tinggi Kota Tomohon Dan Dataran Rendah
Kota Manado Berdasarkan Parameter Fisika. Jurnal e-
Biomedik (eBm). 3 (1), 424-429
Mohsin, M, S. Safdar, F. Asghar, and F. Jamal. 2013.
Assessment of Drinking Water Quality and Its Impact
on Residents Health in Bahawalpur City. International
Journal of Humanities and Social Science. 3 (15), 114-
128
Permenkes No 492 Tahun 2010 Tentang Persyaratan
Kualitas Air Minum
Soemirat, J.S. 1994. Kesehatan Lingkungan. Yogyakarta:
Gadjah Mada University Press.
Voudouris, K, A. Panagopoulos and I. Koumantakis.
2004. Nitrate Pollution in The Coastal Aquifer System
Of The Korinthos Prefecture (Greece). Global Nest:
The Int J. 6 (1),31-38.
Coastal Groundwater Quality Identification of Ternate City
29
