
The Effect of Loan to Deposit Ratio (LDR), Capital Adequacy Ratio
(CAR) and Return on Asset (ROA) against Stock Price
at Sharia Commercial Bank in Indonesia
Sri Rahayu, Heny Triastuti Kurnia Ningsih, Irma Zukhairani
Accounting Department, Faculty of Economics, UISU, Medan,
Keywords: LDR, CAR, ROA, Stock Price.
Abstract: The formulation of the problem in this research is how much influence of Loan to Deposit Ratio (LDR),
Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) and Return on Asset (ROA) to Stocks Price at Sharia Commercial Bank in
Indonesia. The method used in this research is descriptive causal method, that is research method done by
explaining cause-effect relationship by observing. Based on the results of the research, the simultaneous Loan
to Deposit Ratio (LDR), Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR), and Return on Asset (ROA) have significant effect
to Stock price at Indonesian Sharia Commercial Bank. Partially Loan to Deposit Ratio (LDR) has significant
effect to Stock price at Indonesian Sharia Commercial Bank, Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) has a significant
negative effect to Stock price at Indonesian Sharia Commercial Bank and Return on Asset (ROA) has no
significant effect on Stock price at the Indonesian Sharia Commercial Bank.
1 INTRODUCTION
Stock prices are an indicator of the success of a
company's management. If the stock price of a
company always increases, investors or prospective
investors judge that the company is successful in
managing its business. Trust of investors and
prospective investors is very beneficial for the
issuers, because the more people believe in the
issuers, the desire to invest in issuers will be stronger.
The price of a stock in the capital market is
influenced by several factors, both internal and
external factors. Internal factors are those seen from
within the company that are specific to such stocks
such as sales, financial performance, management
performance, company conditions, and the industry in
which the company is engaged. While external
factors are those that are macro in influencing stock
prices in the stock such as inflation, interest rates,
foreign exchange rates, and non-economic factors
such as social conditions, politics, and other factors
(Martalena and Malinda, 2011).
Sharia banking as a Sharia financial institution,
initially grew slowly, but then began to show the
rapid development of achieving growth far above the
development of conventional banking. In Indonesia
Sharia banking has emerged since the issuance of
Law no. 7 of 1992 on Banking, which implicitly has
opened the opportunity of banking business activities
that have operational basis for the results, marked by
the establishment of Bank Muamalat Indonesia
(BMI).
Profit sharing is a common characteristic and
basic foundation for sharia bank operations as a
whole. Shari'a is the principle based on Al-
Mudharabah's rule. Based on this principle, Islamic
banks will serve as partners, both with savers and
with entrepreneurs who borrow funds. With savers,
banks will act as mudharib (fund manager), while
savers act as shahibulmaal (owner of funds). Between
the two held a mudharabah agreement stating the
distribution of benefits of each party. Similar to
conventional banking, sharia banking also relies on
depositors who keep their money in the bank.
Together with the increasing public knowledge of
sharia banking, the profit-sharing rate becomes one of
the incentives for depositors to keep their money in a
sharia bank.
The level of health of the banking itself can be
assessed from several indicators, one of the main
indicators used as a basis in the assessment is the
financial statements of the bank concerned. Based on
these financial statements, a number of financial
ratios that are commonly used as the basis for
Rahayu, S., Kurnia Ningsih, H. and Zukhairani, I.
The Effect of Loan to Deposit Ratio (LDR), Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) and Return on Asset (ROA) against Stock Price at Sharia Commercial Bank in Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0008892406810685
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research (ICMR 2018) - , pages 681-685
ISBN: 978-989-758-437-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
681

assessment of bank soundness will be calculated. A
result of financial statement analysis will help to
interpret the various relationships and trends that can
provide a basis for consideration about the potential
success of a company in the future.
The performance shown by a banking system by
looking at the financial indicators is critical to the
performance of a bank. Health and financial stability
of banks can be seen from several financial indicators
such as Loan to Deposit Ratio (LDR) which is an
indicator of vulnerability and ability of a bank,
Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) is the ratio of bank
performance to measure the capital adequacy of
banks to support assets containing or generate a risk
(Fahmi, 2015), and Return On Assets (ROA) is the
company's financial ratios associated with the profit
potential of measuring the strength of the company
resulting in profits or earnings at the level of income,
assets and also specific stock capital.
1.1 Theoretical Basis
The bank comes from the word bangue (French) and
from the word banco (Italian) which means a chest/
cupboard or bench. The crates and benches explain
the basic functions of commercial banks, namely:
first, providing a place for safe keeping functions;
second, providing a means of payment to purchase
goods and services (Antonio, 2009).
Sharia bank is a financial institution needed by the
community in conducting financial transactions and
other banking transactions. The transactions offered
by the bank differ from bank to bank. Some Islamic
banks offer all banking products, some sharia banks
offer only certain products and so on. Products and
services of sharia banks that can be given to the
community depend on the type (Ismail, 2011).
It is in contrast to a bank conducting its activities
in a conventional manner, and providing services in
general payment traffic based on procedures and
provisions that have been applied under positive law.
Islamic banking acts as a financial intermediary
institution between economic units that have excess
funds with other units that are under-funded.
Therefore, to implement the intermediation function,
sharia pigment institutions will conduct business
activities in the form of collecting funds, channeling
funds, and providing various financial transaction
services to the community (Burhanuddin, 2010).
1.2 Stock Price
Stock is a piece of paper showing the right of the
investor who owns the paper to obtain a share of the
prospect or wealth of the organization issuing the
securities, and the conditions under which the
investor may exercise his right (Husnan, 2008).
Stock is one of the most favored capital market
instruments by investors because it is able to provide
an attractive rate of return. Stocks are clearly stated
papers of nominal value, name of company, and
followed by rights and obligations which have been
explained to each holder (Fahmi, 2012).
Stock (share) is a sign of participation or
possession of a person or entity within a company or
limited liability company. The stock is a piece of
paper explaining that the paper owner is the owner of
the company issuing the securities (Darmadji and
Fakhruddin, 2012).
1.3 Loan to Deposit Ratio (LDR)
Definition of Loan to Deposit Ratio according to
Bank Indonesia Regulation Number 15/7 / PBI / 2013
concerning Statutory Reserves of Commercial Banks
at Bank Indonesia in Rupiah and Foreign Currency is
the ratio of credits extended to third parties in Rupiah
and foreign currency, excluding credit to Bank third
party funds covering demand deposits, savings
deposits and time deposits in Rupiah and foreign
currency, excluding interbank funds. Loan to Deposit
Ratio means to demonstrate the ability of banks in
providing funds to debtors with capital owned by
banks and funds collected from the community
1.4 Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR)
Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) is a ratio showing
how far all bank assets that contain credit risk,
inclusion, securities, and claims to other banks are
financed from the bank's own capital funds. Besides,
it obtains funds from sources outside the bank, such
as funds from the community, loans, and others.
Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) is an indicator of the
bank's ability to cover its decline in assets as a resultof
bank losses caused by risky assets (Darmawi, 2011).
According to Cashmir (Cashmir, 2014), Capital
Adequacy Ratio (CAR) is the ratio between the ratios
of capital to Risk Weighted Assets according to
government regulations. In principle, the level of
Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) is adjusted to the
provisions of the Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) that
apply internationally that is in accordance with the
standards issued by the Bank for Settlement Ratio
(BIS). The increase of Capital Adequacy Ratio
(CAR) aims to improve performance and to ensure
prudential banking principles have always been
ensured.
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
682
1.5 Return on Assets (ROA)
According to Horne and Wachowicz (2012), Return
on Assets (ROA) is a measure of overall effectiveness
in generating profits through available assets; power
to generate profits from invested capital. Horne and
Wachowicz calculate Return on Assets (ROA) using
the net income formula after tax divided by total
assets.
Bambang Riyanto (Bambang Riyanto, 2012)
mentions the term Return on Assets (ROA) with Net
Earning Power Ratio (Rate of Return on Investment /
ROI) is the ability of the capital invested in the overall
assets to generate net profit. The net profit he means
is the net profit after tax
2 METHODOLOGY
2.1 Population and Sample of the
Study
According to Kuncoro (Kuncoro, 2009), population
is a complete group of elements, usually in the form
of people, objects, transactions or events in which we
are interested to learn or become the object of
research. Based on the explanation that has been
presented, the population in this study is tabulation of
financialdata of Sharia Commercial Banks in
Indonesia listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange
period 2014-2016, and data is taken online from the
site www.idx.co.id which amounted to 10 Indonesian
ShariaCommercialBank.
In this research, sampling using purposive
sampling. Purposive sampling is one of the non-
random sampling techniques where the researcher
determines the sampling by determining the specific
characteristics which is suitable with the research
objectives so that it is expected to answer the research
problem. According to Sugiyono (2012) purposive
sampling is a technique to determine the sample of
research with some considerations which aim to
ensure that the data obtained later can be more
representative.
2.2 Data Analysis Technique
Multiple linear regression analysis in this study aims
to determine the magnitude of the influence of
independent variables of LDR, CAR, and ROA to the
dependent variable that is Stock price. In this study,
the authors use multiple linear regression statistical
analysis. The equations used are:
Y = a + b
1
X
1
+ b
2
X
2
+ b
3
X
3
+ e (1)
Information:
Y = Stock Price
a = Constants
b1b2 = Multiple regression coefficients
X1 = LDR dimension score
X2 = CAR dimension scores
X3 = ROA dimension score
e = Standard error
3 RESULT
3.1 Multiple Linear Regression Test
Results of multiple linear regression analysis test in
this study can be seen in table 1 as follows:
Table 1: Results of Multiple Linear Regression Test.
Coefficients
a
Model
Unstandardized
Coefficients
Standardized
Coefficients
T Sig.B
Std.
Erro
r
Beta
1
(
Constant
)
6357,748 1437,815 4,422 ,000
LDR
3910,661 1159,450 ,571 3,373 ,002
CAR
-398,370 110,007 -,713
-
3,621
,001
ROA 694,934 412,429 ,306 1,685 ,104
a. De
p
endentVariable: Stock Price
Source: Data Processed with SPSS
Based on the results of multiple linear regression
test in table 1 above can be described as follows:
Y = 6357,74 + 3910,66X
1
- 398,37X
2
+ 694,93X
3
+ e
(2)
3.2 Hypothesis Testing
3.2.1 Partial Significance Test (t-Test)
The result of partial significance test (t-test) in this
research can be seen in table 2 as follows:
The Effect of Loan to Deposit Ratio (LDR), Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) and Return on Asset (ROA) against Stock Price at Sharia
Commercial Bank in Indonesia
683
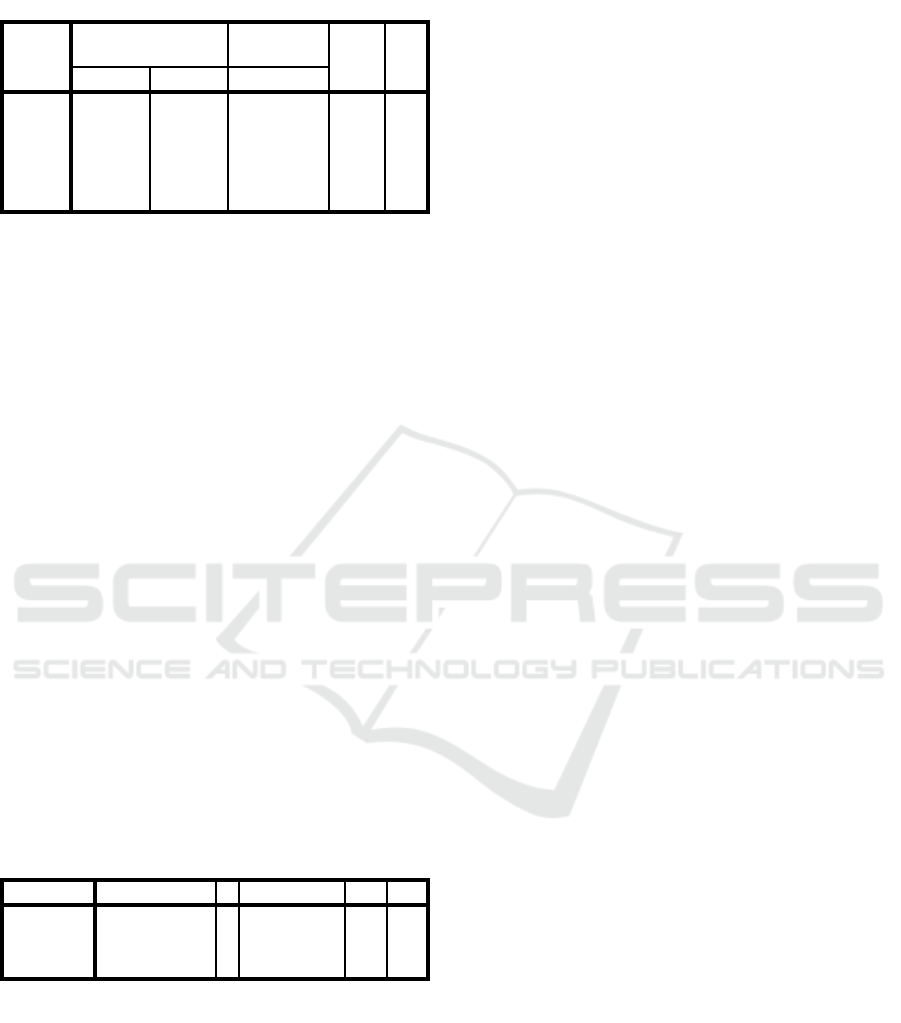
Table 2: Results of Partial Significance Test (t-Test).
Coefficients
a
Model
UnstandardizedCoef
ficients
Standardized
Coefficients
T Si
g
.B Std. Erro
r
Beta
1(Consta
nt)
6357,748 1437,815 4,422 ,000
LDR 3910,661 1159,450 ,571 3,373 ,002
CAR -398,370 110,007 -,713 -3,621 ,001
ROA 694,934 412,429 ,306 1,685 ,104
a. DependentVariable: Stock Price
Source: Data Processed with SPSS
Based on the results of partial significance test (t-
test) in table 2 above, it can be described that Loanto
Deposit Ratio (LDR) has a t-count of 3.373> t-
table1,703 and significance level of 0.00 <0.05.
Further, it can be concluded that Loanto Deposit
Ratio (LDR) has a significant positive effect on Stock
price at Indonesian Sharia Commercial Bank. Capital
Adequacy Ratio (CAR) has t-count value of -3,621>
t-table-1.703 with significance level of 0.00 <0.05,
and it can be concluded that Capital Adequacy Ratio
CAR) have a significant negative effect on Stock
price at Indonesian Sharia Commercial Bank. Return
on Asset (ROA) has a t-count of 1,685 <t-table 1,703
and a significance level of 0.10> 0.05. Further, it can
be concluded that ReturnonAsset (ROA) has no
significant effect on Stock price at Indonesian Sharia
Commercial Bank.
3.2.2 Simultaneous Significance Test
(F-Test)
The result of simultaneous significance test (Test-F)
in this research can be seen in table 3 below:
Table 3: Results of Simultaneous Significance Test (F-
Test).
ANOVA
a
Model Sum ofS
q
uares df MeanS
q
uare F Si
g
.
1Re
g
ression 95216683,235 3 31738894,412 5,940 ,003
b
Residual 138918166,232 26 5343006,394
Total 234134849,467 29
a. DependentVariable: Stoc
k
Price
b
. Predictors:
(
Constant
)
, ROA, LDR, CAR
Source: Data Processed with SPSS
Based on the results of the simultaneous
significance test (Test-F) in table 3 above, it can be
seen that the Loan Deposit Ratio (LDR), Capital
Adequacy Ratio (CAR), and Return On Assets
(ROA) of 5.940> F-table 2.96 with significance level
0,00 <0,05, it can be concluded that simultaneously
Loan to Deposit Ratio (LDR), Capital Adequacy
Ratio (CAR), and Return On Asset (ROA) have
significant effect to Stocks Price at Indonesian Sharia
Commercial Bank.
4 ANALYSIS
4.1 The Effect of Loanto Deposit Ratio
(LDR) on Stock Price at Indonesian
Sharia Commercial Bank
Based on the results of this study, it is concluded that
the high or low value of Loanto Deposit Ratio (LDR)
greatly affects the value of Stocks Price at Indonesian
Sharia Commercial Bank. When the Loanto Deposit
Ratio (LDR) rises, the value of the stock price will
also rise, and if the Loanto Deposit Ratio (LDR)
decreases, then the value of the Stock price will also
come down. Loanto Deposit Ratio (LDR) in this
study has a significant partial influence, because
Loanto Deposit Ratio (LDR) gives a fairly high
assumption of value to the Stock price.
The results of this study are also in line with the
results of research conducted by Dian Fordian (Dian
Fordian, 2017), the results of his research states that
the Loan to Deposit Ratio (LDR) effect on Stock
price.
4.2 The Influence of Capital Adequacy
Ratio (CAR) on Stock Price at
Indonesian Sharia Commercial
Bank
Based on the results of this study, it is concluded that
the high value of Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) will
affect the value of Stocks Price at Indonesian Sharia
Commercial Bank. When the value of the Capital
Adequacy Ratio (LDR) rises, the value of the stock
price will decrease due to significant negative effect,
and if the value of Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR)
decreases, the value of stock price will rise with
positive value.
Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) in this research
has a partial effect because Capital Adequacy Ratio
(CAR) gives the assumption of high negative value to
stock price.
The results of this study are also in line with the
those of research conducted by Diah Purnamasari et
al (Diah Purnamasari et al, 2017), in which the result
of their research states that Capital Adequacy Ratio
(CAR) has a negative effect on stock prices.
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
684

4.3 The Influence of Return on Assets
(ROA) on Stock Price at
Indonesian Sharia Commercial
Bank
Based on the results of this study, it is concluded that
the high or low value of Return on Assets (ROA) does
not affect the value of stocks of Sharia Banks in
Indonesia. When the value of Return on Assets
(ROA) falls, the stock price will not go down, and if
the value of Return on Assets (ROA) rises, the value
of the share price will also not go up.
Return on Asset (ROA) has no partial effect
because Return on Asset (ROA) only gives low value
assumption to increase of Stock Price compared with
Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR). The result of this
research is also in line with that of research conducted
by Y. Sunyoto and Sam'ani (Y. Sunyoto and Sam'ani,
2014) in which the result of their research states that
Return on Assets (ROA) has no effect on Stock Price.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of this study, the conclusions can
be described as the following:
1. Partially Loan to Deposit Ratio (LDR) has a
significant effect on Stock Price at Indonesian
Sharia Commercial Bank. When the Loan to
Deposit Ratio (LDR) drops, the value of the
stock price will come down too, and if the Loan
to Deposit Ratio (LDR) rises, then the value of
the Stock Price will also rise.
2. Partially Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) has a
significant negative effect on Stock Price at
Indonesian Sharia Commercial Bank. When the
value of the Capital Adequacy Ratio (LDR)
falls, the value of the stock price will rise, and if
the Capital Adequacy Ratio CAR value rises,
then the value of the Stock Price will decrease.
This is due to Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR)
has a significant negative effect on Stock Price.
3. Partially Return on Asset (ROA) has no effect
on Stock Price at Sharia Indonesia Commercial
Bank. When the value of Return on Assets
(ROA) falls, the value of stock price will not
come down, and if the value of Return on Assets
(ROA) increases, the value of stock price will
also not go up.
REFERENCES
Antonio, M. Syafi'i, 2009. Fundamentals of Sharia Bank
Management,Alfabeta Library. Jakarta.
Burhanuddin, 2010. Aspects of Sharia Financial
Institutions,GrahaIlmu. Yogyakarta.
Cashmir, 2014. Financial Statement Analysis, PT Raja
GrafindoPersada. Jakarta, Seventh Print.
Darmadji andFakhruddin, 2012. Capital Market in
Indonesia A Question and Answer
Approach,SalembaEmpat. Jakarta.
Fahmi, Irham, 2012. Financial Performance
Analysis,Alfabeta.Bandung.
Fahmi, Irham, 2015. Introduction to Financial
Management Theory and Problems
Answer,Alfabeta.Bandung, Fourth Edition.
Fordian, Dian, 2017. Effect of CAR, LDR, and EPS on
Stock Price (Study on Bank Bumn Listed on
BEI).Business Journal of Darmajaya. 3 (1).
Horne, James C. Van and J. M.,Wachowicz, Jr., 2012.
Principles. Financial Management (Issue
13),SalembaEmpat. Jakarta.
Husnan, Suad, 2008. Financial Management: Book Theory
and Implementation 1, BPFE. Yogyakarta, 4thEdition.
Ismail, 2011. Banking Syariah, Kencana. Jakarta.
Kuncoro, Mudrajad.2009. Metode Riset Untuk Bisnis &
Ekonomi. Penerbit. Erlangga. Jakarta.
Martalena and Malinda, 2011. Introduction to Moda
Market, ANDI Publisher. Yogyakarta, First Edition.
Permatasari, Diah, E.,Nuraini, E., Astuti, 2017. Influence of
Capital Adequacy Ratio, Loan To Deposit Ratio And
Return On Asset To The Price Of Banking Company
Shares.The 9TH FIPA: Forum Scientific Accounting
Education University PGRI Madiun. 5 (1): 264-277.
Sugiyono, 2013. Quantitative Research Methods,
Qualitative and R & D,Alfabeta. Bandung.
Sunyoto, Y. and Sam'ani, 2014. Influence of Capital
Adequacy Ratio, Net Interest Margin and Return on
Asset to Stock Price on Banking, Journal of Economic
Accounting Management. Number 36/YearXXI/April
The Effect of Loan to Deposit Ratio (LDR), Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) and Return on Asset (ROA) against Stock Price at Sharia
Commercial Bank in Indonesia
685
