
Cyber Crime in Brunei Darussalam Viewed from Sociological
Perspective
Fatimah Awg Chuchu and Muhd. Khairul Anwar Abd Gafur
Faculty of Arts & Social Sciences Universiti Brunei Darussalam
Keywords: Cybercrime, social media, defamation, bullying
Abstract: Cyber culture emerged from the use of computer technology networks for business, communication,
entertainment and research. In addition, it is also used to research various internet-related issues and new
forms of networked communication. Overall, cyberspace facilitates communication between people both
domestically and internationally. However, it also has a negative impact on the society when it is misused by
certain parties. In that connection through the cyber network, there are also many criminal activities that can
affect any party, whether individuals or societies as a whole. Cyber Crime in the context of Interpol, is a type
of crime transmitted through the internet technologies in which criminals exploit the advantages of the
technology to perform various criminal actions that have no physical boundaries either physically or
"virtually". These actions can cause serious harms that can pose a very real threat to victims around the world.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cyber culture emerged from the use of computer
technology networks for business, communication,
entertainment and research. In addition, cyber culture
is also used to research various internet-related issues
and new forms of network communication such as
social media, online community, online gaming,
mobile phone applications and including matters
related to networking, privacy and identity. Overall,
cyberspace facilitates communication between
people both domestically and internationally. From a
scientific perspective, the exchange of ideas and
materials amongst students or university lecturers can
be done quickly. However, it also has a negative
impact on the society when it is being misused by
certain parties. "In that connection through the cyber
network there are also many criminal activities that
can affect any party, whether individual or society.
Cyber Crime in the context of Interpol is a type of
crime transmitted through the internet technology
network and these criminals exploit the advantages of
the technology to perform various criminals that do
not know the boundaries either physically or
"virtually" which can cause serious harms that can
pose a very real threat to victims around the world
(International Criminal Police Organization Interpol.
Cybercrime).
In the global economic crime review report made
by PricewaterhouseCoopers, Globally, cyber crime is
the second highest crime reported in 2016 (Kris
McConkey, 2016) and the total loss from cyber crime
in 2015 globally is USD $ 158 Billion (Symantec
Corporation. 2017 Internet Security Threat Report).
From the two facts taken from the results of the
report, it is found that this crime is very heavy, and it
is a problem not only of small society but also of the
whole society in the world. Cyber crimes are directly
affecting individuals or consumers. While in
Australia and New Zealand, we have also witnessed
identity take over to be the fastest growing type of
fraud that reaches 80% of reported cases of fraud
classified in the category (Equifax. Cybercrime Fraud
Report). International companies are also major
victims of cyber crime to obtain confidential
information for profit. Data violations are
increasingly affecting stock prices, including almost
half percent decrease in company shares due to data
breach. According to Gartner, by the end of 2017,
more than half of all cyber crimes targeting the
company at Global will bypass network controls by
using "encrypted traffic".
We know that crime, such as cyber crime is not
only a minor issue but also a critical problem that can
hurt any party both domestically and internationally.
With these problems, countries have made significant
expenditures on upgrading "Cyber Security" or cyber
354
Chuchu, F. and Abd Gafur, M.
Cyber Crime in Brunei Darussalam Viewed from Sociological Perspective.
DOI: 10.5220/0008885103540361
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research (ICMR 2018) - , pages 354-361
ISBN: 978-989-758-437-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

security to monitor crimes that can hurt the
government. Brunei Darussalam is also not "immune"
from cyber-crime, and we in Brunei Darussalam have
also seen an increase in cyber crime. This crime is
also seen as a grave crime in Brunei Darussalam as it
can bring disruption to social harmony and social
security or even affect the overall economy of the
country. His Majesty the Sultan Haji Hassanal
Bolkiah has been focusing on the issue of Cyber
Crime in the king during his 68th birthday. In his
article on cyber crime, he said:
"In this context, I want to remind people of cyber
threats that are harmful to children. The Ministry of
Communications is actively working on the Online
Child Protection framework to protect children who
use the Internet from being exposed to negative
influences and cyber criminal threats."(Azlan
Othman. 2014).
The Government of Brunei Darussalam has taken
the initiative to curb this threat through education and
awareness of the dangers of this cyber crime and
should not be taken lightly. This paper will focus on
cyber crime in Brunei Darussalam viewed from the
sociological perspective and the extent to which
Brunei Darussalam Government deals with these
criminal damage efforts to enhance defence and
awareness of cyber criminal threats.
Therefore, the objectives of the study are:
1. To know the various types of cybercrime
occur in Brunei Darussalam.
2. To identify the connections between the
sociological theories and cyber crime.
3. To investigate the societies awareness on
cyber crime.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Former Education Minister, Pehin Suyoi bin Haji
Osman refers to Cyber Crime statistics derived from
the Criminal Investigation Department of the Royal
Brunei Police Force, the number of individuals
involved fall victim to Cyber Crime for the year 2017
is 207 victims and the number is rising compared with
the number in the previous year, 2016 i.e. 190
victims. Of the total victims, the 123 is their age
within 18-35 years. He argued that this was a very
worrying trend, and it does not want to see abuse of
technology, especially through social media with
negative elements. This will disrupt the various
initiatives planned by the Ministry of Education. He
also stated that the development of social media
cannot be controlled 100% and there is no denying
that social media app raises many serious challenges
to the full the community. Abuse of social media can
trigger adverse effects and can affect a person or an
organization (Azlan Othman, 2017).
The Ministry of education would like to instil
awareness about the use of social media in the school
curriculum. It aims to improve the understanding of
the elements of the moral and ethics involved in the
use of social media. Absorption of ICT into education
not only helps students gain knowledge of the
computer but also prevent them from affected
indirectly in error or fall victim to Cyber Crime. He
expects these initiatives to protect youth and prevent
youths from becoming victims by technological
advances and educate them on how to leverage social
media platform wisely and caution (Azlan Othman,
2017).
According to Protective Security Services IT
Security Services (ITPSS) CEO, Shamsul Bahri Hj
Kamis, Cyber Crime is a very serious problem and
from the statistics provided, it is very sad. We note
that this incident related to abuse through social
media in relation to the internet has increased over the
last few years. He also said a representative from the
Royal Brunei Police Force confirmed that these cases
include sexual grooming, abduction, cyber bullying
and even rape. All sexual crimes against children are
one hundred percent through internet network,
especially social media. Some cyber bullying
incidents which give large problems have been
reported to IT according to the Protective Security
Services Security Services (Nabilah Haris.2013). To
address Cyber Crime issues, he recommended
awareness campaigns should be carried out in
schools. IT Protective Security Services (ITPSS) has
been instructed to attend school visits to give lectures
along with practical sessions where speakers will
show how individuals can protect themselves when
online network the Internet. This half of the
perpetrator exploits the Malay culture that always
gives and always trusts. IT Protective Security
Services (ITPSS) is trying to make people realize that
it may not always be a good practice. Some things
should be kept in private and confidential (Nabilah
Haris. 2013).
Behind this Cyber Crime problem, Brunei
Darussalam has earned praise from the United
Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) on proactively
measures to turn the internet become safer for youth-
youth and children. Representatives of UNICEF have
stated that Brunei is the first country in Southeast
Asia in the framework of online Child Protection built
above International Telecommunication Union
(James Kon, 2017). The current law in Brunei has
made prohibition for possession of child
Cyber Crime in Brunei Darussalam Viewed from Sociological Perspective
355
pornography; causing a person under the age of 16
years to watch sexual stunts, commercial sex with a
person under 18 years in and out of Brunei, sexual
grooming, etc. This provision is one of the most
comprehensive and up to date in the region. He also
praised the Government of Brunei Darussalam has led
in educating children on the importance of practicing
good ethics and security while browsing the internet.
In addition, one of the experiments in promoting
cyber security, Authority for Info-communications
Technology Industry of Brunei Darussalam (AITI)
has launched a series of seminars on safety and ethics
awareness program Internet Cyber to two different
groups of audiences; students and also mothers or
guardians. This activity is a collaboration between the
Authority for Info-communications Technology
Industry of Brunei Darussalam (AITI) with the
Department of Schools under the Ministry of
education and Tech One Global Ltd. Seminars
includes the heading "Introduction to Cybercrime and
safety "," connect to the Internet safely "," security
threats and Attacks "," social networks "," Secure and
instant messaging "as well as" Protect Your
Environment” (AITI ensures that Brunei’s parents
and youths are aware of cyber security and internet
etiquette. 2011).
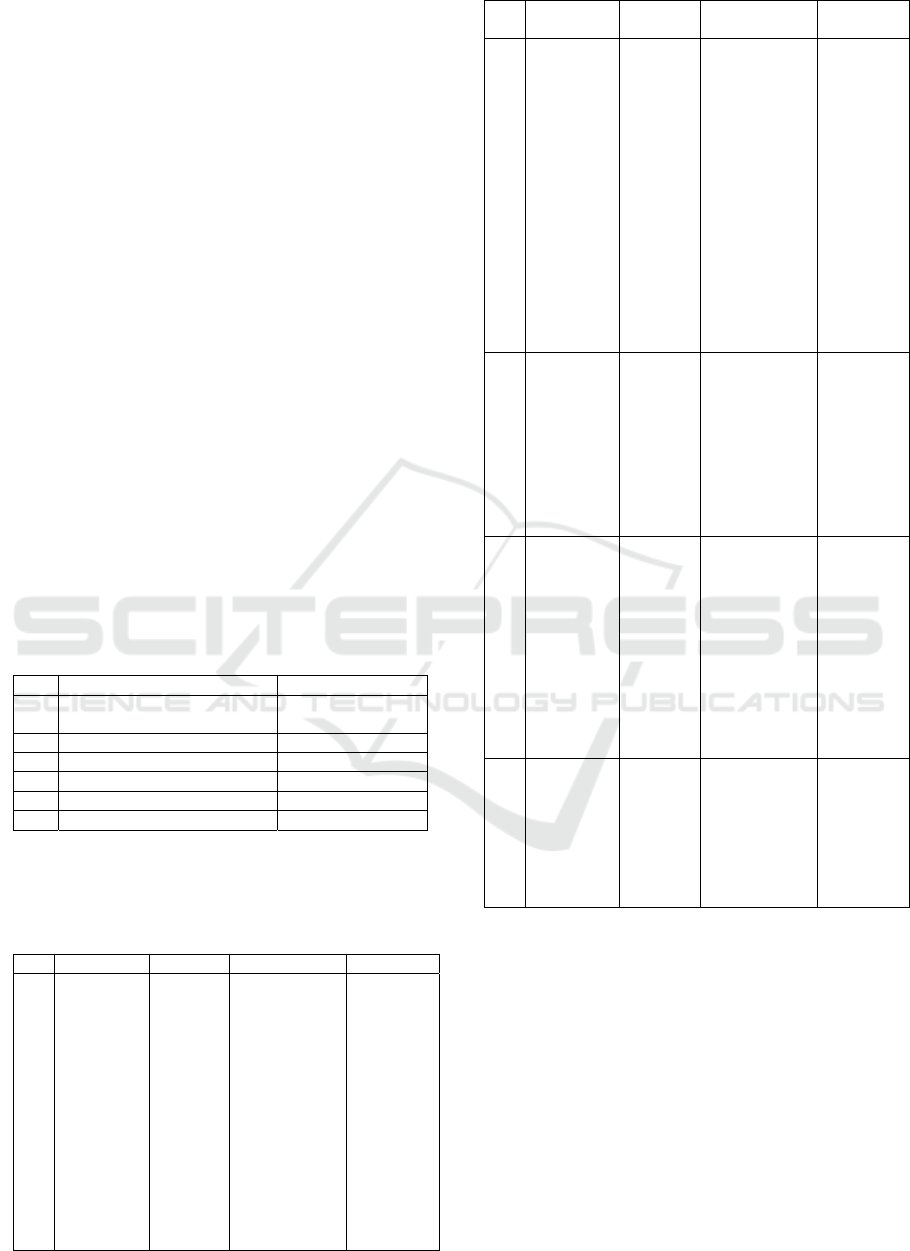
Table 1: Cyber Attacks 2011-2015, in Brunei BruCERT.
Source: BruCERT.
No. Description Percentage (%)
1. Botnet Command & Control
Serve
r
0%
2. Scam 3%
3. Spam 31%
4. Website Defacemen
t
5%
5. Cyber Harassment 0%
6. Malicious Software 61%
Table 2: Record the Cyber Crimes Convicted. Source:
Brunei Times.
Cited in Dr. Susanty Hj Suhaili (2016) Cyber
Security Challenge for Wellbeing Ummah.
No Crime Year Sentence Details
1. Hacking
and data
thieves
(the first
cybercrime
Cases)
2010 28 Months
Prison
Wireless
Access
Point that
is not
locked
cause
criminals
managed
to obtain
credit card
numbers
and use to
pay for
online
purchases
of Bnd
$2720.00.
2. Rape 2011 14 years in
prison / 14
Canes
Rape
under age.
Criminals
were
breaking
into
homes,
raping and
hitting a
victim
under the
age of 13.
Introducto
ry began
on
applicatio
n chat.
3. Cyber
Bullying
2012 10 Months
Prison
Ex-partner
has
revealed
confidenti
al pictures/
videos
with the
aim of
shaming
the latter.
4. Rape 2015 9 years Prison
/ 6 Canes
Offenders
aged 28
years,
sexual
grooming
offence
with two
boys under
recognize
the victims
from
Facebook.
5. Terrorist
Threat
2015 Halt / Under
Surveillance
Through
social
networkin
g, the
desire to
follow
organizati
on terrorist
3 THEORIES
Computers and the internet have become common in
any society today. This new technology has resulted
in the existence of new criminal Cyber Crime. From
various angles, this criminal behavior cannot be
explained solely by a single theory but it requires
some combination of various theories related to such
crimes. Different aspects of each theory can be used
together to offset what each theory failed to explain.
Below are some of the theories that could explain
about the formation of Cyber Crime.
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
356

3.1 Thorstein Veblen Theory of
Institutional Change: Beyond
Technological Determinism
(Classical)
The process of social change is approximately
constant and a change will result to change the other.
Overall, the process of change is inevitable. Social
change indirectly reflects the technological advances
or otherwise. Use of the internet has established the
online community that brings new social relations.
Through the use of technology, the community can
find information about the latest information. It is
common that the community communicate through
the use of mobile phones and the internet. However,
the technology also has given a new route for criminal
activity, namely Cyber Crime. This kind of crime can
be carried out from anywhere and at any time through
the use of computer technology and mobile phones
through a network connection. This technology can
facilitate criminal perpetrator to find victims such as
pornography or pornographic elements of destructive
social values and morals of society especially to the
younger generation (Olivier Brette. 2003).
3.2 General Strain Theory (Modern)
Robert Agnew said that tension leads to negative
emotions that lead to some deleterious results. The
discussions in this theory include the failure to
achieve positive goals such as property or money, the
removal of positive values such as loss of property
and also negative value propaganda presentations
such as physical abuse. The first tension saw the gap
between individual expectations and what they
actually achieved that caused disappointment and
anger. The second is when positive stimulus is
eliminated and the result is a deluge. This criminal
behavior may indicate as an attempt to facilitate or
replace the stimulus. The latter is when faced with
negative stimuli. This can cause delinquency as a way
of ending or avoiding negative stimuli (Patchin,
Justin W. and Hinduja, Sameer. 2011). Tensions do
not directly lead to crime but promote negative
emotions such as aggression and frustration. This is
directly in conjunction with "Frustration-Aggression
Hypothesis" by psychologist at Yale University. They
believe that anger arises before frustration and
frustration can be created into aggressive or non-
aggressive (Runions, Kevin C. 2013). This negative
emotion requires response as a way to relieve internal
stress. Handling through illegal behavior and violence
may be especially true for teens because of their
limited resources and the inability to escape a
disappointing environment.
3.3 Robert K. Martin’s Strain Theory
(Modern)
In contemporary societies, success may be rated
higher than goodness. He suggested that the
underprivileged or under social strata should end up
taking an honest and socially acceptable path to
discover financial success but did not succeed at last
because it was not in the same position. Slowly they
are wondering why to take the honest way where they
can gain more success through behavioral deviation
(Merton, Robert K.1938). Youths in high schools,
college or have graduated but failed to find a job are
best suited to the theory. They may see how they have
put a lot of hard work into their studies and
development of their skills but they realize that it will
not be possible for them to achieve financial success.
Therefore, they may see crime as a way of achieving
great financial success.
3.4 Jean Baudrillard Simulation
(Postmodern)
He believed that there was a time when signs of
holding and standing for something true but now they
refer to a little more than themselves. The difference
between what is real or true and what is design is the
postmodern world base. The difference between signs
and reality has erupted. It is characterized by the
implosive as distinguished from the explosion of the
production system, commodities and technology.
Therefore, just as the modern world undergoes
differentiation processes, the postmodern world can
be seen as undergoing 'dediffentiation' in the world
where signs are no longer meaningful and are
otherwise produced to symbolize meaning.
According to him, we live in a simulation age and it
leads to a breeding of an object or event (Felluga,
Dino. Modules on Baudrillard: On Simulation. 2003).
From here we can see as an example in morphing
photo - one's face can be changed or worn by another
person by wearing a different body and it is very
difficult to distinguish which one is real and fake
(Simran Singh. Riya Dutta. 2015). Jean Baudrillard
describes this postmodern world as Hyper Reality
(Felluga, Dino. Modules on Baudrillard: On
Simulation. 2003).
Cyber Crime in Brunei Darussalam Viewed from Sociological Perspective
357

4 METHODLOGY
The primary method of distribution is through a
survey done manually and via the internet, distributed
to 100 subjects consisting of 36 male respondents and
64 female respondents. In addition, the data and
significant examples for the study are obtained from
the Website, Facebook and Instagram.
5 FINDINGS
On awareness investigation, 100 questionnaires were
distributed randomly to youth comprising of 36.36%
(36) males and 63.64% female respondents. Their
ages ranged from 19 to 40 years old and possessing
various qualifications from A Level to PhD.
1. Question 4 -9 are related to cybercrime as the
knowledge, experience and awareness of
respondents towards the crime. For question
4 'how much do you know about cybercrime?'
Found that all respondents answered in a
simple environment. This means that
respondents still need input or knowledge of
cybercrime.
2. Question 5 'How many times have you been
a victim of cybercrime? Respondents'
responses vary as follows: Never 59.09% (58
respondents) 1 time 22.73% (22 persons), 2-
5 times 9.09% (10 respondents), more than 5
times 9.09% (10 respondents). More than half
of the respondents have yet to experience
cybercrime.
3. Question 6 'How safe do you feel about your
information, when you are?' Happy 22.73%
(23 respondents), no 54.55% (54
respondents) and 22.73% (23 respondents)
answered did not know. In this context,
respondents still need information disclosure
regarding the information security that is
documented in their respective accounts.
4. Question7 ‘What type of cybercrime that
often happen in Brunei?’ Trojan or malware
31.82% (32 respondents,) Auto generated
mails to inbox: 13.64% (14 respondents),
Publishing obscure materials on profiles
9.09% (9 respondents), confidential reports/
information being hacked: 13.64% (13
respondents), never experience such
situations: 27.27% (27 respondents). Others
specified: Sexual Harassment 4.55% (5
respondents). There are various kinds of
cybercrime found in the social media.
5. Question 8 ‘Do you think that the laws in
effect are able to control cyber criminals?’
Agree 31.82% (32 respondents), Disagree
9.09% (8 respondents). Neutral: 59.9% (60
respondents).
6. Question 9 ‘What actions should be taken to
counter this issue?’ Report to the authority:
31.82% (32 respondents) Increase the
awareness through education: 31.82% (32
respondents) Be vigilant on giving personal
information: 36.36% (36respondents)
6 ANALYSIS
The types of cybercrime found in this study are credit
card fraud, defamation or intent to ridicule, cyber
bullying, and unhealthy services. To see the
application of theories on a Cyber Criminal suit, we
will make the link with the Cyber Crime issues that
have taken place in Brunei Darussalam. This analysis
will focus on references found in the press and also in
social media. For example, if in view of the theory of
postmodern simulation Jean Baudrillard together
with modern strain theory of Robert K. Martin, both
theories can be applied to analyse a credit card fraud
case ever happened in Brunei Darussalam. "A
Filipino citizen were taken to the magistrate's Court
on May 4 under charges of hacking into online
internet connection without permission and using
stolen credit cards to make online purchase value in
BND $ According to Police statement 2,720.00. Royal
Brunei, early last month, the perpetrator who lives
next to TMN homeowner rentals. From there, the
perpetrator hack internet connection without the
permission of the owner of the rental home. Visit the
web site and the perpetrator intentionally cheating
website owners where the perpetrator uses a stolen
ked credit to make purchases and lead website
owners to approvethe sale and purchase transaction.
Of the activities performed, the perpetrator in 72 in
court for committing an offence punishable under
section 6 (1) (a) computer misuse Act and under
section 420 of the Penal Code. The perpetrator was
found guilty and sentenced to 6 months imprisonment
on the first offence and receives a sentence of
imprisonment for a 22.5 month more oversight
blames use credit card “(First Cybercrime
Conviction in Brunei. 2010).
From the examples given above, based on the
perspective of cybercrime, perpetrator was driven on
the convenience of shortcuts to earn money easily and
without calculating the risks taken. The perpetrator
took the less honest path because in the eyes of the
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
358

perpetrator, he will not find anything even if he does
good job honestly or decides to take the road
deviation. The perpetrator feels tense due to his social
strata condiition in the country that he thinks that the
road deviation is the best way to earn money. The
perpetrator also sees that he is indirectly in Hyper
Reality where he believes he can escape since the
criminal activity he carries out is through virtual
cyber world. Therefore, Robert K. Martin's Strain
Theory and Jean Baudrillard Simulation can be
applied to explain the steps of the perpetrator as well
as elements that induce the perpetrator to do so in a
practical way.
Examples of other cases were related to slander or
intend to aggravate to happen to the leader of the
country Sultan of Brunei Darussalam. According to a
report from the Jakarta Metro Police "Sultan Haji
Hassanal Bolkiah Mu'izzadin Waddaulah has made a
report against user Instagram in Indonesia as
defamation. The complainant was at the Hotel South
Mahakam, Jakarta Post Instagram look by a user
name ' Anti-Hassanal ' filled photos victim (Sultan)
with contents that promote hate. The identity of the
perpetrator has not been identified” (Teguh
Firmansyah. 2018). Based on the examples of
criminal cases, it can be associated with the theory of
General Strains (GST) and Thorstein Veblen's Theory
of Institutional Change: Beyond Technological
Determinism. From the example, it was found that the
cause that drives the perpetrator to do so is because of
the negative elements influenced by frustration and
anger as encouragement to do the deviation. The
perpetrator will be releasing frustration through cyber
and using social media for making defamatory etc
(Frustration-Aggression Hypothesis). The perpetrator
does defamation through the internet to hide its
identity. The perpetrator also uses instagram to
channel negative activities for the establishment of
new communities and expecting other individuals to
agree with him.
The next example plunges more to cyber
bullies which an individual has been the subject of
bullying victims in social media and defamation.
These activities are none other than mission-
Character Assassination directly and the perpetrator
is usually not an individual but a cluster building
virtual communities on the network, the internet. This
often occurs in any social media outlets like
Facebook, Twitter or Instagram. As the second
example, closely related theories to explain this cyber
bullying was General Strain Theory (GST) as well as
Thorstein Veblen's Theory of Institutional Change:
Beyond Technological Determinism. The picture
below is an example of cyber bullying taken from
social media. As with the second example, the closely
related theory to explain cyberbullying is General
Strain Theory (GST) and also Thorstein Veblen's
Theory of Institutional Change: Beyond
Technological Determinism. The photos below are
examples of cyber bullying taken from social media.
The example above shows that an individual has
made a community commitment and mission-to
lower in fact, intends to destroy the victim through the
application of social outlet; worse than this citation
and mocked a phenomenon in other countries. Such
cybercrimes are closely related to theories such as
Thorstein Veblen's Theory of Institutional Change:
Beyond Technological Determinism because crime
committed not in the victim's country but in other
countries. This means that technology has facilitated
perpetrators to commit crimes through the internet
anywhere or any time. While the event is associated
with the theory of Robert Agnew at General Strain
Theory (GST), from the example above, the
perpetrator was bound by jealousy that sets a negative
pressure to produce feelings of anger and hatred to the
victims. The perpetrator eventually sees cyber
bullying as a way out for easing the tension that is
experiencing. This is already a commonplace with the
facilities like internet network, they are used either for
the benefit and will provide facilities to the
community or used as a channel to make crime and
activities that deviate. This can be considered as
Abuse Technology. The following are other examples
of pictures showing social applications used to give
unhealthy deviant services.
Cyber Crime in Brunei Darussalam Viewed from Sociological Perspective
359
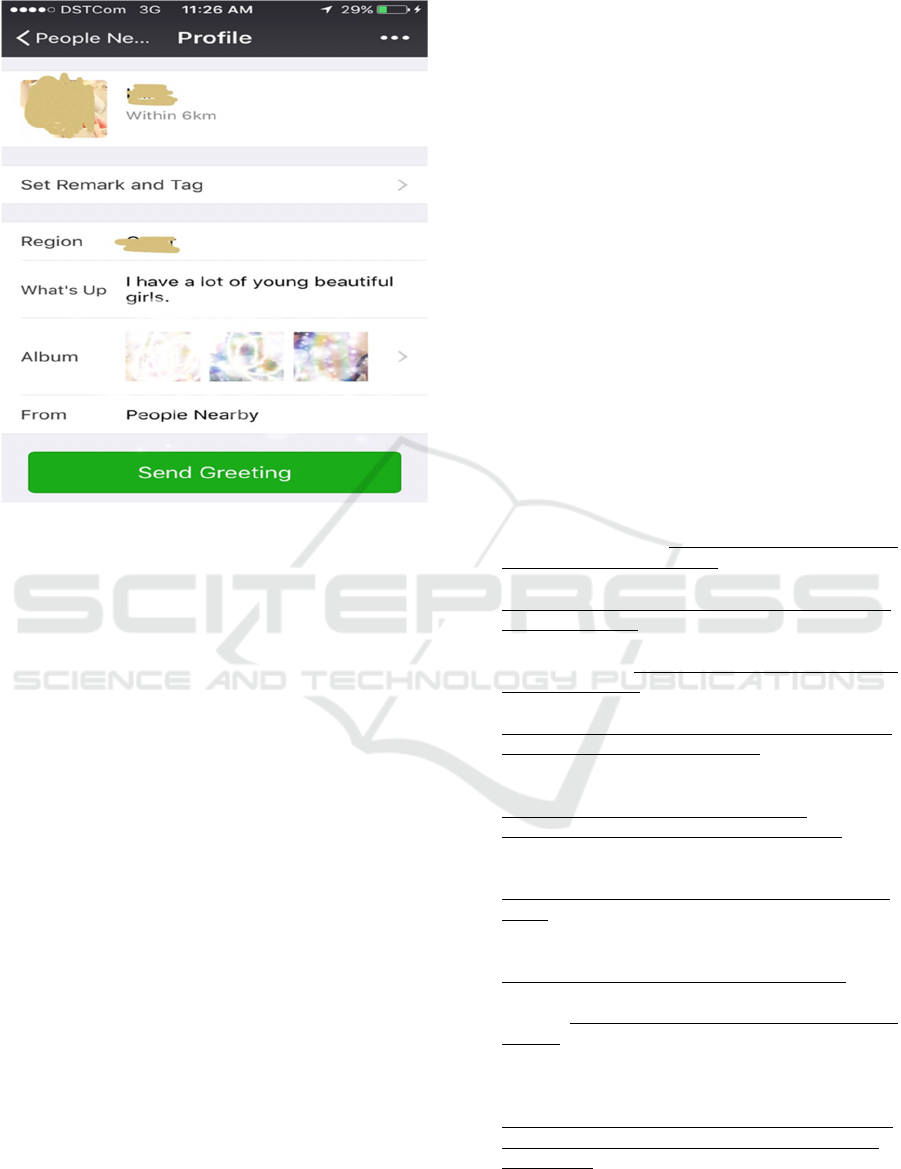
What we obtained from the two pictures above are the
sex services offered through social applications that
are quite popular i.e. Wechat. This often happens
where this service will find its customers and will tell
you in detail about the payment and the place to
perform this unhealthy activity. What is dangerous
about social apps like this is that it is accessible to any
individual regardless of age and career. Young people
particularly vulnerable to such issues are gradually
feared to be affected by the deviant service. Examples
of such issues can be attributed to Robert K. Martin's
Strain Theory as well as Thorstein Veblen's Theory
of Institutional Change: Beyond Technological
Determinism. That technology has been abused to
find negative elements that not only damage an
individual but also a society. From that, it is
concluded that such social problems reflect the
disadvantages of technology such as the internet
because its main goal is deviant. In addition, Robert
K. Martin's Strain Theory also pointed out that this
abuse is one of the ways to make money in a
convenient way and not take risks and impact on
society. The perpetrators feel that working honestly is
not worth because it does not find high profits and is
required not to be the same as carrying out these
unhealthy activities.
7 CONCLUSION
Based on this study, it is found out that Brunei
Darussalam is not exempted from the technology
related crime known as cybercrime. The types of
cybercrime found in this study are credit card fraud,
defamation or intent to ridicule, cyber bullying, and
unhealthy services. The illustrated examples reflected
in this study are appropriately connected to the
sociological theories introduced by Robert Agnew,
Robert K. Martin and Jean Baudrillard. Based on the
results of the Questionnaires, it is very important to
create awareness on cybercrime as it can educate
people on how to handle and solve cybercrime issues.
Through formal education, the incorporation of
cybercrime into the school curriculum is very
significant and relevant. It is the duty of government
and other stakeholder to work together to overcome
the cybercrimes from widespread.
REFERENCES
International Criminal Police Organization Interpol.
Cybercrime. https://www.interpol.int/Crime-
areas/Cybercrime/Cybercrime
Kris McConkey. Cybercrime.
https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/services/advisory/forensi
cs/economic-crime
Symantec Corporation. 2017 Internet Security Threat
Report. https://www.symantec.com/security-
center/threat-report
Equifax. Cybercrime Fraud Report.
https://www.equifax.com.au/sites/default/files/ved562
_cybercrime-fraud-report_fa_hr.pdf
Radware. Protecting from a growing attack vector:
Encrypted Attacks.
https://www.gartner.com/imagesrv/media-
products/pdf/radware/Radware-1-2Y7FR0I.pdf
Azlan Othman. 2014. Affordable educational loan scheme
for students
http://www.sultanate.com/news_server/2014/15_aug_
1.html
Brudirect. 2016. Increase in Cyber Crimes Prompted
Security System Upgrade.
https://www.brudirect.com/news.php?id=12434
Azlan Othman. (2017). Cybercrime on the rise. Borneo
Bulletin. https://borneobulletin.com.bn/cybercrime-on-
the-rise/
Nabilah Haris. (2013). Concern over role of social media in
cybercrimes: Brunei. Brunei Times/Asia News
Network.
http://www.asiaone.com/print/News/Latest%2BNews/
Science%2Band%2BTech/Story/A1Story20130126-
398054.html
James Kon. (2017). Brunei’s cyber protection of children
draws UN applause. Borneo Bulletin / Asia News
Network.
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
360

http://asianews.eu/content/brunei%E2%80%99s-
cyber-protection-children-draws-un-applause-61131
(2011). AITI ENSURES THAT BRUNEI’S PARENTS
AND YOUTHS ARE AWARE OF CYBER
SECURITY AND INTERNET ETIQUETTE. AITI.
Olivier Brette. (2003). “Thorstein Veblen Theory of
Institutional Change: Beyond Technology and
Determinism”.
http://thorstein.veblen.free.fr/index.php/documents/65-
thorstein-veblen-theory-of-institutional-change-
beyond-technology-and-determinism-olivier-
brette.html
Patchin, Justin W. and Hinduja, Sameer. (2011). Traditional
and non-traditional bullying among youth: A test of
general strain theory. Youth & Society, 43(2), 727-751.
Runions, Kevin C. (2013). Toward a conceptual model of
motive and self-control in cyber-aggression: Rage,
reward and recreation. Journal of Youth and
Adolescence, 42(5), 751-771
Merton, Robert K. (1938). Social Structure and Anomie,
American Sociological Review Vol 3,672-682.
http://shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in/bitstream/10603/2479
0/7/07_chapter%201.pdf
Models on Baudrillard: Simulation.
https://www.cla.purdue.edu/english/theory/postmoder
nism/modules/baudlldsimulTnmainframe.html
Simran Singh. Riya Dutta. Net threat: Morphing pictures
for revenge.
https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/chandigarh/N
et-threat-Morphing-pictures-for-
revenge/articleshow/47981141.cms
First Cybercrime Conviction in Brunei.
http://egncbrunei.blogspot.com/2010/05/first-
cybercrime-conviction-in-brunei.html
Teguh Firmansyah. Sultan Brunei
HassanalBolkiahMelaporkePolda.
http://nasional.republika.co.id/berita/nasional/jabodeta
bek-nasional/18/01/22/p2y28o377-sultan-brunei-
hassanal-bolkiah-melapor-ke-polda
Cyber Crime in Brunei Darussalam Viewed from Sociological Perspective
361
