
Factors Forming Seven Layers of the Open System (OSI) Model
Alistraja Dison Silalahi
1
, Masut
2
and Iskandar Muda
3
1
Universitas Muslim Nusantara Al Washliyah
2
Universitas Islam Sumatera Utara
3
Universitas Sumatera Utara
Keywords: OSI, Seven Layers
Abstract: This study aims to examine the understanding of the importance of implementing standards in
communicating in the network and understanding the factors that form the seven layers of Open System
Interconnection. This research was carried out by conducting a survey of communication users in the
network who collected information about the importance of communication standards in the network and
responses about OSI and OSI networks (seven layers of the OSI model). The results showed that the
importance of the communication standards applied in the network found that respondents who strongly
agreed are 40.4%, agreed 55.3% and hesitated 4.3%. The respondents' knowledge for OSI was 82% of
respondents understood and knew while 18% did not understand. Related to the OSI network architecture
that was formed from seven physical layers, namely: data link, network, transportation, session,
presentation, and application, respondents who strongly agreed are 29.2%, agreed 62.5%, and the rest did
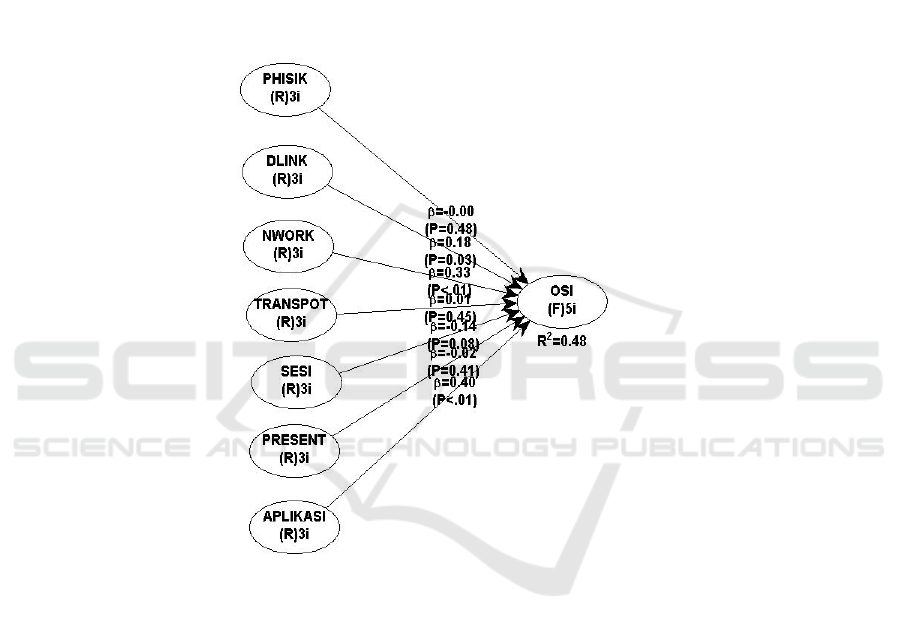
not agree and doubted. The R-Square value in this research model is 0.48 which indicates that this model is
classified as moderate. This shows that the factors forming the OSI network can only be explained by 48%
and the rest are other factors.
1 INTRODUCTION
Communication is very important as an effort to
transfer messages or information from one place to
another, both verbal, written and non-verbal.
Communication acts as information, control,
motivation, and disclosure of actions. The
development of increasingly sophisticated
information technology and telecommunications
requires us to be able to communicate in the form of
virtual or in a network, where the sending and
receiving of information can be done using
hardware, software, and devices connected to the
internet. System software is a very specialized,
integrated and efficient set of computer software
written in machine language designed to
communicate with hardware. System software
performs special functions that support computer
operation. This software provides operating routines
that make the computer work at the computer
application level. The system software performs
three main functions: label checking, protection of
stored data, and memory protection.
Communication in the network is
communication that the way of sending and
receiving messages is done by the internet network.
The internet is very useful as an effective and
efficient communication medium with various
facilities available such as web, chat, email,
Friendster, Facebook, Instagram, line and twitter.
Communication in the network has several types of
communication in the realm of synchronous
networks (real time), and asynchronous
communication (delay) in networks that refers to
reading, writing, and communicating via/ using
computer networks.
This model is based on the proposals from the
International Standard Organization (ISO) as a step
towards standardizing international regulations used
in various layers. This model is called the OSI
Reference Model, because it is shown for Open
System interconnection. Open System is defined as
an open system to communicate with other systems
from different operating systems and architectures.
For easier communication between two devices, it is
necessary to re-examine the standards applied in
computer networks, discuss what OSI is, what layer
446
Silalahi, A., Masut, . and Muda, I.
Factors Forming Seven Layers of the Open System (OSI) Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0008888804460451
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research (ICMR 2018) - , pages 446-451
ISBN: 978-989-758-437-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

forms the OSI network and what functions of the
network layer, and test which layers are considered
to be the most dominant OSI network builders. The
next section, namely the second part explains the
literature review, the third part explains the research
method, the fourth part provides the results of the
analysis and discussion and the fifth part provides
the research conclusions.
1.1 Literature Review
The system is a collection/group of sub-systems/
parts/components, both physical and non-physical
that are interconnected with each other and work
together harmoniously to achieve certain goals
(Susanto, 2004). This can also be considered as a
combination of several elements that are
interconnected, and working together well to achieve
a common goal. Another definition states that when
a word system is used in relation to business
operations, it refers to a group of elements that are
integrated through a common goal to achieve several
objectives (McLeod, 1998, p. 11). In modern
management, a system has been integrated
automatically between the elements involved in the
system. With system integration, communication
channels and data, and information transformation
will be smoother and more accurate. Open system is
a portable application in various hardware
configurations. Open systems have gone a long way
in the last decade. Before 2000, most suppliers
offered exclusive solutions designed to lock
customers with specific solutions (for example,
IBM's main frame). Since then, the open system has
become more than an exception in implementing
web-based solutions and Unix-based operating
systems. However, open systems have not led to the
unlimited interoperability intended by the Open
Creators Standard.
OSI (Open System Interconnection) was
developed in 1978 by ISO with the aim of
facilitating open interconnection on computer
systems. ISO as a multinational body focusing on
international agreements on international standards
developed the OSI because interconnection can
support many vendors in various environments. The
OSI layer model is also used as a framework used to
understand how information runs on networks.
(SandraSenft and Frederick Gallegos, 2009), defines
the text of the communication model of the OSI
model using a seven-level approach to defining
rules. OSI is a communication standard applied in
computer networks that causes all communication
devices to communicate with each other through the
network. In the past when the OSI was not used,
communication devices from different vendors could
not communicate with each other. Communication
tools made by IBM cannot communicate with other
vendors. Thus, the OSI standard is set (SandraSenft
and Frederick Gallegos, 2009). Open System
Interconnection declares network models that can be
interconnected, regardless of the hardware used,
provided the communication software complies with
the standard. This indirectly raises "modularity".
Modularity refers to the exchange of protocols at a
certain level without affecting or damaging
relationships or other level functions. In a layer,
protocols can be exchanged and allow
communication to continue. This exchange occurs
based on hardware from different vendors and
different reasons. Basically, many types of protocols
are developed by many manufacturers of
communication equipment and computers.
OSI has seven layers, each of which stands
alone, but the function of each layer depends on the
success of the previous layer's operation. (Bodner,
1998), (Nurwono, 1994). The seven layers are as
follows: The first layer "physical" determines how
the media form the chosen communication
equipment and how to connect it. The physical layer
is related to cables, emphasizing the level of
electrical connections, and transmitting signals and
data in binary form. This layer also provides
provisions about how to channel data bits through
communication channels, for example "1" bits are
distributed and received as "1" bits too. The second
layer "data l ink" (data chain) determines how to
connect one computer to another computer, stream
data flow, detect and correct transmission errors.
This layer forwards data through the channel to an
error-free network, because the sender sends data in
accordance with the specified procedure, namely by
using the protocol. The protocol makes provisions
(standards) about synchronizing data transmission
between terminals, confirm checks from recipients
and makes error control. The third layer "network"
defines and maintains electronic links between
computers in terms of delivering data from source to
destination. The network layer organizes the routing
of the routes of data transmission (Routing), aand
arrange the activity within the network itself as well
as the activity between the network. Network control
performs network efficiency when there is a long
queue (Congestion Control). The nature of this layer
governs how or what type of network you choose to
communicate. The fourth layer of "transportation"
regulates the transfer of data from one computer to
another. In this layer the quality of data transmission
Factors Forming Seven Layers of the Open System (OSI) Model
447

is ensured, so that no data is repeated, misplaced or
lost. The transportation function is carried out by the
shipping facilities provided. For example, in
communicating between two or more computers
using a modem, the transport function will be carried
out by modem equipment or "modem card". The
fifth layer is the session layer (discussant). This
layer explains how the two-end user dialog, how two
applications are different for exchanging f or
instance data from a spreadsheet to a word
processor. This layer also controls if one computer is
faster than the other, arranges when data must be
sent, when to wait, and when to enter a buffer. The
sixth layer is presentation. This layer governs how
data is formatted (the standard form of data
presentation) to be displayed on the monitor screen.
In this layer, the process of translating data received
from application functions is changed to a more
general form of data. Translations are easier to
understand and use by the application in question,
for example on data received through the dbase
application program modified from ASCI. The
seventh layer is the application. This layer functions
to serve users to establish reciprocal relationships in
the OSI environment. The function of this
application will regulate how the interaction with the
user and what will be sent, so that users of computer
systems directly benefit from data communication
networks between users. In this layer there are also
all data sources that will be sent for example in a
purchase transaction, data on items to be purchased
to the purchase order section, and so on as required
in the procedure of purchasing goods. Another
function of this layer is to control the way in and out
of files on a computer server; this functions as file
transfer.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
This research uses survey research on network
communication users, collects information about the
importance of communication standards in the
network and responds to the OSI and OSI network
builders from users of communication in the
network. The standards applied in computer
networks discuss what OSI is, which layer forms
OSI networks, what functions of the network layer,
and tests which layer is the most dominant OSI
network builder by formulating questionnaire
formats submitted to respondents in the form of a
Likert scale. The sample in this study is a classroom
consisting of students, teachers, lecturers, and
employees who use communication in the network
in UMN Al Washliyah Medan. This study uses
quantitative analysis techniques consisting of
descriptive statistics and PLS using the WarpPLS
5.0 program.
2.1 Research Results and Discussion
The result of the respondent's characteristics based
on sex consisted of 32 men and 15 women with
respondent age 58,3% age 18 - 29 years old, 29,2%
age 30 - 39, and 12,5% age 40 - 50 years. The
respondent's work consisted of 39,6% students, 25%
lecturers, 31,3% employees/ employees and seen
from usage of communication in network, 44,7%
stated frequently, 21,3% very often, and 29,8%
often. This research used WarpPLS 5.0 program to
test first order formative contrast with CPA obtained
model as follows:
Table 1: Latent variable coefficients (z-score).
Phisik DLink NWork Transpo Sesi Present Aplikasi Osi Type SE P value
PH1 0.882 -0.143 -0.021 0.161 -0.397 0.311 0.267 -0.152 Reflect 0.096 <0.001
PH2 0.870 -0.248 -0.002 -0.084 0.409 -0.187 -0.230 0.139 Reflect 0.096 <0.001
PH3 0.381 0.897 0.053 -0.181 -0.015 -0.294 -0.091 0.035 Reflect 0.096 <0.001
DL1 0.431 0.683 0.088 0.023 -0.580 0.160 0.287 0.050 Reflect 0.096 <0.001
DL2 -0.226 0.890 -0.135 -0.034 0.155 -0.424 0.063 -0.061 Reflect 0.096 <0.001
DL3 -0.172 0.542 0.111 0.027 0.476 0.494 -0.465 0.037 Reflect 0.096 <0.001
NW1 -0.045 -0.184 0.881 -0.476 0.205 -0.148 -0.060 -0.092 Reflect 0.096 <0.001
NW2 -0.093 0.046 0.583 0.847 -0.162 -0.048 0.509 -0.179 Reflect 0.096 <0.001
NW3 0.121 0.175 0.774 -0.095 -0.112 0.205 -0.314 0.240 Reflect 0.096 <0.001
TP1 -0.083 -0.120 -0.207 0.850 -0.125 0.008 0.326 -0.161 Reflect 0.096 <0.001
TP2 0.052 0.325 -0.078 0.753 -0.415 0.419 -0.137 -0.136 Reflect 0.096 <0.001
TP3 0.046 -0.210 0.346 0.678 0.619 -0.476 -0.257 0.353 Reflect 0.096 <0.001
SS1 -0.010 -0.146 0.558 -0.296 0.903 -0.268 -0.135 0.015 Reflect 0.096 <0.001
SS2 0.260 -0.030 -0.698 0.623 0.799 -0.026 0.235 -0.232 Reflect 0.096 <0.001
SS3 -0.288 0.226 0.078 -0.335 0.691 0.381 -0.096 0.249 Reflect 0.096 <0.001
PR1 0.362 -0.308 0.503 0.090 -0.256 0.080 0.151 0.162 Reflect 0.096 0.205
PR2 -0.001 0.134 0.301 -0.228 0.178 0.944 -0.154 -0.047 Reflect 0.096 <0.001
PR3 -0.030 -0.108 -0.346 0.222 -0.157 0.938 0.142 0.033 Reflect 0.096 <0.001
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
448
AP1 -0.138 -0.016 0.125 0.114 -0.281 0.255 0.849 -0.062 Reflect 0.096 <0.001
AP2 0.133 0.380 0.091 -0.348 0.099 -0.478 0.788 -0.224 Reflect 0.096 <0.001
AP3 0.015 -0.348 -0.216 0.215 0.195 0.195 0.823 0.279 Reflect 0.096 <0.001
OS1 0.037 0.343 -0.388 -0.339 0.397 -0.262 0.002 0.615 Formati 0.096 <0.001
OS2 0.058 -0.104 -0.018 -0.109 -0.209 0.216 -0.212 0.710 Formati 0.096 <0.001
OS3 -0.073 -0.025 0.377 0.018 0.120 -0.023 -0.258 0.648 Formati 0.096 <0.001
OS4 0.280 0.296 -0.962 0.624 -1.004 0.427 0.660 0.673 Formati 0.096 <0.001
OS5 -0.331 -0.519 1.058 -0.235 0.812 -0.429 -0.207 0.619 Formati 0.096 <0.001
Notes: Loadings are unrotated, and cross-loadings are oblique-rotated. SEs and P values are for loadings. P values < 0.05
are desirable for reflective indicators.
Based on the above table, it can be seen that there is no outlier with the range value less than -4 or 4
Figure 1: Range value.
Table 2: Indicator Reliability.
Type P value VIF WLS ES
Reflect 0.096 <0.001 1.631 1 0.463
Reflect 0.096 <0.001 1.612 1 0.451
Reflect 0.096 0.011 1.030 1 0.086
Reflect 0.096 <0.001 1.298 1 0.300
Reflect 0.096 <0.001 1.483 1 0.511
Reflect 0.096 <0.001 1.199 1 0.189
Reflect 0.096 <0.001 1.615 1 0.453
Reflect 0.096 <0.001 1.157 1 0.198
Reflect 0.096 <0.001 1.429 1 0.349
Reflect 0.096 <0.001 1.484 1 0.413
Reflect 0.096 <0.001 1.312 1 0.324
Reflect 0.096 <0.001 1.192 1 0.262
Reflect 0.096 <0.001 2.045 1 0.422
Reflect 0.096 <0.001 1.667 1 0.331
Factors Forming Seven Layers of the Open System (OSI) Model
449
Reflect 0.096 <0.001 1.319 1 0.247
Reflect 0.096 0.319 1.032 1 0.004
Reflect 0.096 <0.001 2.567 1 0.501
Reflect 0.096 <0.001 2.548 1 0.495
Reflect 0.096 <0.001 1.663 1 0.357
Reflect 0.096 <0.001 1.422 1 0.308
Reflect 0.096 <0.001 1.559 1 0.336
Formati 0.096 0.002 1.226 1 0.177
Formati 0.096 <0.001 1.353 1 0.236
Formati 0.096 0.001 1.277 1 0.197
Formati 0.096 0.001 1.390 1 0.212
Formati 0.096 0.002 1.281 1 0.179
Based on the results of the table above, it can be
seen that the indicator reliability of all items forming
the OSI coil collector is invalid. This is seen because
the value factor loading values vary medium for P-
Value overall <0.001. OSI builder construct
indicator produces weight significance varies VIF
value per indicator generated <3.3. 3.665.
Table 3: Latent variable coefficients.
Phisik D Link NWork Traspo Sesi Present Aplikasi Osi
R-Squared 0.477
Adj. R-Squared 0.381
Composite Reliab 0.775 0.755 0.796 0.806 0.843 0.759 0.860 0.788
Cronbach’c alpha 0.567 0.508 0.611 0.638 0.716 0.538 0.756 0.664
Avg var extrac 0.560 0.517 0.572 0.583 0.643 0.592 0.673 0.428
Full colin VIF 2.188 2.290 3.665 2.330 2.820 2.390 2.009 1.914
Q-Squared 0.495
Min -1.974 -3.156 -3.110 -3.389 -3.255 -4.476 -2.598 -2.202
Max 2.491 2.423 2.310 1.716 2.065 1.489 2.107 2.262
Median -0.230 -0.169 -0.138 -0.056 -0.011 -0.110 -0.245 -0.115
Mode -0.230 -0.169 -0.138 -0.056 -0,011 -0.110 -0.245 -0.688
Skewness 1.065 -0.223 0.106 -1.384 -0.486 -1.851 0.069 0.312
Exc kurtosis 1.301 2.211 1.975 4.283 2.217 7.455 1.390 -0.136
Unimodal-RS Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Unimodal KMV Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Normal JB No No No No No No No No
Normal RJB No No No No No No No No
Histogram View View View View View View View View
Note: Square roots of average variances extracted (AVEs) are shown on diagonal.
From the table above, it can be seen that the
value of AVE for CONSTRUCTS seven-layer OSI
is excellent s ie> 0.5. Therefore it meets the criteria
of convergent validity, and so does the value of
Composite Reliability generated construct of the
seven-layer OSI whhich is also very good ie> 0.7
that it also meets internal consistency reliability. Full
Collinearity VIF values for each construct are also
very good ie<3.3 but on the NWork construct there
is a collinearity problem in model > 3.3 ie 3.665.
Tabel 4: Correlations among l.vs. with sq. rts. of AVEs.
Phisik D Link NWork Traspo Sesi Present Aplikasi Osi
Phisik (0.748) 0.476 0.620 0.446 0.526 0.380 0.539 0.423
D Link 0.476 (0.719) 0.647 0.501 0.393 0.503 0.334 0.463
NWork 0.620 0.647 (0.756) 0.690 0.276 0.263 0.503 0.605
Traspo 0.446 0.501 0.690 (0.764) 0.360 0.128 0.424 0.443
Sesi 0.526 0.393 0.276 0.360 (0.802) 0.659 0.465 0.195
Present 0.380 0.503 0.263 0.128 0.659 (0.769) 0.231 0.154
Aplikasi 0.539 0.334 0.503 0.424 0.465 0.231 (0.820) 0.558
Osi 0.423 0.463 0.605 0.443 0.195 0.154 0.558 (0.654)
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
450

Note: Square roots of average variances extracted (AVEs) shown on diagonal.
P values for correlations
Phisik D Link NWork Traspo Sesi Present Aplikasi Osi
Phisik 1.000 <0.001 <0.001 0.002 <0.001 0.009 <0.001 0.003
DLink <0.001 1.000 <0.001 <0.001 0.007 <0.001 0.024 0.001
NWork <0.001 <0.001 1.000 <0.001 0.064 0.078 <0.001 <0.001
Transpo 0.002 <0.001 <0.001 1.000 0.014 0.397 0.003 0.002
Sesi <0.001 0.007 0.064 0.014 1.000 <0.001 0.001 0.195
Present 0.009 <0.001 0.078 0.397 <0.001 1.000 0.122 0.305
Aplikasi <0.001 0.024 <0.001 0.003 0.001 0.122 1.000 <0.001
Osi 0.003 0.001 <0.001 0.002 0.195 0.305 <0.001 1.000
From the results of the table above, it can be seen
that the value of the square root of AVE for the OSI
seven-layer construction is greater than the
correlation between constructs so as to show good
discriminative validity.
From the survey results on the importance of the
communication standards applied in the network, it
was obtained that respondents strongly agreed
40.4%, agreed 55.3% and doubted 4.3%. The
respondents' knowledge of the OSI, which is a
standard for communication in the network that is
applied globally, 82% of respondents understand and
know while 18% do not understand. In terms of
establishing OSI network architecture consisting of
seven layers, namely physical, data link, network,
transportation, session, percentage, and application,
respondents strongly agreed 29.2%, agreed 62.5%,
and the rest did not agree and were hesitant. The R-
Square value in this research model is 0.48, and this
shows that this model is moderate, and shows that
the factors forming the OSI network are only able to
explain 48% and the rest form other factors. This is
due to respondents who do not know and understand
about OSI (Open System Interconnection) and form
the OSI network, respondents in the previous survey
were information system managers who had
understood and understood Open Interconnected
Systems.
3 CONCLUSION AND
SUGGESTIONS
Communication is very important as an effort to
transfer messages or information from one place to
another, both verbally (verbal), written and non-
verbal. Communication acts as information, control,
motivation, and as an expression of action. OSI is a
communication standard that is applied in computer
networks. Standard that causes all communication
devices to communicate with each other through the
network. Open System Interconnection (OSI) is a
model of a globally accepted framework for the
development of complete and open standards. The
OSI model helps create open standards between
systems to interact and communicate with each
other, especially in the field of information
technology. OSI can provide a network architecture
display that is divided into 7 (seven) layers. Based
on the discussion above, the OSI model can only be
explained by 48% and the rest form other factors.
This is caused by respondents who do not know and
understand about OSI (Open System
Interconnection) and form the OSI network.
Respondents in the previous survey were
information system managers who had understood
and understood Open System Interconnected so this
study was still very weak and needed to conduct
research with respondents who really understand and
understand about OSI (Open System
Interconnection).
REFERENCES
Azhar Susanto., 2004. Accounting Information System:
Computer Based Concept and Development, First
Edition. Bandung: Lingga Jaya
Bodner, H. George., 1998. Accounting Information
System, 7th Ed. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall
International, Inc.
Mcleod, JR. Raymond., 1998. Management Information
System: A Study of Computer Based information
Systems, 6th ed., New Jersey: Prentice Hall, Inc.
Sandra Senft and Frederick Gallegos., 2009. Information
Technology Control and Audit, Third Edition ISBN:
978-1-4200-6550-3
Imam, Ghozali., 2017. Partial Least Squares, Concepts,
Methods and Applications Using the WarpPLS 5.0
Program. Diponegoro University Publishing Agency.
Factors Forming Seven Layers of the Open System (OSI) Model
451
