
The Effect of Business Development Assistance Program and
Religiosity on the Economic Performance of Zakat Recipients
through Their Participations using Structural Equation Model
Estiningsih, Adi Kuswanto and Budi Hermana
Economics Department, Gunadarma University, Depok, West Java, Indonesia
Keywords: Business Development Assistance Program, Religiosity, Economic Rerformance, Participations.
Abstract: The benefit of zakat for productive business that is still not being explored optimally is the main motivation
of this research. The structural equation model is applied to test the impact of business development
assistance program and religiosity on the economic performance of zakat recipients through their
participation in the Special Region of Yogyakarta and we we conducted a survey of 365 respondents. The
research instrument uses 5 likert scale that have high reliability and validity based on the value of Alpha and
Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin. The empirical model with SEM analysis shows that a high goodness of fit. Busienss
developmentassistance program and religiosity have a significant effect on the participation of recipients of
zakat in the development of business with a positive direction, and the participation will then have a
significant and positive effect on the economic performance of zakat recipients. The direct effect of business
developmentassistance program and religiosity is lower than their indirect effect on economic performance
through participation.
1 INTRODUCTION
Indonesia is a country with a Muslim majority
population of 216.66 million people or 85 % of the
total population (BPS, 2015). The Muslim
population can increase the potential for the
collection and distribution of very large zakat.
Referring to the National Zakat Statistics issued by
the National Zakat Authority (BAZNAS), the total
zakat collection in 2017 was recorded at 6224.4
billion rupiah or an increase of 24.06 % compared to
2016. Zakat distribution was recorded at 4860.2
billion rupiah or increased compared to the previous
year of 65.81 %, with absorption of 78.08 %. The
allocation of zakat distribution based on their
respective fields is 8825 billion rupiah, for the
economic sector (20.33 %), 941.9 billion rupiah for
education (21.69 %), 979.5 billion rupiah for the
field of da'wah ( 22.56 %), 413.5 billion rupiah for
the health sector (9.52 %), and 1124.2 billion rupiah
for the field of Social Humanity (25.89 %).
According to the Law of the Republic of
Indonesia number 23 of 2011 concerning Zakat
Management, zakat management aims to: (a)
improve the effectiveness and efficiency of services
in the management of zakat; and (b) increasing the
benefits of zakat to realize community welfare and
poverty reduction. The benefits of zakat to realize
community welfare and poverty alleviation are still
a problem, because various studies reveal that zakat
distribution tends to be consumptive, or
unproductive. The Law on Zakat states that zakat
can be utilized for productive business in the context
of handling the poor and improving the quality of
the people if the basic needs of mustahik have been
fulfilled. The distribution of zakat is currently
dominated by consumptive activities. There are
various forms of zakat distribution carried out by
zakat institutions, one of which is the distribution of
zakat in the form of business capital allocated to
productive recipients of zakat known as
microfinance mechanisms (Ibrahim and Ghazali,
2014). Zakat and Waqf (Endowments) are basically
tools to create stability of economy through the
distribution of the right funds for the right people so
that they can decrease the gap between the poor and
the rich (Hassanain, 2015).
The Financial Services Authority (2016), which
is stated in the 2015-2019 Indonesia Financial
Services Sector Master Plan document states that
Indonesia holds enormous potential for the growth
Estiningsih, ., Kuswanto, A. and Hermana, B.
The Effect of Business Development Assistance Program and Religiosity on the Economic Performance of Zakat Recipients through Their Participations using Structural Equation Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0008896500050010
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning (ICTL 2018), pages 5-10
ISBN: 978-989-758-439-8
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
5
of the Islamic financial services sector, supported
by a large Muslim population of around 88.1%.
Indonesia is also the largest Muslim country in the
world with 12.7 % of Muslims in the world.
Referring to the report: "State of the Global
Islamic Economy" 2017-2018 edition, Indonesia
only occupies 11th position out of 73 countries in
the world based on Global Islamic Economy
Indicator which covers 6 sectors, including the
Islamic financial sector where Indonesia ranks 10th
(Thomson Reuters, 2018). Various data and
indicators show that Islamic finance in Indonesia
has not shown a performance optimally.
Considering that zakat has proven to be a very
effective way to help the poor, the collection and
distribution of zakat must be increased (Abdullah,
Derus and Al-Malkawi, 2015). According to Jaelani
(2015), optimizing the high potential of zakat in
Indonesian society, cooperation between
stakeholders, and government regulations can be a
solution in reducing poverty. The role of the
government which is the main stakeholder in the
management of zakat is represented by BAZNAS.
The challenge is how to allocate zakat to those
productive businesses. According to Hamzah
(2017), zakat has not been used intensively for
empowerment of mustahiq (recipients of zakat) in
the form of productive economic endeavors.
BAZNAS as a collection authority and fund
manager has compiled various utilization strategies
so that the utilization of zakat is more productive
which leads to business continuity in the three target
groups namely; the beginner mustahik businessman,
businessman mustahik and Z-mart. The problems
faced by entrepreneurs mustahik are access to:
capital, raw materials, production, and markets.
This research will examine the use of zakat for
the development of productive businesses by
recipients of zakat in the Special Region
Yogyakarta whose zakat management is carried
out by the BAZNAS Yogyakarta. The research
questions are whether the success of the
development of its business is influenced by
individual factors, external factors, and the
participation of zakat recipients in the development
of its business. The individual factor is religiosity
while the external factor is the role of business
development assistance program.
2 RESEARCH METHOD
The research was conducted in Bantul, Gunung
Kidul, Kulon Progo, Sleman, and Yogyakarta with
305 respondents. The measurement of variables
using 5likert scale with statement items are
presented in Table 1 below.
Table 1: Research Variables and Measurement.
Variable
Item
Reference
Religiosity
Attend attend recitation
groups
Abdullah and
Sapiei (2018),
Farouk et al.
(2018), Somu and
Sujatha (2015)
Pray at the mosque
Attend religious events
Assistance
Motivation
Hamzah (2015)
Learning
Entrepreneurship
Participation
Attend business meeting
Langerodi and
Dinpanah (2017);
Hamzah (2015);
and Radzi, Nor,
and Ali (2017)
Regularly save money
Loan payment
Capital empowerment
Economic cooperation
empowerment
Economic
Equity increasing
Berguiga (2017)
and Hamzah
(2015)
Income increasing
Business development
Business collaboration
Reliability test of the research instruments
using Cronbach Alpha while test of the validity
using Kaisser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO). Testing the
hypothesis using an analysis of structural equation
models with two exogenous variables, namely
business development assistance program and
religiosity, one mediator namely participation in
business development, and economic performance
variables as an endogenous variable.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Reliability and Validity
Table 2: Reliability and Validity of Research Instruments.
Variable
Code
Cronbach Alpha
KMO
Religiosity
R1
0.814
0.680
R2
R3
Assistance
A1
0.836
0.700
A2
A3
Participation
P1
0.764
0.785
P2
P3
P4
P5
Economic
E1
0.842
0.773
E2
E3
E4
ICTL 2018 - The 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning
6
Research instruments have high reliability and
validity as indicated by the cronbach alpha value
above 0.75 and the KMO value above 0.65. The
results of the reliability and validity testing are
presented in the table below.
3.2 Respondent Profile
The number of respondents who filled out
complete questionnaire was 305 which consists of
56 % of men, 40 % of high school education, 34 %
of the age group 31-40 years, 51 % living in
Gunung Kidul, and 49.51 % engaged in the trade
sector. Most respondents (56 %) have business
experience under 5 years, 59 % have income
ranging from 1-2 million Rupiah per month, and
62 % receive zakat in the amount of 3-5 million.
Female respondents generally showed
religiosity and the role of Business Development
Assistance Program was higher than male
respondents. The group of respondents with high
education showed higher economic performance
and participation compared to those with
elementary, middle and high school education, but
the group of college graduates showed the lowest
role of Business Development Assistance Program.
Respondents in agricultural business sector
relatively found the importance of role of Business
Development Assistance Program and showed
higher participation compared to other business
sectors. Respondents in manufacturing showed
higher religiosity and participation than
agricultural sector, trade sector and service sector.
Respondents with age of 41-50 years showed
higher religiosity, the role of Business
Development Assistance Program, participation,
and economic performance compared to other age
groups.
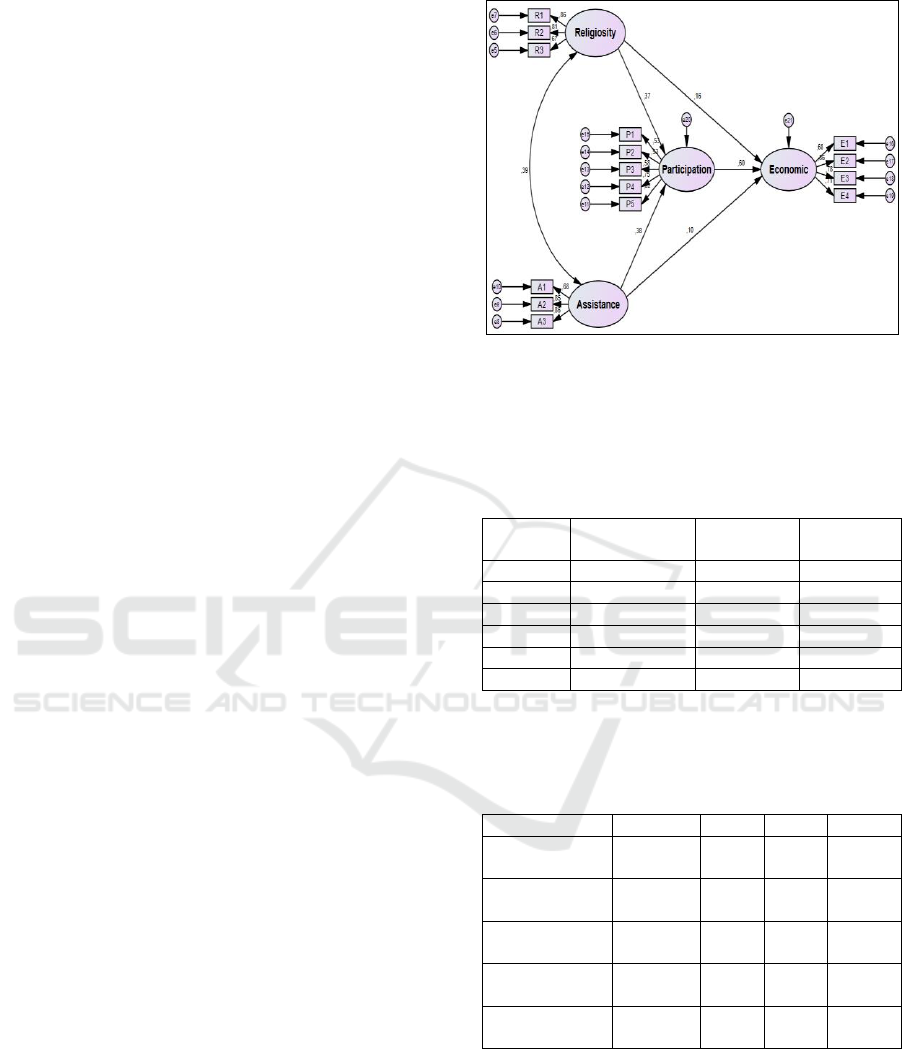
3.3 Structural Equation Model
Participation which mediates the relationship
between religiosity and the role of Business
Development Assistance Program on the economic
performance of the productive business conducted
by zakat recipients are tested by using structural
equation model analysis. The results of the
structural equation model analysis are presented in
Figure 2 below.
Figure 1: Standardized Model.
The empirical model has a very good goodness
of fit as measured by several statistical parameters
as presented in table 3 below.
Table 3: Model Fit Analysis Summary.
Statistics
Independence
Model
Default
Model
Saturated
Model
CMIN
2252.830
330.992
0.000
GFI
0.342
0.876
1.000
CFI
0.000
0.885
1.000
FMIN
7.411
1.089
0.000
RMSEA
0.259
0.098
-
AIC
2282.830
402.992
240.000
This research has five hypotheses with the
complete test results presented in table 4 below.
Table 4: Hypotheses Test.
Relationship
Estimate
S.E.
C.R.
P
Religiosityto
Participation
0.450
0.085
5.269
***
AssistancetoParti
cipation
0.282
0.050
5.587
***
Participation to
Economic
0.346
0.050
6.958
***
AssistancetoEcon
omic
0.043
0.027
1.555
0.120
Religiosityto
Economic
0.112
0.045
2.461
0.014
Religiosity and the role of business development
assistance program to participation has a very
significant influence with a positive direction which
means that the higher the level of religiosity and the
role of business development assistance program,
the higher the level of participation of recipients of
zakat in developing and improving their businesses.
Both variables show relatively similar roles as
The Effect of Business Development Assistance Program and Religiosity on the Economic Performance of Zakat Recipients through Their
Participations using Structural Equation Model
7
indicated by the path coefficients of 0.37 and 0.38. It
means that the success in encouraging the level of
participation is strongly influenced by religiosity
and business development assistance program
(external factor) to zakat recipients in conducting
their productive business.
Research on the effect of religiosity of tax
recipients is relatively rare because most of the
previous research has linked religiosity to
compliance with zakat payments, as done by
Abdullah and Sapiei (2018) and Farouk, Idris, and
Jaffri (2018), or relates religiosity to business
performance or economic empowerment program,
as done by Somu and Sujatha (2015) which shows
that spiritual empowerment has a significant
impact on economic empowerment. According to
Abdullah and Sapiei (2018), three dimensions of
religious and virtue (akhlaq) dimensions are the
driving factors for zakat compliance. This research
is different from the research conducted by
Farouket al. (2018) which places religiosity as a
moderator that is significant to the relationship
between attitude and subjective norms with the
intention to pay zakat.
Significant influence of business development
assistance program on participation shows the
central role of education or training programs for
zakat authority in developing business. Business
development assistance program are needed to
reduce various problems that are still being faced,
especially in the management of businesses
financed by zakat. Although this research has not
yet studied about the application of sharia
principles in the management of businesses of
zakat recipients, several studies in the field of
Islamic finance are used as a comparison.
Lack of economic independence becomes a
problem in implementing sharia-based
microfinance such as lack of funding and lack of
skills in managing business (Rahim, 2015).
According to Abbas and Shirazi, 2015) Islamic
microfinance faces obstacles namely lack of
knowledge, experience and professionalism of
supporting staff. Various technical constraints in
business management can be overcome by
business development assistance program or other
forms of empowerment, with reference to several
research results, including Hamzah (2018) for
productive management. The last researcher
included technical support and managerial support
factors as support variables, in addition to five
other variables, namely external factors, individual
factors of business owners, business aspects,
management, and resources.
The indirect effect of religiosity and business
development assistance program to economic
performance through participation is greater than
the direct influence of the population, as presented
in table 5.
Tabel 5: Total Effect, Direct Effect, and Indirect Effect
(Standarized Model).
Assistance
Religiosity
Participation
Economic
Direct effect
Participation
0.377
0.373
0.000
0.000
Religiosity
0.100
0.162
0.604
0.000
Indirect Effect
Participation
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
Economic
0.228
0.225
0.000
0.000
Total Effect
Participation
0.377
0.373
0.000
0.000
EconoMic
0.327
0.387
0.604
0.000
Economic performance is directly influenced
by participation with a path coefficient of 0.604
and is influenced by religiosity and direct and
indirect assistance with a total effect of 0.387 from
Religiosity and 0.327 from business development
assistance program. Greater indirect influence on
economic performance through participation is one
of the empirical evidences for zakat managers,
especially BAZNAS Yogyakarta, to increase the
participation of zakat recipients in productive
business development programs funded by zakat.
Efforts to increase participation need to take into
account the characteristics of respondents whose
participation rates vary from respondent
demographics, type of business, age group, and
level of education. As a comparison, the Langerodi
and Dinpanah (2017) study on the participation of
farmers in environmental protection programs, the
level of participation of participants in the
empowerment program was significantly
influenced by social features, information sources,
and attitudes of program participants. Participation
as mediator was examined by Langford, Parkes,
and Metcalf (2006) which states that participation
is a mediator that is significant to the relationship
between business objectives and property with
business development which includes
organizational goals, change and innovation, and
customer satisfaction.
Radzi, Nor, and Ali (2017) use the concept of
knowledge sharing as one of the success factors of
small businesses. Sharing knowledge can occur
when respondents gather with each other in
training activities. Two indicators that measure the
participation variable in this study are the
activeness of zakat recipients in meetings and
ICTL 2018 - The 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning
8

collaboration empowerment. Increased
participation will encourage the exchange of
experience, knowledge, and skills in business
development and finally it can ultimately support
increased economic performance. Referring to the
significant relationship between the role of
facilitator and the level of participation, the level
of participation of zakat recipients is expected to
increase more by increasing the role of facilitator
as one of the sources of knowledge in business
management by recipients of zakat.
Distribution of zakat for productive businesses
still needs to be strengthened in Indonesia,
especially in its financial management. During this
time, financial assistance to zakat providers for
productive businesses is still considered to be
funding assistance that is not demanded for
refunds. Strengthening the zakat management
program for the development of productive
businesses is a challenge from BAZNAS, which
does not rule out the possibility of its own financial
management system as in the form of microfinance
institutions that continue to apply sharia principles.
Balancing social performance and financial
performance is a major challenge for microfinance
institutions. The aspects of Islamic microfinance,
especially those whose funds are from zakat and
waqf, are still lagging behind. For example, there
is a need to establish financial management
guidelines related to governance to increase the
credibility of microfinance institutions, and to
support the sustainability and improvement of
operations. According to Berguiga, Said, and Adair
(2017), microfinance institutions face a two
challenges, namely that they must ensure increased
financial inclusion from the poor, while financially
sustainable without relying on subsidies.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The central role of the participation of zakat
recipients in the development of productive
business is the main finding of this study. This
participation increased with the increasing level of
religiosity and the role of business development
assistance program, which in turn had a significant
impact on improving the economic performance of
its productive businesses. The challenge is how
zakat recipients can increase their participation in
business development which is still relatively
diverse and the direct influence on economic
performance has not been significant. The business
development assistance program can provide
knowledge and skills in business management that
have been an obstacle, including the role of
BAZNAS in conducting more effective business
empowerment programs so that their productive
business show an increasing economic
performance.
This research will be continued by expanding
individual factors and external or institutional
factors to assess their effects on the economic
performance of businesses managed by zakat
recipients, including entrepreneurial ability,
financial literacy, and courage to take risks as other
individual factors; and social and religious
environmental influences and institutional support,
especially from BAZNAS. The aspect of financial
literacy is important because the zakat
management program is also linked to financial
inclusion programs that are prioritized programs in
the financial sector in Indonesia. According to
Ahmed and Salleh (2016), integrating zakat and
waqf into financial inclusive planning such as
money management through savings and
microfinance programs ensures that poor people
have access to financial products and services.
REFERENCES
Abbas, K., and Shirazi, N. 2015. The Key Players’
Perception on the Role of Islamic Microfinance in
Poverty Alleviation: The case of Pakistan. Journal of
Islamic Accounting and Business Research, Vol. 6
Issue: 2, 244-267.
Abdullah, M., and Sapiei, N. S. 2018. Do Religiosity,
Gender and Educational Background Influence
Zakat Compliance? The Case of Malaysia.
International Journal of Social Economics, Vol. 45
Issue: 8, 1250-1264.
Abdullah, N., Derus, A. M., and Al-Malkawi, H. N.
2015. The Effectiveness of Zakat in Alleviating
Poverty and Inequalities: A Measurement using a
newly developed technique. Humanomics, Vol. 31
Issue: 3, 314-329.
Ahmed, H., and Salleh, H. A. 2016. Inclusive Islamic
Financial Planning: a Conceptual framework.
International Journal of Islamic and Middle Eastern
Finance and Management, Vol. 9.
Alam, M. M, Hassan, S., and Said, J. 2015. Performance
of Islamic Microcredit in Perspective of Maqasid Al-
Shariah: A case study on Amanah Ikhtiar Malaysia.
Humanomics, Vol. 31 Issue: 4, 374-384.
Badan Amil Zakat Nasional. (2018). Statistik Zakat
Nasional 2017. BAZNAS, Juni 2018.
Berguiga, I., Said, Y., and Adair, P. (2017). The Social
and Financial Performance of Microfinance
Institutions in the MENA Region: Do Islamic
institutions perform better?. 34th Spring
The Effect of Business Development Assistance Program and Religiosity on the Economic Performance of Zakat Recipients through Their
Participations using Structural Equation Model
9

International Conference, French Finance
Association (AFFI), May 2017, Grenoble, France.
Farouk, A. U., Idris, K. M., and Jaffri, R. A. 2018.
Moderating Role of Religiosity on Zakat
Compliance Behavior in Nigeria. International
Journal of Islamic and Middle Eastern Finance and
Management, Vol. 11 Issue: 3, 357-373.
Hamzah. 2017. Empowerment of Mustahiq Zakat Model
Towards Business Independency. International
Journal of Nusantara Islam, Vol.5(1), 85-96.
Hassanain, K. M. 2015. Integrating Zakah, Awqaf and
IMF for Poverty Alleviation: Three Models of
Islamıc Micro Finance. Journal of Economic and
Social Thought, Vol.2 (3), 193-211.
Ibrahim, P., and Ghazali, R. 2014. Zakah as an Islamic
Micro- Financing Mechanism to Productive Zakah
Recipients. Asian Economic and Financial Review,
4(1), 117-125.
Langerodi, M. C., and Dinpanah, R. 2017. Structural
Equation Modeling of Rice Farmers’ Participation in
Environmental Protection. Applied Ecology and
Environmental Research, Vol.15(3), 1765-1780.
Langford, P. H., Parkes, L. P., and Metcalf, L. 2006.
Developing a Structural Equation Model of
Organisational Performance and Employee
Engagement. Psychology Bridging the Tasman:
Science, Culture and Practice, Mary Katsikitis (Ed.),
The Australian Psychological Society Ltd,
Melbourne, Australia.
Radzi, K. M., Nor, M. N. M., and Ali, S. M. 2017. The
Impact of Internal Factors on Small Business
Success: A Case of Small Enterprises Under The
Felda Scheme. Asian Academy of Management
Journal, Vol. 22, No. 1, 27–55.
Rahim, N. A. 2015. Cash Waqf: An Alternative Source
of Funding for Shariah Compliant Microfinance
Business In Malaysia. WIEF-UiTM Occasional
Papers, 2nd Edition.WIEF-UiTM International
Centre, Universiti Teknologi Mara.
Somu, A., and Sujatha, V. S. 2015. Spirituality and Its
Impact onEconomic Empowerment of Self Help
Group Members. IOSR Journal of Business and
Management, Vol. 17 (4), 11-18.
Undang-Undang Republik Indonesia Nomor 23 Tahun
2011 tentang Pengelolaan Zakat.
Thompson Reuters. 2018. State of the Global Islamic
Economy Report 2017/2018: Outpacing The
Mainstream.
ICTL 2018 - The 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning
10
