
Over-the-Counter Medication Leaflet in Context of Situation:
Systemic Functional Linguistic Study
Liesna Andriany
Universitas Islam Sumatera Utara, Jl. Sisingamangaraja. Teladan-Medan. Medan. Indonesia
Keywords: medicine leaflet, context of situation, SFL.
Abstract: This study aims to explain the relationship between ideational metafunction and social context. The research
method is descriptive with qualitative and quantitative approaches. Sources of data are from over-the-
counter medication leaflets analyzed by the theory of Systemic Functional Linguistics (LSF). The results
show that the schematic structure use descriptive and instructive genres containing remarks and steps of
medication use. Based on the ideational metafunction analysis and the context of situation, the purpose of
the producer to issue the leaflet can be known. The conclusion is through the material and circumstantial
processes associated with the context of situation as the producer wants to convey to the consumers what
medication is to be completely understood. Through diction well- understood by the public, the consumers
understand the nature and the way of consuming the medication.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Indonesian people generally overcome any type
of disease by their own experience and knowledge
without consulting a doctor, known as
swamedikasior self-medication. The legal basis of
the self-medication is the regulation of the Minister
of Health No. 919 Minister of Health/Per/X/1993.
The Indonesian self-medication behavior is still very
large (BPS, 2016) or 61.05% (Susenas, 2014). Given
the magnitude behavior of this self-medication, the
role of over-the-counter leaflet/etiquette is very
important as accurate and targeted information.
Every medication packaging contains a leaflet or
etiquette concerning the medication information.
The medication leaflet provides related information
such as; name of the medication, composition,
indication, information on the workings of the
medication, dosage, warning (specifically for limited
medication), attention, manufacturer, batch/lot,
registration (registration number is indicated as the
legitimate authorization permit issued by the
government on each medication packaging), and
expiry date.Before consuming the medication,
consumers should read the nature and manner of use
on etiquette, leaflet or packaging of medication for
proper use and safe. Every medication circulating in
Indonesia shall include leaflet in its box in
accordance with the regulations on the packaging
and labeling of medication issued by the Minister of
Health No. 193/Kab/B.VII/71. By reading the
medication label then the consumer has certain
information that can help to make decisions
regarding medication or vitamins in accordance with
the needs and conditions.
So important is the etiquette or medication leaflet
for the consumer that it is necessary to analyze the
extent to which the information listed on the label or
drug brochure reaches its target. Errors and lack of
information will be fatal to the consumers.
This paper will discuss only the context of the
situation because this context is concretely related to
culture and language. In other words, the context of
situation is the door of the social context to the
language. Therefore, the researcher is interested to
see the extent to which the medication leaflet is
linked to the context of situation providing
information needed by medication users. The
objective of the study is to evaluate whether the text
of the medication leaflet reaches the target. The
medication leaflet is very important for the public
who do not understand about medication and by
reading the medication leaflet in the pack, the
consumer will get necessary information about the
medication.
422
Andriyany, L.
Over-the-Counter Medication Leaflet in Context of Situation: Systemic Functional Linguistic Study.
DOI: 10.5220/0008886204220426
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research (ICMR 2018) - , pages 422-426
ISBN: 978-989-758-437-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 LITERATURE REVIEW
The use of language in medication leaflet or
etiquette is inseparable from the context. Two
medication leaflets are analyzed using systemic
linguistic school pioneered by M.A.K. Halliday from
the University of Sydney, Australia. Systematic
Functional Linguistics (SFL) is a systemic theory
that has a great deal of attention to language
relations with the context. One can hardly
understand the meaning uttered or written by others
unless they know something about the language and
context studied. The idea of context originated from
Malinowski which is later passed on by his disciple
Firth. The disciples of Firth then continue the
systemic school by naming themselves Neo-Firthian,
Halliday, Gregory, Martin, et al. They develop a
more sophisticated framework in describing
language relationships with the context of situation
(register), cultural context (genre), and ideology.
The dimension of language variation in the
context of situation consisting of field, participant
and mode is a contextual variable that characterizes
the intrinsic functionality of a context of situation.
The field discusses interaction activities having two
dimensions: what is discussed and for what; the
participant refers to who talks about, and the mode
is how the conversation takes place.
The context of situation occurs from three
components: the field, the participant and the mode,
three of which are the content explaining what is
going on. (Halliday & Hasan, 1985: 12). The
elements that construct the content are (a) the arena
or activity, (b) the characteristics of the participant
and (c) the semantic domain (Saragih, 2006).
Following the SFL hypothesis, the function of
language organizational intrinsic interacts closely
with the extrinsic organizational context of social
functions.The main functions of language are
ideational functions, interpersonal functions, and
textual or metaphysical functions (Matthiesen,
1992/1995, p. 6; Halliday and Martin, 1993, p. 29;
Halliday andMatthiesen, 1999, p. 7-8). The field has
a close relationship with ideational function,
participant with interpersonal function, and mode
with textual function. The field construes as
ideational, the participant as interpersonal, and the
mode as textual.
The relationship of language to context is the
realization of language as a social semiotic system
(Sinar, 200, p. 56). In other words, language is the
manifestation in context and there is no language
without a social context. The social context system
consists of context of situation, culture and ideology.
Thus in the study of language, interpretation focused
on the text must consider the social environment that
is the context of situation.
3 METHOD
This research is descriptive using qualitative and
quantitative methods. The data collection
instruments are reading techniques and transcript
ingesting. The object of the study is the text derived
from an over-the-counter medication leaflets of skin
medication (See Text 1) and Antelmintik (See Text
2). The existing data are analyzed with systemic
functional linguistics: context of situations, and then
interpreted.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Schematic Structure
The structure of texts 1 and text 2 can be categorized
as a combination of description and instruction
genres. The text of this paper refers to Brown and
Yule (Brown and Yule, 1996, p. 26-35) which is
seen as a complete recording of language in a
communication event. The description genre is an
explanation of an individual or something that has
certain characteristics (Sinar, 1998, p. 69). In text 1
and text 2 the writings are also factual so are neither
creative nor imaginative because this text describes
how the skin medication and Antelmintik actually are
and what their shape and benefits are when used.
While the instruction genre in text 1 and text 2 is
a word that shows the goal of the oriented steps. The
words used are 'rubbed', 'smeared', and 'drunk'.
Words that indicate goal-oriented steps are seen in
the word attention', one time treatment', 'before or
after meals'. The structure of schematic text 1 and
text 2 can be seen in the following:
Figure 1: Schematic Structure Figures of Text 1 and Text
2.
Over-the-Counter Medication Leaflet in Context of Situation: Systemic Functional Linguistic Study
423
The picture above shows that both texts have the
same description and instruction structures. The
composition of the genre and the description of the
instructions are the same. Description genre
describes the type of medication, its usefulness, side
effects, and contra indications. Instruction genre is in
the form of an explanation of how the medication is
used to be useful and appropriate. The instruction
genre is used for operations. The instructions are
included in a text type consisting of a procedure that
tells something done through the steps. The goal is
how to do or make something. Both genres are
sufficient for the information the user needs,
although the sequence of information is different.
4.2 Context of Situation
From the analysis of the two texts it is known that
the participants determine one another and refer to
the interpersonal, are seen in Text 1 of 38 clauses
and text 2 of 61 clauses. The second most dominant
text is a statement realized by the declarative mode,
2 clauses constituting command mode and 2
interrogative modes. From the results of the analysis
of both texts it is known that the field is 'constrained'
(mutually determining and referring) with ideational.
Ideal metafunctions can be seen in the following
table.
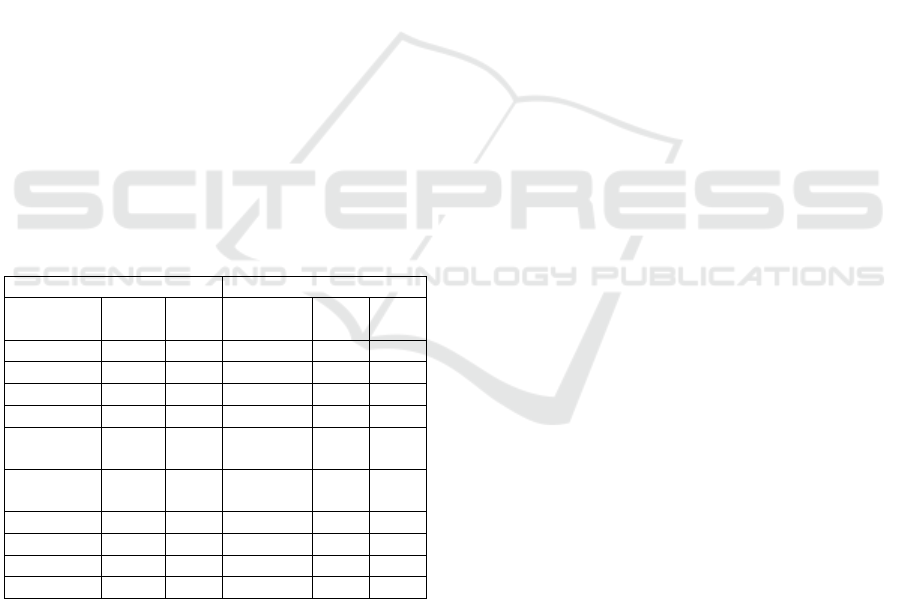
Table 1: Ideational.
Ex
p
eriental Circumstance
Teks
I
Teks
2
Teks
1
Tek
s 2
Material 65,2 57,4 Location 5 4
Mental 8,8 10,8 Duration 0 0
Relational 14 16,6 Mode 23,5 18,5
Behavior 12 15,2 Cause 60,5 63
Verbal 0 0 Environ
ment
0 0
Exsistenti
al
0 0 Existenc
e
11 14,5
Context 0 0
Teno
r
0 0
View 0 0
Total 100 100 100 100
The intrinsic function of language organization
interacts closely with the extrinsic organizational
social context functions. It can be seen that the field
is closely related to ideational metafunction. Both in
text 1 and text 2 the dominant material process is
realized to 65.2% and 57.4%, more than half of the
number of clauses. This material process indicates
the physical activity observable by the senses to be
emphasized. Medication manufacturers want to
emphasize that the consumers have to use a lot of
sense judgments instead of feelings. Likewise with
circumcision, the dominant is circumstantial because
in text 1 (60.5%) and text 2 (63%). The use of
circumstance is because this explains that the
medication has a great benefit when used correctly
in accordance with the instructions in the leaflet.
The metafunctionconstruent of the context of the
situation when viewed from the field of text of the
medication manufacturer indicates that the
medication participant/consumer does not
understand the chemical term. Thus the chosen
diction also uses words that participants/consumers
understand in accordance with the social cultural
conventions. The words do not require special
knowledge because everyone can read them even
though used in medical terms. Manufacturers expect
the words in the text are expected to be understood
by everyone.
The tenor of text or participants involved in the
text of the medication when viewed from a social
perspective can be various of status, ranging from
doctors, patients, intellectual communities, to the
public. The tenor specifically in terms of content
elements show the physical and mental
characteristics and knowledge of participant when
interacting in the text. The participant status on both
texts here may be the same or not the same. It can be
the same status when read by a doctor, or
pharmacist.In an unequal status relationship, one
participant is higher than the writer of the text.
These differences may be in knowledge (such as
Professor of Pharmacologist), age differences
(grandpa, grandma), or higher social standing
(owners of medication companies, Health Minister,
President) or a lesser difference in the knowledge of
the reader (ordinary people who do not understand
about medication), age differences (children), or
social differences (scavengers, beca drivers,
homeless people)
Affect shows emotional involvement. The
interrelationships between the two texts are in
positive affect with the understanding that both the
medication company or the consumers/reader need
each other. Medication companies need their
medicine to be bought or used while consumers
expect the medication to cure the disease.
Mode shows how the role of language in
interaction; in details such as, how to show the role
of language in an interaction, the expectation of the
role of language in a situation, language status, and
medium or channel. The elements that construct the
mode consist of 'planning', 'distance', 'medium' or
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
424

'channel'. Planning indicates the preparation made
for the realization of the text. The second way the
text is made based on the plan (+) because the text is
arranged in a planned manner in other words
previously planned interactions in writing by the
medication manufacturer to be read by a person who
will use the medicine. Thus the medication leaflet
has been prepared with careful planning and has met
the leaflet criteria set by the existing rules.
Distance refers to the feedback given to each
other by interpretants or among the language users
and the involvement of language with the reality it
represents. The distances in the two texts can be
distinguished to be experiental and interpersonal
(how fast to get the feedback). Based on the
experiental both texts belong to the
generation/reflection because the distance between
the text and the activity can be very far away and the
use of language does not indicate the activities that
take place or called that the language to be a
reflection. The language involvement of the two
texts (+) is semantic which means there is a gap
between the text and the activity performed. Text 1
and text 2 show clarity about medication description
and instruction. The distance between the
manufacturer and the remote does not quickly get
the feedback, then the leaflet should be as clear as
possible exposing the medication profile.
Medium shows the means that realize the
language. Medium used is text, meaning that the
language is realized by encoding such as scratches,
lines, symbols of the sounds (letters) on paper, in
other words the unit of realization is the letter. Text
1 and text 2 use big Latin letters so they can be read
properly. The manner does not have strata (-) strata
field either because it is for everyone and the diction
used is also general with only a few medical terms
as there is no equivalence of such medical terms in
common.
5 CONCLUSION
The study of medication leaflet discourse is a study
of language in the context of situation to understand
how language users use the language when
interacting in social contexts. The context of the
situation relates to the linguistic features of skin
medication and Antelmintik leaflets.
Skin medication and Antelmintikleaflets.are not
much different, although some are incomplete when
viewed in terms of their schematic structure because
there are points in the Antelmintik leaflet that are not
found in the skin medication leaflet such as
medication work, warning and attention, and
overdose. The genre in Antelmintik and skin
medication leaflets are a combination of descriptive
and instructive genres.
The field in Antelmintik and skin medication
leaflets has a close relationship with ideational
metaphors and the most dominant material processes
are the causal circumstance. The participants
determine one another, referring to the interpersonal,
seen in the Antelmintik and skin medication leaflets;
the most dominant is declarative realized by
declarative mode. The mode also determines one
another referring to textual.
Skin drug brochures and worm medicine
brochures have fulfilled the target, namely the reader
/ user gets the necessary information about the drug.
The language used also does not use medical terms,
although there are still some medical terms used, and
even then because it is difficult to get the
equivalence in Indonesian terms.
Antelmintik and skin medication leaflets have
already met the target that readers/consumers get the
necessary information about the medication. The
language used does not use medical terms either,
although there are still some medical terms that have
no equivalence in Bahasa Indonesia.
REFERENCES
Halliday
&
R. Hasan. 1985. Context and Text: Aspects of
Language tnSoctal Semiotic Perspectives. Geelong:
Deakin University Press.
Halliday, M.A.K & Matthiessen. 2004. An Introduction to
Function Grammar, Third Edition. Great Britain:
Hodder Education.
Eggins, Suzanne. 2004. 2
nd
Ed. An Introduction Systemic
Functional Linguistics. London & By: Continuum.
Badan Pusat Statistik. 2014. SurveiSosialEkonomi
Nasional (SUSENAS).
Badan Pusat Statistik. 2016. SurveiSosialEkonomi
Nasional (SUSENAS)
Brown,G. and Yule G. 1996. Discourse Analysis.
Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
Regulation of the Minister of Health No.
919/Menkes/Per/X/1993 on Medication Criteria
without a prescription.
Regulation of the Head of POM RI N0 HK 00.06.323.295
Year 2009 on Guidelines for the Supervision of
Promotion and Medication Advertisement.
Regulation of the Minister of Health of the Republic of
Indonesia no 193/Kab/B.VII/71 on the Regulation of
Packaging and Medication Marking
Saragih, Amrin. 2006. Bahasa dalamKonteksSosial.
Medan: Universitas Negeri Medan
Over-the-Counter Medication Leaflet in Context of Situation: Systemic Functional Linguistic Study
425

Sinar, Tengku Silvana. 2003. Teort clan Analists Wacana.
Pendekatan Fungstonal Sistemik. Pustaka Bangsa
Pers.
Sinar, Tengku Silvana. 1998. Analists Struktur Skemattka
Genre. Medan: Universitas Sumatera Utara Press.
Law of the Republic of Indonesia Number 36 Year 2009
on Health.
Law of the Republic of Indonesia Number 8 Year 1999 on
Consumer Protection.
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
426
