
Virgin Coconut Oil Inhibits Candida Albicans Growth In-vitro
Umi Fitriyani
1
, Meizly Andina
1
1
Faculty of Medicine, University of Muhammadiyah Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Virgin coconut oil, Candida albicans.
Abstract: Candida albicans is the commensal organism act as a normal flora of the human body that can turn into
pathogens. Virgin Coconut Oil (VCO) is an oil obtained from coconut meat (Cocos nucifera l.). The
purpose of this research is to obtain the inhibitory power of pure coconut oil (virgin coconut oil) to Candida
albicans growth in-vitro. Preparation of VCO was set up in four concentrations, i.e. VCO 100%, 50%, 25%,
12.5%, fluconazole and distilled water as the control. The VCO antifungal test is performed through
diffusion using the disc diffusion method (Kirby and Bauer test). VCO 50% has an average resistor of 5 cm
larger than the average inhibition power of VCO 100% that is 4.5 cm, 1 cm on VCO 25% and 0.7 cm on
VCO 12.5%. The inhibitory power of the fluconazole drug discs showed significantly different inhibitory
power results (P-value <0.05) compared with VCO with 100%, 50%, 25%, 12.5% concentration, and
distilled water. While the results of Mann Whitney-Test all VCO concentrations did not show differences in
inhibitory results on the growth of C. albicans (P> 0.05), except in VCO concentrations 50% compared with
12.5% and distilled water (p <0.05). All VCO concentrations can inhibit the growth of Candida albicans in-
vitro starting from concentration but the inhibitory power of the VCO test group is not as effective as the
inhibitory power of the fluconazole drug disc.
1 INTRODUCTION
Candidiasis is a fungal disease that is caused by
Candida sp. The most common cause is Candida
albicans species. Candida albicans infection may
affect the mouth, vagina, skin, nails, respiratory
tract, and at some point can also cause septicemia,
endocarditis, or meningitis if not adequately treated
(Kuswadji, 2007).
Candida albicans is one of the commensal
organisms that act as a normal flora of the human
body especially in the gastrointestinal mucous
membranes (24%) and the vaginal mucosa (5-11%)
and this species is in normal state, therefore it is
harmless to our body (Kayser, 2010). However, in
the event of a disruption such as a weak immune
system (in the case of HIV-AIDS), Candida
albicans, originally a normal flora in the body, may
become pathogenic, causing various diseases, such as
vulvovaginal candidiasis. Based on the results of the
study, three out of four women had at least once
experienced vulvovaginal candidiasis in their lives
(Hidalgo, 2012).
Pure coconut oil or Virgin Coconut Oil (VCO)
is an oil obtained from old and fresh coconut meat
(Cocos nucifera l.) processed by squeezing with or
without water addition, with or without heating that
is not more than 60oC and safe for human
consumption (SNI, 2008). Based on the research,
the content of lauric acid and capric acid in VCO
can kill C. albicans by destroying the C. albicans
plasma membrane and making its cytoplasm
shattered and shrunk. Therefore, the VCO is
possible when used as an infectious treatment
caused by Candida albicans that infects the skin
and mucosa, and is also possible to be used as an
antibiotic therapy for long periods of time
(Bergsson, 2001). Another research results on the
antimicrobial power of VCO indicate that VCO has
minimum inhibitory level and minimum killing rate
of 25% by dilution and diffusion method
(Nurjannah, 2012).
Based on the results of research conducted by
Kabara (2005) showed that lauric acid contained in
VCO has a bacteriostatic effect on gram-positive
bacteria and also Candida albicans fungi. Where
the researcher used fatty acid and its derivatives as
antimicrobial substances tested on 9 gram-positive
bacteria, i.e. S. aureus, S. epidermidis,
Streptococcus beta-hemolytic group A,
Fitriyani, U. and Andina, M.
Virgin Coconut Oil Inhibits Candida Albicans Growth In-vitro.
DOI: 10.5220/0008790100230026
In Proceedings of the 2nd Syiah Kuala International Conference on Medicine and Health Sciences (SKIC-MHS 2018), pages 23-26
ISBN: 978-989-758-438-1
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
23
Streptococcus beta-hemolytic group non-A,
Streptococci group D, Corynebacteria,
Micrococcus sp., Nocardia asteroides,
Pneumococci, and also Candida albicans. In the
treatment of Candida albicans, the result obtained
was the lauric acid having a minimum inhibitory
level of 2.49 micromol/ml, the capric acid had a
minimum inhibitory level of 2.9 micromol/ml,
while the caprylic acid had no minimum inhibitory
content.
According to Bergsson (2001), the sensitivity
of Candida albicans to fatty acids and some of its
monoglycerides tested by short-acting inactivation,
and ultrathin were studied using an electron
transmission microscope (TEM) after being given a
capric acid. The results showed that the capric acid
(C-10) caused the quickest and most effective
killings of all three C. albicans strains tested,
leaving the cytoplasm in an irregular and shrunken
state due to the disruption or destruction of the
Candida albicans plasma membrane. Lauric acid
(C-12), is the most active at lower concentrations
and after incubation time is longer. Here's a picture
of electron microscope Candida albicans
morphology after being given capric acid.
The objective of this research is to see the
inhibitory power of virgin coconut oil to the growth
of Candida albicans in-vitro.
2 METHOD
The type of this research is laboratory
experiments. This study examined the minimum
inhibitory levels of virgin coconut oil (Virgin
Coconut Oil) on the growth of Candida albicans in
vitro. The research was conducted at the
Microbiology Laboratory, Faculty of Medicine,
University of North Sumatera. The sample of this
study is the culture of Candida albicans fungus
taken from the Microbiology Laboratory, University
of North Sumatera.
The culture of Candida albicans is done by
making the germ suspension made by taking the
culture result (+) with osse, then diluted with 0.9%
NaCl sterile and adjusted to 0.5 McFarland solution.
The germ solution is taken with a sterile cotton
swab, emphasized on the edge of the tube until it
does not drip when removed. Then the cotton swab
was evenly applied on the surface of the Saboraud
Dextrose Agar medium and waited until it dried.
After drying, the disc to be tested is taken with
sterile tweezers and placed on Saboraud Dextrose
Agar media for 24 media. Then incubated for 24
hours at 37
o
C.
VCO preparations were made into four
concentrations. A total of 12 sterile 3 ml volume
reaction vessels were provided for 3 series VCO
dilutions. For each series of dilutions prepared 4
sterile reaction tubes, then numbered from 1 to 4. As
much as 2 ml VCO is inserted in tube 1 (for 100%
VCO concentration). Then as much as 1 ml VCO is
inserted in tube no.2 and mixed with tween 80 as
much as 1 ml (total volume 2 ml) then stirred until
homogeneous (for making VCO concentration
50%). The VCO has then added as much as 0.5 ml
on tube number 3, then mixed with tween 80 as
much as 1.5 ml, then mixed until homogeneous (to
make VCO concentration 25%). Then as much as
VCO 0.25 is inserted into tube number 4, then mixed
with tween 80 as much as 1.75 ml (for making VCO
concentration 12.5%). Furthermore, blank disc paper
is inserted into each test material cylinder (100%
VCO, 50%, 25%, 12.5%, distilled water) for 10
minutes for the solution to be absorbed into the disc
paper properly.
3 RESULT
The VCO antifungal test is performed by
diffusion using the disc diffusion method (Kirby and
Bauer test). Each sabouraud dextrose agar medium
that has been planted with Candida albicans affixed
to each paper disc containing 100%, 50%, 25%,
12.5% VCO, distilled water, and fluconazole drug
solutions. The preparation is made up of 4 media
and each medium is repeated 4 times.
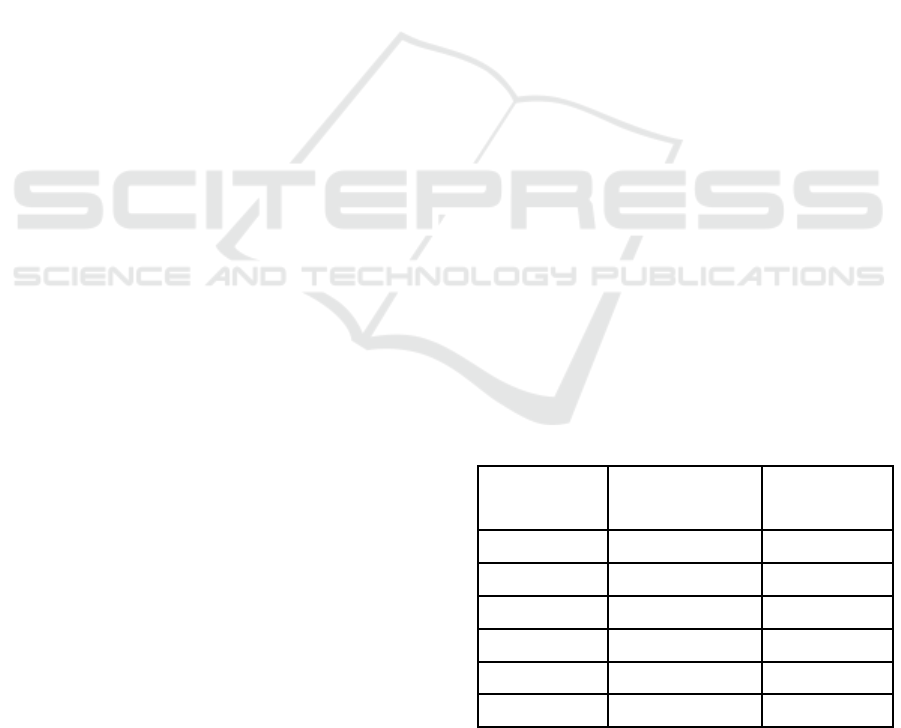
Table 1: The inhibitory power of all test groups on the
growth of Candida albicans in-vitro
Group
Mean inhibitory
zone diameter
(
mm
)
Standard
deviation
(
mm
)
Fluconazole 17.7 1.78
VCO 100% 4.5 6.22
VCO 50% 5 1.76
VCO 25% 1 2.23
VCO 12.5% 0.7 1.56
Distilled water 0 0
Then all treated media were incubated for 24
hours at 37 ° C in the incubator. Then perform the
drag zone measurements by using the sliding term
SKIC-MHS 2018 - The 2nd Syiah Kuala International Conference on Medicine and Health Sciences
24
on the clear area that occurs around the hole and
measured with the measuring paper. The clear area
is the diameter of the growing resistance of the
fungus being tested. Then interpret the results of the
measurement of the clear zone.
The result of the inhibitory zone diameter of all
VCO concentrations above is then analyzed by using
SPSS with the initial stage determining the
normality and homogeneity of the data. From the
normality and homogeneity test, the result is that the
data distribution is not normal (p> 0.05).
Furthermore, non-parametric analysis of the Kruskal
Wallis method was performed. The results obtained
are p <0.05 (ie 0.006), this indicates that all the test
groups there is no significant difference.
Mann Whitney-Test was then performed by
comparing each test group. Then the results obtained
are Fluconazole drug disc's inhibitory effect showed
significantly different inhibitory power results (P
<0.05) compared with VCO 100%, 50%, 25%,
12.5%, and distilled water. While the results of
Mann Whitney-Test all VCO concentrations did not
show differences in inhibitory results on the growth
of C. albicans (P> 0.05), except in VCO
concentrations 50% compared with VCO 12.5% and
distilled water (p <0.05) (Table 2).
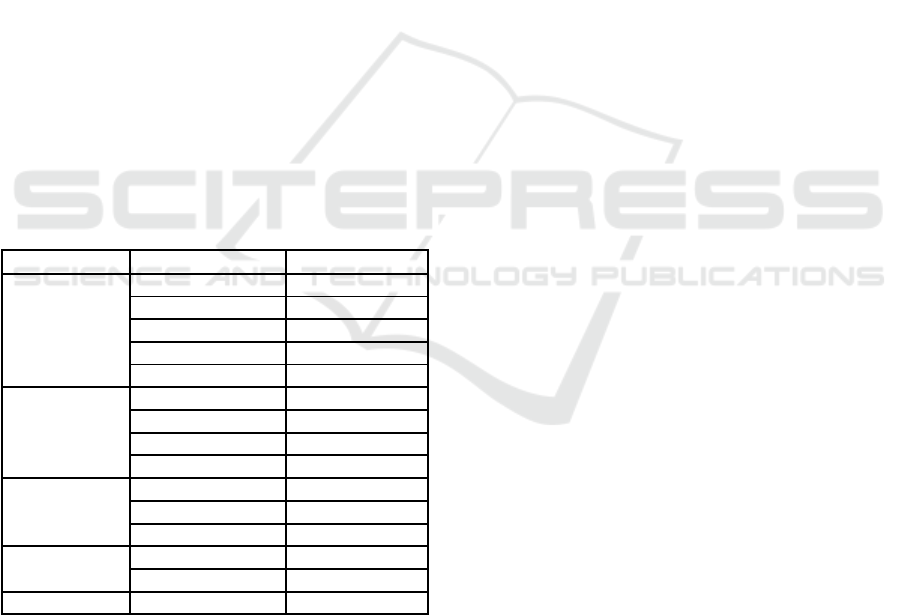
Table 2: Differences of inhibitory zone results on the
growth of C. albicans.
Group Comparison P-value
Flukonazol
VCO 100% 0.020
(p
<0.05
)
VCO 50% 0.020
(p
<0.05
)
VCO 25% 0.018
(p
<0.05
)
VCO 12,5 % 0.018
(p
<0.05
)
Distilled wate
r
0.014 (p<0.05)
VCO 100%
VCO 50% 1.000 (p>0.05)
VCO 25% 0.321 (p>0.05)
VCO 12,5 % 0.321
(p
>0.05
)
Distilled wate
r
0.131
(p
>0.05
)
VCO 50 %
VCO 25% 0.069
(p
>0.05
)
VCO 12,5 % 0.037 (p<0.05)
Distilled wate
r
0.013 (p<0.05)
VCO 25%
VCO 12,5 % 0.850 (p>0.05)
Distilled wate
r
0.317
(p
>0.05
)
VCO 12,5 % Distilled wate
r
0.317
(p
>0.05
)
4 DISCUSSION
VCO concentrations of 100%, 50%, 25%, and
12.5% on average can inhibit the growth of Candida
albicans fungi. The results obtained are in
accordance with the results of research conducted by
Diana,(2009) who also conducted research on the
antifungal effects of VCO against C. albicans. Based
on the results he obtained, the Minimum Depression
Level (KHM) VCO 100% was 14 mm, VCO 50%:
11 mm, VCO 25%: 10 mm and VCO 12.5%: 8mm.
Other studies have also been conducted by
Nurjannah (2012) about the antimicrobial power of
VCO against C. albicans with the tube dilution
method. The results show that VCO has anti mycotic
power against C. albicans with Minimum Fungicidal
Concentrations (MFCs) and Minimum Inhibitory
Concentrations (MICs) are 25%.
However, other studies show that VCO cannot
inhibit the growth of C. albicans in-vitro (Yulian,
2007) (S.S Dewi, T Aryadi, 2010). According to
research the factors that influence is due to the poor
solubility of VCO in the air (Yulian, 2007). Because
in making the concentration of VCO that is by
mixing VCO with tween 80 and distilled water with
ratio 1:1:2.
The use of tween 80 in this study was as a
solvent VCO in the manufacture of concentrations.
Tween 80 is a nonionic surfactant and emulsifier
derived from polyethoxylated sorbitan and oleic
acid. Surfactants are molecules that have hydrophilic
groups and lipophilic groups. Can dissolve in the
form of air or oil. Tween 80 can lower the voltage
between drugs and medium and various micelles.
This building will be carried away by micelles
dissolved in the medium (Zulkarnain, 2008)
In this study, four repetitions were conducted, it
aims to estimate the variations of the experimental
error, to estimate the standard error of the treatment
rate, to improve the test provision, to extend the
precision of the experimental conclusions through
the selection and use of experimental units which is
more varied. If the number of replications increases,
then the alleged population mean value through the
midpoint of the observed treatment becomes more
thorough. The research error is a measure of
diversity among all observations derived from the
experimental units that received the same treatment
(Raupong, 2011).
5 CONCLUSIONS
All VCO concentrations can inhibit the growth of
Candida albicans in-vitro from VCO concentrations
of 12.5% to 100% VCO. However, the inhibitory
power of the VCO test group is not as effective as
the inhibitory power of the fluconazole drug disc.
Virgin Coconut Oil Inhibits Candida Albicans Growth In-vitro
25

REFERENCES
Bergsson, G., 2001. In vitro Killing of Candida
albicans by Fatty Acids and Monoglycerides. [Online]
Available at:
http://aac.asm.org/content/45/11/3209.full
[Accessed 16 June 2012].
Diana, E., 2009. Efek Antifungi Virgin Coconut Oil
Terhadap Candida albicans. Malang, Fakultas
Kedokteran Universitas Muhammadiyah Malang.
Hidalgo, J., 2012. Candidiasi. [Online]
Available at:
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/213853-
overview#a0199
[Accessed 16 June 2012].
Kabara, e. a. 1., 2005. Fatty Acids and Derivatives as
Antimicrobial Agents. American Society for
Microbiology, Volume Vol 2, pp. 23-28.
Kayser, 2010. Medical Microbiology. In: Candida
albicans. Pekanbaru: FK UNRI.
Kuswadji, 2007. Kandidiosis. In: Ilmu Penyakit Kulit
dan Kelamin. Jakarta: FK UI.
Nurjannah, N., 2012. Daya Antimikotik Dari VCO
(Virgin Coconut Oil) terhadap Candida Albican,
Yogyakarta: Fakultas Kedokteran Univrsitas
Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta.
Raupong, 2011. Bahan Ajar Mata Kuliah Rancangan
Percobaan.. Makassar: Fakultas Matematika & Ilmu
Pengetahuan Alam. Universitas Hasanuddin.
S.S Dewi, T Aryadi, 2010. Efektifitas Virgin Coconut
Oil ( vco ) terhadap Kandidiasis secara In-vitro,
Semarang: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas
Muhammadiyah Semarang.
SNI, 2008. Minyak Kelapa Virgin (VCO). ICS
67.200.10 ed. Jakarta: Badan Standar Nasional.
Yulian, A. I., 2007. Uji Banding Efektivitas Virgin
Coconut Oil dengan Ketokonazol 2% Secara In Vitro
Terhadap Pertumbuhan Candida albicans. Semarang,
Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Diponegoro.
Zulkarnain, A., 2008. Pengaruh Penambahan Tween 80
dan Poli-etilen Glikol 400 terhadap Absorpsi
Piroksikam melalui Lumen Usus in situ. Majalah
Farmasi Indonesia, 19(1).
SKIC-MHS 2018 - The 2nd Syiah Kuala International Conference on Medicine and Health Sciences
26
