
The Influence of Liquidity and Deposit Insurance on Market
Discipline at Regional Development Bank in Indonesia
Syarief Fauzie and M. Deni Rahman Sitepu
Economic Development Department, Faculty of Economic, University of Sumatera Utara, Medan
Keywords: Market Discipline, Deposit Growth, Interest Rates, Liquidity, Deposit Insurance.
Abstract: The purpose of this study is to determine the effect of liquidity on the influence of overhead, short term
debt, inflation and regional growth of gross domestic product on deposit growth and interest rates as market
discipline variables. In the research also use dummy variable in the form of policy of deposit insurance
either implicitly or explicitly by Government of Indonesia as variable which moderate influence of liquidity
to growth of deposit and interest rate. This study used 19 regional development banks in the region during
the period of 2002-2014. In testing the influence of independent variable to dependent variable, this
researchuse multiple linear regression fixed effect model. While the data in this research is secondary data
sourced from annual report published by Bank Indonesia. The results show that liquidity is a variable that
can mediate the influence of short term debt and regional growth of gross domestic product on the growth of
deposits and also can mediate the influence of overhead, short term debt, inflation and regional growth of
gross domestic product against interest rate. The results also show that the implementation of the deposit
insurance policy explicitly is a variable that strengthens the effect of liquidity on deposit growth and interest
rate.
1 INTRODUCTION
Based on the last two decades in the banking world,
there has been a series of crises that systematically
caused bankruptcy of banks that culminated in 1997
in Asian countries such as Thailand, Indonesia,
Malaysia and Korea. The crisis not only resulted in
bankruptcy of banks but also resulted in economic
downturn and devaluation of currencies in countries
that experienced the crisis. In addition, the banking
crisis also affected the decline in public confidence
in the banking industry. This is due to moral hazard
perpetrated by banking actors who have harmed the
public in general and ultimately impacted the public
panic to withdraw their funds from the banks due to
lack of confidence in the community to the bank at
that time.
The incidence of banking crisis in Asian
countries especially in Indonesia resulted in Bank
Indonesia adopting Basel II on the Banking
Architecture which explicitly emphasized the
strengthening of market discipline as stated in Pillar
3 within the Indonesian Banking Architecture (API)
which was enacted in 2004. This is done to improve
banking stability in Indonesia, as well as to avoid
bank failures in the future and to restore public
confidence to banks.
Market discipline is an act by customers,
creditors, and investors in disciplining banks that
take the risk are too big. Market discipline currently
used in banking literature includes two components:
the ability of market actors to precisely judge the
condition of a company and the supervision and
ability of market participants to influence the actions
of corporate management as a way of reflecting
judgments (Flannery. 2000). To achieve these
objectives, in the banking context, adequate
information is needed for the community regarding
the condition of the bank and the ability of the
community itself to assess the condition of the bank
through analysis of available information. In this
case the role of banks as financial institutions to be
trusted by the public is required to provide correct
information about their conditions to customers or
investors.
Based on this, it can be concluded that banks that
have a high risk tend to make customers feel worried
about their deposits. The action taken by the
customers is to discipline the bank, that is by
demanding higher interest rates. This phenomenon
706
Fauzie, S. and Sitepu, M.
The Influence of Liquidity and Deposit Insurance on Market Discipline at Regional Development Bank in Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0008892807060714
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research (ICMR 2018) - , pages 706-714
ISBN: 978-989-758-437-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

may still be overcome by the banking sector by
maintaining bank liquidity. But if the customer
withdraws the deposit and is not something that is
impossible, based on fear and to avoid losses due to
risk taken by the bank, the customer may withdraw
all deposits to the bank.
According to Murata and Hori in Taswan that
banks havenegative correlation relationship between
the growth rate of deposits with bank risk and have a
positive correlation relationship between the interest
rate demanded and bank risk(Murata and Hori,
2013). This leads to a decrease in deposit growth in
the bank resulting from market discipline by
customers through interest rates, even worse that
bankruptcy or bank failure, if the customer
withdraws all deposits to the bank. The consequence
of this problem is the decreasing of public
confidence, especially the customers to the bank and
it is not impossible that will have an impact on the
banking crisis.
As already mentioned in the previous
phenomenon that bank liquidity can overcome
market discipline conducted by the customer
through the interest rate demanded by the customer.
Good liquidity management can give confidence to
depositors or savers that they can take funds at any
time or at maturity. The bank's liquidity also has a
negative effect on the market discipline; the better
the management of bank liquidity, the market
discipline undertaken by the customers can be
overcome by the banks.
However, market discipline does not always
carry out its duties to monitor risk. Market discipline
will weaken when customer deposits are fully
guaranteed by the government (Yaling and Yingzi,
2012). AsDermiguc-Kunt and Huizinga, who say the
deposit insurance program is one indication that the
banking system in the country is in a systemic crisis
(Dermiguc-Kunt and Huizinga, 1998). This
guarantee has a positive influence on the banking
sector, the flow of public funds has gradually re-
entered the banking sector, the panic has been eased
and the recovery of public trust in banking has taken
place. But market discipline becomes relatively
lower or weaker when full guarantee is carried out
(Prean and Stix, 2011). The same was stated by
Dermiguc-Kunt and Huizinga, who said that deposit
insurance did indeed weaken market discipline
through deposit rates (Dermiguc-Kunt and Huizinga,
2004).
Yan, etal.said that the condition of market
discipline cannot happen, because all the risks
caused by the bank's decision have been borne by
the deposit guarantee. However, if the guarantee is
done in a limited way and enforced in general, then
the customer can still perform market discipline or
act on bank risk (Yan etal.2011). The same thing
was also expressed by Berger and Turk-Ariss, who
say that market discipline will decrease when the
government takes full or implicit deposit insurance
(Berger and Turk-Ariss, 2012). In contrast to
Distinguin said that market discipline is more
effective if there is an explicit deposit insurance
(Distinguin etal.2011).
Moreover, Distinguin finds that market discipline
is stronger when an explicit deposit insurance is
applied, whereas when the insurance is implicit,
market discipline cannot function
(Distinguinetal.2012). Market discipline performed
by the customer when the implicit period of implied
deposit insurance applies by controlling through the
withdrawal of the deposit because of the bank taking
a high risk. This shows the higher the risk taken by
the bank, the lower the bank's savings.
Conversely, in an explicit deposit insurance
period, market discipline is more sensitive than
when the insurance period is implicit. Market
discipline that customers make when an explicit
deposit insurance period applies is to demand a
higher interest rate or withdraw their savings. This
shows the higher risk taken by the bank, the higher
the interest rate demanded by the customers.
Based on the above problem, firstly, this paper
examines whether banking liquidity affects market
discipline by using the indicator deposit growth and
interest rates. This test includes control variables
consisting of overhead, short term debt,inflationand
regional gross domestic product (RGDP). The use of
these four control variables is due to having an effect
on the growth of deposits. In this test, the liquidity
variable is used as an intermediate variable to see
whether the liquidity variable is an intermediate
variable of indirect relationship between the control
variable to the deposit growth and interest rates
variable as an indicator of market discipline.
Secondly, our test is done to see the influence of
the effect of deposit insurance on the relationship
between banking liquidity to deposit growth and
interest rates by making deposit insurance variable
as a moderating variable to test whether insurance
deposit is a variable that strengthens or weakens the
effect of liquidity on deposit growth and interest
rates.
The research sample used is the Regional
Development Bank located within the Province of
Indonesia. The use of Regional Development Bank
as a sample of this study is due to have a less
competitive level of competition against national
The Influence of Liquidity and Deposit Insurance on Market Discipline at Regional Development Bank in Indonesia
707
banks located in the territory of Indonesia in terms
of technology, marketing,etc. Therefore, the
Regional Development Bank which is a bank owned
by the Regional Government in Each Province in
Indonesia has average interest rate higher than
national bank.Therefore, the research questions in
this research are:
1. How does bank liquidity mediate the effect of
overhead cost, short term debt, inflation and
regional gross domestic product growth on
deposit growth and interest rates?
2. What is the effect of deposit insurance on the
relationship between liquidity and deposit
growth and interest rates?
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
The results of research conducted by Taswan
through the results of estimation and testing
conducted between the banking risk to interest rate,
indicating that the risk of banking has a positive and
significant impact on interest rates (Taswan, 2013).
These results indicate that the higher the risk of
banking, the higher the interest rate demanded by
customers as market discipline against banks that
take high risks. This result is consistent with
research conducted by Dermiguc-Kunt and Huizinga
who found that depositors can discipline banks
involved in excessive risk taking by demanding
higher interest rates (Dermiguc-Kunt and Huizinga,
2004).
Taswan found that bank risk negatively affects
changes in deposit growth in banks. Customers
conduct market discipline in banks by punishing
banks through withdrawal of funds because of taking
high risk banks. Depositors prefer to withdraw their
funds rather than keep their deposits in the bank
(Taswan, 2013).
Furthermore, Dermiguc-Kunt and Huizingafound
out that bank liquidity is the most appropriate
attempt by banks to overcome market discipline by
customers by asking for higher interest rates. While
higher government interest rates lead to lower
liquidity.
Dermiguc-Kunt and Huizinga also found that the
existence of an explicit deposit guarantee reduces
the market discipline of the bank by the customers
(Dermiguc-Kunt and Huizinga, 2004). In contrast to
research conducted by Taswan suggests that market
discipline in the period of implicit deposit
guarantees and explicit deposit guarantee periods is
not statistically different (Taswan, 2013). The effect
of risk taking on changes in deposits in the explicit
underwriting period and the effect of risks on
changes in deposits in the implicit guarantee period
apply equally. Each has a negative effect on the
deposit changes. The similarity of these influences
indicates that market discipline applies regardless of
the difference in the deposit guarantee scheme.
Market discipline applies because solely banks take
high risks.
Based on the research questions and literature
review above, the researchers draw their hypothesis
as follows:
1. H
0
1:There is no significant effect overhead
cost, short term debt, inflation and regional
gross domestic product growth ondeposit
growth through liquidity.
2. H
0
2: There is no signficant effect deposit
insurance on the relationship between liquidity
and deposit growth.
3. H
0
3: There is no significant effect overhead
cost, short term debt, inflation and regional
gross domestic product growth on interest rate
through liquidity.
4. H
0
2: There is no signficant effect deposit
insurance on the relationship between liquidity
and interest rate.
Hypothesis description of the above research is
presented as follows:
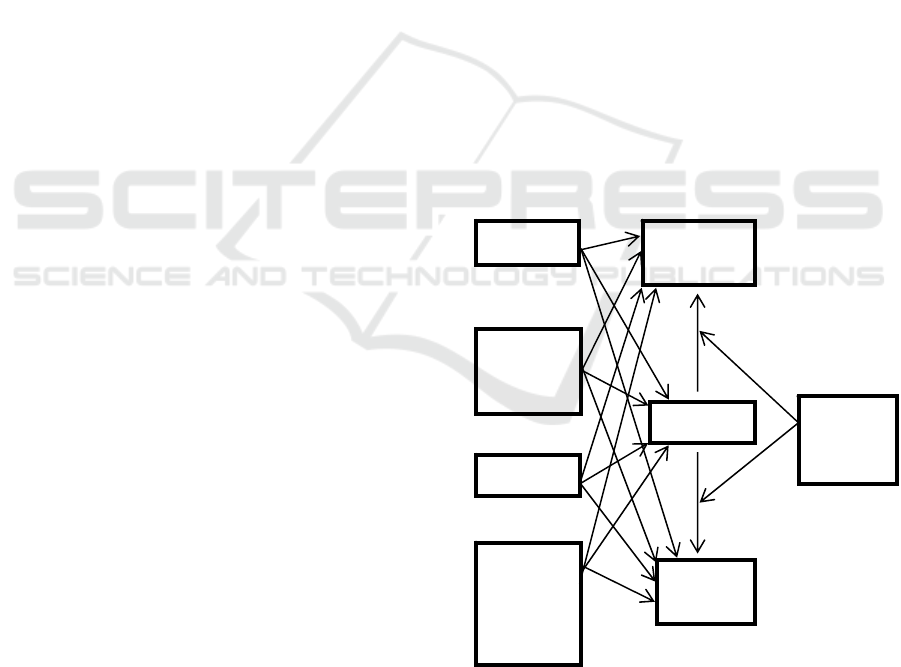
Figure 1: Hypothesis description.
Overhea
Shor
Term
Debt
Inflation
Regional
Gross
Domestic
Product
Growth
Liquidity
Deposit
Growth
Interest
Rate
Deposit
Insuranc
e
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
708
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Research Data
The data used in this study is the data of Regional
Development Bank located in each Province in
Indonesia. The population used in this research is 26
Regional Development Banks registered with Bank
Indonesia for the period of 2002-2014.In this study
used a way to determine the sample data with non-
probability sampling that the data used as a sample
must meet the specific criteria. The selection of
banks through criteria based on purposive sampling
which is a group of subjects based on certain
characteristics believed to haveclose connection with
the characteristics or properties of the population. In
the selection of this criterion is the Regional
Development Bank registered with Bank Indonesia
by including the following sample bank criteria
1. Regional Development Bank which has been
operational within the period of 2002 - 2014.
2. The Bank publishes its annually financial
statements from period 2002 to 2014 completely.
The total sample used in this research is 19
Regional Development Banks in Indonesia that have
been operating in the period 2002-2014. Data
collection is sourced from the financial statements of
Regional Development Banks published by Bank
Indonesia.
Table 1: Sample Research.
No. Bank
1. PT. Bank Aceh
2. PT. BPD Bengkulu
3. PT. Bank DKI
4. PT. BPD Jambi
5. PT. BPD Jawa Barat danBanten, Tbk
6. PT. BPD JawaTimur
7. PT. BPD Kalimantan Barat
8. PT. Bank Kalimantan Tengah
9 PT. BPD Kalimantan Timur
10. PT. BPD Lampung
11. PT. BPD Maluku
12. PT. BPD Papua
13. PT. BPD Riau, Kepri
14. PT. BPD Sulawesi Tenggara
15. PT. BPD Sulawesi Utara
16. PT. BPD Sumatera Barat
17. PT. BPD Sumatera Selatan dan Bangka
Belitung
18 BDP Sumatera Utara
19 BPD Yogyakarta
3.2 Variable and Definition
Operational definitions of each variable in this study
are as follows:
Table 2: Research Variable and Definition.
Variable Definition
Dependent Variable:
Deposit Growth Percentage growth in real
deposits
Interest Rate The ratio of interest expense
to interest paying debt
Intervening Variable:
Liquidity Liquid assets to total assets
Independent Variable:
Overhead Cost Personnel expenses and other
non-interest expenses over
total assets
Short Term Debt Short term funding to total
interest paying debt
Inflation The annual inflation rate
from the Regional Gross
Domestic Product deflator
Regional Gross
Domestic Product
Regional gross domestic
product per capitaeach
province in Indonesia
Deposit insurance The period of the
government's deposit
insurance policy which
comprises three periods
consisting of an implicit
period of deposit insurance,
an explicit deposit insurance
period with up to 100 million
guarantees and an explicit
deposit guarantee period of
up to 2 billion. Variables
used in differentiating this
period using dummy
variables.
4 RESULT
4.1 Hypothesis Test
4.1.1 Hypothesis 1
Depositors in applying market discipline will
withdraw their savings from high risk banks. In
reducing the risk of high withdrawal of customer
deposits, most banks will increase their investment
in assets with high liquidity. Therefore, bank
liquidity can be endogenous variable as banks can
try to avoid market discipline to some extent by
increasing their liquidity (Dermiguc-Kunt and
The Influence of Liquidity and Deposit Insurance on Market Discipline at Regional Development Bank in Indonesia
709

Huizinga, 2004). In this study, the use of liquidity as
a variable that mediate the influence of controlling
variables such as overhead cost, short term debt,
inflation and regional gross domestic product. As an
intervening variable, liquidity will be treated as an
exogenous and endogenous variable. In the first
stage, we examine the effect of all exogenous
variables on the endogenous variables with the
following equations:
Y
it α β1X1it β2X2it β3X3it β4X4it
β5Zit eit
(1)
WhereY
it
is deposit growth, X
1it
is overhead cost,
X
2it
is short term debt, X
3it
is inflation, X
4it
is regional
gross domestic product andZ
5it
is liquidity. The
result of the panel data regression equation is as
follows:
Table 3: Test for Hypothesis 1.
Variables Coefficient
Overhead -5.360008
Short Term Debt -6.001317***
Inflation -3.715142
RGDP Growth -4.027879*
Liquidity -3.018555**
No. Of Obs 247
No. Of Banks 19
Adj. R
2
0.279069
F value 5.140236***
***,** and * indicate statistical significant at 1,5 and 10
percent, respectively.
In the second stage, in testing liquidity as an
intervening variable then we do the regression as
follows:
Y
t α β1Xit β2Zit
(2)
Zt α β3Xit
(3)
Whrere: Y
it
is deposit growth,X
it
is each control
variable consist overhead cost,short-term
debt,inflation,regional gross domestic productand
Z
5it
is liquidity
To determine whether the magnitude of the
direct effect or through the mediation (intervening)
is significant or not, it is necessary to test with Sobel
test between each control variable with liquidity to
deposit growth with the following equation
(Ghozali, 2011):
2β3
β2
2
β33
2
3
(4)
Whereβ
2
is coefficient control liquidity on
interest,β
3
is coefficient each control variable on
liquidity, Sp2is Standard error β
2
, Sp3 is standard
error β
3
. The result of the Sobeltest of each control
variable to the growth of deposit as follows:
Table 4: Sobel Test for Hypothesis 1.
Variables Coefficient T-test
Overhead 14.489664 0.391089
Short Term
Debt
-1.349224*** -3.94707***
Inflation -0.435502 -1.09030
RGDP Growth -1.023942*** -2.93556***
***,** and * indicate statistical significant at 1,5 and 10
percent, respectively.
From the result of regression of fixed effect
model shows that short term debt is significant to the
growth of deposits with statistically significant 1
percent, while the liquidity and regional gross
domestic product (RGDP) have a statistically
significant effect of 5 percent and 10 percent,
respectively. While liquidity has an indirect effect
between short term debt and regional gross domestic
product (RGDP) on the growth of deposits. These
results indicate that increased investment in liquid
assets in banks with high risk does not make
depositors to increase the deposit of funds at the
Regional Development Bank. The increase in RGDP
in each province provides bank motivation to
increase liquid asset investment but does not attract
customers to increase their savings.
4.1.2 Hypothesis 2
The Indonesian Government implements the deposit
insurance policy implicitly before 2005, the adoption
of an explicit deposit insurance policy began in 2005
through the establishment of Deposit Insurance
Agency/LembagaPenjaminSimpanan(LPS) by
pledging savings not exceeding Rp 100 million in
the period 2005 to 2007. Period 2008 and so on, the
Government increased its deposit guarantee to Rp 2
billion. Therefore, to test the impact of deposit
insurance on the effect of liquidity on deposit
growth using the dummy variable. Where the
dummy variable is used to provide the difference
consisting of the period prior to 2004 which is the
period of the deposit insurance policy implicitly, the
2005-2007 period is an explicit period with deposit
insurance up to Rp 100 million and the period 2008-
2014 which is an explicit period with the deposit
insurance until with Rp 2 billion. The dummy
variables for each period of deposit insurance are
(1,0,0), (0,1,0) and (0,0,1). Regression model used to
test the variable of influence of deposit insurance in
moderating liquidity relation to growth of deposit is
as follows:
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
710
Y
it
= α + β
1
X
1it
+ β
2
X
2it
+ β
3
X
3it
+ β
4
X
4it
+ β
5
X
5it
+ β
6
Z
it
+β
7
( X
5it
* Z
it
) + e
it
(5)
Where Y
it
is deposit growth, X
1it
is overhead cost,
X
2it
is short term debt, X
3it
is inflation, X
4it
is
regional gross domestic product, X
5it
is liquidity and
Zit is Dummy Variable Period. The results of
multiple linear regression equations are as follows:
Table 5: Test for Hypothesis 2.
Variables
Implicit
Period
Explicit
Period
<100Million
Explicit
Period
<2Billion
Overhead 11.999 -4.7756 -12.159
Short Term
Debt
2.097** -5.157*** 4.038**
Inflation -4.765* -4.749 0.106
RGDP
Growth
-9.614*** -2.660 -2.570
Liquidity -3.406*** -6.861*** 4.398***
Dummy
Implicit
Periode
-5.019***
Dummy
Explicit
<200 Mil
-2.091**
Dummy
Explicit
<2Bil
6.660***
Liquidity x
Dummy
Implicit
4.276**
Liquidity x
Dummy
Explicit
<100Mil
7.478**
Liquidity x
Dummy
Explicit<2Bil
-
10.942***
No. Of Obs 247 247 247
No. Of
Banks
19 19 19
Adj. R
2
0.464 0.315 0.638
F value 31.468*** 5.526*** 18.417***
***,** and * indicate statistical significant at 1,5 and 10
percent, respectively.
From the above results indicate that the implicit
period, the customer retains at high risk Bank with
the overall guarantee by the Government for the
saving in the Bank but when the explicit deposit
guarantee is applied the customer starts to choose
the bank which has low risk as the storage of funds.
In the 2008 and subsequent periods, customers
withdrew their savings to Banks with high liquidity
risk.
4.1.3 Hypothesis 3
Depositors can discipline Banks that take excessive
risk action by requesting high interest rates,
therefore, to avoid high demand for interest rates,
the Bank will lower its liquidity by reducing its
investment in liquid assets. Because generally liquid
assets have a low rate of return. In general, the
Regional Development Bank pays higher interest
expense compared to the national commercial banks
in Indonesia. This is because the national
commercial banks provide more income from other
services than the Regional Development Bank. In
addition, the Regional Development Bank in its
industrial competition tends to offer higher interest
rates to attract customers to keep their funds in the
Bank. The use of liquidity as an intervening variable
in mediating the effects of overhead cost, short term
debt, inflation and regional gross domestic product
on interest rates is based on a strategy by banks to
invest in providing higher returns to cover higher
interest expenses. As with hypothesis 1, then in
testing hypothesis 3 using the liquidity variable as
exogenous and endogenous variable with the
following equation:
Y
it α β1X1it β2X2it β3X3it β4X4it
β5Zit eit
(6)
Where Y
it
isinterest rate, X
1it
is overhead cost,
X
2it
is short term debt, X
3it
is inflation, X
4it
is
regional gross domestic product and Z
5it
is liquidity.
The result of the panel data regression equation is as
follows:
Table 6: Test For Hypothesis 3.
Variables Coefficient
Overhead -0.079211
Short Term Debt -0.015333
Inflation 0.000178
RGDP Growth -0.025820*
Liquidity -0.003430
No. Of Obs 247
No. Of Banks 19
Adj. R
2
0.394068
F value 7.955922***
***,** and * indicate statistical significant at 1,5 and 10
percent, respectively.
Same as testing on hypothesis 1, then in testing
the indirect effect of overhead cost, short term debt,
inflation, regional gross domestic product against
interest rate through liquidity variable by doing the
Sobel test. The result of the test is as follows:
The Influence of Liquidity and Deposit Insurance on Market Discipline at Regional Development Bank in Indonesia
711
Table 7: Sobel Test For Hypothesis 3.
Variables Coefficient T-test
Overhead 0.016464*** 12.444***
Short Term
Debt
-0.001533*** -134.367***
Inflation -0.000494*** -140.985***
RGDP Growth -0.001163*** -152.291***
***,** and * indicate statistical significant at 1,5 and 10
percent, respectively.
From the regression results shown in Table 6,
only regional gross domestic product affects the
interest rate with statistically significant 10 percent.
The result of the Sobel test shows that short term
debt, inflation and regional gross domestic product
have indirect relationship to the interest rate through
liquidity. Regional Development Banks will raise
investment in liquid assets when there is an increase
in short term debt, inflation and regional gross
domestic product. This is done because an increase
in interest expense on short-term debt will make
additional funds by customers. Therefore, additional
short-term investments are needed to avoid liquidity
risk. An increase in inflation will have an impact on
increase of interest rate, therefore the Bank will
increase liquidity to reduce interest rates. The same
strategy is also carried out when regional gross
domestic product increases, which will lead to an
increase in deposits and the Bank will invest in
liquid assets to justify interest rates. Short term debt
that increases (decrease) will be followed by
andecrease (increase) in interest rates, therefore the
bank will undertake a strategy to increase (decrease)
investment in liquid assets to offset the decrease
(increase) in interest rates
4.1.4 Hypothesis 4
As with the tests on hypothesis 2, we will examine
the effect of three different periods of different
deposit insurance policies on the relationship
between liquidity and interest rates.Regression
model used to test the variable of influence of
deposit insurance in moderating liquidity relation to
interest rates is as follows:
Y
it
= α + β
1
X
1it
+ β
2
X
2it
+ β
3
X
3it
+ β
4
X
4it
+
β
5
X
5it
+β
6
Z
it
+ β
7
( X
5it
* Z
it
) + e
it
(7)
Where Y
it
isinterest, X
1it
is overhead cost, X
2it
is
short term debt, X
3it
is inflation, X
4it
is regional gross
domestic product, X
5it
is liquidity and Zit is Dummy
VariabelPeriod.The results of multiple linear
regression equations are as follows:
Table 8: Test For Hypothesis 4.
Variables
Implicit
Period
Explicit
Period
<100Millio
n
Explicit
Period
<2Billion
Overhead -0.026 -0.014 -0.056
Short
Term
Debt
-0.073*** -0.062*** -0.073***
Inflation 0.012 0.008 -0.019
RGDP
Growth
-0.001 -0.017 -0.021
Liquidity 0.008 0.023** -0.025***
Dummy
Implicit
Period
0.019***
Dummy
Explicit
<200 Mil
0.013**
Dummy
Explicit
<2Bil
-0.025***
Liquidity
x Dummy
Implicit
-0.009207
Liquidity
x Dummy
Explicit
<100Mil
-0.044***
Liquidity
x Dummy
Explicit<
2Bil
0.042***
No. Of
Obs
247 247 247
No. Of
Banks
19 19 19
Adj. R
2
0.366 0.244 0.352
F value 21.336*** 12.355*** 20.094***
***,** and * indicate statistical significant at 1,5 and 10
percent, respectively.
The regression results show that when the
deposit insurance policy is explicitly applied it gives
significant effect on the interest rate through
liquidity. This explains that the existence of an
explicit deposit insurance policy makes the customer
to act reduction deposit at banks at risk. Therefore,
the risky bank will raise the interest rate to withdraw
the customer's deposit and the bank will act to
improve the liquidity. The deposit insurance policy
in full or implicitly does not impact the market
discipline behaviour because the customer does not
request higher interest rate payment to the Bank
having the risk high. On the other hand, the
customer is only interested in the bank offering high
interest rate, thereby lowering the investment in
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
712

liquid assets to transfer funds to portfolios that
provide higher returns in order to pay for the
increase in interest to increase the deposits of funds
customers. The explanation can be illustrated by the
regression result indicating that liquidity has
negative and statistically significant effect on the
interest rate in the explicit period.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In the face of banking competition in Indonesia,
Regional Development Banks with limited ability to
provide other services, generally use high interest
rates to attract customer deposits. This condition is
particularly vulnerable for the Regional
Development Bank to disburse loan funds to
customers because the loans granted will require
high interest to cover the interest expense to deposit
customers. This will cause some loans to be
channelled to customers who are at risk of failing to
repay the loan. This problem can be seen from this
research where the indirect effect of short-term debt
and regional gross domestic product on the growth
of deposits and interest rates through liquidity has a
negative and significant effect.
This result is also supported by the result of the
research which shows the liquidity has a negative
and statistically significant effect on the growth of
savings in the period of deposit insurance with the
guarantee of up toRp 2 billion. Likewise, the
liquidity of the interest rate which gives a positive
and statistically significant relationship to the
interest rate in the deposit insurance period explicitly
with the guarantee of maximum fund of Rp 2
Billion.
ACKNOWLEGEMENTS
The findings, interpretations, and conclusions
expressed in this paper are entirely from the authors.
We are grateful to the University of North Sumatra
for his assistance in this research and the Islamic
University ofSumatera Utara for his opportunity in
publishing this paper.
REFERENCES
Berger, A. N., & Turk-Ariss, R., 2012. Do Depositors
Discipline Banks and Did Government Actions During
the Recent Crisis Reduce this Discipline? An
International Perspective. Journal of Financial Service
Research, 48(2), 103-126.
Cubillas, E., Fonseca, A. R., & Gonzalez, F., 2012.
Banking Crises and Market Discipline: International
Evidence. Journal of Banking & Finance, 36(8), 2285-
2298.
Dermiguc-Kunt, A., and Huizinga, H., 1998. Market
Discipline and Financial Safety Net Design. Policy
Research Working Paper, 2183. World
Bank.Retrieved from:
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=6
29175.
Dermiguc-Kunt, A., and Huizinga, H., 2004. Market
Discipline And Deposit Insurance.Journal of
Monetary Economics, 51(2). 375-399.
Distinguin, T., Kouassi, I., &Tarazi, A., 2011.Bank
Deposit Insurance, Moral Hazard and Market
Discipline: Evidence from Central and Eastern
Europe.SSRN Electronic Journal.Retrieved from
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=1
83026.
Distinguin, I., Kouassi, T., &Tarazi, A., 2013. Interbank
Deposits and Market Discipline: Evidence from
Central and Eastern Europe. Journal of Comparative
Economics, 41(2), 544–560.
Flannery, M. J., 2001. The Faces Of Market Discipline.
Journal of Financial Services Research, 20(2/3),107-
119.
Ghozali, I., 2011. AplikasiAnalisis Multivariate Dengan
Program IBM SPSS 19. Semarang:
BadanPenerbitUniversitasDiponegoro.
Hermanto. S. Analisis Bi Rate, Inflasi, Overhead Cost, Net
Interest Margin, Dan Resiko Kredit Terhadap Suku
Bunga Kredit Modal Kerja Pada Bank Umum Milik
Negara Periode 2005 – 2013. Retrieved from
http://jurnalmahasiswa.unesa.ac.id/index.php/jim/articl
e/viewFile/17462/15891.
Karas, A., Pyle, W.,&Schoors, K., 2010. The Effect Of
Deposit Insurance On Market Discipline: Evidence
From A Natural Experiment On Deposit Flows.
BOFIT Discussion Paper, 8. Retrieved from:
https://helda.helsinki.fi/bof/bitstream/handle/1234567
89/8008/166887.pdf?sequence=1.
Martinez Peria, M. S., and Schmukler, S., 2001. Do
Depositors Punish Bank For Bad Behavior?
MarketDiscipline, Deposit Insurance And Banking
Crises. The Journal of Finance, 56(3), 1029-1051.
Miskhin, Frederic S., 2011. Ekonomi Uang, Perbankan,
dan Pasar Keuangan.Edisi 8. Buku 1. Salemba Empat.
Jakarta
Murata, K., and Hori, M., 2006. Do Small Depositors Exit
from Bad Banks? Evidence from Small Financial
Institutions In Japan. The Japanese Economic Review,
57(2). 260-278
Nopiyanti, Duwi. 2010. Utang Jangka Pendek.Retrieved
from http://dnopiyanti.blogspot.com/2010/06/utang-
jangka-pendek.html
The Influence of Liquidity and Deposit Insurance on Market Discipline at Regional Development Bank in Indonesia
713

Prean, N., and Stix, H., 2011. The Effect of Raising
Deposit Insurance Coverage in Times of Financial
Crisis: Evidence from Croatia Microdata. Economic
Systems, 35(4), 496-511.
Riandika, A. F., and Taswan., 2014. Pengujian Disiplin
Pasar Perbankan Berdasarkan Posisi CAR, LDR,
ROA, Dan NPL.Prosiding Seminar Nasional Multi
DisiplinIlmu& Call for Papers Unisbank
Taswan., 2013. Pengujian Empiris Disiplin Pasar Periode
Penjaminan Simpanan Implisit Dan Eksplisit Di
Indonesia. Jurnal KeuangandanPerbankan,
17(2),278–287
Yaling, W., & Yingzhi, L., 2012. Market Discipline and
City Commercial Banks’ Risk Taking. Management
Science and Engineering. 6(3), 26-29. Retrieved from
http://www.cscanada.net/index.php/mse/article/view/j.
mse.1913035X2012603.Z0124/2995.
Yan, X., Skully, M., Avram, K., & Vu, T., 2011. Market
Discipline and Deposit Guarantee: Evidence from
Australian Banks. International Review of Finance,
14(3), 431-457.
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
714
